Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (22): 3527-3532.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0846
Previous Articles Next Articles
Oxidized dextran/aminated carboxymethyl chitosan two-component hydrogel adhesive based on Schiff base reaction
Li Dan-dan, Mo Xiu-mei
- School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China
-
Received:2018-01-24Online:2018-08-08Published:2018-08-08 -
Contact:Mo Xiu-mei, M.D., Doctoral supervisor, Professor, School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China -
About author:Li Dan-dan, Master candidate, School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Dan-dan, Mo Xiu-mei . Oxidized dextran/aminated carboxymethyl chitosan two-component hydrogel adhesive based on Schiff base reaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(22): 3527-3532.
share this article
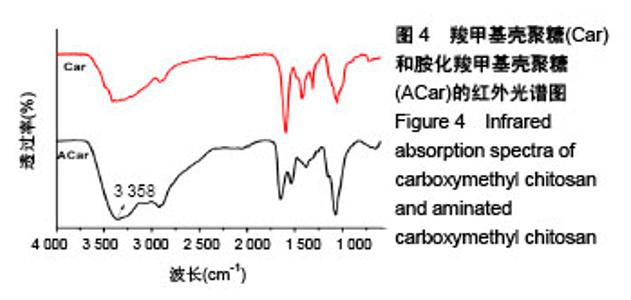
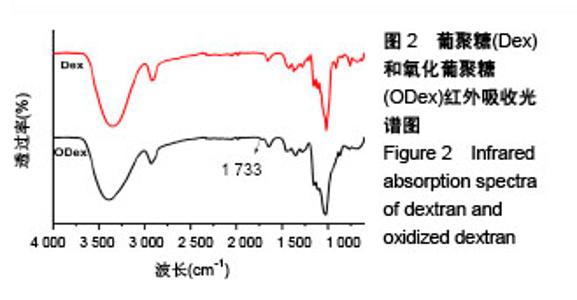
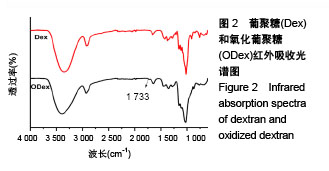
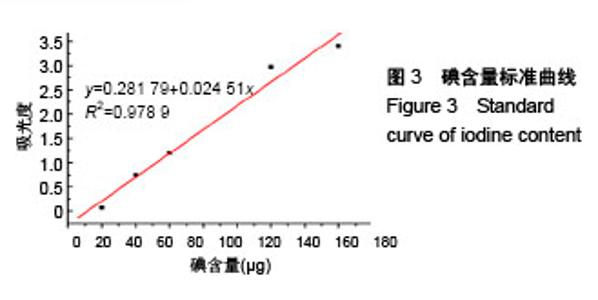
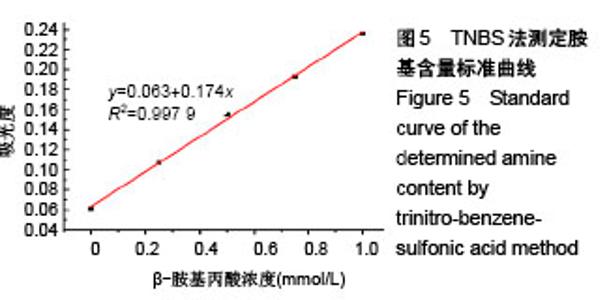
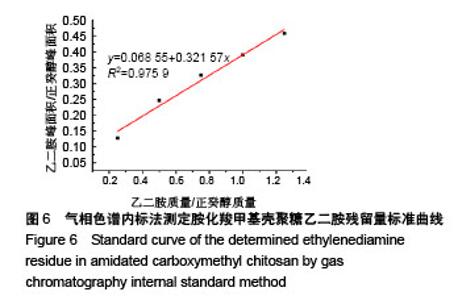
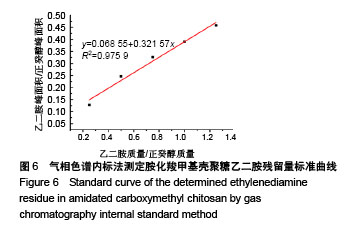
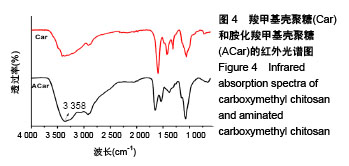
2.2 胺化羧甲基壳聚糖 2.2.1 胺化羧甲基壳聚糖胺化度分析 羧甲基壳聚糖本身具有胺基,在图4中3 358 cm-1处的宽峰对应于胺基与羟基的伸缩振动。实验利用乙二胺在EDC的作用下,对羧甲基壳聚糖上的羧基基团进行胺基化改性,从而增加羧甲基壳聚糖的胺基含量。从图4可看到,胺化羧甲基壳聚糖在 3 358 cm-1吸收峰大幅度增强,说明了胺基化后羧甲基壳聚糖胺基-NH2与羟基-OH的伸缩振动频率增加,证明了胺基化后羧甲基壳聚糖的胺基含量确实在进一步增加。 β-胺基丙酸溶液的胺基含量标准曲线如图5所示,拟合方程为y=0.063+0.174x,R2=0.997 9。在415 nm波长下对胺化羧甲基壳聚糖和未胺化羧甲基壳聚糖进行同样测试,其吸光度平均值分别为0.174和0.137,通过标准曲线标定并计算后可得出胺化羧甲基壳聚糖中的胺基含量平均值为0.012 8 mmol/g,未胺化羧甲基壳聚糖的胺基含量平均值为0.008 5 mmol/g。 "
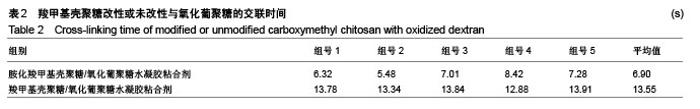
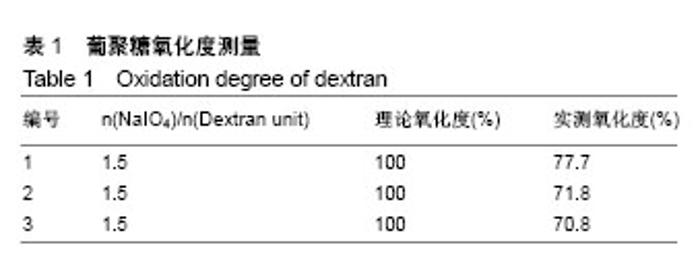
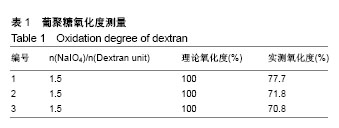
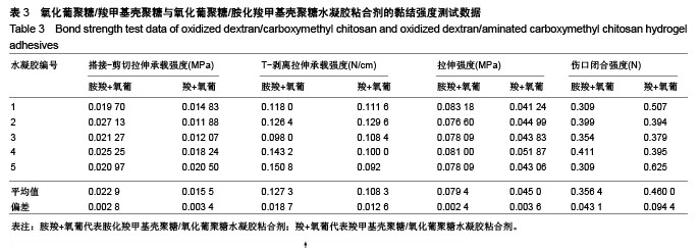
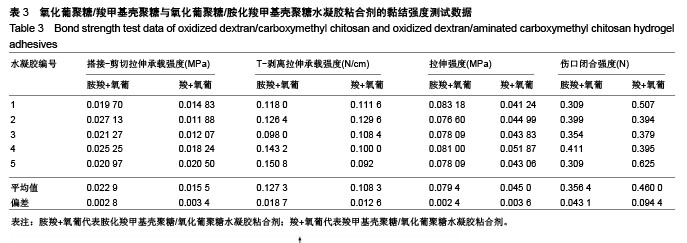
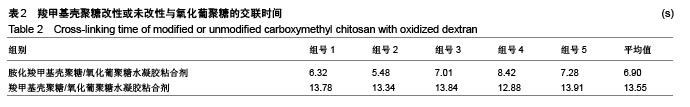
2.3 水凝胶结合剂 2.3.1 交联时间的测定与分析 利用胺化羧甲基壳聚糖和羧甲基壳聚糖与氧化葡聚糖交联,制备出基于席夫碱反应的双组分水凝胶粘合剂,其成胶时间如表2所示。 由表2可知,胺化羧甲基壳聚糖与氧化葡聚糖交联的平均时间为6.90 s,而羧甲基壳聚糖与氧化葡聚糖交联的平均时间为13.55 s,可见胺基化后的羧甲基壳聚糖胺基含量的增加,导致其与氧化葡聚糖的交联时间显著降低,减少了50%左右,有利于成胶。 2.3.2 水凝胶粘合剂的黏结强度分析 表3是两种水凝胶粘合剂的搭接-剪切拉伸承载强度、T-剥离拉伸承载强度、拉伸强度和伤口闭合强度的测试数据,可以看到,氧化葡聚糖/胺化羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶粘合剂的搭接-剪切拉伸承载强度、T-剥离拉伸承载强度和拉伸强度平均值分别为0.022 86 MPa、0.127 3 N/cm和0.793 9 MPa,较未改性水凝胶分别增大47.48%,17.54%和76.42%,增幅明显。这是由于羧甲基壳聚糖经胺化处理后,其胺基含量增加,水凝胶的交联度随之增大,同时氢键等分子间作用力增大,故强度更高。此外,伤口闭合强度由于测试接触面积小而具有较大的误差,有待进一步验证。"
| [1] 胡亮,郑昌琼,冉均国.医用粘合剂研究进展[J].国外医学:生物医学工程分册,1998,21(1):26.[2] Pfister WR.Silicone PSAS of ferflexibility for medical,pharmaceutical use.Adhesives Age.1990;33(3):2.[3] Han JM,Hong G,Hayashida K,et al.Influence of composition on the adhesive strength and initial viscosity of denture adhesives.Dent Mater J.2014;33(1):98-103.[4] Imazato S,Ma S,Chen JH,et al.Therapeutic polymers for dental adhesives: loading resins with bio-active components.Dent Mater. 2014;30(1):97-104.[5] Avre WN,Denver SP,Evans SL.Ageing and moisture uptake in polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) bone cements.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2013;32C:76-88.[6] Howe N,Cherpelis B.Obtaining rapid and effective hemostasis: Part 1. Update And review of topical hemostatic agents.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(5):659.e1-659.e17.[7] Duarte AP,Coelho JF,Bordado JC,et al.Surgical adhesives: systematic review of the main types and development forecast.Prog Polymer Sci. 2012;37:1031-1050.[8] Sanders L,Nagatomi J.Clinical applications of surgical adhesives and sealants.Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2014;42(3-4):271-292.[9] Amosi N,Zarzhitsky S,Gilsohn E,et al.Acidic Peptide Hydro-gel Scaffolds Enhance Calcium Phosphate Mineral Turnover intoBone Tissue.Acta Biomaterialia. 2012;8(7):2466-2475.[10] Li S,Wang J,Song L,et al.Injectable PAMAM/ODex double-crosslinked hydrogels with high mechanical strength.Biomed Mater. 2016;12(1): 015012.[11] Bae KH,Wang LS,Kurisawa M.Injectable biodegradable hydrogels: progress and challenges.J Mater Chem B. 2013;1(40):5371-5388.[12] Shekaran A,Garcia JR,Clark AY,et al.Bone regeneration using an alpha 2 beta 1 integrin-specific hydrogel as a BMP2delivery vehicle. Biomaterials.2014;35(21):5453-5461.[13] Balakrishnan B,Joshi N,Banerjee R.Borate aided Schiff's base formation yields in situ gelling hydrogels for cartilage regeneration.J Mater Chem B.2013;1:5564-5577.[14] Yuan L,Wu Y,Gu QS,et al.Injectable photo crosslinked enhanced double-network hydrogelsfrom modified sodium alginate and gelatin. Int J Biol Macromol.2017;96:569-577. [15] Geng X,Yuan L,Mo X.Oxidized dextran/amino gelatin/hyaluronic acid semi- interpenetrating network hydrogels for tissue engineering application.Adv Mater Res. 2013;627:745-750.[16] Weng L,Romanov A,Rooney J,et al.Non-cytotoxic, in situ gelable hydrogels composed of N-carboxyethyl chitosan and oxidized dextran. Biomaterials.2008;29(29):3905-3913.[17] Balakrishnan B,Mohanty M,Umashankar PR,et al.Evaluation of an in situ forming hydrogel wound dressing based on oxidized alginate and gelatin.Biomaterials. 2005;26(32):6335-6342.[18] Mo X,Iwata H,Matsuda S,et al.Soft tissue adhesive composed of modified gelatin and polysaccharides. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2000; 11(4):341-351.[19] Nowakowska M,Zapotoczny S,Sterzel M,et al. Novel Water-Soluble Photosensitizers from Dextrans. Biomacromolecules. 2004;5(3): 1009-1014.[20] Maia J,Ferreira L,Carvalho R,et al.Synthesis and characterization of new injectable and degradable dextran-based hydrogels.Polymer. 2005;46(23):9604-9614.[21] Schacht E,Bogdanov B,Bulcke AVD,et al.Hydrogels prepared by crosslinking of gelatin with dextran dialdehyde.React Functl Polym. 1997;33(2-3):109-116.[22] Massia SP,Stark J,LetbetterDS.Surface-immobilized dextran limits cell adhesion and spreading.Biomaterials.2000;21(22):2253-2261.[23] Wang T,Mu X,Li H, et al.The photocrosslinkable tissue adhesive based on copolymeric dextran/HEMA. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;5;92(2):1423-1431.[24] 崔莉,贾军芳,熊子豪,等.羧甲基壳聚糖/藻酸钠半互穿网络水凝胶的制备及性能研究[J].高分子学报,2014, 58(3):361-368.[25] Dodane V,Vilivalam VD.Pharmaceutical applications of chitosan. Pharm Sci Tech Today.1998;1(6): 246-253.[26] 孙立苹,杜予民,陈凌云,等.羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶制备及其在药物控释中的应用[J].高分子学报,2004,48(2):191-195.[27] Zhao SP,Ma D,Zhang LM.New semi-interpenetrating network hydrogels: Synthesis, characterization and properties. Macromol Biosci.2006;6(6):445-451.[28] Sarem M,Moztarzadeh F,Mozafari M.How can genipin assist gelatin/carbohydrate chitosan scaffolds to act as replacements of load-bearing soft tissues? Carbohydr Polym. 2013; 93(2):635-643.[29] Tseng HJ,Tsou TL,Wang HJ.Characterization of chitosan-gelatin scaffolds for dermal tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013; 7(1):20-31.[30] 王琴梅,廖燕红,滕伟,等.盐酸羟胺-电位滴定法测定氧化海藻酸钠上的醛基浓度[J].分析试验室,2008,27(s1):83-86.[31] Zhao H,Heindel ND.Determination of degree of substitution of formyl groups in polyaldehyde dextran by the hydroxylamine hydrochloride method.Pharm Res.1991;8(3):400-402.[32] 马有香,焦淑婷,张金生,等.分光光度法测定核黄素碘盐碘含量方法的研究[J].中国卫生检验,2008,18(3):460-461.[33] 李人宇,李咏梅,张成燕.分光光度法测定食盐中碘含量方法的评述[J].中国地方病防治杂志, 2008,28(2):105-107.[34] 孙言蓓.新型海藻酸盐-明胶水凝胶的研究[D].天津大学硕士学位论文,2007.[35] 韦广辉.电位滴定法测定胺茶碱片中乙二胺的含量[J].中国药房, 2011, 22(12):1136-1137.[36] 陈赞民,陈颖江.气相色谱法测定胺茶碱及其制剂中乙二胺的含量[J].药物分析杂志,2012,32(9):1673-1676.[37] YY/T 0729.1-2009,组织粘合剂粘接性能试验方法 第1部分:搭接-剪切拉伸承载强度.[38] YY/T 0729.2-2009,组织粘合剂粘接性能试验方法 第2部分:T-剥离拉伸承载强度.[39] YY/T 0729.3-2009,组织粘合剂粘接性能试验方法 第3部分:拉伸强度.[40] YY/T 0729.4-2009,组织粘合剂粘接性能试验方法 第4部分:伤口闭合强度.[41] 王艳红,顾汉卿.医用粘合剂的发展及临床应用进展[J].透析与人工器官, 2008,19(3):23.[42] 侯彪,谢松林.医用粘合剂在血管吻合及修复中应用的研究进展[J].岭南现代临床外科,2016,16(1):1115-120.[43] 张国栋.关于对医用粘合剂的研究[J].化学工程与装备, 2016,45(3): 167-169.[44] 刘加鹏,蒋臻,杨丙晔,等.海洋贻贝粘附蛋白类的结构与功能[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2007,23(11):899-904.[45] Neha T,Manohar V.Enhanced drug release by selective cleavage of cross-links in a double-cross-linked hydrogel.RSC Adv. 2016;6: 102453-102461.[46] Bao D,Chen M,Wang H,et al.Preparation and characterization of double cross-linked hydrogel films from carboxymethyl chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose.Carbohydr Polym. 2014;110:113-120.[47] Ye MM,Jiang R,Zhao J,et al.In situ formation of adhesive hydrogels based on PL with laterally grafted catechol groups and their bonding efficacy to wet organic substrates.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26:273. [48] Yu F,Cao XD,Du J,et al.Multifunctional Hydrogel with Good Structure Integrity, Self-Healing, and Tissue-Adhesive Property Formed by Combining Diels-Alder Click Reaction and Acylhydrazone Bond ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:24023-24031. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Liu Fang, Shan Zhengming, Tang Yulei, Wu Xiaomin, Tian Weiqun. Effects of hemostasis and promoting wound healing of ozone sustained-release hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3445-3449. |
| [13] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||