Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (30): 4894-4899.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0991
Previous Articles Next Articles
Antitumor properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles: further investigations is needed on its mechanism and safety
He Guan-ping, Liu Xiao-guang
- Department of Orthopedics, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2018-05-20Online:2018-10-28Published:2018-10-28 -
Contact:Liu Xiao-guang, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China -
About author:He Guan-ping, Doctoral candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81472041
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Guan-ping, Liu Xiao-guang. Antitumor properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles: further investigations is needed on its mechanism and safety[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(30): 4894-4899.
share this article
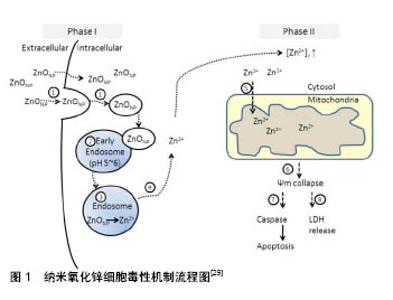
2.1 纳米氧化锌抗肿瘤治疗基础 当前,纳米氧化锌的抗癌特性被广泛研究,主要与其具有以下几个优点有关, 2.1.1 生物相容性 锌是细胞内代谢的重要辅助因子,在维持细胞内环境的稳定起着重要的作用[38]。纳米氧化锌易降解,可参与人体的代谢过程,为其提供营养原料。 2.1.2 增强细胞毒性 尽管细胞外氧化锌具有良好的生物相容性,然后当进入细胞内氧化锌水平过度升高,能够通过锌介导的蛋白活性失衡和氧化应激的影响,增强细胞毒性[11,19-20,22-23,25,30,33]。纳米氧化锌诱导过量活性氧产生,导致氧化应激,当细胞抗氧化能力达到极限,细胞最终死亡[39]。 2.1.3 选择性 大量文献报道,与传统化疗药物相比,纳米氧化锌能够选择性杀伤肿瘤细胞,主要与其在酸性环境中快速水解,肿瘤细胞与正常细胞内活性氧水平差异,以及纳米材料肿瘤细胞内增强渗透与保留效应有 关[6-7,36-37]。 2.2 锌和肿瘤 据报道,纳米氧化锌抗瘤作用与其在水溶液中释放的自由锌离子具有密切关系[6,24,27-29,31-32],因此在此总结锌与肿瘤的关系。 2.2.1 锌及其在人体中的作用 锌元素是体内仅次于铁的最重要和丰富微量元素。锌在体液免疫和细胞免疫方面起着重要的作用,它能够稳定膜和细胞成分的组成,维持细胞和器官的完整性。锌具有调节体内大量酶的作用,参与碳水化合物的降解、合成脂类、蛋白质和核酸,以及其他微量元素的代谢,在维持内环境稳态方面起着至关重要的作用。同时,锌还能通过调节核酸转录,调节基因表达。锌的吸收主要发生在小肠,具有浓度依赖性,其主要是通过肾脏、皮肤和肠排出。 2.2.2 锌与肿瘤发生的关系 锌是哺乳动物体内超过300多种酶的共同辅助因子,其在宿主防御癌症发生和发展中起着至关重要的作用[40]。肿瘤抑制因子p53基因及Caspase酶帮助定期检查和防止细胞癌变。如果细胞一旦显示出恶变倾向,DNA修复机制会立马被激活,修复DNA。如果这种机制不能完成修复DNA,细胞会发生程序性死亡,称为细胞凋亡。研究表明,p53蛋白的一个特定DNA结合结构域通过锌来稳定。因此,锌在维持肿瘤抑制基因p53的活性方面起着重要作用[41]。同样,锌在激活Caspase-6酶活性方面起着重要作用,该酶主要负责凋亡,是细胞凋亡相关分子靶点中对锌最敏感的酶,能够激活Caspase-3,导致细胞死亡[42]。同时锌离子通道能够控制进入细胞内的锌离子量,在维持生命和细胞死亡之间的平衡中起着重要作用[43]。文献表明,低浓度的锌可导致癌症的发生和发展,但高浓度的锌能够杀死细胞[44]。当锌含量超过锌稳态系统的容量,导致锌转运系统故障,增加细胞内锌浓度,最终激活细胞凋亡,导致细胞死亡[45]。然而,缺锌会打破细胞稳态,导致DNA损伤,引起DNA损伤应答机制障碍,损害DNA的完整性,增加癌症的潜在风险。研究报道,细胞内低锌能够诱导大鼠胶质瘤细胞系中DNA氧化损伤,破坏p53及DNA修复[46]。同样,在肺癌、乳腺癌、胃肠道和妇科恶性肿瘤患者血液中血清铜/锌比值增加[47]。此外,在食管癌中锌含量明显低于正常组织[48]。同样,有证据表明,锌在前列腺癌的进展和发展中起着重要作用,其主要和下调锌离子转运蛋白ZIP1,导致细胞内锌含量降低有关[49]。 这些研究结果表明,细胞癌变与细胞内锌浓度的变化具有密切关系。缺乏锌可使细胞稳态发生改变,易于诱导癌症发生。同时,细胞内高浓度锌离子能够杀伤细胞。因此,锌介导的癌症化学预防可能应用于多种癌症的预防和治疗。 2.3 纳米氧化锌选择性杀伤肿瘤细胞 近10年来的研究表明,纳米氧化锌对肿瘤细胞具有强且广泛的杀伤作用。自2008年首次发现纳米氧化性具有选择性杀伤白血病细胞之后[37],陆续报道其对神经胶质[36]、头颈部鳞状细胞癌[33]、肺癌[32]、乳腺癌[6]、宫颈癌等肿瘤细胞均能有效杀伤[7]。综合文献可知对于不同的肿瘤细胞系,纳米氧化锌显出的抗瘤作用也不尽相同,比如:纳米氧化锌杀伤白血病细胞的IC50为0.17 mmol/L[37],然后对于神经胶质瘤其IC50达到1 mmol/L[36],其余报道的肿瘤细胞类型基本处于这个区间之内,主要集中在0.5 mmol/L左右。与此同时,相对于传统的化疗药物,纳米氧化锌显示出很好的选择性杀伤肿瘤细胞能力。Hanley等[37]研究中指出,纳米氧化锌对白血病细胞的杀伤作用能达到正常血液淋巴细胞的28-35倍。Ostrovsky等[36]将乳腺癌细胞与正常乳腺细胞及胰腺癌细胞与正常胰腺癌细胞同时暴露在10 mmol/L纳米氧化锌溶液中,结果两种癌细胞显著死亡,然后两种正常细胞未见明显影响。Sasidharan等[6]研究也表明,纳米氧化锌对脐静脉内皮细胞的杀伤作用明显小于乳腺癌及口腔癌细胞。综合文献可知,纳米氧化锌具有明确选择性杀伤肿瘤细胞的作用。目前的研究主要集中于纳米氧化锌抗瘤的体外研究,体内研究还很缺乏。只有2017年Hassan等[20]的研究明确了通过静脉注射纳米氧化锌能够很好地抑制肝癌细胞生长。因此,需要更多的纳米氧化锌体内抗瘤研究,为其应用于临床提供更加强有力的证据。 2.4 纳米氧化锌的抗瘤机制 目前的研究表明,纳米氧化锌的细胞毒性机制主要是纳米颗粒在细胞内溶解释放出锌离子,诱导活性氧产生,导致锌介导的蛋白活性失衡和氧化应激,最终杀死细胞。最近的研究表明,纳米氧化锌在细胞外释放锌离子,会形成难溶性的无定形磷酸沉淀碳酸锌,保护细胞免受毒性锌损害;另一方面,进入细胞内的纳米氧化锌能够激活Caspase通路,诱导细胞毒性[50],可从3个主要方面论述。 2.4.1 锌介导的蛋白活性失衡 锌是存在于人体内的一种主要微量元素,在细胞内维持一定浓度[51]。细胞内锌浓度的改变可能会造成严重后果,因为锌是哺乳动物体内超过300种酶的辅助因子[40]。随着锌离子在细胞内的释放,细胞内锌浓度超过正常水平,导致锌介导的蛋白活性失衡。这将广泛影响细胞重要的生理过程,包括DNA复制、DNA损伤修复、细胞凋亡、氧化应激、电子传递链、细胞稳态、细胞毒性等,减弱细胞对毒性的耐受能力。如图1所示,纳米氧化锌通过内吞进入细胞,其中一些纳米粒子直接进入细胞,而一些颗粒通过胞饮或吞噬作用进入细胞,同时和内体及溶酶体融合[29]。随着pH值的减小,纳米氧化锌颗粒的溶解速率迅速增加,导致溶酶体不稳定[52]。早期内体的pH值较低(大概6.3),有利于可溶性锌离子的释放。晚期在内体(pH值5.5)和溶酶体内(pH值4.7)进一步降低,能检测到纳米氧化锌快速降解。这表明较低的pH值对锌离子的释放是必要的,因此在血液和细胞外液中其pH接近中性,不利于锌离子的释放[14]。因此,这个过程会导致细胞内锌离子释放增加,导致锌介导的蛋白活性失衡,导致细胞损伤。此外,细胞内锌离子浓度增强,也会导致活性氧增加,通过氧化应激导致细胞损伤。 2.4.2 活性氧的产生和氧化应激 活性氧产生于细胞内的各种过程,包括线粒体呼吸、炎症反应、过氧化物酶活性等。活性氧作为一个生物分子,在维持细胞信号平衡中起着重要的作用。外源性活性氧来源于各种刺激的反应,包括纳米材料的诱导[18,21,26,53]。纳米氧化锌诱导活性氧的方式有2种,一是细胞对纳米颗粒的炎症反应产物;另一方面是激活细胞内氧化还原反应系统,从而产生活性氧[39,54]。同时有研究进一步证明,细胞内纳米氧化锌释放的高浓度锌离子能够聚集至线粒体内,导致线粒体损伤,释放大量活性氧,诱导过度氧化应激,诱导细胞凋亡及坏死发生[14-15,55-56]。 2.4.3 DNA损伤和凋亡 文献表明,细胞内过高的活性氧水平能够导致DNA损伤[13,44]。DNA损伤形式主要是DNA链断裂和DNA蛋白质交联[57-58]。活性氧可与DNA反应元件反应,改变DNA成分的组成,使DNA发生突变。比如,OH自由基是细胞内的一种高活性的活性氧,能够通过形成8-羟基脱氧鸟苷(8-OHdG)导致DNA单链断裂[59]。这些DNA的断裂和交联能够破坏DNA,导致线粒体凋亡途径的激活,诱导凋亡发生,最终导致细胞死亡[31]。同时也有研究证明,纳米氧化锌释放的锌离子能够直接损伤DNA,这种损伤并不受活性氧控制[60],然而锌离子直接损伤DNA机制并不清楚,还需要深入研究。 2.4.4 自噬诱导及自噬性死亡 一直以来,对于纳米氧化锌的细胞毒性机制研究主要集中在通过诱导细胞凋亡发生方面[21,27,31-32,35]。近年来有研究发现,在纳米氧化锌诱导的细胞死亡中并没有检测到凋亡的发生,然而纳米氧化锌处理后的细胞自噬水平明显升高,并且与细胞死亡密切相关[16-17,56,61]。通过自噬抑制剂处理后,细胞死亡几乎都得到了逆转,说明纳米氧化锌诱导的自噬促进细胞死亡。然而,细胞发生自噬并不等于发生自噬性死亡,判断细胞发生自噬行死亡需要满足以下3点:确定在没有凋亡发生的情况下;通过自噬抑制剂能够阻止细胞死亡;明确有自噬流增加。但综述所有与纳米氧化锌杀伤肿瘤相关的文献,皆没有从这3个方面系统的研究和论证。目前,在纳米氧化锌杀伤肿瘤细胞的研究中,对于自噬是直接还是辅助作用亦或只是细胞企图拯救细胞死亡无果的过程,还不明确。因此,自噬在纳米氧化锌导致细胞死亡中的角色还需要深入研究。 2.5 选择性杀伤肿瘤细胞机制 纳米氧化锌选择性杀伤癌细胞的特性,为其应用于体内靶向杀伤肿瘤细胞提供了良好的前期基础。综述文献,纳米氧化锌选择性可能与下列因素有关。 2.5.1 通过增强渗透和保留效应及静电相互作用选择性定位 纳米颗粒由于其小尺寸和表面性质,在肿瘤细胞内显示出增强渗透和保留效应。由于肿瘤细胞生长快速,导致其血管和淋巴管及细胞之间的紧密连接发育不完全。肿瘤内在血管间隙大小介于100 nm到1 μm之间,纳米颗粒很容易通过血管向肿瘤细胞扩散,从而显示出选择性增强渗透入肿瘤细胞。这种纳米材料从血液运输到肿瘤内部的过程称为外渗。外渗液和颗粒能够被健康组织中的淋巴迅速带走。然而,由于肿瘤细胞淋巴系统发育不完全,致使流入其内的纳米颗粒阻滞,增加纳米颗粒在肿瘤组织内的存留时间,提高纳米颗粒在肿瘤细胞内的扩散。因此,增强渗透和保留效应能使纳米颗粒专门定位在肿瘤细胞内,从而显示出更强的杀伤能力[62]。 2.5.2 通过静电特性选择性杀伤肿瘤细胞 纳米氧化锌的静电特性也有利于其选择性的靶向杀伤肿瘤。纳米氧化锌表面有中性羟基附着,在其表面电荷行为中扮演着重要角色。一方面,纳米氧化锌颗粒的等电点为9.0-10.0,导致其在生理环境下带正电荷。另一方面,癌细胞外膜上通常有高浓度的阴离子磷脂[63]。这导致纳米氧化锌和癌细胞存在静电吸引力,促进肿瘤细胞对选择性定位,摄取和吞噬。 2.5.3 通过活性氧水平差异选择性杀伤 细胞内活性氧水平的差异,为纳米氧化锌选择性杀伤癌细胞提供了另外一种合理解释。研究表明,癌细胞内产生的活性氧水平相对大于正常细胞内水平[6,36]。活性氧及各种信号分子大量存在于快速增殖的细胞,如癌细胞,主要是由于与正常细胞相比,其新陈代谢率相对更快[64]。当纳米氧化锌处理后,癌细胞内激活的化学物质和信号分子,使细胞产生更多的活性氧,造成严重的氧化应激,导致细胞死亡。相比之下,纳米氧化锌处理后,正常细胞产生活性氧的生成量相对是比较低,所产生的氧化应激不足以杀死细胞,具有较低的细胞毒性反应。因此,这可能是纳米氧化锌选择性杀伤过度增殖细胞,包括癌细胞的潜在机制。 2.5.4 肿瘤酸性环境 前述总结,锌离子在纳米氧化锌抗瘤作用中起着决定性作用。相对于正常细胞,肿瘤细胞酸性环境有利于锌离子从纳米氧化锌表面快速释放,能够在肿瘤细胞内及细胞微环境中快速集聚高浓度锌离子,导致肿瘤细胞死亡[6,29]。 2.6 纳米氧化锌颗粒的主要性质与细胞生物学关系 2.6.1 尺寸 尺寸是纳米粒子的一个关键性质。10- 100 nm尺寸范围被认为生物应用最佳。这个范围内的较低尺寸是基于对肾小球毛细血管壁-外筛分系数的测量,因肾脏第一次消除的阈值约为10 nm。一些研究表明,纳米颗粒直径小于10 nm的积累可更有效和深入地渗透在肿瘤,然而大量研究表明,小于10 nm的颗粒对机体正常细胞毒性较大。纳米尺寸的粒子不容易被细胞膜阻挡,易进入细胞,进入细胞的纳米粒子可与生物分子相互作用,通过调控细胞周期诱导细胞凋亡,破坏细胞内在的动态平衡,进而产生细胞毒性。肝脏和脾脏内在的巨噬细胞会迅速清除大部分进入血管的纳米颗粒。被称为“调理素”的血液蛋白,能吸附任何进入血液的异物,最终被组织巨噬细胞靶向摄取。 2.6.2 高表面积/体积比 纳米颗粒具有很高的表面积/体积比。这种特性能够增加其与物质的表面接触,增加其反应活性和溶解度等。因此,各种配体和靶向分子可结合在颗粒表面,介导纳米药物输送。 2.6.3 其他 纳米颗粒的表面电荷对其生物活性也有重要影响。高表面电荷能够增加巨噬细胞的清除活性,快速清除纳米粒子。纳米粒子的其他特性还包括高纯度、结晶度和化学成分、量子效应等影响其化学活性的因素等。 "
| [1] Smalley KS,Herlyn M.Towards the targeted therapy of melanoma.Mini Rev Med Chem.2006;6(4):387-393.[2] Langer R.Drug delivery and targeting.Nature.1998;392(6679 Suppl): 5-10.[3] Gowda R,Jones NR,Banerjee S,et al.Use of Nanotechnology to Develop Multi-Drug Inhibitors For Cancer Therapy.J Nanomed Nanotechnol.2013;4(6).pii:184.[4] Wang J,Lee JS,Kim D,et al.Exploration of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as a Multi-target and Multi-functional Anticancer Nanomedicine.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(46):39971-39984.[5] Liu J,Kang Y,Yin S,et al.Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce toxic responses in human neuroblastoma SHSY5Y cells in a size-dependent manner.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:8085-8099.[6] Sasidharan A,Chandran P,Menon D,et al.apid dissolution of ZnO nanocrystals in acidic cancer microenvironment leading to preferential apoptosis.Nanoscale.2011;3(9):3657-3669.[7] Sirelkhatim A,Mahmud S,Seen A,et al.Preferential cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticle towards cervical cancer cells induced by ROS-mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest for cancer therapy.J Nanopart Res. 2016;18(8):219.[8] Zhang Y,Nayak TR,Hong H,et al.Biomedical applications of zinc oxide nanomaterials.Curr Mol Med. 2013;13(10):1633-1645.[9] Zhang AP,Sun YP.Photocatalytic killing effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on Ls-174-t human colon carcinoma cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2004; 10(21):3191-3193.[10] Wason MS,Colon J,Das S,et al.Sensitization of pancreatic cancer cells to radiation by cerium oxide nanoparticle-induced ROS production. Nanomedicine.2013;9(4):558-569.[11] Shen C,James SA,de Jonge MD,et al.Relating cytotoxicity, zinc ions, and reactive oxygen in ZnO nanoparticle-exposed human immune cells.Toxicol Sci.2013;136(1:120-130.[12] Narayanan KB,Sakthive Nl.Biological synthesis of metal nanoparticles by microbes.Adv Colloid Interface Sci.2010;156(1-2):1-13.[13] Bhattacharyya S,Kudgus RA,Bhattacharya R,et al.Inorganic nanoparticles in cancer therapy, Pharm Res. 2011;28(2):237-259.[14] Ba DP, Zhang XF,Zhang GL,et al.Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis and autophagy in human ovarian cancer cells.Int J Nanomedicine.2017;12:6521-6535.[15] Arakha M,Roy J,Nayak PS,et al.Zinc oxide nanoparticle energy band gap reduction triggers the oxidative stress resulting into autophagy- mediated apoptotic cell death.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;110:42-53.[16] Roy R,Singh SK,Chauhan LK,et al.Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy via PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibition. Toxicol Lett.2014;227(1):29-40.[17] Yu KN,Yoon TJ,Minai-Tehrani A,et al.Zinc oxide nanoparticle induced autophagic cell death and mitochondrial damage via reactive oxygen species generation.Toxicol In Vitro. 2013;27(4):1187-1195.[18] Xia T,Kovochich M,Liong M,et al.Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties.ACS Nano. 2008;2(10): 2121-2134.[19] Ezhuthupurakkal PB,Ariraman S,Arumugam S,et al.Anticancer potential of ZnO nanoparticle-ferulic acid conjugate on Huh-7 and HepG2 cells and diethyl nitrosamine induced hepatocellular cancer on Wistar albino rat.Nanomedicine.2018;14(2):415-428. [20] Hassan HF,Mansour AM,Abo-Yousse AMf,et al.Zinc oxide nanoparticles as a novel anticancer approach; in vitro and in vivo evidence.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;44(2):235-243.[21] Chakraborti S,Chakraborty S,Saha S,et al.PEG-functionalized zinc oxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells through reactive oxygen species-dependent impairment of DNA damage repair enzyme NEIL2.Free Radic Biol Med.2017;103:35-47.[22] Boroumand Moghaddam A, Moniri M,Azizi S,et al.Eco-Friendly Formulated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in the MCF-7 Cancer Cell Line.Genes (Basel). 2017;8(10). pii: E281.doi:10.3390/genes8100281.[23] Paino IM,J Gonçalves F,Souza FL,et al.Zinc Oxide Flower-Like Nanostructures That Exhibit Enhanced Toxicology Effects in Cancer Cells.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016;8(48):32699-32705.[24] Moon SH,Choi WJ,Choi SW,et al.Anti-cancer activity of ZnO chips by sustained zinc ion release.Toxicol Rep. 2016;3:430-438. [25] Al-Ajmi MF,Hussain A,Ahmed F.Novel synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their enhanced anticancer activity: Role of ZnO as a drug carrier. Ceramic Int.2016;42(3):4462-4469.[26] Wahab R,Siddiqui MA,Saquib Q,et al.ZnO nanoparticles induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF-7 cancer cells and their antibacterial activity.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;117: 267-276. [27] Setyawati MI,Tay CY,Leong DT.Effect of zinc oxide nanomaterials- induced oxidative stress on the p53 pathway. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(38):10133-10142. [28] Daniel AG,Peterson EJ,Farrell NP.The bioinorganic chemistry of apoptosis: potential inhibitory zinc binding sites in caspase-3.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.2014;53(16):4098-4101.[29] Kao YY,Chen YC,Cheng TJ,et al.Zinc oxide nanoparticles interfere with zinc ion homeostasis to cause cytotoxicity.Toxicol Sci. 2012; 125(2):462-472.[30] Wahab R,Kaushik NK,Verma AK,et al.Fabrication and growth mechanism of ZnO nanostructures and their cytotoxic effect on human brain tumor U87, cervical cancer HeLa, and normal HEK cells.J Biol Inorg Chem.2011;16(3):431-442.[31] Ng KW,Khoo SP, Heng BC,et al.The role of the tumor suppressor p53 pathway in the cellular DNA damage response to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials.2011;32(32):8218-8225.[32] Ahamed M,Akhtar MJ,Raja M,et al.ZnO nanorod-induced apoptosis in human alveolar adenocarcinoma cells via p53, survivin and bax/bcl-2 pathways: role of oxidative stress. Nanomedicine. 2011;7(6):904-913.[33] Hackenberg S,Scherzed A,Kessler M,et al.Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce photocatalytic cell death in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines in vitro.Int J Oncol.2010;37(6):1583-1590.[34] Chandrasekaran M,Pandurangan M.In Vitro Selective Anti-Proliferative Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Against Co-Cultured C2C12 Myoblastoma Cancer and 3T3-L1 Normal Cells.Biol Trace Elem Res.2016;172(1):148-154.[35] Akhtar MJ,Ahamed M,Kumar S,et al.Zinc oxide nanoparticles selectively induce apoptosis in human cancer cells through reactive oxygen species.Int J Nanomedicine.2012;7:845-857.[36] Ostrovsky S,Kazimirsky G,Gedanken A,et al.Selective cytotoxic effect of ZnO nanoparticles on glioma cells.Nano Res.2009;2(11):882-890.[37] Hanley C,Layne J,Punnoose A,et al.Preferential killing of cancer cells and activated human T cells using ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechnology. 2008;19(29):295103.[38] Brandt EG,Hellgren M,Brinck T,et al.Molecular dynamics study of zinc binding to cysteines in a peptide mimic of the alcohol dehydrogenase structural zinc site.Phys Chem Chem Phys.2009;11(6):975-983.[39] Rasmussen JW,Martinez E,Louka P,et al.Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications.Expert Opin Drug Deliv.2010;7(9):1063-1077.[40] Ho E.Zinc deficiency, DNA damage and cancer risk.J Nutr Biochem. 2004;15(10):572-578.[41] Cho Y,Gorina S,Jeffrey PD,et al.Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science.1994;265(5170):346-355.[42] Dhawan DK,Chadha VD.Zinc: a promising agent in dietary chemoprevention of cancer.Indian J Med Res. 2010;132:676-682.[43] Kagara N,Tanaka N,Noguchi S,et al.Zinc and its transporter ZIP10 are involved in invasive behavior of breast cancer cells.Cancer Sci.2007; 98(5):692-697.[44] Bisht G,Rayamajhi S.ZnO Nanoparticles: A Promising Anticancer Agent. Nanobiomedicine.2016;3:9.[45] Maret W.Zinc in Cellular Regulation: The Nature and Significance of "Zinc Signals".Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(11).pii: E2285.doi: 10.3390/ijms18112285.[46] Ho E,Ames BN.Low intracellular zinc induces oxidative DNA damage, disrupts p53, NFkappa B, and AP1 DNA binding, and affects DNA repair in a rat glioma cell line.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(26): 16770-16775.[47] Zowczak M,Iskra M,Torlinski L,et al.Analysis of serum copper and zinc concentrations in cancer patients.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2001;82(1-3): 1-8.[48] Abnet CC,Lai B,Qiao YL,et al.Zinc concentration in esophageal biopsy specimens measured by x-ray fluorescence and esophageal cancer risk.J Natl Cancer Inst.2005;97(4):301-306.[49] Costello LC,Franklin RB,Feng P,et al.Zinc and prostate cancer: a critical scientific, medical, and public interest issue (United States). Cancer Causes Control.2005;16(8):901-915.[50] Turney TW,Duriska MB,Jayaratne V,et al.Formation of zinc-containing nanoparticles from Zn(2)(+) ions in cell culture media: implications for the nanotoxicology of ZnO.Chem Res Toxicol.2012;25(10):2057-2066.[51] Chasapis CT,Loutsidou AC,Spiliopoulou CA,et al.Zinc and human health: an update, Arch Toxicol.2012;86(4):521-534.[52] Casey JR,Grinstein S,Orlowski J.Sensors and regulators of intracellular pH.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.2010;11(1):50-61.[53] Manke A,Wang L,Rojanasakul Y. Mechanisms of nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress and toxicity, Biomed Res Int.2013;2013:942916.[54] Wilson MR,Lightbody JH,Donaldso K,et al.Interactions between ultrafine particles and transition metals in vivo and in vitro.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.2002;184(3):172-179.[55] Song W,Zhang J,Guo J,et al.Role of the dissolved zinc ion and reactive oxygen species in cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles.Toxicol Lett.2010;199(3):389-397.[56] Zhang J,Qin X,Wang B,et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles harness autophagy to induce cell death in lung epithelial cells.Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(7):e2954.[57] Kawanishi S,Hiraku Y,Murata M,et al.The role of metals in site-specific DNA damage with reference to carcinogenesis, Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;32(9):822-832.[58] Shi H,Hudson LG,Liu KJ.Oxidative stress and apoptosis in metal ion-induced carcinogenesis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;37(5):582-593.[59] Valavanidis A,Vlachogianni T,Fiotakis C.8-hydroxy-2' -deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG): A critical biomarker of oxidative stress and carcinogenesis.J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2009;27(2): 120-139.[60] Heim J,Felder E,Tahir MN,et al.Genotoxic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles.Nanoscale.2015;7(19):8931-8938.[61] Johnson BM,Fraietta JA,Gracias DT,et al.Acute exposure to ZnO nanoparticles induces autophagic immune cell death. Nanotoxicology. 2015;9(6):737-748.[62] Davis ME,Chen ZG,Shin DM.Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for cancer.Nat Rev Drug Discov.2008;7(9):771-782.[63] Abercrombie M,Ambrose EJ.The surface properties of cancer cells: a review.Cancer Res.1962;22:525-548.[64] Liou GY,Storz P.Reactive oxygen species in cancer.Free Radic Res. 2010;44(5):479-496. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||