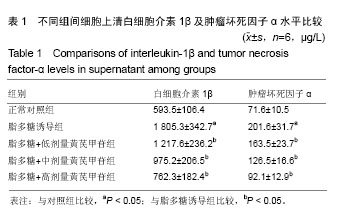
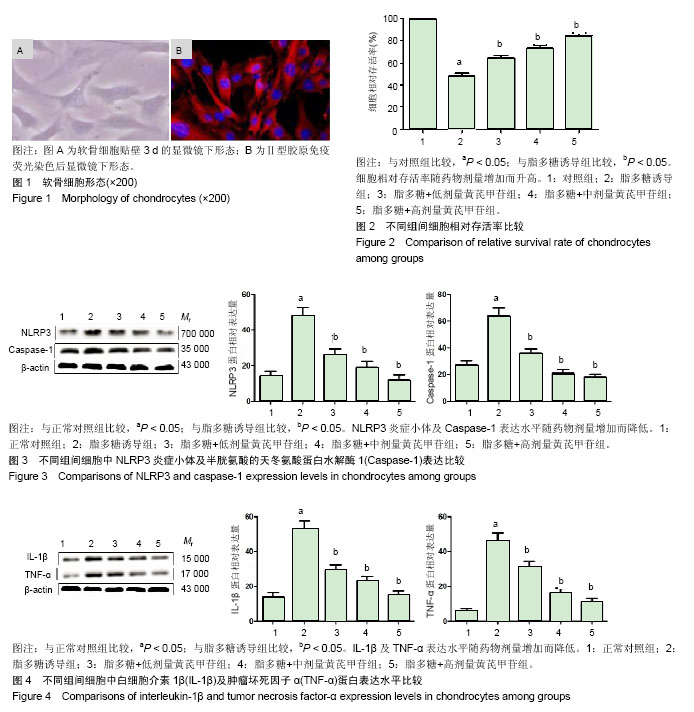
| [1] Wang GL, Wu YB, Liu JT, et al. Upregulation of miR-98 inhibits apoptosis in cartilage xells in osteoarthritis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2016;20(11):645-653. [2] Zhang Y, Vasheghani F, Li YH, et al. Cartilage-specific deletion of mTOR upregulates autophagy and protects mice from osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(7):1432-1440. [3] 赵文杰,张斌,高松,等.低能量性髋部骨折与膝关节退变的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(37)5938-5942.[4] Greene MA, Loeser RF. Aging-related inflammation in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015; 23(11):1966-1971. [5] Lieberthal J, Sambamurthy N, Scanzello CR. Inflammation in joint injury and post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015; 23(11):1825-1834. [6] Alfonso-Loeches S, Ureña-Peralta J, Morillo-Bargues MJ, et al. Ethanol-induced TLR4/NLRP3 neuroinflammatory response in microglial cells promotes leukocyte infiltration across the BBB. Neurochem Res. 2016;41(1-2):193-209. [7] Banerjee S. RNase L and the NLRP3-inflammasome: an old merchant in a new trade. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016;29(11):63-70. [8] Mishra AR, Zheng J, Tang X, et al. Silver nanoparticle-induced autophagic-lysosomal disruption and NLRP3-inflammasome activation in HepG2 cells is size-dependent. Toxicol Sci. 2016;150(2):473-487. [9] Winkler S, Rösen-Wolff A. Caspase-1: an integral regulator of innate immunity. Semin Immunopathol. 2015;37(4):419-427. [10] Kahlenberg JM, Yalavarthi S, Zhao W, et al. An essential role of caspase 1 in the induction of murine lupus and its associated vascular damage. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(1):152-162. [11] Son CN, Bang SY, Kim JH, et al. Caspase-1 level in synovial fluid is high in patients with spondyloarthropathy but not in patients with gout. J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28(9):1289-1292. [12] Jin C, Frayssinet P, Pelker R, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of hydroxyapatite-associated arthropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(36):14867-14872. [13] Vande Walle L, Van Opdenbosch N, Jacques P, et al. Negative regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by A20 protects against arthritis. Nature. 2014;512(7512):69-73. [14] 孙书龙,姜宏,汤晓晨,等.黄芪甲苷对人膝骨关节炎退变关节软骨细胞基质金属蛋白酶-1及基质金属蛋白酶-3 mRNA表达的影响[J].中医正骨,2012, 24(10):5-9.[15] 汤晓晨,俞峰,孙书龙,等.黄芪甲苷对人膝骨关节炎退变关节软骨IL-1β表达的影响[J].南京中医药大学学报,2013,29(1):48-52.[16] Zhao Y, Li Q, Zhao W, et al. Astragaloside IV and cycloastragenol are equally effective in inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the endothelium. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;169(6):210-218. [17] Song MT, Ruan J, Zhang RY, et al. Astragaloside IV ameliorates neuroinflammation-induced depressive-like behaviors in mice via the PPARγ/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018; 32(9):251-263. [18] Wan Y, Xu L, Wang Y, et al. Preventive effects of astragaloside IV and its active sapogenin cycloastragenol on cardiac fibrosis of mice by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018; 833(6): 545-554. [19] 王一凡,杨霄鹏,曾志磊,等.姜黄素对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠MMP-2活性和血脑屏障通透性的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(2):280-282.[20] 孟祥奇,黄桂成,惠礽华,等.黄芪甲苷对人膝骨关节炎退变软骨细胞MMP-1和MMP-3 mRNA表达的影响[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2012,14(7): 88-90.[21] 刘建红,孟庆刚,胡佳卉,等.黄芪甲苷对早期骨关节炎软骨细胞基质金属蛋白酶-1表达的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2017,37(2):532-534.[22] Wang B, Chen MZ. Astragaloside IV possesses antiarthritic effect by preventing interleukin 1β-induced joint inflammation and cartilage damage. Arch Pharm Res. 2014;37(6):793-802. [23] Zhu ZH, Wan HT, Li JH. Chuanxiongzine-astragaloside IV decreases IL-1β and Caspase-3 gene expressions in rat brain damaged by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion: a study of real-time quantitative PCR assay. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2011;63(3):272-280. [24] Oh HA, Choi HJ, Kim NJ, et al. Anti-stress effect of astragaloside IV in immobilized mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;153(3):928-932. [25] Kim MH, Kim SH, Yang WM. Beneficial effects of Astragaloside IV for hair loss via inhibition of Fas/Fas L-mediated apoptotic signaling. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e92984. [26] Segovia JA, Tsai SY, Chang TH, et al. Nedd8 regulates inflammasome-dependent caspase-1 activation. Mol Cell Biol. 2015; 35(3):582-597. [27] Guey B, Bodnar M, Manié SN, et al. Caspase-1 autoproteolysis is differentially required for NLRP1b and NLRP3 inflammasome function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(48):17254-17259. [28] imard JC, Cesaro A, Chapeton-Montes J, et al. S100A8 and S100A9 induce cytokine expression and regulate the NLRP3 inflammasome via ROS-dependent activation of NF-kappaB. PLoS One. 2013;8(8): e72138. [29] Mathews RJ, Robinson JI, Battellino M, et al. Evidence of NLRP3-inflammasome activation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA); genetic variants within the NLRP3-inflammasome complex in relation to susceptibility to RA and response to anti-TNF treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):1202-1210. [30] Sode J, Vogel U, Bank S, et al. Anti-TNF treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis patients is associated with genetic variation in the NLRP3-inflammasome. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100361. |