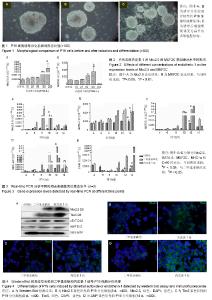
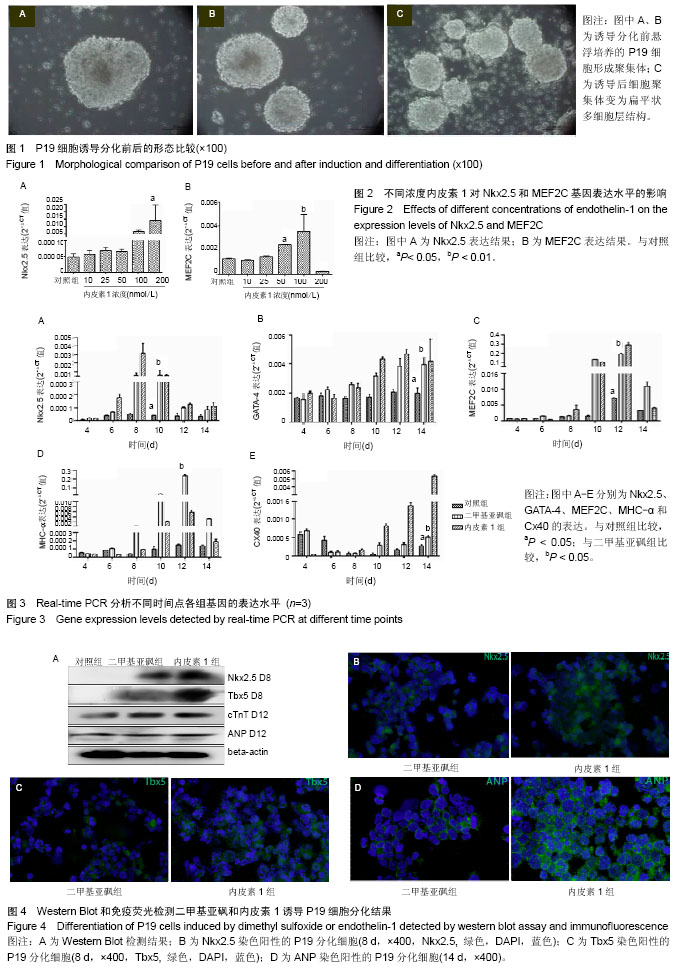
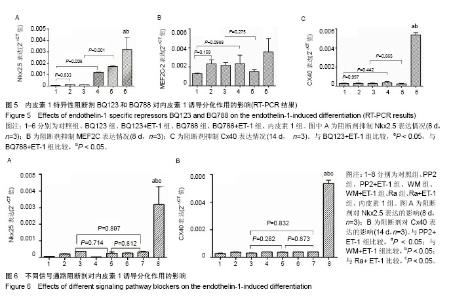
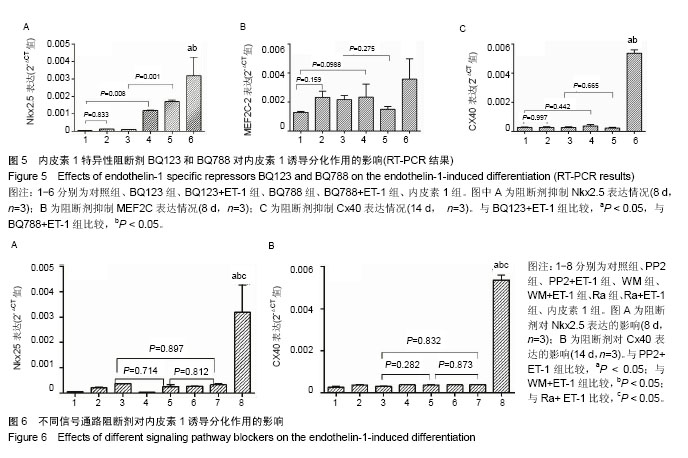
| [1] Munshi NV.Gene regulatory networks in cardiac conduction system development. Circ Res. 2012;110(11):1525-1537.[2] Meyers JD,Jay PY,Rentschler S.Reprogramming the conduction system: Onward toward a biological pacemaker. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2016;26(1):14-20.[3] Nam YJ,Lubczyk C,Bhakta M,et al.Induction of diverse cardiac cell types by reprogramming fibroblasts with cardiactranscriptionfactors.Development. 2014;141(22): 4267-4278.[4] Bressan M,Yang PB,Louie JD,et al.Reciprocal myocardial- endocardial interactions pattern the delay in atrioventricular junction conduction.Development. 2014;141(21):4149-4157.[5] Samsa LA,Yang B, Liu J.Embryonic cardiac chamber maturation: Trabeculation, conduction, and cardiomyocyte proliferation.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2013; 163C(3):157-168.[6] Gassanov N,Er F,Zagidullin N,et al.Endothelin induces differentiation of ANP-EGFP expressing embryonic stem cells towards a pacemaker phenotype. FASEB J.2004; 18(14): 1710-1712.[7] Chen M,LinYQ,Xie SL,et al.Mitogen-activated protein kinase in endothelin-1-induced cardiac differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells.J Cell Biochem. 2010; 111(6): 1619-1628.[8] Zhang X,Zhang CS,Liu YC,et al.Isolation, culture and characterization of cardiac progenitor cells derived from human embryonic heart tubes. Cells Tissues Organs. 2009; 190(4):194-208.[9] Draus JM Jr,Hauck MA,Goetsch M,et al.Investigation of somatic NKX2-5 mutations in congenital heart disease.J Med Genet.2009; 46(2):115-122.[10] George V,Colombo S,Targoff KL.An early requirement for nkx2.5 ensures the first and second heart fieldventricular identity and cardiac function into adulthood.Dev Biol. 2015; 400(1):10-22.[11] Harris BS,Spruill L,Edmonson AM,et al.Differentiation of cardiac Purkinje fibers requires precise spatiotemporal regulation of Nkx2.5 expression. Dev Dyn.2006; 235(1): 38-49.[12] Briggs LE, Takeda M, Cuadra AE,et al.Perinatal loss of Nkx2.5 results in rapid conduction and contraction defects. Circ Res. 2008;103(6):580-590.[13] Waldron L, Steimle JD, Greco TM,et al.The Cardiac TBX5 Interactome Reveals a Chromatin Remodeling Network Essential for Cardiac Septation. Dev Cell. 2016;36(3): 262-275.[14] Moskowitz IP, Kim JB, Moore ML,et al.A molecular pathway including Id2, Tbx5, and Nkx2-5 required for cardiac conduction system development.Cell. 2007; 129(7): 1365-1376.[15] Patel R,Kos L.Endothelin-1 and Neuregulin-1 convert embryonic cardiomyocytes into cells of the conduction system in the mouse.Dev Dyn. 2005; 233(1):20-28.[16] Mikawa T,Hurtado R.Development of the cardiac conduction system. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2007;18(1):90-100.[17] Han H, Chen Y, Liu G,et al.GATA4 transgenic mice as an in vivo model of congenital heart disease.Int J Mol Med. 2015; 35(6):1545-1553.[18] Luna-Zurita L,Stirnimann CU,Glatt S,et al.Complex Interdependence Regulates Heterotypic Transcription Factor Distributionand Coordinates Cardiogenesis.Cell. 2016;164(5): 999-1014.[19] Wang L,Liu Z,Yin C,etal.Stoichiometry of Gata4, Mef2c, and Tbx5 influences the efficiency and quality of induced cardiac myocyte reprogramming.Circ Res. 2015;116(2):237-244.[20] Linhares VL,Almeida NA,Menezes DC,et al.Transcriptional regulation of the murine Connexin40 promoter by cardiac factors Nkx2-5, GATA4 and Tbx5. Cardiovasc Res. 2004; 64(3):402-411.[21] Hua LL,Vedantham V,Barnes RM,et al.Specification of the mouse cardiac conduction system in the absence of Endothelin signaling.Dev Biol.2014; 393(2):245-254.[22] Asai R,Kurihara Y,Fujisawa K,et al.Endothelin receptor type A expression defines a distinct cardiac subdomain within the heart field and is later implicated in chamber myocardium formation. Development.2010; 137(22):3823-3833.[23] Andrés-Delgado L, Mercader N.Interplay between cardiac function and heart development.BiochimBiophys Acta. 2016; 1863(7 Pt B):1707-1716.[24] Zhang HH, Huang J, DüvelK,etal.Insulin stimulates adipogenesis through the Akt-TSC2-mTORC1 pathway. PLoS One. 2009; 4(7):e6189.[25] Isomoto S,Hattori K,Ohgushi H,et al.Rapamycin as an inhibitor of osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Sci. 2007; 12(1):83-88.[26] Csibi A, Cornille K, Leibovitch MP,et al.The translation regulatory subunit eIF3f controls the kinase-dependent mTOR signaling required for muscle differentiation and hypertrophy in mouse. PLoS One.2010; 5(2):e8994.[27] Endo M,Antonyak MA,Cerione RA.Cdc42-mTOR signaling pathway controls Hes5 and Pax6 expression in retinoic acid-dependent neural differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2009; 284(8):5107-5118. |