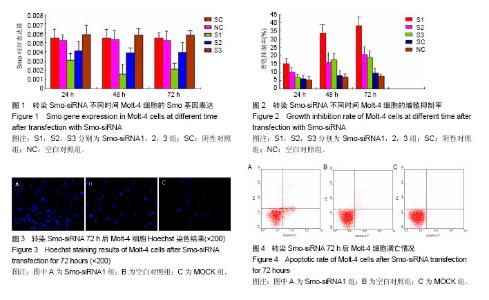
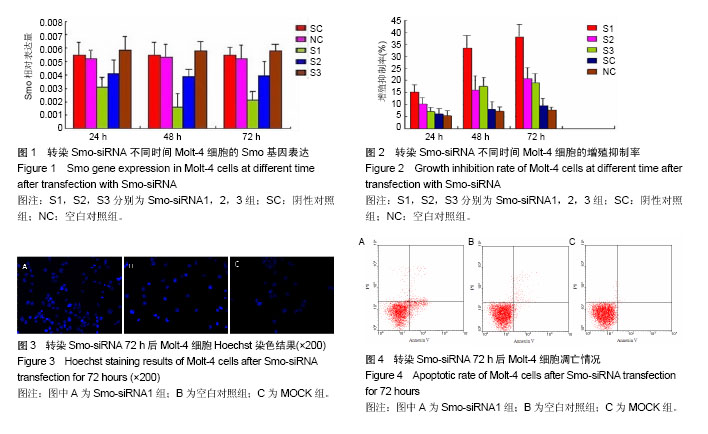
| [1] de Lima M, Porter DL, Battiwalla M, et al. Proceedings from the National Cancer Institute's Second International Workshop on the Biology, Prevention, and Treatment of Relapse After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: part III. Prevention and treatment of relapse after allogeneic transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20(1):4-13. [2] 李扬秋, 刘启发. 血液肿瘤靶向治疗和免疫治疗[J]. 肿瘤防治研究,2004, 31(6):封二,335.[3] Taipale J, Beachy PA. The Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature. 2001;411(6835):349-354.[4] Clement V, Sanchez P, de Tribolet N, et al. HEDGEHOG-GLI1 signaling regulates human glioma growth, cancer stem cell self-renewal, and tumorigenicity. Curr Biol. 2007;17(2):165-172.[5] Stecca B, Mas C, Clement V, et al. Melanomas require HEDGEHOG-GLI signaling regulated by interactions between GLI1 and the RAS-MEK/AKT pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(14):5895-5900.[6] Ingham PW, McMahon AP. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 2001; 15(23):3059-3087.[7] Tasaki A, Akiyoshi T, Koga K, et al. Immunohistochemical staining of hedgehog pathway-related proteins in human thymomas. Anticancer Res. 2005;25(6A):3697-3701.[8] Frank-Kamenetsky M, Zhang XM, Bottega S, et al. Small-molecule modulators of Hedgehog signaling: identification and characterization of Smoothened agonists and antagonists. J Biol. 2002;1(2):10.[9] Cooper MK, Porter JA, Young KE, et al. Teratogen-mediated inhibition of target tissue response to Shh signaling. Science. 1998;280(5369):1603-1607.[10] Fan CM, Porter JA, Chiang C, et al. Long-range sclerotome induction by sonic hedgehog: direct role of the amino-terminal cleavage product and modulation by the cyclic AMP signaling pathway. Cell. 1995;81(3):457-465.[11] 朱华民,李扬秋. 实时定量PCR检测慢性粒细胞白血病患者Shh、Smo基因的表达水[J].第三军医大学学报学报, 2014,36(3): 267-270.[12] Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402-408.[13] Singh RR, Cho-Vega JH, Davuluri Y, et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway is activated in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2009;69(6):2550-2558.[14] Pola R, Ling LE, Silver M, et al. The morphogen Sonic hedgehog is an indirect angiogenic agent upregulating two families of angiogenic growth factors. Nat Med. 2001;7(6): 706-711.[15] Litingtung Y, Chiang C. Specification of ventral neuron types is mediated by an antagonistic interaction between Shh and Gli3. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3(10):979-985.[16] Goodrich LV, Scott MP. Hedgehog and patched in neural development and disease. Neuron. 1998;21(6):1243-1257.[17] Grimm D, Kay MA. Therapeutic application of RNAi: is mRNA targeting finally ready for prime time. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(12): 3633-3641.[18] Taipale J, Chen JK, Cooper MK, et al. Effects of oncogenic mutations in Smoothened and Patched can be reversed by cyclopamine. Nature. 2000;406(6799):1005-1009.[19] Taipale J, Cooper MK, Maiti T, et al. Patched acts catalytically to suppress the activity of Smoothened. Nature. 2002;418(6900): 892-897. |