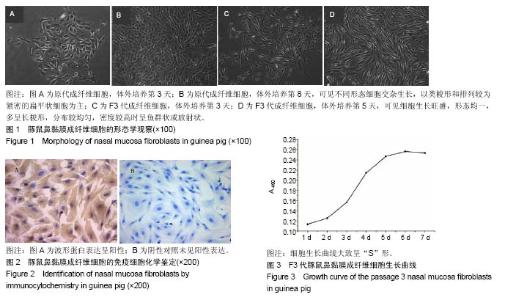
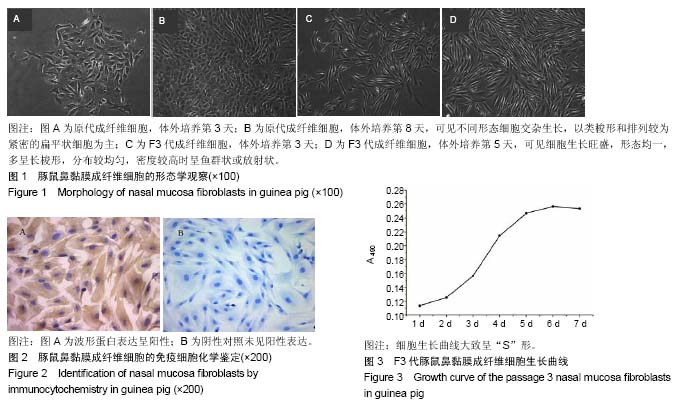
| [1] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编委会鼻科学组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南(2009年,武夷山)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2009, 44(12): 977-978.[2] Higashino M, Takabayashi T, Takahashi N, et al. Interleukin-19 downregulates interleukin-4-induced eotaxin production in human nasal fibroblasts. Allergol Int. 2011; 60(4): 449-457.[3] Cho JS, Han IH, Lee HR, Lee HM. Prostaglandin E2 Induces IL-6 and IL-8 Production by the EP Receptors/Akt/NF-κB Pathways in Nasal Polyp-Derived Fibroblasts. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.2014;6(5):449- 457. [4] Park IH, Um JY, Cho JS, et al. Histamine Promotes the Release of Interleukin-6 via the H1R/p38 and NF-κB Pathways in Nasal Fibroblasts. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.2014; 6(6): 567-572.[5] Kim JA, Cho JH, Park IH, et al. Diesel Exhaust Particles Upregulate Interleukins IL-6 and IL-8 in Nasal Fibroblasts. PLoS One. 2016; 11(6): e0157058.[6] 司徒镇强,吴军正. 细胞培养[M]. 西安: 界图书出版西安公司, 2007: 5.[7] 杨志明. 组织工程[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2002: 41-42, 158.[8] Richert MM, Schwertfeger KL, Ryder JW, et al. An atlas of mouse mammary gland development. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2000; 5(2): 227-241.[9] 李涛,朱慧涛,周杰玉,等.鼻息肉成纤维细胞在常氧与低氧环境下的原代培养及鉴定[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2014,20(2): 76-80.[10] 刘建国,刘月辉,谢冰斌.丙酸氟替卡松对变应性鼻炎大鼠鼻黏膜中碱性成纤维细胞生长因子蛋白和mRNA表达的影响[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2009,23(14): 649-651,655.[11] 夏忠芳,孔维佳,乐建新,等.人正常鼻黏膜及鼻息肉黏膜上皮细胞的原代培养及鉴定[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版), 2008,37(4): 541-543.[12] 李吉平,王家东,张淳,等.鼻渊舒口服液抑制鼻黏膜成纤维细胞生长的实验研究[J].中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2006,14(6): 344-346. [13] 商爱民,吴靖芳,薛刚,等.张耕大鼠胚胎成纤维细胞的分离培养及生物学特性[J]河北北方学院学报(医学版), 2010,27(3):17-20.[14] 王烨,米文娟,韩宇,等.乔莉蜗轴螺旋动脉平滑肌的培养及其鉴定[J].现代生物医学进展,2010,10(9):1624-1627.[15] 崔哲洙,刘艳丽,崔春莲,等.变应性鼻炎与慢性单纯性鼻炎鼻黏膜成纤维细胞中组胺受体蛋白的表达[J].延边大学医学学报, 2008, 31(4):281-283.中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程 |