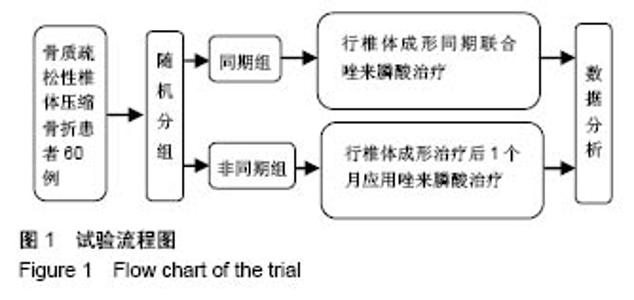
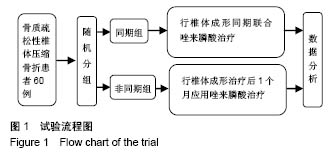
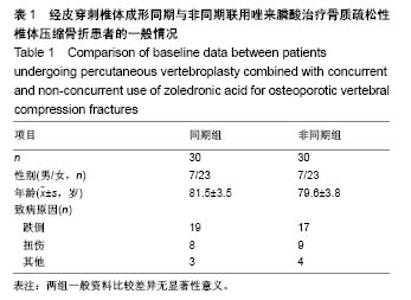
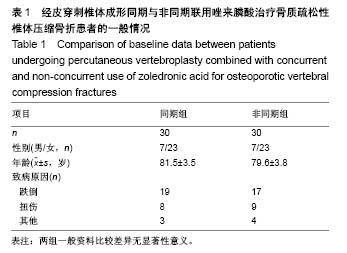
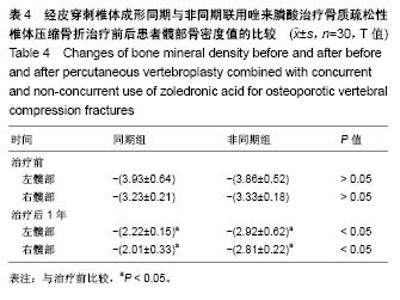
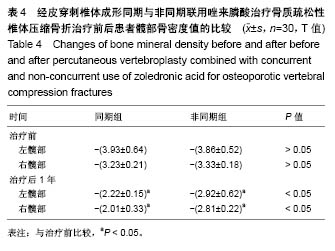
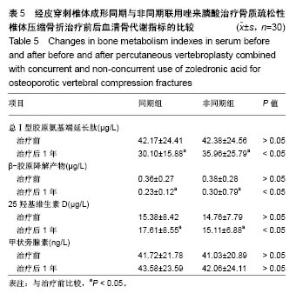
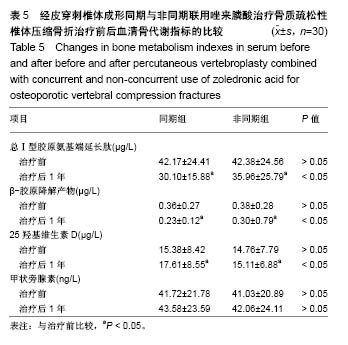
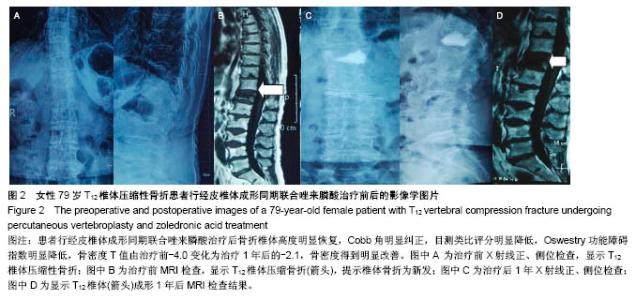
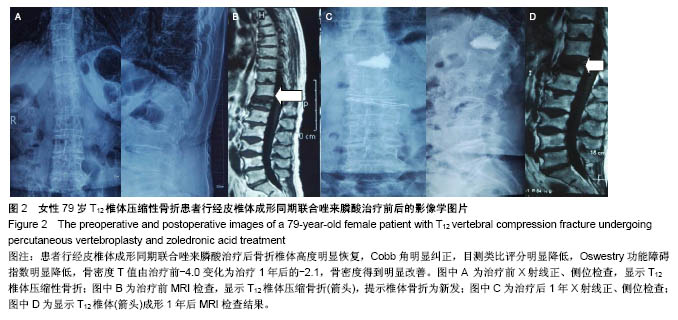
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (30): 4788-4793.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0980
Previous Articles Next Articles
Percutaneous vertebroplasty combined with concurrent and non-concurrent use of zoledronic acid in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a 1-year follow-up comparison
Li Ji, Zhao Wei-biao, He Zi-wei, Li Yi
- Second Department of Orthopedics, Jinqiu Hospital of Liaoning Province, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2018-08-07Online:2018-10-28Published:2018-10-28 -
Contact:Zhao Wei-biao, Chief physician, Professor, Second Department of Orthopedics, Jinqiu Hospital of Liaoning Province, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Li Ji, Master, Attending physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, Jinqiu Hospital of Liaoning Province, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Ji, Zhao Wei-biao, He Zi-wei, Li Yi. Percutaneous vertebroplasty combined with concurrent and non-concurrent use of zoledronic acid in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a 1-year follow-up comparison[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(30): 4788-4793.
share this article
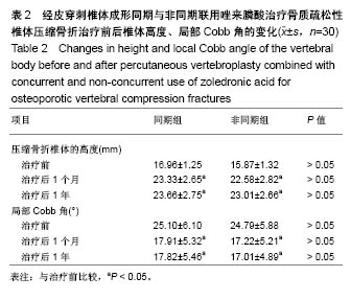
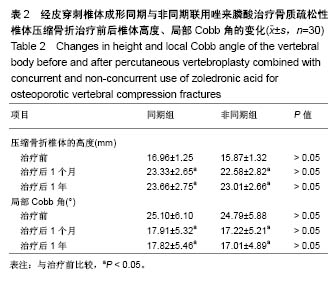
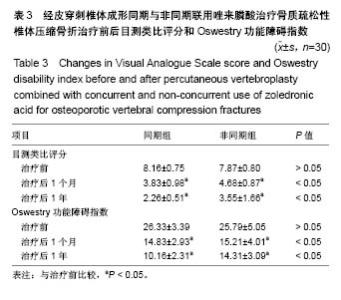
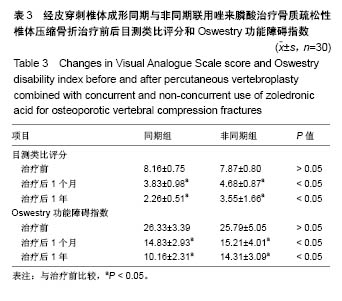
| [1] Clark W, Bird P, Diamond T, et al. Vertebroplasty for acute painful osteoporotic fractures (VAPOUR): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16:159. [2] Matos AC, Marques CF, Pinto RV, et al. Novel doped calcium phosphate-PMMA bone cement composites as levofloxacin delivery systems. Int J Pharm. 2015;490(1-2):200-208.[3] Miller FG, Kallmes DF, Buchbinder R. Vertebroplasty and the placebo response. Radiology. 2011;259(3):621-625. [4] Wong CC, McGirt MJ. Vertebral compression fractures: a review of current management and multimodal therapy. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2013;6:205-214. [5] 徐苓.骨质疏松症[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2011:279.[6] Venmans A, Klazen CA, Lohle PN, et al. Natural history of pain in patients with conservatively treated osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: results from VERTOS II. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(3):519-521. [7] Cox M, Levin DC, Parker L, et al. Vertebral Augmentation After Recent Randomized Controlled Trials: A New Rise in Kyphoplasty Volumes. J Am Coll Radiol. 2016;13(1):28-32.[8] Chang X, Lv YF, Chen B, et al. Vertebroplasty versus kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a meta-analysis of prospective comparative studies. Int Orthop. 2015;39(3):491-500. [9] Yang DL, Yang SD, Chen Q, et al. The Treatment Evaluation for Osteoporotic Kummell Disease by Modified Posterior Vertebral Column Resection: Minimum of One-Year Follow-Up. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:606-612.[10] 张智海,刘忠厚,李娜,等.中国人骨质疏松症诊断标准专家共识(第三稿•2014版)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(9):1007-1010.[11] Watts NB, Harris ST, Genant HK. Treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Osteoporos Int. 2001;12(6):429-437.[12] Alexandru D, So W. Evaluation and management of vertebral compression fractures. Perm J. 2012;16(4):46-51.[13] Vodi?ar M, Košak R, Vengust R. Long-term Results of Surgical Treatment for Symptomatic Anterior Cervical Osteophytes: A Case Series With Review of the Literature. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29(9): E482-E487.[14] Chen LH, Hsieh MK, Liao JC, et al. Repeated percutaneous vertebroplasty for refracture of cemented vertebrae. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(7):927-933. [15] Palacios S, Neyro JL, Fernández de Cabo S, et al. Impact of osteoporosis and bone fracture on health-related quality of life in postmenopausal women. Climacteric. 2014;17(1):60-70.[16] Esses SI, McGuire R, Jenkins J, et al. The treatment of symptomatic osteoporotic spinal compression fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19(3):176-182.[17] 胡成栋,刘曦,周玉军,等.椎体成形治疗中聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(21):3823-3830.[18] Lee HM, Park SY, Lee SH, et al. Comparative analysis of clinical outcomes in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs): conservative treatment versus balloon kyphoplasty. Spine J. 2012;12(11):998-1005. [19] Nussbaum DA, Gailloud P, Murphy K. A review of complications associated with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty as reported to the Food and Drug Administration medical device related web site. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004;15(11):1185-1192.[20] Lee BJ, Lee SR, Yoo TY. Paraplegia as a complication of percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(19):E419-422.[21] 常青,史相钦.PKP结合抗骨质疏松药物治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015,30(5):522-523.[22] Montazerolghaem M, Rasmusson A, Melhus H, et al. Simvastatin-doped pre-mixed calcium phosphate cement inhibits osteoclast differentiation and resorption. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(5):83.[23] 朱洲,王生介,厉晓龙,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥椎体成形与保守治疗胸腰椎体新鲜骨质疏松性压缩骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(39):6271-6275.[24] NIH Consensus Development Panel on Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. JAMA. 2001;285(6):785-795.[25] 朱汉民,邱贵兴,李梅,等.原发性骨质疏松症的治疗与预防[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2015,8(5):377-384.[26] 邱贵兴,裴福兴,胡侦明,等.中国骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南(骨质疏松性骨折诊断及治疗原则)[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2015,10(5): 371-374.[27] Moriwaki K, Mouri M, Hagino H. Cost-effectiveness analysis of once-yearly injection of zoledronic acid for the treatment of osteoporosis in Japan. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(6):1939-1950.[28] Orimo H, Yaegashi Y, Hosoi T, et al. Hip fracture incidence in Japan: Estimates of new patients in 2012 and 25-year trends. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(5):1777-1784. [29] Byun JH, Jang S, Lee S, et al. The Efficacy of Bisphosphonates for Prevention of Osteoporotic Fracture: An Update Meta-analysis. J Bone Metab. 2017;24(1):37-49. [30] Compston J, Cooper A, Cooper C, et al. UK clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Arch Osteoporos. 2017; 12(1):43.[31] Heini PF, Berlemann U. Bone substitutes in vertebroplasty. Eur Spine J. 2001;10 Suppl 2:S205-213.[32] Canalis E, Giustina A, Bilezikian JP. Mechanisms of anabolic therapies for osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(9):905-916.[33] Bukata SV, Puzas JE. Orthopedic uses of teriparatide. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2010;8(1):28-33. [34] Bashutski JD, Eber RM, Kinney JS, et al. Teriparatide and osseous regeneration in the oral cavity. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(25): 2396-2405. [35] Peichl P, Holzer LA, Maier R, et al. Parathyroid hormone 1-84 accelerates fracture-healing in pubic bones of elderly osteoporotic women. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(17):1583-1587. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [12] | Feng Guancheng, Fang Jianming, Lü Haoran, Zhang Dongsheng, Wei Jiadong, Yu Bingbing. How does bone cement dispersion affect the early outcome of percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3450-3457. |
| [13] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||