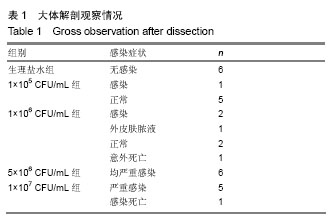
| [1] Harris LG,Richards RG.Staphylococci and implant surfaces:a review.Injury.2006;37(2):3-14.[2] European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System. EARSS Annual Report 2002.[3] Maurer DJ,Merkow RL,Gustilo RB.Infection after intramedullary nailing of severe open tibial fractures initially treated with external fixation.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1989; 71(6):835-838.[4] 杨立民.当今骨科感染的特点与对策[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,1999, 14(2):139-141.[5] 杨小卫,李小康,郭征,等.骨科金属置入物并发感染的动物模型构建方法及效果评价[J],中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(16): 1505-1509.[6] 唐辉,徐永清,郑天娥,等.耐药金黄色葡萄球菌注射总量对兔感染性骨缺损形成的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,9:700-702.[7] 卢旻鹏,蒋电明,权正学,等.兔胫骨慢性骨髓炎动物模型的建立[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2010,5:664-666.[8] Gaudin A,Amador DV,Hamel A,et al.A new experimental model of acute osteomyelitis due to methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus in rabbit.Lett Appl Microbiol.2011;3: 253-257.[9] Patel M,Rojavin Y,Jamali AA,et al.Animal models for the study of osteomyelitis.Semin Plast Surg.2009;2:148-154.[10] 刘春秀.C-反应蛋白定量检测与白细胞计数的敏感性比较[J].中国民康医学,2012,24(18):2204-2205.[11] 王文静,郭丙申.C-反应蛋白与白细胞联合检测的临床应用[J].医学理论与实践,2009,22(6):701-702.[12] Hashimoto H,Kitagawa K,Hougaku H,et al.Relationship between C-reactive protein and progression of early carotid atherosclerosis in hypertensive subjects.Stoke.2004; 35(7): 1625-1630.[13] Mendicino RW,Bowers CA, DPM,Catanzariti AR. Antibiotic- coated Intramedullary Rod.J Foot Ankle Surg. 2009;48(2): 104-110.[14] Lucke M,Schmidmaier G,Sadoni S,et al.Gentamicin coating of metallic implants reduces implant-related osteomyelitis in rats. Bone.2003;32: 521-531.[15] Gustilo RB,Mendoza RM,Williams DN.Problems in the management of type Ⅲ(severe)open fractures:a new classification of type Ⅲ open fractures.J Trauma.1984;24: 742-746. |