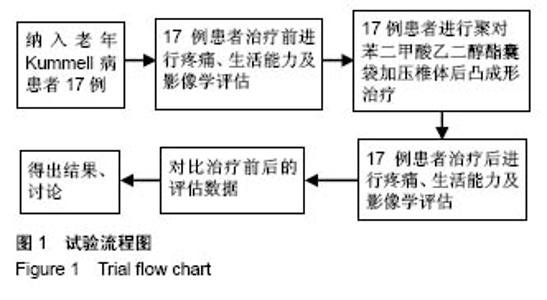
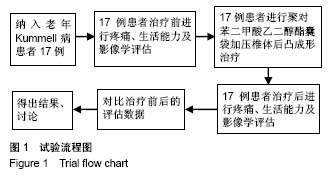
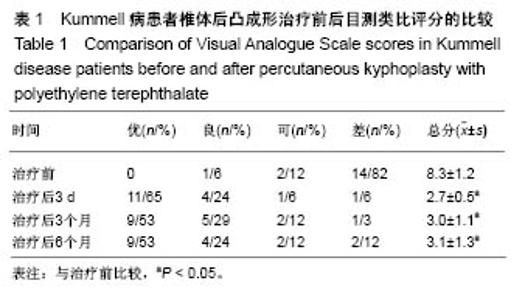
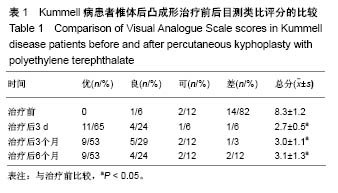
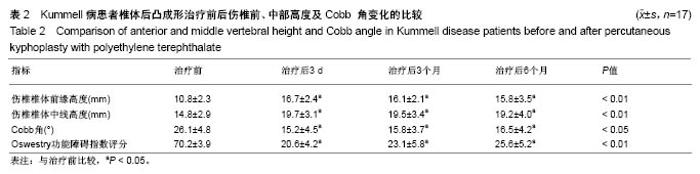
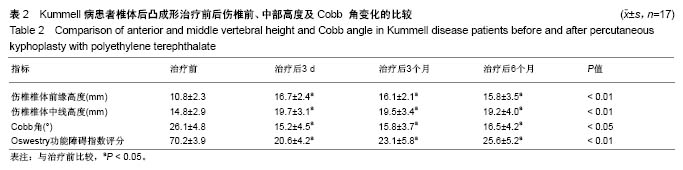
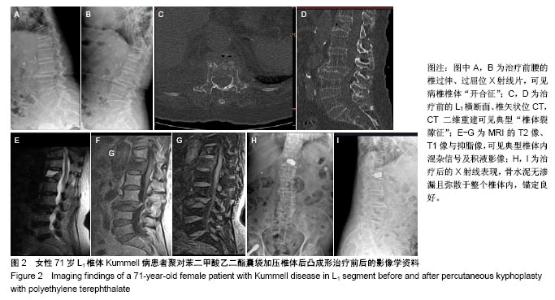
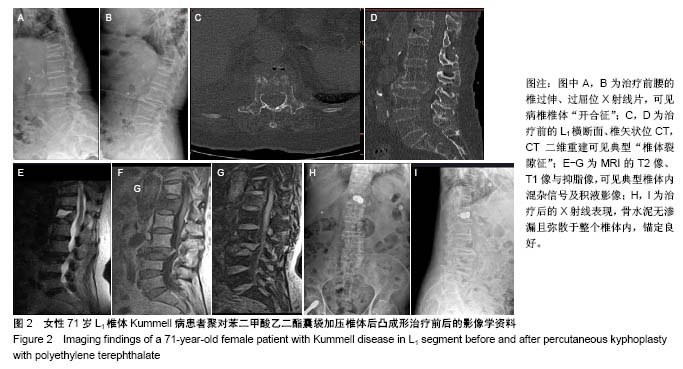
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (34): 5433-5438.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0637
Previous Articles Next Articles
Kyphoplasty with polyethylene terephthalate treats Kummell disease
Li Zhijun, Ci Yuan, Zheng Yupeng, Zhang Guangyu
- Department of Spinal Surgery, Second People’s Hospital of Dalian, Dalian 116011, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2018-06-26Online:2018-12-08Published:2018-12-08 -
Contact:Li Zhijun, Department of Spinal Surgery, Second People’s Hospital of Dalian, Dalian 116011, Liaoning Province, China) -
About author:Li Zhijun, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Spinal Surgery, Second People’s Hospital of Dalian, Dalian 116011, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhijun, Ci Yuan, Zheng Yupeng, Zhang Guangyu. Kyphoplasty with polyethylene terephthalate treats Kummell disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(34): 5433-5438.
share this article
| [1] Li H,Liang CZ,Chen QX.Kummells disease,an uncommon and complicated spinal disorder:a riview.J Int Med Res. 2012;40(2):406-414.[2] 杨惠林,王根林,姜为民,等.分次灌注骨水泥技术治疗Kummell病[J].脊柱外科杂志,2012,10(1):22-24.[3] 陈锋,方文来,倪文飞.Kummell病的治疗进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013,10(1):95-96.[4] 黎一兵,闫宏伟.经椎弓根椎体内骨水泥强化结合后路短节段内固定治疗Kummell病43例[J].陕西医学杂志, 2015,44(3):317-320.[5] 黄吉军,冯新民,杨建东,等.内固定联合椎体成形治疗Ⅲ型Kummell病疗效观察[J].实用骨科杂志,2016,22(7):577-581.[6] 张磊磊,李健.Kummell病的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,23(9): 816-819.[7] 石华刚,熊小明,邓轩赓,等.经皮椎体成形术及后凸成形术治疗Kümmell病的疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(3):278-281.[8] 李东华,刘训伟,彭湘涛,等.骨填充网袋灌注骨水泥修复椎体压缩骨折:可降低骨水泥椎体外渗漏率[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(3):358-363.[9] 印平,马远征,马迅,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的治疗指南[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):643-648.[10] Matzaroglou C,Georgiou CS,Panagopoulos A,et al.Kummells disease:Clarifying the Mechanisms and Patients Inclusion Criteria.Open Orthop J.2014;15(8):288-297. [11] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].4版.北京:人民军医出版社, 2012: 1813.[12] Johnell O,Kanis JA.An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2006; 17(12):1726-1733.[13] Kado DM,Duong T,Stone KL,et al.Incident vertebral fractures and mortality in older women: a prospective study.Osteoporos Int.2003; 14(7):589-594.[14] 梁德,叶林强,江晓兵,等.骨水泥-椎体体积比及椎体骨壁裂口与椎体成形骨水泥渗漏的相关性分析[C].第十届中国南方骨质疏松论坛暨重庆市医学会骨质疏松年会,重庆,2014.[15] Ma R,Chow R,Shen FH.Kummell’s disease:delayed post-traumatic osteonecrosis of the vertebral body.Eur Spine J.2010;19(7):1065-1070. [16] 谢胜荣,卢小刚,伍成东,等.Kummell病的发病机制研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2014,8(20): 3675-3678.[17] 罗文正,陈诚,唐廷波骨质疏松性椎体骨折不愈合的临床特点与手术方法探讨[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(3):269-271.[18] He D,Yu W,Chen Z,et al.Pathogenesis of the intravertebral vacuum of Kümmell's disease. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(2):879-882. [19] Lee SH,Kim ES,Eoh W.Cement augmented anterior reconstruction with short posterior instrumentation: a less invasive surgical option for Kummell's disease with cord compression.J Clin Neurosci.2011;18: 509-514.[20] 盛孝永,任少君,朱烨,等.骨质疏松性椎体塌陷伴迟发性神经损害的手术干预[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(1):110-111.[21] 李厚坤,王晓东,杨小卫,等.单侧椎弓根入路与双侧椎弓根入路PKP 治疗Kummell's 病的临床对比研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2016,24(18): 1660-1665.[22] 孙育良,熊小明,万趸,等.单双侧穿刺经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗Kummell病的疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2017,31(9):1-6.[23] Esses SI,McGuire R,Jenkins J,et al.The treatment of symptomatic osteoporotic spinal compression fractures.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2011; 19(3):176-182.[24] Chen L,Dong R,Gu Y,et al. Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell's Disease.Pain Physician. 2015;18(4):373-381. [25] 周毅,海涌,苏庆军,等.椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折疗效分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2012,18(5):429-433.[26] Wu AM,Lin ZK,Ni WF,et al.The existence of intravertebral cleft impact on outcomes of nonacute osteoporotic vertebral compressionfractures patients treated by percutaneous kyphoplasty.A comparativestudy.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(3):E88-93.[27] Ha KY,Lee JS,Kim KW,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for vertebral compression fractures with and without intravertebral clefts.J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2006;88(5):629-633.[28] 李石岩,钮俊杰,宋达玮,等.椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折伴或不伴裂隙征的对比研究[J].浙江临床医学, 2014,16(6):843-845.[29] 郝定均,贺宝荣,许正伟,等.胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折经皮椎体成形术后骨水泥渗漏的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志, 2016,36(17):1142-1148.[30] Silva Gonzalez A,Alfonso Olmos M,Villas Tome C,et al.Model of induced leakage of polymethylmethacrilate inside epidural space and prevertebral muscles during vertebrolplasty in pigs:clinical,macroscopical,and histological study.Asian Spine J.2013;7(3):159-166.[31] Nieuwenhuijse MJ,Putter H,Van Erkel AR,et al.New vertebral fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures:a clustered analysis and the relevance of intradiscal cement leakage.Radiology.2013;266(3):862-870.[32] 许正伟,贺宝荣,郝定均,等.经皮椎体成形术改为开放手术的原因分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(10): 951-956.[33] 王东来,冯建刚.经皮椎体成形术并发脊髓梗死1例报告[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008,18(5):372-376.[34] 孙钰,吴乃庆,曹晓建,等.硅胶薄膜囊预防椎体后凸成形术中骨水泥渗漏的实验研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2007,22(11):913-915.[35] Klingler JH,Sirear R,Deininger MH,et al.Vesselplasty: a new minimally invasive approach to treat pathological vertebral fractures in selected tumor patients - preliminary results. Rofo. 2013;185(4):340-350.[36] 王太平,郑召民,王华,等.新型骨材料填充器的研制及其生物相容性研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2013,10(1):1-4.[37] 唐海,贾璞,陈浩,等.新型Vessel—X经皮椎体强化系统在脊柱微创治疗的临床应用[J]中华医学杂志,2017,97(33):2567-2572.[38] 贾璞,陈浩,包利,等.国产骨填充网袋治疗后壁破损的椎体转移瘤疗效[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2018,7(1):72-76.[39] 张凯斌,张茗.网袋加压椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折效果观察[J].中国药物与临床,2017,17(3):405-406.[40] 董智勇,高玉盛,杨吉坤,范学辉.新型骨填充网袋椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(16):1526-1529.[41] Capel C,Fichten A,Nicot B,et al.Should we fear cement leakage during kyphoplasty in percutaneous traumatic spine surgery?A single experience with 76 consecutive cases. Neurochirurgie.2014;60(6): 293-298.[42] Yu W,Jiang X,Liang D,et al.Intravertebral Vacuum Cleft and Its Varied Locations within Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Effect on Therapeutic Efficacy.Pain Physician. 2017;20(6):E979-E986. [43] 苟永胜,李海波.骨填充网袋灌注骨水泥治疗合并椎体裂隙征骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(9):953-955.[44] 白明,银和平,李树文,等.骨填充网袋修复椎体后壁破损骨质疏松性椎体骨折:可有效防止骨水泥渗漏[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(47):7545-7549.[45] 张亮,王静成,冯新民,等.不同黏度骨水泥椎体成形术治疗重度骨质疏松性骨折的疗效研究[J].实用骨科杂志, 2016,22(7):577-581. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [3] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [6] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [7] | Xiao Fangjun, Chen Shudong, Luan Jiyao, Hou Yu, He Kun, Lin Dingkun. An insight into the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza intervention on osteoporosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 772-778. |
| [8] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [9] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [10] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [11] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [12] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [13] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [14] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [15] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||