Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (29): 4706-4712.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0630
Previous Articles Next Articles
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein can affect the function of endothelial progenitor cells: how to increase cell number and function?
Wang Feng-jiao1, 2, Gao Xiang2, Yin Hang2, Chen Li3, Qin Shu-cun1, Yang Na-na1
- 1Institute of Atherosclerosis, 2School of Basic Medicine, 3School of Nursing, Taishan Medical University, Taian 271000, Shandong Province, China
-
Revised:2018-06-25Online:2018-10-18Published:2018-10-18 -
Contact:Yang Na-na, MD, Associate professor, Institute of Atherosclerosis, Taishan Medical University, Taian 271000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wang Feng-jiao, Institute of Atherosclerosis, Taishan Medical University, Taian 271000, Shandong Province, China; School of Basic Medicine, Taishan Medical University, Taian 271000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81170785, 81370381; the Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province, No. 200867); the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. NZR2012HL18; Shandong Science and Technology Development Plan, No. 2014GSF118105; and Science and Technology Project of Shandong Provincial Universities, No. J14LK03
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Feng-jiao, Gao Xiang, Yin Hang, Chen Li, Qin Shu-cun, Yang Na-na. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein can affect the function of endothelial progenitor cells: how to increase cell number and function?[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(29): 4706-4712.
share this article
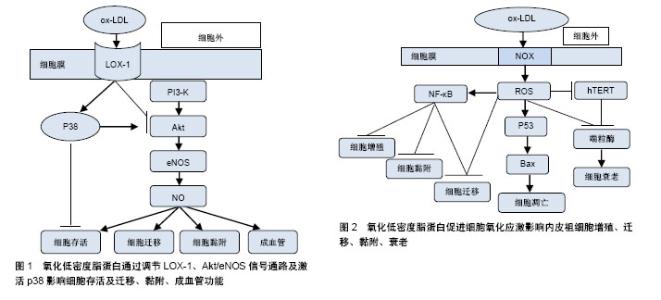
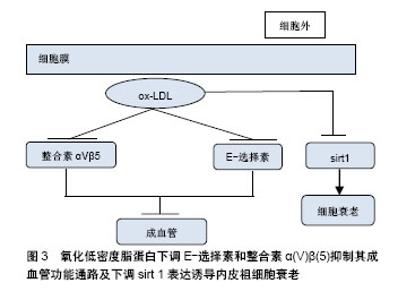
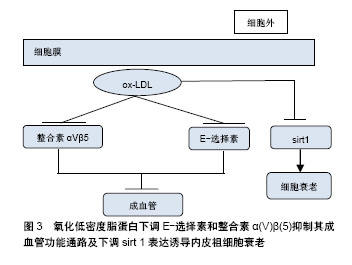
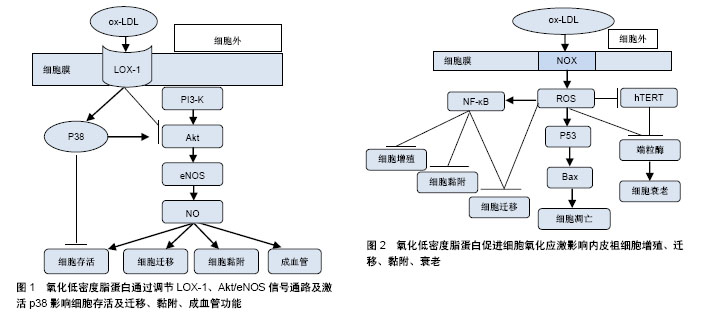
2.1 EPCs与动脉粥样硬化 2.1.1 EPCs的特征 1997年,Asahara等发现人外周血中存在CD34+造血干细胞,该细胞在一定的条件下可以定向分化为成熟的内皮细胞,具有促进缺血组织血管新生的作用,即EPCs。EPCs是一类尚未表达成熟血管内皮细胞表型,也就是还未形成血管的一类内皮前体细胞。在体外培养的外周血来源EPCs具有吞噬乙酰化低密度脂蛋白(acety-lated low density lipoprotem,ac-LDL)和结合荆豆凝集素1(ulexeuropaeus agglutinin-1,UEA-1)的特性,因此大多学者认为DiI-ac-LDL和FITC-UEA-1双阳性细胞为正在分化的EPCs。EPCs可分为2类:早期EPCs和晚期EPCs,早期EPCs可分泌较多的血管生长因子,更能促进新血管的生成,但晚期EPCs表现出更强的管状结构形成能力和较强的增殖潜能[3]。 2.1.2 EPCs对动脉粥样硬化病变过程的影响 动脉粥样硬化病变的形成是动脉壁发生非常复杂的慢性炎症的过程,诸多危险因素所造成的动脉内皮细胞损伤以及功能失调都被认为是动脉粥样硬化发生的始动环节[4]。内皮细胞具有抗血小板、纤维蛋白溶解和抗凝血等重要特性。此外,它被发现在维持血管健康,如细胞黏附、内分泌和旁分泌功能、平滑肌增殖和维持血管紧张度等方面也起着重要的作用[5]。内皮结构和功能的损伤是导致动脉粥样硬化的一个常见因素,而内皮再生平衡对动脉粥样硬化的发生发展至关重要[6]。 (1) EPCs与内皮修复过程:内皮损伤通常是由于血压升高、吸烟、高血糖或其他心血管危险因素诱导的,这些危险因素有诱导生物化学毒性的可能性,从而导致内皮细胞凋亡。成熟内皮细胞被破坏,形成内皮微粒进入血液循环,这些内皮微粒可以用作替代标志物来检测血管损伤并评估其严重程度[7-8]。动脉粥样硬化过程始于内皮损伤和功能障碍,该损伤及障碍诱导低密度脂蛋白胆固醇颗粒在受损血管壁中聚集和氧化,而脂质的积累进一步诱导单核细胞从血液迁移到内膜并转化为巨噬细胞,从而进一步积累脂质,形成动脉粥样硬化斑块的脂质核[9]。各种危险因素引起内皮细胞衰老和凋亡所致的内皮功能障碍是动脉粥样硬化性疾病的标志。因此,受损内皮单层的修复和重建是预防动脉粥样硬化斑块形成的必要条件。 内皮细胞本身具有一定损伤修复的能力,但是大面积内膜损伤时,成熟的内皮细胞不具有大量复制的能力,因此需要包括EPCs在内的其他细胞参与到增殖修复过程中。EPCs具有很强的增殖潜能,它们在骨髓和其他组织中增殖,并迁移到血管损伤部位进行复制、成熟和修复,整个过程被称为内皮(血管)修复。血管内皮不仅仅是阻止动脉粥样硬化始动环节的屏障,在某种意义上也是人体内最大内分泌器官。血管损伤时,内皮分泌的某些细胞因子可以促进骨髓EPCs动员,募集到血管损伤部位分化成为成熟的内皮细胞。 (2)EPCs与动脉粥样硬化斑块的形成和发展:动脉粥样硬化病变过程中,除了脂质代谢之外,血栓形成和炎症过程也是其病变形成中的重要因素。在动脉粥样硬化病变过程中,炎症、弹性蛋白、胶原蛋白和其他细胞外基质大量产生,这些物质在斑块进展和纤维帽形成过程中起着重要的作用。血管平滑肌细胞的迁移和增殖促进动脉粥样硬化的发生发展。研究发现无动脉粥样硬化的年轻ApoE-/-小鼠骨髓来源干祖细胞可以延缓受体ApoE-/-小鼠动脉粥样硬化的进程。然而,EPCs具有多向分化潜能,在一定环境下可向平滑肌细胞分化,归巢到血管损伤部位的骨髓源性EPCs如果分化为平滑肌细胞,会导致内膜过度增生反而加速了动脉粥样硬化斑块的形成。 斑块的不稳定也增加了心血管疾病的风险。斑块自身的破裂是在纤维帽变薄、平滑肌细胞受损,以及巨噬细胞吞噬脂质形成的泡沫细胞浸润在斑块核心之后发生的复杂变化。如果纤维帽不够稳定,斑块可能会变薄甚至破裂[10]。斑块内存在大量促血栓物质,一旦它暴露在血液中,将发生血栓级联反应[11-12]。血栓的持续形成使得管腔狭窄,导致动脉阻塞和缺血,可表现为心肌梗死、缺血性脑卒中或坏疽[13-14]。EPCs可促进损伤内皮细胞的修复,促进血管的新生,因此有可能促进斑块内血管的生成,从而增加斑块的不稳定性,但是目前尚无令人信服的证据。 2.2 ox-LDL与动脉粥样硬化 2.2.1 LDL的氧化修饰 动脉粥样硬化是动脉壁的一种慢性炎症疾病,也是世界范围内导致死亡的主要疾病之一[15]。LDL在体内的氧化修饰是动脉粥样硬化发生发展过程中较为重要的因素。 LDL是一个巨球型的分子集团,它的标志性蛋白是包埋在LDL最外层的载脂蛋白B分子,它是LDL-R的配体。载脂蛋白B分子中带有正电荷的赖氨酸残基是LDL-R识别所必需的关键抗原决定簇。当体内的LDL浓度升高、内皮损伤时,LDL渗透进入动脉内皮下不再受血浆以及细胞间液中的抗氧化物质的保护,如果此时动脉粥样硬化的危险因素可诱导内皮细胞、平滑肌细胞和单核细胞产生大量氧自由基,则LDL就会在内皮下发生氧化修饰。 LDL氧化过程是一种自由基链式连锁反应,可以划分为3个阶段:①迟滞阶段使得LDL抗氧化活性丧失;②增殖阶段,最终生成过氧化脂质,而过氧化脂质本身又是一种氧自由基,可以与另外的不饱和脂肪酸自由基分子连锁循环反应下去,形成恶性循环,生成大量的过氧化脂质;③分解阶段,生成活跃的反应性醛类物质,这些醛类可以和载脂蛋白B发生交联共价结合,使得与LDL-R结合的正电荷区转变为负电荷区,产生了新的抗原决定簇,完全丧失了与LDL-R的结合作用[16]。 2.2.2 ox-LDL参与动脉粥样硬化过程的机制[17] LDL被氧化后,其表面的抗原决定簇发生改变,可以被巨噬细胞和血管平滑肌细胞表面的清道夫受体A1识别结合,巨噬细胞摄入ox-LDL转变为泡沫细胞。这些含有ox-LDL和其他脂蛋白的细胞在内皮下积聚,代表着脂肪条纹病变的形成,这是早期动脉粥样硬化的标志[18]。在此之后,免疫反应通过释放促炎症介质引发慢性炎症反应从而推动了斑块的形成[19]。因此,ox-LDL在动脉粥样硬化发病机制中起重要作用,并形成了动脉粥样硬化的“氧化修饰”假说[20]。 在内皮细胞中,ox-LDL可引起内皮细胞功能障碍。研究发现ox-LDL可上调植物血凝素样氧化低密度脂蛋白受体(lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor,LOX-1)的表达[21],刺激内皮细胞中单核细胞化蛋白1(monocyte chemotactic protein 1,MCP-1)的释放;ox-LDL通过抑制内皮细胞内皮一氧化氮合成酶的表达以及增加活性氧抑制一氧化氮的产生[22],从而削弱了一氧化氮相关的抗动脉粥样硬化特性以及其介导的血管舒张特性;ox-LDL刺激内皮素1的生成以及血管紧张素转化酶的表达,从而进一步加剧血管张力障碍[20]。除此之外,ox-LDL还能激活内皮细胞核因子κB、caspase-9和caspase-3来增加Fas受体的表达[23],从而进一步调节了促炎基因的表达[20]。研究发现ox-LDL还能促进血管平滑肌细胞的迁移[24]、增殖以及血小板的激活[21],从而促进血管炎症引起内皮功能障碍[25]。 2.3 ox-LDL与内皮祖细胞 研究表明,ox-LDL通过上调LOX-1的表达等途径促进动脉粥样硬化的形成及发生发展过程,同时,ox-LDL也可以通过其他信号通路影响EPCs的增殖分化及其功能。 2.3.1 ox-LDL对EPCs的影响 (1)ox-LDL对EPCs的损伤作用:EPCs被定义为不成熟的细胞,它可以分化成血管内皮细胞,在维持血管完整性和损伤修复方面起着关键作用[26]。研究表明,损伤的血管内皮细胞可由骨髓来源EPCs修复,延缓了动脉粥样硬化的发生发展[27]。然而在糖尿病和高胆固醇血症这类疾病中,循环EPCs数量减少,功能减弱[28-29],血清中ox-LDL的浓度升高。因此,循环EPCs数量与高胆固醇血症之间存在强烈的负相关性[30],高胆固醇血症患者EPCs减少归因于ox-LDL水平的增加。ox-LDL能抑制EPCs增殖、迁移、黏附和成血管能力,同时还使EPCs对血管的修复能力下降,打破了损伤和修复之间的动态平衡,从而导致血管功能损伤。因此,ox-LDL抑制EPCs功能可能会促进动脉粥样的发生发展[31]。 (2)ox-LDL对于EPCs成血管功能具有双相作用:大部分研究表明ox-LDL可能对EPCs有不利影响。然而,这些研究的局限性在于它们使用早期EPCs,且大多数研究使用的ox-LDL浓度超过50 mg/L,远远高于健康人群(5.7-14.8 mg/L)和患病人群(18.8-20.2 mg/L)的血清浓度。经实验研究证明,ox-LDL对于EPCs的成血管功能具有双相作用[32]。 低浓度的ox-LDL(约5 mg/L)通过激活p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38mitogen-activated protein kinase,p38 MAPK)和SAPK/JNK相关途径使Akt活化来增强体外和体内EPCs成血管的能力。用0.1-5 mg/L ox-LDL处理EPCs 4 h后,ox-LDL明显诱导了p38 MAPK和SAPK/JNK的磷酸化。用SP600125(SAPK/JNK抑制剂)和SB203580(p38MAPK抑制剂)预处理1 h后可抑制5 mg/L ox-LDL诱导EPCs成血管的能力,同时抑制ox-LDL诱导的Akt激活。这些结果提示,低浓度ox-LDL处理的EPCs通过p38 MAPK和SAPK/JNK相关通路介导了Akt的激活,从而增强了EPCs的成血管能力。 较高浓度的ox-LDL(10-50 mg/L)通过激活NADPH氧化酶而抑制EPCs成血管功能。NADPH氧化酶是由两种膜结合组分(gp91 phox和p22 phox)和胞质溶胶中的3种组分(Rac1,p40 phox,p47 phox和p67 phox)组成的复合酶。特异性NADPH氧化酶抑制剂明显抑制ox-LDL(50 mg/L)诱导EPCs成血管功能下降;50 mg/L ox-LDL抑制EPCs中AKT和eNOS活性,敲除gp91 phox可以恢复上述Akt和eNOS的活性;另外,用LOX-1抗体预处理可阻断ox-LDL对Akt和eNOS活化的抑制作用;gp91 phox siRNA转染并用20 μmol/L Rac1抑制剂预处理1 h,可以有效抑制50 mg/L ox-LDL诱导的EPCs膜上的LOX-1表达。综上所述,高浓度ox-LDL激活的NADPH氧化酶通过促进LOX-1表达抑制Akt和eNOS的活化,从而损害EPCs的成血管功能[32]。 2.3.2 ox-LDL影响EPCs功能的信号通路 (1)调节Akt/eNOS信号通路:Akt是一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,由多种生长因子和细胞因子以依赖于磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase,PI3-K)的方式激活。活化的Akt激活eNOS1177位点处的丝氨酸,从而促进EPCs的动员、迁移及成血管功能。Akt的抑制剂(triciribine)能抑制EPCs的迁移、黏附及成血管功能。研究发现ox-LDL降低了EPCs的存活率,并且以剂量依赖性的方式抑制了其黏附、迁移和成血管能力。蛋白质印迹分析显示ox-LDL剂量依赖性地抑制Akt的磷酸化和eNOS蛋白表达。ox-LDL还可诱导eNOS mRNA表达降低。ox-LDL对Akt磷酸化的抑制途径可分为:①ox-LDL可能激活丝氨酸/苏氨酸磷酸酶,使Akt去磷酸化。ox-LDL通过诱导神经酰胺激活具有蛋白磷酸酶2A(PP2A)样活性的蛋白磷酸酶,从而使Akt去磷酸化;②ox-LDL也可能激活脂质磷酸酶,从而使PI3-K的磷脂产物失活并阻断Akt上游的活化,达到抑制Akt磷酸化的作用。研究发现ox-LDL还可通过抑制Akt活性来抑制血管内皮生长因子诱导的EPCs分化。血管内皮生长因子和他汀类药物通过PI3-K/Akt途径诱导EPCs分化。分离的人单核细胞在1,5,10 mg/L ox-LDL中孵育,ox-LDL剂量依赖性地抑制血管内皮生长因子诱导的EPCs分化和黏附。由此说明,ox-LDL可通过抑制Akt的活性来抑制血管内皮生长因子诱导的EPCs分化,下调EPCs数量(图1)。 (2)激活p38:p38是MAPK的主要亚群,并调节由多种应激因子诱导的细胞凋亡、增殖或分化。p38MAPK被ox-LDL激活,参与EPCs数量和功能的调控。早期研究报道,用特异性p38抑制剂SB203580预处理EPCs可以抑制ox-LDL诱导EPCs功能降低,包括凋亡增加、增殖减少和血管生成能力减弱[22]。Lox-1阻断抗体也显著降低ox-LDL诱导的p38磷酸化。然而最近研究发现,ox-LDL激活p38,并抑制Akt的磷酸化,损伤EPCs的功能,诱导其凋亡,但用SB203580处理后却进一步抑制了EPCs中Akt的活化,增加了ox-LDL诱导的EPCs凋亡[33]。综上所述,p38 MAPK是一种抗凋亡通路,EPCs受到ox-LDL损伤导致Akt活性受到抑制,可通过抑制p38 MAPK通路来激活Akt(图1)。 (3)LOX-1介导:1997年,Sawamura等在内皮细胞上发现了一种ox-LDL的新型受体,称为LOX-1[34]。LOX-1可介导ox-LDL对内皮细胞的损伤,研究发现EPCs也可表达LOX-1[35]。通过蛋白质印迹分析显示ox-LDL可增加LOX-1的蛋白表达,同时还可增加LOX-1的mRNA表达[35],且ox-LDL对EPCs的损伤均可通过LOX-1单克隆抗体的预处理而减弱,说明ox-LDL通过LOX-1介导来损伤EPCs的功能(图1)。 (4)促进细胞氧化应激抑制内皮祖细胞功能:ox-LDL可诱导gp91 phox的上调,作为NOX的亚基,gp91 phox的上调增强了NOX活性。NOX是ROS的主要来源,它通过将电子从NADPH转移到氧来产生超氧阴离子,超氧阴离子又自发地或通过SOD催化歧化成H2O2。动物和细胞实验结果显示,ox-LDL处理后,伴随着NOX活性增加和ROS的产生,EPCs功能(迁移和黏附)受损[36]。研究表明,NOX衍生的ROS在多种病理条件下(如缺血、高血糖和高血压)可导致细胞氧化损伤,因此推测NOX来源的ROS也参与EPCs的功能障碍。因此,ox-LDL通过增强NOX活性,产生ROS从而促进细胞氧化应激,导致EPCs的损伤和功能障碍。但是体内ox-LDL对NOX活性、ROS形成和EPCs功能产生的影响尚未完全证明,在未来的研究中,有必要通过体内NOX的干预来验证体外结果[37](图2)。 ox-LDL还可通过氧化应激和Akt/hTERT通路共同抑制端粒酶活性[38],从而造成EPCs的衰老[36]。细胞衰老是有丝分裂细胞不可逆的生长停滞,其被认为可以损害组织功能并使组织出现病变倾向,如动脉粥样硬化。研究发现端粒缩短是细胞衰老过程中的一个关键分子事件。端粒是染色单体两端的一个重复核苷酸序列(TTAGGG)的区域,它保护染色体的末端免遭退化或防止其与相邻染色体融合。由于时间的推移,端粒末端随细胞分裂变短。越来越多的证据表明,渐进性端粒缩短与心血管疾病密切相关,细胞可以通过提高端粒酶活性来减轻衰老。端粒酶是一种具有反转录酶活性的酶,EPCs作为祖细胞显示端粒酶活性。端粒酶活性受多种因素的调控,研究发现,ox-LDL增强了细胞内的氧化应激从而直接抑制端粒酶活性;同时,随着NOX活性的增强,人端粒酶反转录酶的磷酸化被抑制,使得端粒酶活性下降。因此,ox-LDL通过氧化应激和Akt/hTERT通路抑制端粒酶活性,从而促进EPCs的衰老[36](图2)。 另外有研究发现,氧化应激可以激活NF-κB通路从而损害EPCs的功能[39]。NF-κB是一种氧化反应转录因子,调节许多参与炎症反应的基因表达。研究发现,ox-LDL诱导内皮祖细胞NF-κB P65 mRNA表达和易位,引起NF-κB的活化。因此可以推测ox-LDL促进EPCs发生氧化应激,随后引起NF-κB活化。此外还有研究表明,NF-κB在EPCs中的激活与EPCs增殖、迁移和黏附的减少有关。由此推测ox-LDL可以通过氧化应激激活NF-κB途径,上调EPCs促炎细胞因子的表达[12] (图2)。 ox-LDL通过产生线粒体来源的活性氧物质激活肿瘤抑制基因从而刺激p53依赖的前凋亡蛋白(Bcl-2 Associated X Protein,Bax)活化促进EPCs凋亡[40]。研究发现,ox-LDL诱导EPCs和内皮细胞凋亡的关键是诱导Bax的构象变化,导致Bax活化而不改变其表达,构象改变的Bax转位到线粒体可刺激细胞凋亡。实验证明,p53敲除抑制了ox-LDL诱导的Bax活化和EPCs凋亡,ox-LDL可导致线粒体衍生的超氧化物阴离子向p53的转移增加,促进Bax的构象变化并转运至线粒体诱导EPCs凋亡(图2)。 (5)通过下调E-选择素和整合素α(V)β(5)抑制其成血管功能[41]:E-选择素和整合素α(V)β(5)是EPCs与内皮细胞相互作用的重要介质,DiSanto等发现,EPCs与ox-LDL共同孵育显著降低了E-选择素和整合素α(V)β(5)的表达,且抗体阻断E-选择素和整合素α(V)β(5)可有效抑制EPCs成血管能力和其黏附内皮细胞的能力,因此说明ox-LDL通过下调E-选择素和整合素α(V)β(5)来抑制EPCs的成血管功能(图3)。 (6)ox-LDL通过下调sirt1表达诱导EPCs衰老[42]:sirtuin蛋白家族是一类NAD+-依赖性蛋白脱乙酰酶,是调节细胞周期、细胞凋亡、代谢和炎症等的关键蛋白。据报道,sirt 1是衰老的调节因子,其表达增加或激活延长了低等动物的寿命。实验证明,下调的sirt 1表达与ox-LDL诱导的EPCs衰老有关,沉默sirt1可明显促进EPCs的衰老和p53的表达,进一步研究发现ox-LDL通过PI3-K/Akt/ERK途径下调sirt1表达从而诱导EPCs衰老(图3)。"
| [1] Werner N, Kosiol S, Schiegl T, et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells and cardiovascular outcomes.N Engl J Med. 2005;353(10):999-1007.[2] Yu P, Li Q, Liu Y, et al. Pro-angiogenic efficacy of transplanting endothelial progenitor cells for treating hindlimb ischemia in hyperglycemic rabbits.J Diabetes Complications. 2015;29(1):13-19.[3] Kim H, Kim S, Baek SH, et al. Pivotal Cytoprotective Mediators and Promising Therapeutic Strategies for Endothelial Progenitor Cell-Based Cardiovascular Regeneration.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:8340257.[4] Suciu CF, Prete M, Ruscitti P, et al. Oxidized low density lipoproteins: The bridge between atherosclerosis and autoimmunity. Possible implications in accelerated atherosclerosis and for immune intervention in autoimmune rheumatic disorders.Autoimmun Rev. 2018;17(4):366-375.[5] Rajendran P, Rengarajan T, Thangavel J, et al. The vascular endothelium and human diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2013;9(10): 1057-1069.[6] Zhang L, Xu Q.Stem/Progenitor cells in vascular regeneration. ArteriosclerThrombVasc Biol. 2014;34(6):1114-1119.[7] Avogaro A, Albiero M, Menegazzo L, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes: the role of reparatory mechanisms. Diabetes Care. 2011;34Suppl 2:S285-290.[8] Lee PS, Poh KK.Endothelial progenitor cells in cardiovascular diseases.World J Stem Cells. 2014;6(3):355-366.[9] Altabas V, Altabas K, Kirigin L.Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) in ageing and age-related diseases: How currently available treatment modalities affect EPC biology, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular outcomes.Mech Ageing Dev. 2016;159:49-62.[10] Alsheikh-Ali AA, Kitsios GD, Balk EM, et al. The vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque: scope of the literature.Ann Intern Med. 2010;153(6):387-395.[11] Bentzon JF, Otsuka F, Virmani R, et al. Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture.Circ Res. 2014;114(12):1852-1866.[12] Sun Z.Atherosclerosis and atheroma plaque rupture: normal anatomy of vasa vasorum and their role associated with atherosclerosis.Scientific World Journal. 2014;2014:285058.[13] Alsheikh-Ali AA, Kitsios GD, Balk EM, et al. The vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque: scope of the literature.Ann Intern Med. 2010;153(6):387-395.[14] Bentzon JF, Otsuka F, Virmani R, et al. Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture.Circ Res. 2014;114(12):1852-1866.[15] Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK.Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis.Nature. 2011;473 (7347):317-325.[16] 王建礼,徐兴华,林娜. 氧化型低密度脂蛋白与动脉粥样硬化研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2009, 15(9):1307-1310.[17] Trpkovic A, Resanovic I, Stanimirovic J, et al. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein as a biomarker of cardiovascular diseases.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2015;52(2):70-85.[18] Orsó E, Grandl M, Schmitz G.Oxidized LDL-induced endolysosomalphospholipidosis and enzymatically modified LDL-induced foam cell formation determine specific lipid species modulation in human macrophages.Chem Phys Lipids. 2011;164(6):479-487.[19] Samson S, Mundkur L, Kakkar VV.Immune response to lipoproteins in atherosclerosis.Cholesterol. 2012;2012: 571846.[20] Steinberg D.The LDL modification hypothesis of atherogenesis: an update.J Lipid Res. 2009;50 Suppl: S376-381.[21] Pirillo A, Norata GD, Catapano AL.LOX-1, OxLDL, and atherosclerosis.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:152786.[22] Ma FX, Zhou B, Chen Z, et al. Oxidized low density lipoprotein impairs endothelial progenitor cells by regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase.J Lipid Res. 2006;47(6): 1227-1237.[23] Chen J, Mehta JL, Haider N, et al. Role of caspases in Ox-LDL-induced apoptotic cascade in human coronary artery endothelial cells.Circ Res. 2004;94(3):370-376.[24] Auge N, Garcia V, Maupas-Schwalm F, et al. Oxidized LDL-induced smooth muscle cell proliferation involves the EGF receptor/PI-3 kinase/Akt and the sphingolipid signaling pathways.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22(12): 1990-1995.[25] Yu BL, Zhao SP, Huang XS.Oxidized low-density lipoprotein: a double-edged sword on atherosclerosis.Med Hypotheses. 2007;69(3):553-556.[26] Fadini GP, Agostini C, Sartore S, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells in the natural history of atherosclerosis.Atherosclerosis. 2007;194(1):46-54.[27] Zampetaki A, Kirton JP, Xu Q.Vascular repair by endothelial progenitor cells.Cardiovasc Res. 2008;78(3):413-421.[28] Vasa M, Fichtlscherer S, Aicher A, et al. Number and migratory activity of circulating endothelial progenitor cells inversely correlate with risk factors for coronary artery disease.Circ Res. 2001;89(1):E1-7.[29] Tepper OM, Galiano RD, Capla JM, et al. Human endothelial progenitor cells from type II diabetics exhibit impaired proliferation, adhesion, and incorporation into vascular structures.Circulation. 2002;106(22):2781-2786.[30] Yamamoto K, Kondo T, Suzuki S, et al. Molecular evaluation of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with ischemic limbs: therapeutic effect by stem cell transplantation. Arterioscler ThrombVasc Biol. 2004;24(12):e192-196.[31] Stancu CS, Toma L, Sima AV.Dual role of lipoproteins in endothelial cell dysfunction in atherosclerosis.Cell Tissue Res. 2012;349(2):433-446.[32] Lin FY, Tsao NW, Shih CM, et al. The biphasic effects of oxidized-low density lipoprotein on the vasculogenic function of endothelial progenitor cells.PLoS One. 2015;10(5): e0123971.[33] Tie G, Yan J, Messina JA, et al. Inhibition of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Enhances the Apoptosis Induced by Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein in Endothelial Progenitor Cells.J Vasc Res. 2015;52(6):361-371.[34] Li D, Chen H, Romeo F, et al. Statins modulate oxidized low-density lipoprotein-mediated adhesion molecule expression in human coronary artery endothelial cells: role of LOX-1.J Pharmacol ExpTher. 2002;302(2):601-605.[35] 马凤霞,任倩,韩忠朝. 植物血凝素样氧化型低密度脂蛋白受体介导氧化型低密度脂蛋白对内皮祖细胞存活和功能的影响[J]. 中国医学科学院学报, 2007, 29(3):336-341.[36] Li TB, Zhang YZ, Liu WQ, et al. Correlation between NADPH oxidase-mediated oxidative stress and dysfunction of endothelial progenitor cell in hyperlipidemic patients.Korean J Intern Med. 2018;33(2):313-322.[37] Li TB, Zhang JJ, Liu B, et al. Dysfunction of endothelial progenitor cells in hyperlipidemic rats involves the increase of NADPH oxidase derived reactive oxygen species production.Can J PhysiolPharmacol. 2017;95(5):474-480.[38] Lai P, Liu Y.Angelica sinensis polysaccharides inhibit endothelial progenitor cell senescence through the reduction of oxidative stress and activation of the Akt/hTERT pathway.Pharm Biol. 2015;53(12):1842-1849.[39] Ji KT, Qian L, Nan JL, et al. Ox-LDL induces dysfunction of endothelial progenitor cells via activation of NF-κB.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:175291.[40] Cheng J, Cui R, Chen CH, et al. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein stimulates p53-dependent activation of proapoptoticBax leading to apoptosis of differentiated endothelial progenitor cells.Endocrinology. 2007;148(5): 2085-2094.[41] Di Santo S, Diehm N, Ortmann J, et al. Oxidized low density lipoprotein impairs endothelial progenitor cell function by downregulation of E-selectin and integrin alpha(v)beta5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;373(4):528-532.[42] Ming GF, Tang YJ, Hu K, et al. Visfatin attenuates the ox-LDL-induced senescence of endothelial progenitor cells by upregulating SIRT1 expression through the PI3K/Akt/ERK pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2016;38(2):643-649. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Jiang Xin, Qiao Liangwei, Sun Dong, Li Ming, Fang Jun, Qu Qingshan. Expression of long chain non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 in serum of renal transplant patients and its regulation of human glomerular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 741-745. |
| [5] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [6] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [7] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [8] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [9] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [11] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [12] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [13] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||