Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (36): 5889-5896.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0612
Previous Articles Next Articles
Physical activity of people with intellectual disability measured by motion sensor
Wang Dandan, Zhang Lei, Wu Xueping
- (School of Physical Education and Sport Training, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China)
-
Received:2018-08-07 -
Contact:Wu Xueping, PhD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Physical Education and Sport Training, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China -
About author:Wang Dandan, Doctoral candidate, School of Physical Education and Sport Training, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China -
Supported by:the Science Research Program of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission, No. 15490503000
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Dandan, Zhang Lei, Wu Xueping . Physical activity of people with intellectual disability measured by motion sensor[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5889-5896.
share this article
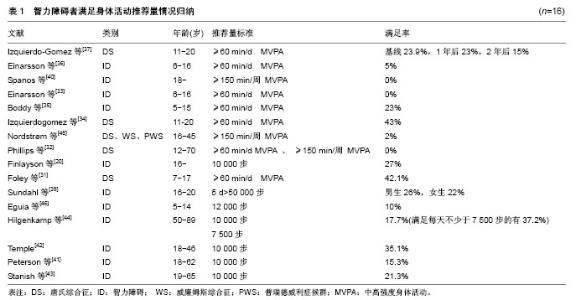
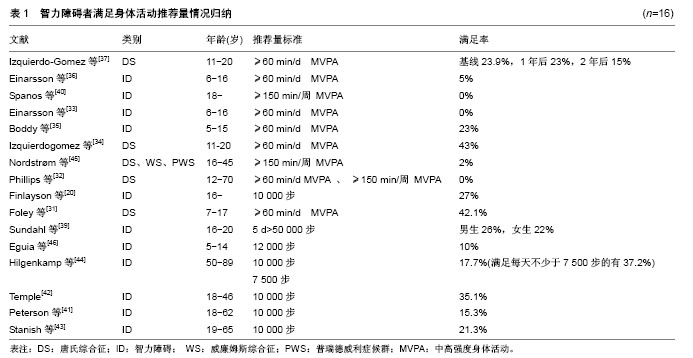
身体活动研究的泰斗Biddle教授认为身体研究的主题主要包括5个方面:①身体活动的精确测量;②身体活动与健康的关系;③身体活动行为的相关因素;④评估设计的身体活动的干预方案;⑤将研究结果应用于实践操作[16]。 依据Biddle教授的身体活动研究主题分类,同时根据智力障碍者身体活动研究现状,该研究主要从5个方面梳理智力障碍者身体活动研究进展:①运动传感器测量智力障碍者身体活动的有效性;②智力障碍者身体活动水平;③智力障碍者身体活动水平与健康的关系;④智力障碍者身体活动参与的影响因素;⑤智力障碍者身体活动水平的干预及效果。 2.1 运动传感器测量智力障碍者身体活动的有效性 有效性也称之为效度,是指选择的测量工具或手段测量出的结果能够反映所要测量内容的精确程度以及能够测量所要测量事物的准确程度[17]。该文运动传感器测量智力障碍者身体活动的有效性主要是验证加速度计和计步器的精确性和准确性。 2.1.1 加速度计和计步器测量智力障碍者身体活动的精确性 为了验证加速度计和计步器测量智力障碍者身体活动的精确性,Johnson等[18]使用身体活动问卷(Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey)、加速度计(Actiwatch)和计步器(Omron HJ-112)同时测量37名19-74岁智力障碍者,结果发现智力障碍者自我报告的身体活动水平与加速度计和计步器测量结果的会聚效度中低一致(r=0.34,P < 0.05);而加速计和计步器之间的会聚效度高度一致(r=0.85,P < 0.01)。Dairo等[19]使用国际身体活动问卷(International Physical Activity Questionnaire-short version)和 Axivity AX3、GENEActiv加速度计,对不同障碍程度的20名22-70岁的智力障碍者的测量数据进行分析,发现问卷会高估每周总的身体活动时间,低估中高强度的身体活动时间。Finlayson等[20]对62名16岁以上的轻中度智力障碍的身体活动情况进行半结构式访谈,同时使用加速度计(activPAL)对其身体活动水平进行监控,结果发现自我报告与加速度计测量的总体身体活动水平一致性较差(Kappa=0.147,P=0.13),仅有41%的人能比较精确的报告他们总的身体活动水平。 由此可见,问卷在评估智力障碍者的身体活动水平时会存在不同程度的偏差,加速度计和计步器测量一致性更高,是更可靠的评估智力障碍者身体活动水平的工具。 2.1.2 加速度计和计步器测量智力障碍者身体活动的准确性 唐氏综合征(DS)是由于基因问题引起的智力障碍[21]。与健全人和单纯智力障碍者相比,唐氏综合征患者的平衡能力更差[22]、动作发展水平更低,有其独特的步态特征,可能会影响运动传感器测量其身体活动水平的准确性[23]。Agiovlasitis等[24-25]为了验证加速度计输出的活动计数能否作为唐氏综合征和单纯智力障碍者代谢率和能量消耗的预测指标,使用Actigraph 7164测量唐氏综合征和单纯智力障碍者的活动计数、使用便携式心肺功能测量仪(K4b2)测量代谢当量(METs),结果表明两个群组的活动计数(Actigraph7164)均能预测代谢率(R2=0.60和0.56,P < 0.001),也可以作为能量消耗的预测指标(R2=0.61和0.37,P < 0.005)。为了验证计步器测量唐氏综合征步行数的精确性,Pitchford等[26-27]以直接观察法为校标,同时使用Omron HJ-112(OM)和Yamax Digiwalker SW-200(YM)2种计步器测量唐氏综合征和健全人的步行数,结果发现2种计步器的测量误差确实与人群有关:与健全人相比,计步器测量唐氏综合征患者快走、自定步速和慢走的绝对误差都更大;唐氏综合征自定步速步行时,计步器的测量结果高于实际水平,与YM相比,OM的绝对效度和相对效度都更高 (Φ=0.79,G=0.98),即虽然计步器测量唐氏综合征的步行数时,OM的计步功能会产生系统误差和随机误差,但测量结果仍然有效,仍可作为有效的测量工具。 综上可见,加速度计输出的活动计数可以作为智力障碍者能量消耗和代谢率的预测指标,计步器也可以作为唐氏综合征患者步行数的有效测量工具。但唐氏综合征患者的步态稳定性低、有氧运动能力弱的特点还是影响了计步器的精确性,然而他们步行的独特性并未影响其行走过程中的代谢率,也没有改变加速计的输出活动计数与代谢率之间的关系,因此未影响加速度计测量能量消耗的准确性。 2.2 智力障碍者的身体活动水平 世界卫生组织推荐5-17岁青少年儿童每天至少进行60 min的中高强度身体活动(MVPA),18-64岁的成年人每周至少进行 150 min中等强度身体活动(MPA),而65岁以上成人每周至少150 min的中等强度身体活动或75 min高强度身体活动(VPA),每次持续活动时间不少于10 min。步行10 000步也是公认的推荐量,但也有研究发现 11 500-14 000步相当于儿童青少年60 min中高强度身体活动水平,老年人和特殊人群每天7 000-10 000步即能满足每周至少150 min中高强度身体活动推荐量的要求,因此建议以12 000步作为青少年儿童的身体活动推荐量标准,7 000-10 000步作为老年人和特殊人群身体活动量推荐标准[28-30]。但到目前为止,并未有官方的、标准的、通用的智力障碍者身体活动推荐量标准,因此归纳文献,发现文献中使用的推荐量有多样性的特点:每天不少于60 min中高强度身体活动,每周不少于 150 min中高强度身体活动,每天不少于7 500、10 000步和12 000步,5 d不少于50 000步等。 梳理文献中智力障碍者满足身体活动推荐量的人数比例发现:总体而言,0%-43%的青少年儿童能满足每天不少于60 min中高强度身体活动的推荐量[31-37],10%能满足每天不少于12 000步的推荐量[38],分别有26%和22%的男生和女生能满足5 d不少于50 000步的推荐量[39]。0%-2%的智力障碍成年人能满足每周不少于150 min中高强度身体活动的推荐量[32,36,40],15.3%-35.1%能满足每天不少于10 000步的推荐量[32,41-44],37.2%能满足每天不少于7 500步的推荐量[44],见表1。"
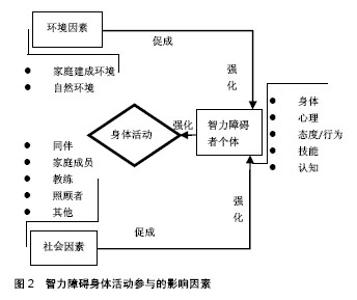
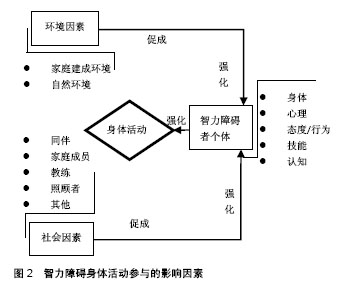
进一步深入分析,发现无论是青少年儿童还是成年人,满足推荐量的人数远少于同龄健全人[33,36,39];男性满足推荐量的人数都高于女性[33,39,45];工作日能满足推荐量的人数多于周末[33,46];低龄组能满足身体活动推荐量的人数多于高龄组[34,37];在没有满足推荐量的人群中,超重者所占比例大于正常体质量者就遗传因素造成染色体异常的智力障碍者而言[20],满足推荐量的人数最多的是普瑞德威利症候群(Prader-Willi syndrome,PWS)组,最少的是唐氏综合征组[45]。 2.3 智力障碍者身体活动与健康的关系 梳理纳入文献发现智力障碍者身体活动与健康的关系研究主要是身体活动水平与肥胖、心血管功能的关系,具体的指标包括体质量指数、脂肪百分比(%fat)、腰围、最大耗氧量(VO2peak)、血压等,其中讨论最多的是身体活动与体质量指数的关系[39,43,47-50]。结果发现,与健全人研究不同,虽然智力障碍者的身体活动水平与体质量指数、腰围、脂肪率呈负相关关系,与VO2peak呈正相关关系,但相关系数低且都不具有显著性差异,分析原因可能与智力障碍者研究的样本量小有关[39,47-50]。Stanish等[43]与他人研究基本相符,但也有不同的发现:将智力障碍者的步行水平分为少于5 000步、 5 000-7 499步、7 500-9 999步、不少于10 000步4个等级,其他3个步行水平等级,智力障碍者的血压、体质量指数和腰围与身体活动水平正相关,但步行不少于10 000步的智力障碍者组却相反,呈负相关,探索原因可能是后者生活独立性较强,可以自由挑选他们喜欢的食物,摄入高脂肪含量的食物较多,致使血压更高,体质量指数和腰围值更大。因此对自主、独立能力较强的智力障碍者,照顾者应加强科学的膳食管理。 综上可见,智力障碍者身体活动水平总体上与健康指标的相关系数都较低,且不具有显著性。但这并不表明智力障碍者的身体活动水平与健康之间不存在关系。当前智力障碍者身体活动与健康的关系都是通过横向研究来分相关性,然而无论是肥胖还是心血管机能的影响因素都是多样化,除了身体活动之外,基因、膳食习惯、遗传、疾病等也都是关键影响因素,因此仅通过横向研究来建立的智力障碍者身体活动水平与健康的关系是有限制的。未来研究需加强纵向研究,通过长期跟踪,建立动态的身体活动行为与肥胖、心肺功能及慢性疾病的关系,如智力障碍者青少年儿童时期身体活动水平低,是否成年和中年后肥胖和慢性疾病的发生率高,最终确立身体活动水平预测疾病的程度,建立身体活动水平与健康的关系。 2.4 智力障碍者身体活动参与的影响因素 探索智力障碍者身体活动参与的促进和阻碍因素,对身体活动水平改善方案的设计具有针对性意义。智力障碍者身体活动参与的影响因素总体上可以归纳为个人因素、社会因素和环境因素[51],见图2。"
| [1] Katikireddi SV. Global, regional, and national incidence and prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries in 195 countries, 1990-2016: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211-1259. [2] 冬雪. 美国智力障碍定义的演变及其启示[J]. 中国特殊教育,2011,(5): 34-39.[3] Walsh PN, Kerr M, van Schrojenstein Lantman-de-Valk HM. Health indicators for people with intellectual disabilities: A european perspective. Eur J Public Health. 2003;13(S3): 47-50.[4] Krahn GL, Hammond L, Turner A. A cascade of disparities: Health and health care access for people with intellectual disabilities. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2006;12(1):70-82. [5] Martin E, Mckenzie K, Newman E, et al. Care staff intentions to support adults with an intellectual disability to engage in physical activity: An application of the theory of planned behaviour. Res Dev Disabil. 2011;32(6):2535-2541.[6] Pauline H, Gyles G. Mortality of people with intellectual disabilities in england: A comparison of data from existing sources. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2015;28(5):414-422.[7] Caspersen CJ, Powell KE, Christenson GM. Physical activity, exercise, and physical fitness: Definitions and distinctions for health-related research. Public Health Rep. 1985;100(2):126-131.[8] Duplant A, Vingren J, Kellerl J. Physical activity and intellectual disability. Strength & Conditioning Journal. 2014;36(2): 26-28.[9] Bartlo P, Klein PJ. Physical activity benefits and needs in adults with intellectual disabilities: Systematic review of the literature. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2011;116(3):220-232.[10] Willems M, Hilgenkamp TI, Havik E, et al. Use of behaviour change techniques in lifestyle change interventions for people with intellectual disabilities: A systematic review. Res Dev Disabil. 2016; 60:256-268.[11] Brooker K, Van DK, Mcpherson L, et al. A systematic review of interventions aiming to improve involvement in physical activity among adults with intellectual disability. J Phys Act Health. 2015;12(3): 434-444.[12] Finlay WM, Lyons E. Methodological issues in interviewing and using self-report questionnaires with people with mental retardation. Psychol Assess. 2001;13(3):319-335.[13] 戴剑松,孙飙. 体力活动测量方法综述[J]. 体育科学, 2005,25(9): 69-75.[14] Mcgarty AM, Penpraze V, Melville CA. Accelerometer use during field-based physical activity research in children and adolescents with intellectual disabilities: A systematic review. Res Dev Disabil. 2014;35(5): 973-981.[15] 王超,贺刚,李建忠,等.残疾青少年体力活动水平及其与运动自我效能的关系:基于加速度计的初步研究[J].首都体育学院学报, 2016, 28(4): 380-384.[16] Biddle SJ, Gorely T, Stensel DJ. Health-enhancing physical activity and sedentary behaviour in children and adolescents. J Sports Sci. 2004; 22(8): 679-701.[17] Thomas JR, Nelson JK, Silverman SJ/李红娟, 花勇民, 郜艳晖译. 体力活动研究方法[M]. 6版.北京:北京体育大学出版社, 2016:180.[18] Johnson M, Yun J, Mccubbin JA. Validity evidence for self-report with assistance to measure physical activity behavior in adults with intellectual disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2014;52(4):273-281.[19] Dairo YM, Collett J, Dawes H. A feasibility study into the measurement of physical activity levels of adults with intellectual disabilities using accelerometers and the international physical activity questionnaire. British J Learning Disabil. 2017; 20(45): 129-137.[20] Finlayson J, Turner A, Granat MH. Measuring the actual levels and patterns of physical activity/inactivity of adults with intellectual disabilities. J Appli Res Intellect Disabil. 2011; 24(6): 508-517.[21] Mahy J, Shields N, Taylor NF, et al. Identifying facilitators and barriers to physical activity for adults with down syndrome. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2010; 54(9): 795-805.[22] Black DP, Smith BA, Wu J, et al. Uncontrolled manifold analysis of segmental angle variability during walking: Preadolescents with and without down syndrome. Exp Brain Res. 2007; 183(4): 511-521.[23] Carr J. Mental and motor development in young mongol children. J Ment Defic Res. 2010;14(3): 205-220.[24] Agiovlasitis S, Motl RW, Fahs CA, et al. Metabolic rate and accelerometer output during walking in people with down syndrome. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011; 43(7): 1322-1327.[25] Agiovlasitis S, Motl RW, Foley JT, et al. Prediction of energy expenditure from wrist accelerometry in people with and without down syndrome. Adapt Phys Activ Q. 2012;29(2):179-190.[26] Pitchford EA, Yun J. The accuracy of pedometers for adults with down syndrome. Adapt Phys Activ Q. 2010; 27(4):321-336.[27] Pitchford EA, Yun J. Pedometer variance in adults with down syndrome during free walking: A generalizability study. J Phys Act Health. 2011;8(8):1143-1151.[28] Tudor-Locke C, Craig CL, Brown WJ, et al. How many steps are enough? For adults. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2011;8(2):207-211. [29] Marc A, Johnson, William D, et al. Steps/day translation of the moderate-to-vigorous physical activity guideline for children and adolescents. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2013; 10(1): 49-49.[30] Fontana FE, Silva MPD, Marston R, et al. Step-count guidelines referenced on 60-minutes of moderate/vigorous physical activity. Motriz Revista De Educação Física. 2015; 21(1): 92-99.[31] Foley JT, Mccubbin JA. An exploratory study of after-school sedentary behaviour in elementary school-age children with intellectual disability. J Int Dev Disabil. 2009; 34(1): 3-9.[32] Phillips AC, Holland AJ. Assessment of objectively measured physical activity levels in individuals with intellectual disabilities with and without down's syndrome. Plos One. 2011; 6(12): e28618.[33] Einarsson IO, Olafsson A, Hinriksdóttir G, et al. Differences in physical activity among youth with and without intellectual disability. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(2):411-418.[34] Izquierdo-Gomez R, MartãNez-Gã³mez D, Acha A, et al. Objective assessment of sedentary time and physical activity throughout the week in adolescents with down syndrome. The up&down study. Res Dev Disabil. 2014;35(2): 482-489.[35] Boddy LM, Downs SJ, Knowles ZR, et al. Physical activity and play behaviours in children and young people with intellectual disabilities: A cross-sectional observational study. School Psychology International. 2015; 36(2): 154-171.[36] Einarsson IÞ, Jóhannsson E, Daly D, et al. Physical activity during school and after school among youth with and without intellectual disability. Res Dev Disabil. 2016; 56:60-70.[37] Izquierdo-Gomez R, Martinez-Gómez D, Esteban-Cornejo I, et al. Changes in objectively measured physical activity in adolescents with down syndrome: The up&down longitudinal study. J Int Disabil Res. 2017; 61(4): 1-10.[38] Lante KA, Walkley JW, Gamble M, et al. An initial evaluation of a long-term, sustainable, integrated community-based physical activity program for adults with intellectual disability. J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2011; 36(3): 197-206.[39] Sundahl L, Zetterberg M, Wester A, et al. Physical activity levels among adolescent and young adult women and men with and without intellectual disability. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2016; 29(1): 93-98.[40] Spanos D, Hankey CR, Melville CA. The effectiveness of a weight maintenance intervention for adults with intellectual disabilities and obesity: A single stranded study. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2016; 29(4): 317-329.[41] Peterson JJ, Janz KF, Lowe JB. Physical activity among adults with intellectual disabilities living in community settings. Prev Med. 2008; 47(1):101-106. [42] Temple VA. Factors associated with high levels of physical activity among adults with intellectual disability. Int J Rehabil Res. 2009; 32(1): 89-92.[43] Stanish HI, Draheim CC. Walking activity, body composition and blood pressure in adults with intellectual disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2010; 20(3): 183-190.[44] Hilgenkamp TI, Reis D, Van WR, et al. Physical activity levels in older adults with intellectual disabilities are extremely low. Res Dev Disabil. 2012 Mar-Apr;33(2):477-483.[45] Nordstrøm M, Hansen BH, Paus B, et al. Accelerometer-determined physical activity and walking capacity in persons with down syndrome, williams syndrome and prader–willi syndrome. Res Dev Disabil. 2013; 34(12): 4395-4403.[46] Eguia KF, Capio CM, Simons J. Object control skills influence the physical activity of children with intellectual disability in a developing country: The philippines. J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2015; 40(3): 1-10.[47] Temple VA. Barriers, enjoyment, and preference for physical activity among adults with intellectual disability. Int J Rehabil Res. 2007; 30(4): 281-287.[48] Esposito PE, Macdonald M, Hornyak JE, et al. Physical activity patterns of youth with down syndrome. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2012; 50(2): 109-119.[49] Shields N, Hussey J, Murphy J, et al. An exploratory study of the association between physical activity, cardiovascular fitness and body size in children with down syndrome. Dev Neurorehabil. 2015; 20(2): 92-98.[50] Queralt A, Vicente-Ortiz A, Molina-García J. The physical activity patterns of adolescents with intellectual disabilities: A descriptive study. Disabil Health J. 2016;9(2):341-345.[51] Bodde AE, Seo DC. A review of social and environmental barriers to physical activity for adults with intellectual disabilities. Disabil Health J. 2009;2(2):57-66.[52] Horvat M, Pitetti KH, Croce R. Isokinetic torque, average power, and flexion/extension ratios in nondisabled adults and adults with mental retardation. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1997; 25(6): 395-399.[53] Morris CA, Demsey MSA, Leonard CO, et al. Natural history of williams syndrome: Physical characteristics. J Pediatr. 1988; 113(2): 318-326.[54] Korenberg JR, Chen XN, Schipper R, et al. Down syndrome phenotypes: The consequences of chromosomal imbalance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(11):4997-5001.[55] Amaro AS, Mesquita MLGD, Rodrigues GM, et al. Physiological adaptation after a 12-week physical activity program for patients with prader–willi syndrome: Two case reports. J Med Case Rep. 2016; 10(1):181-187.[56] Morris CA, Mervis CB, Paciorkowski AP, et al. 7q11.23 duplication syndrome: Physical characteristics and natural history. Am J Med Genet A. 2016; 167(12): 2916-2935.[57] Schlosser RW, Wendt O, Bhavnani S, et al. Use of information-seeking strategies for developing systematic reviews and engaging in evidence-based practice: The application of traditional and comprehensive pearl growing. A review. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2006;41(5):567-582.[58] Toomey E, Coote SB. Physical rehabilitation interventions in nonambulatory people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review. Int J Rehabil Res. 2012; 35(4): 281-291.[59] Downs SJ, Knowles ZR, Fairclough SJ, et al. Exploring teachers’ perceptions on physical activity engagement for children and young people with intellectual disabilities. Eur J Special Needs Education. 2014; 29(3): 402-414.[60] Mcgarty AM, Melville CA. Parental perceptions of facilitators and barriers to physical activity for children with intellectual disabilities: A mixed methods systematic review. Res Dev Disabil. 2018; 73:40-57.[61] Izquierdo-Gomez R, Veiga OL, Villagra A, et al. Correlates of sedentary behaviour in youths with down syndrome: The up&down study. J Sports Sci. 2015; 33(14): 1504-1514.[62] Hutzler Y, Korsensky O. Motivational correlates of physical activity in persons with an intellectual disability: A systematic literature review. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2010; 54(9): 767-786.[63] Shields N, Taylor NF, Fernhall B. A study protocol of a randomised controlled trial to investigate if a community based strength training programme improves work task performance in young adults with down syndrome. BMC Pediatr. 2010;10:17.[64] Shields N, Taylor NF, Wee E, et al. A community-based strength training programme increases muscle strength and physical activity in young people with down syndrome: A randomised controlled trial. Res Dev Disabil. 2013; 34(12): 4385-4394.[65] Taylor NF. The feasibility of a physical activity program for young adults with down syndrome: A phase ii randomised controlled trial. J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2015; 40(2): 115-125.[66] Melvill CA, Boyle S, Miller S, et al. An open study of the effectiveness of a multi-component weight-loss intervention for adults with intellectual disabilities and obesity. Br J Nutr. 2011;105(10):1553-1562.[67] Bodde AE, Seo DC, Frey GC, et al. The effect of a designed health education intervention on physical activity knowledge and participation of adults with intellectual disabilities. Am J Health Promot. 2012; 26(1): 313-316. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Peng Kun, Lin Yimin, Gan Xiaoling, Wu Zhiyong. Development prospect of orthopedic rehabilitation medicine based on three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 632-637. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||