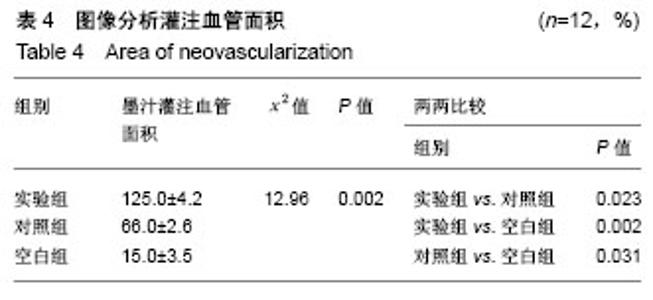
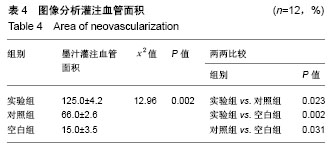
| [1] Ichiseki T,Ueda S,Ueda Y,et al.Involvement of necroptosis, a newly recognized cell death type, in steroid-induced osteonecrosis in a rabbit model.Int J Med Sci.2017;14(2): 110-114.[2] Nabi S,Rao B,Gulati R,et al.Abstracts from the 38th Annual Meeting of the Society of General Internal Medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30 Suppl 2:45-551.[3] Bai R,Liu W,Zhao A,et al.Nitric oxide content and apoptosis rate in steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Exp Ther Med. 2015;10(2):591-597. [4] Riemenschneider SB,Mattia DJ,Wendel JS,et al.Inosculation and perfusion of pre-vascularized tissue patches containing aligned human microvessels after myocardial infarction. Biomaterials.2016;97: 51-61. [5] Asahara T,Murohara T,Sullivan A,et al.Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis.Science.1997; 275(5230): 964-967.[6] Wang S,Chen Z,Tang X,et al.Transplantation of vascular endothelial growth factor 165-transfected endothelial progenitor cells for the treatment of limb ischemia. Mol Med Rep.2015;12(4): 4967-4974.[7] Herzog B,Pelletmany C,Britton G,et al.VEGF binding to NRP1 is essential for VEGF stimulation of endothelial cell migration, complex formation between NRP1 and VEGFR2, and signaling via FAK Tyr407 phosphorylation.Mol Biol Cell.2011;22(15): 2766-2776.[8] Müller CE,Schiedel AC,Zimmermann H.PURINES 2014: nucleotides, nucleosides and nucleobases - international conference on signalling, drugs and targets.Purinergic Signal.2014;10(4): 651-656. [9] 王皓,李谌,郜玉忠. 突变型低氧诱导因子1α加速骨缺损部位新血管生成的实验观察[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2015, 36(4): 455-461.[10] Tang W,Yang F,Li Y,et al.Transcriptional Regulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) by Osteoblast-specific Transcription Factor Osterix (Osx) in Osteoblasts*.J Biol Chem. 2012;287(3):1671-1678.[11] 戚超,效军,效强,等.多壁碳纳米管改善激素性股骨头坏死模型兔的股骨头形态[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(16): 2493-2498.[12] Zwetsloot KA, Westerkamp LM, Holmes BF,et al.AMPK regulates basal skeletal muscle capillarization and VEGF expression but is not necessary for the angiogenic response to exercise. J Physiol. 2008;586(24):6021-6035.[13] Fulkerson J, Lowe R, Anderson T, et al.Effects of Intraosseous Tibial vs. Intravenous Vasopressin in a Hypovolemic Cardiac Arrest Model. West J Emerg Med. 2016;17(2):222-228.[14] Neves N,Linhares D,Costa G,et al.In vivoand clinical application of strontium-enriched biomaterials for bone regeneration:A systematic review. Bone Joint Res. 2017 ; 6(6):366-375. [15] Billaud M,Lohman AW,Johnstone SR,et al.Regulation of Cellular Communication by Signaling Microdomains in the Blood Vessel Wall.Pharmacol Rev.2014;66(2): 513-569.[16] Michan S,Juan AM,Hurst CG,et al.Sirtuin1 over-expression does not impact retinal vascular and neuronal degeneration in a mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy.Plos One. 2014; 9(1): e85031.[17] Zhu G, Tang Y, Geng N, et al.HIF-α/MIF and NF-κB/IL-6 Axes Contribute to the Recruitment of CD11b+Gr-1+ Myeloid Cells in Hypoxic Microenvironment of HNSCC 1, 2. Neoplasia.2014; 16(2):168-179.[18] Biscetti F,Flex A,Pecorini G,et al.The role of High-mobility group box protein 1 in collagen antibody-induced arthritis is dependent on Vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016;184(1):62-72.[19] 王维军,李嗣生,牛东生,等. 股骨头缺血性坏死骨质含量与VEGF、bFGF、BMP-2 mRNA表达的相关性研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(8): 984-991.[20] Chang KH,Smith SE,Sullivan T,et al.Long-Term Engraftment and Fetal Globin Induction uponBCL11AGene Editing in Bone-Marrow-Derived CD34+Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2017;4: 137-148.[21] He MQ,He MQ,Wang JF,et al.Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Cluster of Differentiation 34 for Assessment of Perioperative Bleeding Risk in Gastric Cancer Patients.Chin Med J (Engl). 2016;129(16):1950-1954.[22] Balaji S,Lesaint M,Bhattacharya SS,et al.Adenoviral Mediated Gene Transfer of IGF-1 Enhances Wound Healing and Induces Angiogenesis. J Surg Res.2014;190(1):367-377.[23] Hatanpaa KJ,Burma S,Zhao D,et al.Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Glioma: Signal Transduction, Neuropathology, Imaging, and Radioresistance. Neoplasia.2010;12(9): 675-684. |