Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (23): 3660-3666.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1310
Previous Articles Next Articles
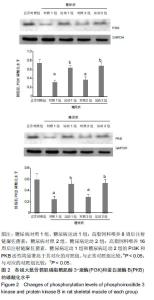
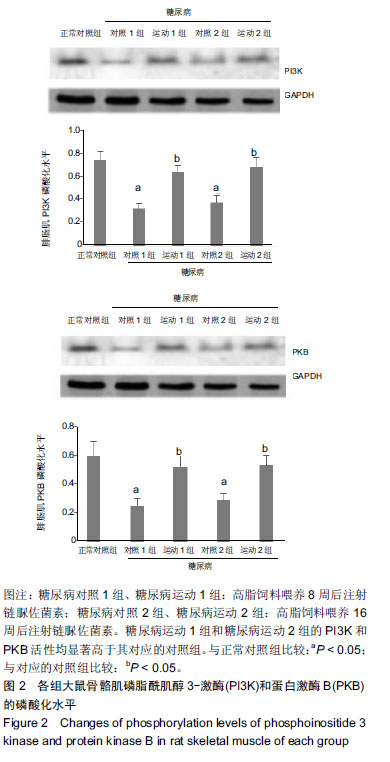
Changes of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-protein kinase B signaling pathway in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes rat models after 8-week aerobic exercise
Zhao Dalin1, Li Jing1, Ma Tie1, Gao Haining1, Liu Haopeng1, Zhang Shicheng1, Xu Sitong1, Xiao Jiayu1, Li Yiran1, Yan Shengnan1, Chang Bo1, 2
- (1College of Sports Human Science, 2Department of Sports Physiology and Biochemistry, Shenyang Sport University, Shenyang 110102, Liaoning Province, China)
-
Received:2019-01-29Online:2019-08-18Published:2019-08-18 -
Contact:Chang Bo, MD, Professor, College of Sports Human Science, Department of Sports Physiology and Biochemistry, Shenyang Sport University, Shenyang 110102, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zhao Dalin, Associate professor, College of Sports Human Science, Shenyang Sport University, Shenyang 110102, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National natural science foundation of China, No. 30971414; the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, No. 2015020704 (to CB); the Basic Scientific Research Project of Universities in Liaoning Province, No. LQN2017ST02 (to GHN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Dalin1, Li Jing1, Ma Tie1, Gao Haining1, Liu Haopeng1, Zhang Shicheng1, Xu Sitong1, Xiao Jiayu1, Li Yiran1, Yan Shengnan1, Chang Bo1, 2. Changes of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-protein kinase B signaling pathway in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes rat models after 8-week aerobic exercise[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3660-3666.
share this article
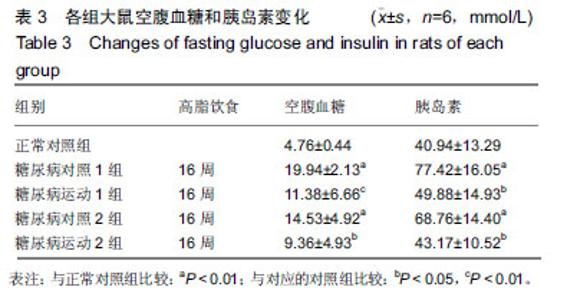
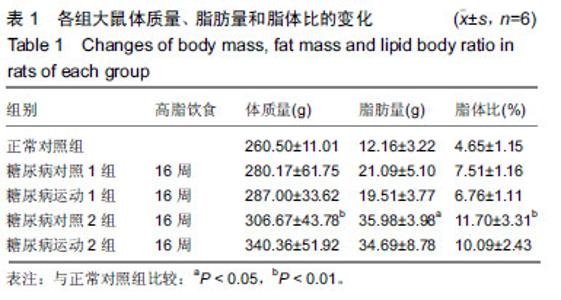
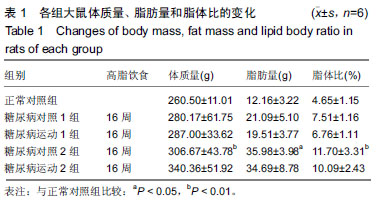
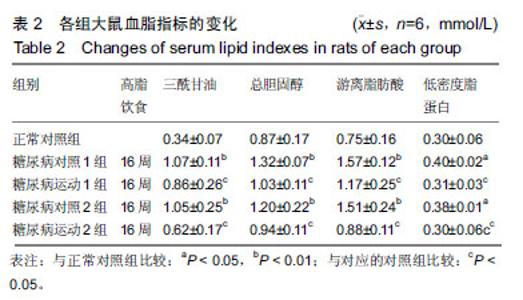
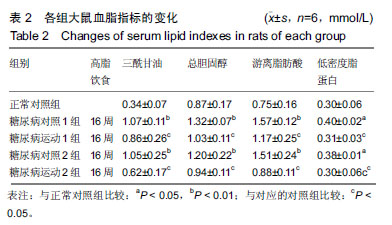
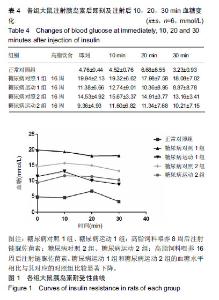
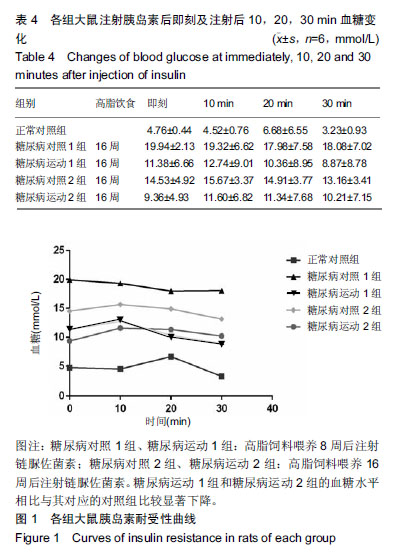
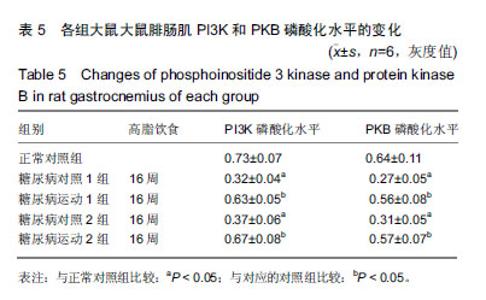
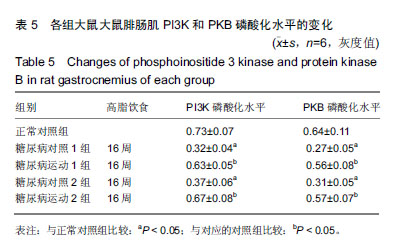
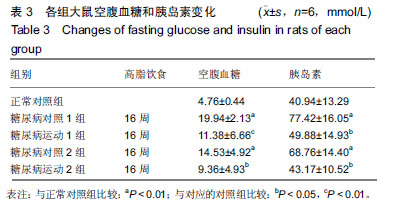
2.4 各组大鼠空腹血糖、胰岛素水平和胰岛素耐受性的变化 ①实验结束时5组大鼠空腹血糖水平,糖尿病对照1组和糖尿病对照2组空腹血糖明显高于正常对照组(P < 0.01);而糖尿病运动1组和糖尿病运动2组的空腹血糖水平相比与其对应的对照组则显著下降(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);②糖尿病对照1组和糖尿病对照2组空腹胰岛素明显高于正常对照组(P < 0.01,P <0 .01);而糖尿病运动1组和糖尿病运动2组的空腹胰岛素水平相比与其对应的对照组则显著下降(P < 0.01,P < 0.05),见表3,4。各组大鼠腹腔注射胰岛素后测量即刻、10、20、30 min后血糖值,并绘制胰岛素耐受性曲线,见图1。 "
| [1]况志彬.2型糖尿病合并非酒精性脂肪肝与胰岛素抵抗及心血管疾病的相关性[J].医学理论与实践.2018,31(5):667-669.[2]Hu X,Wang S,Xu J,et al.Triterpenoid saponins from Stauntonia chinensis ameliorate insulin resistance via the AMP-activated protein kinase and IR/IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathways in insulin-resistant HepG2 cells.Int J Mol Sci.2014; 15(6):10446-10458.[3]李斌,范源,李鑫.基于PI3K /Akt信号通路的中药改善2型糖尿病胰岛素抵抗研究进展[J],中成药,2017,39(1):151-154. [4]章晓君,孙佳,赵新,等.6min步行试验对老年2型糖尿病患者干预效果分析[J].山西医药杂志,2015,44(4):420-422.[5]李洪臣,邱玥,铁英,等.陈式太极拳功法对老年2型糖尿病患者血液生化指标和心肺功能的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2015,35(5): 1293-1294.[6]罗晓玲,李东锋,朱树贞.社区集体运动功能锻炼对老年2型糖尿病病人预后的影响[J].护理研究,2015,29(4):1196-1199.[7]牛衍龙,陈德明.运动治疗2型糖尿病训练学处方制定的分析[J].哈尔滨体育学院学报,2015,33(3):91-96.[8]Palmer NO,Bakos HW, Owens JA,et al. Diet and exercise in an obese mouse fed a high-fat diet improve metabolic health and reverse perturbed sperm function.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2012;302(7): E768-E780.[9]Srinivasan K,Viswanad B,Asrat L,et al.Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat:a model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screen-ing.Pharmacol Res. 2005;52(4):313-320.[10]Zhang M,Lv XY,Li J,et al.The Characterization of High-Fat Diet and Multiple Low-Dose Streptozotocin Induced Type 2 Diabetes Rat Model.Exp Diabetes Res.Exp Diabetes Res. 2008;2008:704045.[11]王子木,陈晓彤,慧梅.2型糖尿病患者的早期胰岛素强化改善[J].大连医科大学学报,2017,39(5): 503-506.[12]Sangeetha KN, Sujatha S, Muthusamy VS, et al.Current trends in small molecule discovery targeting key cellular signaling events towards the combined management of diabetes and obesity.Biomedical Informatics.2017;13(12): 394-399 [13]中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2013年版) [J].中国糖尿病杂志,2014,22(8):后插2-后插42页.[14]冯召岚,董爱武,谢鑫,等.运动干预对高脂饮食大鼠脂类代谢异常和胰岛素敏感性的影响[J].江苏医药,2018,44(2):125-128.[15]Liang H,Tantiwong P,Sriwijitkamol A,et al. Effect of a sustained reduction in plasma free fatty acid concentration on insulin signalling and inflammation in skeletal muscle from human subjects.J Physiol.2013;591(11): 2897-2909.[16]Shibata E,Kanno T,Tsuchiya A,et al.Free fatty acids inhibit protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and activate Akt. Cell Physiol Biochem.2013;32(4):871-879. [17]Li HB,Yang YR,Mo ZJ,et al. Silibinin improves palmitate-induced insulin resistance in C2C12 myotubes by attenuating IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition.Braz J Med Biol Res.2015;48(5): 440-446.[18]Huri HZ,Makmor-Bakry M,Hashim R,et al. Optimisation of glycaemic control during episodes of severe/acute hyperglycaemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Clin Pharm. 2012;34(6):863-870.[19]孙子林,刘莉莉.《中国糖尿病运动指南》解读[J]. 国际内分泌代谢杂志,2013,33(6):373-375, 378.[20]Kjobsted R,Munk-Hansen N,Birk JB,et al. Enhanced Muscle Insulin Sensitivity After Contraction/Exercise Is Mediated by AMPK.Diabetes.2017;66(3):598-612.[21]李艳辉,衣雪洁.有氧运动对2型糖尿病大鼠骨骼肌 ERK1/2活性的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2017, 33(1): 33-37.[22]赵金香,胡章云,李耀华,等.菊粉联合游泳训练对代谢综合征大鼠骨骼肌胰岛素受体底物1及葡萄糖转运子4表达的影响[J].中国糖尿病杂志, 2017,25(9): 831-835.[23]王月秋,王丽宏,车慧,等.微小RNA与胰岛素PI3K/AKT信号转导通路[J].新医学,2017,48(7): 438-442.[24]Winnay JN, Dirice E, Liew CW, et al. p85α deficiency protects β-cells from endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.2014;111(3):1192-1197.[25]Nelson VL, Jiang YP, Dickman KG, et al. Adipose tissue insulin resistance due to loss of PI3K p110α leads to decreased energy expenditure and obesity.Am J Physiol EndocrinolMetab.2014;306(10):E1205-E1216.[26]Sylow L,Kleinert M,Richter EA,et al.Exercise-stimulated glucose uptake-regulation and implications for glycaemic control. Nat Rev Endocrinol.2017;13(3):133-148.[27]Zierath JR, Krook A, Wallberg-Henriksson H. Insulin action and insulin resistance in human skeletal muscle. Diabetologia. 2000;43(7):821-35.[28]Uarvey WT,Huecksteadt TP,Matthaei S,et al. Role of glucose transporters in the cellular insulin resistance of type II non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1988; 81(5):1528-1536.[29]Hohn P. Kirwanl,etc. Regular exercise enhacnes insulin activation of IRS-1-associated PI3-kinase in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 2000;88:793-803[30]李常富.有氧运动对肥胖大鼠脂肪组织LC3泛素样系统相关蛋白表达的影响[D].北京体育大学,2017[31]顾兰馨,王志法,殷强,等.有氧运动对CSD引起的大鼠IR的影响[J].心脏杂志,2017, 29(6): 652-658.[32]Chibalin AV, Yu M, Ryder JW, et al. Exercise-induced changes in epression and activity of proteins involved in insulin signal transduction skeletal muscle: differential effects on insulin receptor substrates 1 and Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:38-43.[33]Wojtaszewski JF, Nielsen P, Kiens B, et al.Regulation of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 in Human Skeletal Muscle: Effects of Food Intake and Bicycle Exercise. Diabetes.2001; 50:265-269.[34]Christ-Roberts CY, Pratipanawatr T,Pratipanawatr W,et al. Exercise training icnreases glycogen synthase activity and GLUT4 expression but not insulin signaling in overweight nondiabetic and type 2 diabetic subjects. Metabolism.2004; 53(9):1233-1242.[35]O'Gorman DJ, Karlsson HK, Mc Quaid S, et al. Exercise training icnreases insulin-stimulated glucose disposal and GLUT4 (SLC2A4) protein content in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia.2006;49(12): 2983-2992. |
| [1] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [2] | Wen Miaomiao, Fan Junbai. Relationship between biological activities of Apelin and Elabela and diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5735-5740. |
| [3] | Zheng Feng, Zhang Fucai, Xu Zhe. MicroRNA-98-5p promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation: possibilities and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(26): 4112-4117. |
| [4] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [5] | Yang Caihui, Liu Qicheng, Dong Ming, Wang Lina, Zuo Meina, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Serine/threonine protein kinases can promote bone destruction in mouse models of chronic periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3654-3659. |
| [6] | Liu Yulin, Li Guotai. Combined effects of hyperbaric oxygen, vibration training and astaxanthin on bone mineral density, glucose metabolism and oxidative stress in diabetic osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3117-3124. |
| [7] | Fei Jing, Zheng Hongdi, Yu Liya, Li Leiji. Involvement of GDNF/PI3K/AKT pathway in promoting facial nerve regeneration using electroacupuncture in a rabbit model of facial nerve crush injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1094-1100. |
| [8] | Chen Zegang, Ding Haili, Li Long, Wang Chun. Changes of bone metabolism after different intensity endurance exercises in growing rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5582-5588. |
| [9] | Tian Shenglan, Wang Guoyan, Yang Yang. Mechanism of YKL-40 regulating apoptosis of rabbit osteoarthritis chondrocytes via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5108-5113. |
| [10] |
Li Ying, Lin Wentao, Weng Xiquan.
Effects of different exercise intensities on visfatin level and glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4196-4200. |
| [11] | Jiang Han, Ding Jie, Chen Gen, Xie Qiang, Li Wei, Wang Zhibin, Zhu Lei. Hypoxia-mediated miRNAs affect glucose metabolism: new recognition of preventing and controlling glucose metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 303-311. |
| [12] | Liu Yuetong, Wang Qin, Yang Ye, Zhu Jun, Abulikemu•Tuerdi. Effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on microRNA-130b and transforming growth factor beta 1 in renal tissue of rat models of diabetic nephropathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 248-253. |
| [13] | Zhao Jianfeng, Geng Yu, Chen Qianbo, Yang Jinghui, Li Yan. Changes in insulin resistance and inflammatory factors in cataract patients with glaucoma after phacoemulsification and trabeculectomy: a self-controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1750-1755. |
| [14] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Pan Xinghua. Allogeneic umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for metabolic syndrome in a tree shrew model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 51-58. |
| [15] | Liang Min, Wang Hainiu, Huang Peng, Zhu Weihua, Li Shunchang . Systematic review and meta-analysis of effect of resistance exercise on glucose and lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5718-5726. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||