Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (15): 2308-2313.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1175
Previous Articles Next Articles
Relationship between p38 signaling pathway and periodontal ligament fibroblasts secreting inflammatory factors under static pressure
Tang Haifang1, 2, 3, 4, Peng Juanmin1, 2, 3, 4, Kang Na1, 2, 3, 4
-
Received:2018-12-18Online:2019-05-28Published:2019-05-28 -
Contact:Kang Na, MD, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, Hospital of Stomatology, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Key Laboratory of Oral and Maxillofacial Restoration and Reconstruction of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Craniomaxillofacial Clinical Research Center of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Key Laboratory of Diagnosis and Treatment of Maxillofacial Surgery (Key Laboratory of Guangxi University), Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Tang Haifang, Master candidate, Hospital of Stomatology, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Key Laboratory of Oral and Maxillofacial Restoration and Reconstruction of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Craniomaxillofacial Clinical Research Center of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Key Laboratory of Diagnosis and Treatment of Maxillofacial Surgery (Key Laboratory of Guangxi University), Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81360170 (to KN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Haifang, , , , Peng Juanmin, , , , Kang Na, , , . Relationship between p38 signaling pathway and periodontal ligament fibroblasts secreting inflammatory factors under static pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2308-2313.
share this article
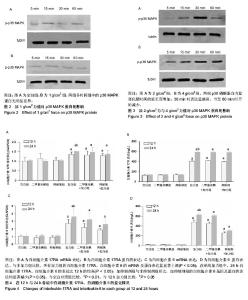
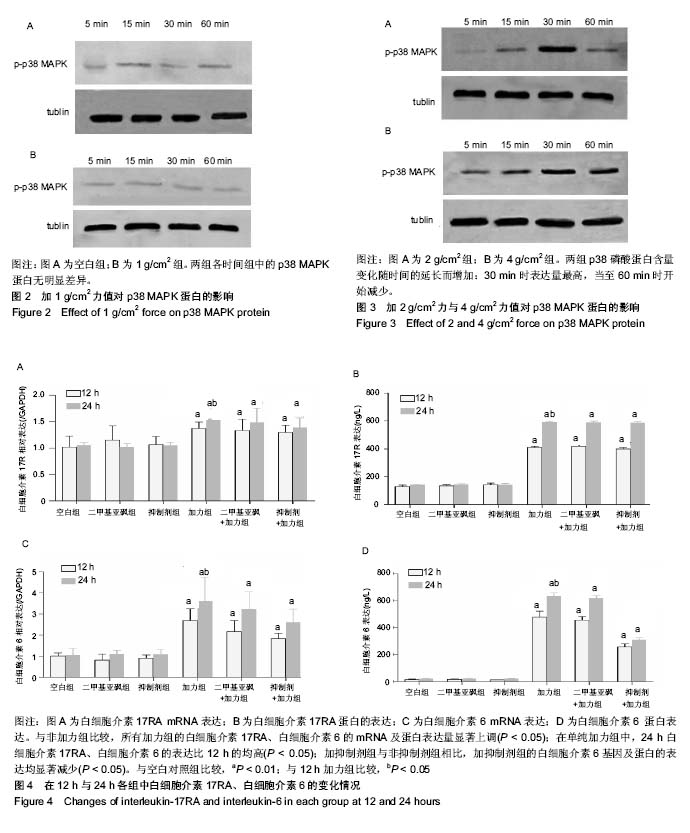
2.1 细胞体外重力加载模型的成功建立 见图1。 2.2 静压力刺激牙周膜成纤维细胞后p38MAPK磷酸化反应结果 在0 g/cm2和1 g/cm2组中,各时间组中的p38 MAPK蛋白无明显差异,见图2。 而在2 g/cm2和4 g/cm2组中,p38磷酸蛋白含量变化随时间的延长而增加:在15 min时p38磷酸化开始表达, 30 min时表达量最高,当至60 min时开始减少,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。见图3。 2.3 p38 MAPK阻断剂对牙周膜成纤维细胞静压力下表达白细胞介素17,白细胞介素6的影响 与非加力组比较,所有加力组的白细胞介素17RA、白细胞介素6的mRNA及蛋白表达量显著上调(P < 0.05)。在单纯加力组中,加力24 h时白细胞介素17RA、白细胞介素6水平比12 h的均高(P < 0.05)。 加抑制剂组与非抑制剂组相比,加抑制剂组的白细胞介素6基因及蛋白表达均显著减少(P < 0.05),加抑制剂组中白细胞介素17RA表达减少,但差异无显著性意义(P=0.246,P=0.372)。见图4。"
| [1] Kikuta J, Yamaguchi M, Shimizu M,et al. Notch signaling induces root resorption via RANKL and IL-6 from hPDL cells. J Dent Res. 2015;94(1):140-147.[2] Chang L, Feng X, Gao W. Proliferation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes is enhanced by IL-17-mediated autophagy through STAT3 activation. Connective tissue research. Connect Tissue Res. 2018 Nov 26. .[3] Batool H, Nadeem A, Kashif M, et al. Salivary Levels of IL-6 and IL-17 Could Be an Indicator of Disease Severity in Patients with Calculus Associated Chronic Periodontitis. BioMed research international. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:8531961. [4] Wang ZX, Yang L, Tan JY, et al. [Effects of T helper 1 cells and T helper 17 cells secreting cytokines on rat models of experimental periodontitis]. Zhonghua kou qiang yi xue za zhi.2017;52(12):740-747.[5] Meikle MC. The tissue, cellular, and molecular regulation of orthodontic tooth movement: 100 years after Carl Sandstedt. Eur J Orthod. 2006;28(3):221-240.[6] Lee YH, Nahm DS, Jung YK, et al. Differential gene expression of periodontal ligament cells after loading of static compressive force. J Periodontol. 2007;78(3):446-452.[7] Schindler JF, Monahan JB, Smith WG. p38 pathway kinases as anti-inflammatory drug targets. J Dent Res. 2007;86(9): 800-811. [8] 张宝平. 癌细胞力学性质测量及放射诱导下细胞损伤的生物力学研究[D]: 兰州:兰州大学,2016.[9] 张西正,匡震邦,蔡绍皙,等. 细胞力学实验技术研究[J]. 实验力学,2001,16(1):66-76.[10] Redlich M, Roos H, Reichenberg E, et al. The effect of centrifugal force on mRNA levels of collagenase, collagen type-I, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases and beta-actin in cultured human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. J Periodontal Res. 2004;39(1):27-32.[11] Yousefian J, Firouzian F, Shanfeld J, et al. A new experimental model for studying the response of periodontal ligament cells to hydrostatic pressure. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1995;108(4):402-409..[12] 朱庆党,巢永烈,陈新民,等. 动态张、压应力刺激下人牙周膜成纤维细胞细胞骨架变化[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志. 2008,24(4): 559-562.[13] Kanzaki H,Chiba M,Shimizu Y,et al.Periodontal ligament cells under mechanical stress induce osteoclastogenesis by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand up-regulation via prostaglandin E2 synthesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(2):210-220.[14] 张建兴,黄生高,钟孝欢,等. 人牙周膜细胞体外培养和机械压力模型构建[J].口腔医学研究,2006,22(1):38-42.[15] Yamaguchi M, Aihara N, Kojima T, et al. RANKL increase in compressed periodontal ligament cells from root resorption. J Dent Res. 2006;85(8):751-756.[16] Cargnello M, Roux PP. Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews : MMBR. 2011; 75(1):50-83.[17] Ouyang W,Kolls JK,Zheng Y.The biological functions of T helper 17 cell effector cytokines in inflammation. Immunity. 2008;28(4):454-67.[18] Xing J,Yu Z,Zhang X, et al. Epicatechin alleviates inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;66:146-153.[19] Ziegler N, Alonso A, Steinberg T, et al. Mechano-transduction in periodontal ligament cells identifies activated states of MAP-kinases p42/44 and p38-stress kinase as a mechanism for MMP-13 expression. BMC cell biology. 2010;11:10.[20] 李菲菲,阎潇,王庆,等. p38丝裂素活化蛋白激酶信号通路在应力调控成肌细胞分化中的作用.[J] 华西口腔医学杂志, 2012;30(6): 574-578.[21] Yang JZ, Li Y, Sun LX, et al. Interleukin-17 receptor expression on vascular endothelial cells of masses of skeletal extramedullary disease in myeloma patients. Pathol Res Pract. 2014;210(9):586-590..[22] Hayashi N, Yamaguchi M, Nakajima R,et al. T-helper 17 cells mediate the osteo/odontoclastogenesis induced by excessive orthodontic forces. Oral Dis. 2012;18(4):375-388[23] Funaki Y, Hasegawa Y, Okazaki R, et al. Resolvin E1 Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis and Bone Resorption by Suppressing IL-17-induced RANKL Expression in Osteoblasts and RANKL-induced Osteoclast Differentiation. Yonago Acta Med. 2018;61(1):8-18.[24] Yamada K, Yamaguchi M, Asano M, et al. Th17-cells in atopic dermatitis stimulate orthodontic root resorption. Oral Dis. 2013;19(7):683-693.[25] Liu Y, Song F, Wu S, et al. Protein and mRNA expressions of IL-6 and its key signaling factors under orthodontic forces in mice: An in-vivo study.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2017; 152(5):654-662..[26] Koyama Y, Mitsui N, Suzuki N, et al. Effect of compressive force on the expression of inflammatory cytokines and their receptors in osteoblastic Saos-2 cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2008 ; 53(5):488-496. [27] Ganesan R,Rasool M.Interleukin 17 regulates SHP-2 and IL-17RA/STAT-3 dependent Cyr61, IL-23 and GM-CSF expression and RANKL mediated osteoclastogenesis by fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Immunol. 2017;91:134-144 .[28] Johnson RW,McGregor NE,Brennan HJ,et al.Glycoprotein130 (Gp130)/interleukin-6 (IL-6) signalling in osteoclasts promotes bone formation in periosteal and trabecular bone. Bone. 2015; 81:343-351.[29] 余学清,李锦华,黄凌虹,等. p38信号通路在脂多糖诱导的大鼠系膜细胞产生白细胞介素1β中的作用[J].中华肾脏病杂志. 2000, 16(2):98-101. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Li Jun, Zuo Xinhui, Liu Xiaoyuan, Zhang Kai, Han Xiangzhen, He Huiyu, . Effect of over expression of miR-378a on osteogenic and vascular differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheet [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4939-4944. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||