Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (29): 4643-4649.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0621
Previous Articles Next Articles
Measurements of T-cell receptor excision cycles in early stage of immune reconstitution after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Wang Kun, Han Jun-yong, Chen Jin-yan, Liu Shen-min, Xue Shi-jie, Jin Jing-jun
- Immunology Research Institute of Fujian Academy of Medical Sciences, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Analysis, Fuzhou 350001, Fujian Province, China
-
Revised:2018-05-19Online:2018-10-18Published:2018-10-18 -
Contact:Jin Jing-jun, Researcher, Immunology Research Institute of Fujian Academy of Medical Sciences, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Analysis, Fuzhou 350001, Fujian Province, China -
About author:Wang Kun, Master, Assistant researcher, Immunology Research Institute of Fujian Academy of Medical Sciences, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Analysis, Fuzhou 350001, Fujian Province, China -
Supported by:the Basic Research Special Fund for Scientific Research Institutes for Public Welfare, No. 2014R1031-2; Fujian Medical Innovation Topics, No. 2016-CXB-2
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Kun, Han Jun-yong, Chen Jin-yan, Liu Shen-min, Xue Shi-jie, Jin Jing-jun. Measurements of T-cell receptor excision cycles in early stage of immune reconstitution after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(29): 4643-4649.
share this article
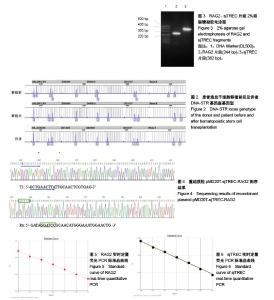
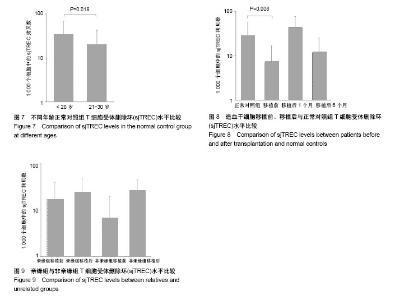
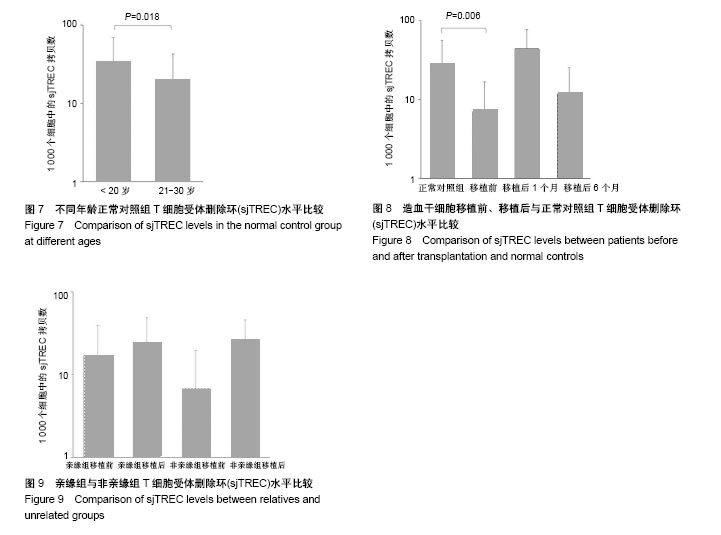
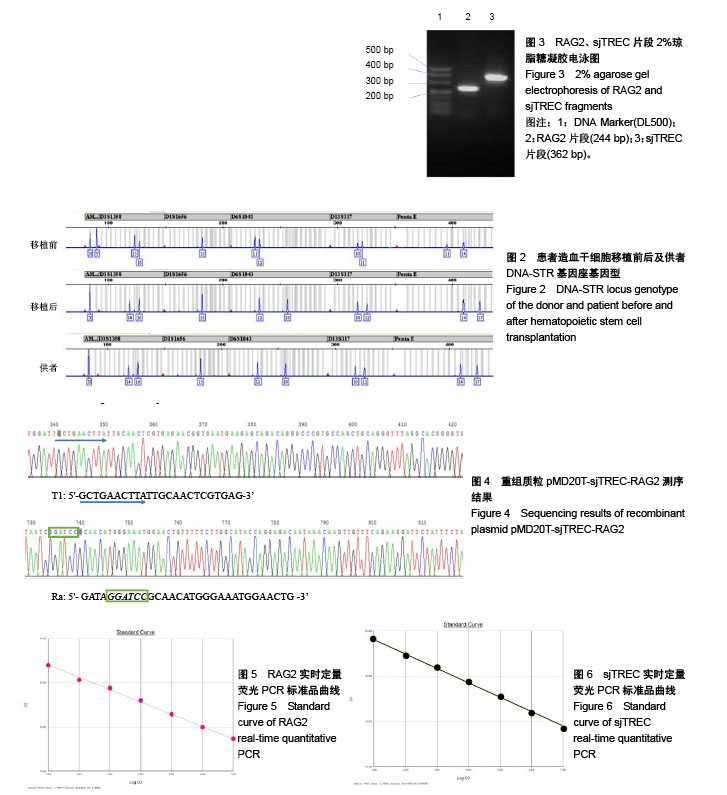
2.1 造血干细胞移植病例植入存活状况 收集的6例造血干细胞移植患者样本均获得满意的20个STR基因座基因型和1个性别基因座基因型的分型结果(图2),患者移植后STR表型均完全表现为供者源型,未检测到供受者嵌合状态。 2.2 标准品制备 2.2.1 构建重组质粒pMD20T-sjTREC-RAG2及鉴定结果 对重组质粒pMD20T-sjTREC-RAG2用T1、T2与R1、R2进行PCR扩增,得到的片段大小与文献[10]报道的RAG2片段(244 bp)和sjTREC片段(362 bp) 大小一致(图3)。DNA测序结果显示,sjTREC片段在重组质粒342 bp处插入,RAG2片段在735 bp处插入(图4),经核对其序列表达与文献[10]报道一致。 2.2.2 标准品曲线 在制备实时荧光绝对定量PCR体系时,根据质粒pMD20T-sjTREC-RAG2标准品的7个浓度梯度:0.5×107,0.5×106,0.5×105,0.5×104,0.5×103,0.5×102,5拷贝/μL,每个反应体系加入2 μL标准品,使反应体系中起始DNA模板量分别为1×107,1×106,1×105,1×104,1×103,1×102,10拷贝,根据7个浓度梯度标准品扩增的Ct值,绘制标准曲线(图5,6)。RAG2标准曲线斜率=-2.788 670,截距=36.805 401,R2=0.998 5;sjTREC标准曲线斜率=-3.218 531,截距=41.414 780,R2=0.997 076。两条标准曲线的R2均大于0.99。 2.3 sjTREC水平的比较分析 2.3.1 正常健康人群sjTREC平均水平 29例正常健康对照组外周血每1 000个细胞中的sjTREC拷贝数为26.99±29.33。按年龄将正常健康对照组分为20岁以下(n=14)与21-30岁(n=15)两组,其外周血1 000个细胞中sjTREC拷贝数分别为34.08±34.99与20.37±22.059,进行两独立样本的t 检验,P=0.018,差异有显著性意义(图7)。按性别分组,男性组(n=17)和女性组(n=12) sjTREC拷贝数分别为27.91±33.45,25.68±23.65,男女之间差异无显著性意义。 2.3.2 移植前、移植后外周血中sjTREC平均水平比较 移植前患者(n=19)外周血1 000个细胞中sjTREC拷贝数为6.97±9.50,与正常对照组进行两独立样本的t 检验,P=0.006,差异有显著性意义。按年龄分析,其中20岁以下患者(n=7)拷贝数为7.62±11.86;21岁以上患者(n=12)拷贝数为6.59±8.40,进行两独立样本的t 检验,P=0.592,差异无显著性意义。按性别分析,男性(n=14)拷贝数为8.75±10.52;女性(n=5)拷贝数为1.99±1.96,进行两独立样本的t 检验,P=0.071,差异无显著性意义。 移植后1个月患者(n=5)外周血1 000个细胞中sjTREC拷贝数为43.49±32.80;移植后6个月患者(n=4)外周血1 000个细胞中sjTREC拷贝数为11.83±13.13 (图8)。 按移植方式分析[11],HLA半相合亲缘移植患者(n=2)移植前拷贝数为17.05±22.28,移植后6个月拷贝数为24.26±25.50;HLA全相合非亲缘移植患者(n=4)移植前拷贝数为6.74±12.85,移植后6个月拷贝数为28.30± 19.12(图9)。 按疾病类型分析,6例患者涉及4种疾病分型,移植前的sjTREC水平均很低,移植后1个月时1例3岁急性淋巴细胞白血病亲缘移植患者sjTREC水平最高,为78.362 4拷贝,但其他2例22岁和19岁急性淋巴细胞白血病患者sjTREC水平很低,为1.513 2,8.609 1拷贝;同时1例44岁再生障碍性贫血患者未检出sjTREC,1例急性髓系白血病患者和1例急性单核细胞性白血病患者的sjTREC水平居中,5例检出的sjTREC范围从1.513 2-78.362 4拷贝,差异很大。"
| [1] Storek J, Dawson MA, Storer B, et al. Immune reconstitution after allogeneic marrow transplantation compared with blood stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2001;97(11):3380-3389.[2] Small TN. Immunologic reconstitution following stem cell transplantation. Curr Opin Hematol. 1996;3(6):461-465.[3] Elhasid R, Ben Arush MW, Pollack S, et al. Immune and hematopoietic reconstitution after transplantation of cord blood progenitor cells: case report and review of the literature. Leukemia. 2000;14(5):931-934.[4] Talvensaari K, Clave E, Douay C, et al. A broad T-cell repertoire diversity and an efficient thymic function indicate a favorable long-term immune reconstitution after cord blood stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2002;99(4):1458-1464.[5] Geenen V, Poulin JF, Dion ML, et al. Quantification of T cell receptor rearrangement excision circles to estimate thymic function: an important new tool for endocrine-immune physiology. J Endocrinol. 2003;176(3):305-311.[6] Douek DC, McFarland RD, Keiser PH, et al. Changes in thymic function with age and during the treatment of HIV infection. Nature. 1998;396(6712):690-695.[7] Ferrando-Martinez S, De Pablo-Bernal RS, De Luna-Romero M, et al. Thymic Function Failure Is Associated With Human Immunodeficiency Virus Disease Progression. Clin Infect Dis. 2017; 64(9):1191-1197. [8] De Voeght A, Martens H, Renard C, et al. Exploring the link between innate immune activation and thymic function by measuring sCD14 and TRECs in HIV patients living in Belgium. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0185761.[9] Walsh PS, Metzger DA, Higuchi R. Chelex 100 as a medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material. Biotechniques. 1991;10(4):506-513.[10] 李扬秋,杨力建,陈少华,等.实施定量PCR检测正常人外周血T细胞和胸腺细胞中sjTRECs水平[J]. 现代临床医学生物工程学杂志, 2001, 7(6):397-400.[11] 王坤,金静君,杨婷,等.荧光定量PCR检测T细胞受体删除环在亲缘与非亲缘异基因造血干细胞移植后免疫重建早期的应用[J].福建医药杂志, 2017,39(5):139-143.[12] Parkman R, Weinberg K. Immunological reconstitution following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. In: Thomas ED, Blume KG, Forman SJ, eds. Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. 2nd ed. Oxford, England: Blackwell Science, 1999:704-711.[13] Ochs L, Shu XO, Miller J, et al. Late infections after allogeneic bone marrow transplantations: comparison of incidence in related and unrelated donor transplant recipients. Blood. 1995;86(10): 3979-3986.[14] Socié G, Stone JV, Wingard JR, et al. Long-term survival and late deaths after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Late Effects Working Committee of the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(1):14-21.[15] Hazenberg MD, Otto SA, de Pauw ES, et al. T-cell receptor excision circle and T-cell dynamics after allogeneic stem cell transplantation are related to clinical events. Blood. 2002;99(9):3449-3453.[16] Lorenzi AR, Patterson AM, Pratt A, et al. Determination of thymic function directly from peripheral blood: a validated modification to an established method. J Immunol Methods. 2008;339(2):185-194.[17] Douek DC, Vescio RA, Betts MR, et al. Assessment of thymic output in adults after haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation and prediction of T-cell reconstitution. Lancet. 2000;355(9218): 1875-1881.[18] Aversa F, Terenzi A, Tabilio A, et al. Full haplotype-mismatched hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: a phase II study in patients with acute leukemia at high risk of relapse. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23(15):3447-3454.[19] Jiang Q, Xu LP, Liu DH, et al. Imatinib mesylate versus allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in the accelerated phase. Blood. 2011;117 (11):3032-3040.[20] Odriozola A, Riancho JA, Mijares V, et al. Chimerism detection by short tandem repeat analysis when donor and recipient genotypes are not known. Clin Chim Acta. 2012;413(5-6):548-551.[21] Weinberg K, Blazar BR, Wagner JE, et al. Factors affecting thymic function after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2001;97(5):1458-1466.[22] Storek J, Joseph A, Dawson MA, et al. Factors influencing T-lymphopoiesis after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Transplantation. 2002;73(7):1154-1158.[23] Lewin SR, Heller G, Zhang L, et al. Direct evidence for new T-cell generation by patients after either T-cell-depleted or unmodified allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantations. Blood. 2002; 100(6):2235-2242.[24] Ringhoffer S, Rojewski M, Döhner H, et al. T-cell reconstitution after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: assessment by measurement of the sjTREC/βTREC ratio and thymic naive T cells. Haematologica. 2013;98(10):1600-1608.[25] Ferrando-Martinez S, De Pablo-Bernal RS, De Luna-Romero M, et al. Thymic Function Failure Is Associated With Human Immunodeficiency Virus Disease Progression. Clin Infect Dis. 2017; 64(9):1191-1197.[26] Sutherland JS, Goldberg GL, Hammett MV, et al. Activation of thymic regeneration in mice and humans following androgen blockade. J Immunol. 2005;175(4):2741-2753. [27] Storek J, Joseph A, Espino G, et al. Immunity of patients surviving 20 to 30 years after allogeneic or syngeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 2001;98(13):3505-3512. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||