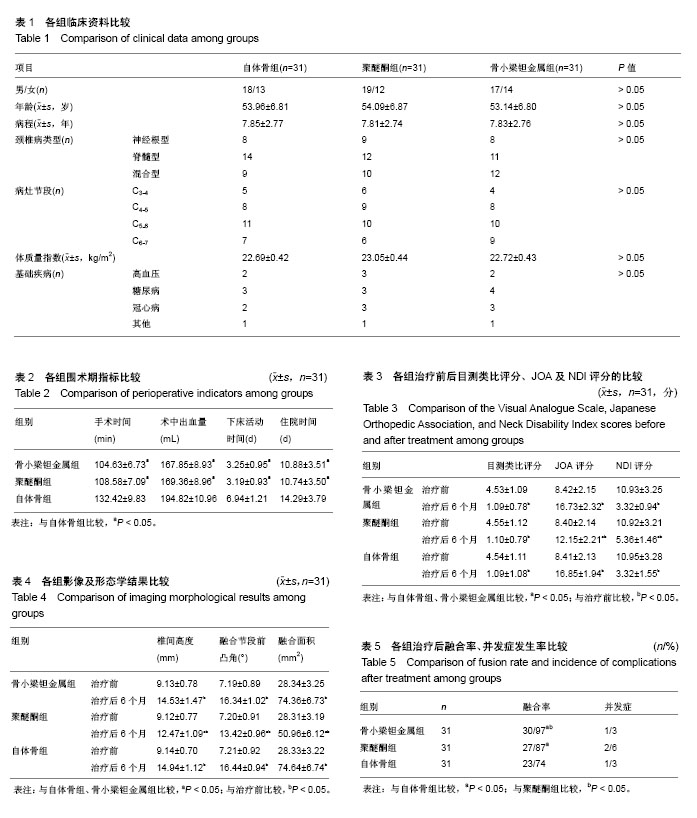
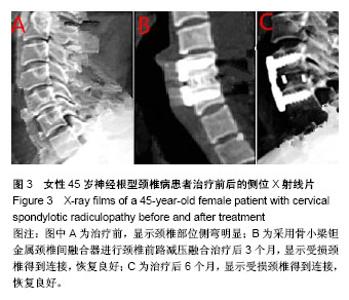
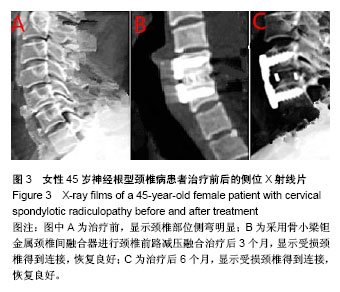
| [1] 徐文华,谭明生,杨峰,等.纳米羟基磷灰石椎间融合器与钛钢板固定在颈椎病前路手术中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24 (13):1170-1174.[2] 雷高,张丁城,徐响阳,等.零切迹锚定式颈椎间融合器在颈前路颈椎融合术中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(5):461-463.[3] 金成春,鲍广全,徐宏光.颈前路减压椎间融合器植骨融合术治疗单节段脊髓型颈椎病临床观察[J].山东医药,2017,57(16):64-66.[4] 孙佳佳,杨惠林,周军,等.同种异体骨与自体骨填充椎间融合修复脊髓型颈椎病的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,9(3): 329-334.[5] Zhang J, Meng F, Yan D, et al. Hybrid Surgery Versus Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion in Multilevel Cervical Disc Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Medicine. 2016;95(21):e3621. [6] 李玉伟,王海蛟,严晓云,等.颈前路减压零切迹椎间融合器与钉板系统内固定治疗脊髓型颈椎病的疗效比较[J].中华骨科杂志, 2015,35(11):1136-1141.[7] 梁英杰,尹庆水,张光明,等.颈椎前路椎间融合器植入术治疗脊髓型颈椎病22例疗效分析[J].中华显微外科杂志, 2015,38(3): 287-289.[8] Ajiboye RM, D'Oro A, Ashana AO, et al. Routine Use of Intraoperative Neuromonitoring During ACDFs for the Treatment of Spondylotic Myelopathy and Radiculopathy Is Questionable: A Review of 15, 395 Cases. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(1):14-19. [9] 王强,张良,纪泉,等.老年患者短节段颈椎病应用零切迹椎间融合器的疗效观察[J].中华老年医学杂志,2015,34(11):1170-1173.[10] 许艺荠,张雪松,孙太存,等.新型Zero-P与cage钛板椎间融合器修复颈椎病:早期稳定性对比[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(22):3227-3234.[11] Hou Y, Nie L, Pan X, et al. Effectiveness and safety of Mobi-C for treatment of single-level cervical disc spondylosis: a randomised control trial with a minimum of five years of follow-up. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(6):829. [12] 李斌,夏卿,华永新,等.多孔钽金属的骨外科应用:关节置换假体及软骨重建支架[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,9(12):1943-1947.[13] 曹盛生,饶敏杰,秦育宏,等.前路颈椎间盘桥式自锁定PEEK椎间融合器的临床应用及中远期疗效研究[J].中国全科医学, 2017, 20(5):603-606.[14] 蒋新祥,徐海栋,路晓.颈椎间盘置换与前路椎间植骨融合修复中年颈椎病:颈椎功能及活动度比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(48):7717-7723.[15] Puvanesarajah V, Jain A, Shimer AL, et al. Complications and Mortality Following One to Two-Level Anterior Cervical Fusion for Cervical Spondylosis in Patients Above 80 Years of Age. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(9):E509. [16] 陈博来,林涌鹏,赵帅,等.零切迹自稳型颈椎融合器(ROI-C)在颈椎前路减压融合术中的安全性与有效性评价[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(10):894-898.[17] 王敏,郝定均,刘团江,等.应用新型PeekPrevail椎间融合内固定系统治疗颈椎病的近期疗效观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2015, 25(6):484-490.[18] Puvanesarajah V, Hassanzadeh H, Shimer AL, et al. Readmission Rates, Reasons, and Risk Factors Following Anterior Cervical Fusion for Cervical Spondylosis in Patients Above 65 Years of Age. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2016;16(10):78-84. [19] 李会明,夏刚,田融.两种颈前路减压重建术治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的疗效比较[J].中华实验外科杂志,2016,33(5):1409-1411.[20] 程俊杰,代杰,马原,等.零切迹颈前路融合钢板(Zero-P)在颈椎前路减压植骨融合内固定中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(48):7747-7751.[21] Wang T, Wang H, Liu S, et al. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion versus anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion in multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy: A meta-analysis. Medicine. 2016;95(49):e5437. [22] 熊绪,刘家明,陈宣银,等.颈椎椎板作为椎体间植骨材料在颈椎一期后前路手术中的应用[J].解放军医学杂志, 2015,40(2): 147-150.[23] 王治栋,朱若夫,杨惠林,等.前路减压椎间桥形融合器ROI-C置入治疗连续双节段脊髓型颈椎病的疗效对比[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(2):124-130.[24] Liu JM, Peng HW, Liu ZL, et al. Hybrid Decompression Technique Versus Anterior Cervical Corpectomy and Fusion for Treating Multilevel Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Which One Is Better? World Neurosurg. 2015;84(6): 2022-2029. [25] 孙璟川,史建刚,王元,等.颈椎前路椎体骨化物复合体前移融合术治疗严重颈椎后纵韧带骨化症[J].第二军医大学学报, 2017, 38(8):1053-1059.[26] Mao N, Wu J, Zhang Y, et al. A Comparison of Anterior Cervical Corpectomy and Fusion Combined With Artificial Disc Replacement and Cage Fusion in Patients With Multilevel Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(16):1277-1283. [27] 叶有晨,赵新华,杨永宏.前路颈椎桥形锁定融合器(ROI-C)治疗退变性颈椎间盘疾病的临床应用分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(3):209-213.[28] Ament JD, Yang Z, Chen Y, et al. A Novel Quality of Life Utility Index in Patients with Multilevel Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease: Comparison of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion with Total Disc Replacement. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(14):1072-1078. [29] Ament JD, Yang Z, Nunley P, et al. Cost Utility Analysis of the Cervical Artificial Disc vs Fusion for the Treatment of 2-Level Symptomatic Degenerative Disc Disease: 5-Year Follow-up. Neurosurgery. 2016;79(1):135-145. |