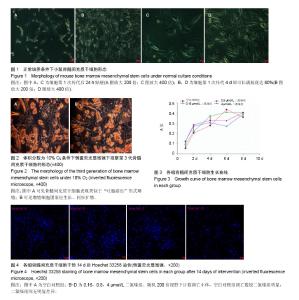
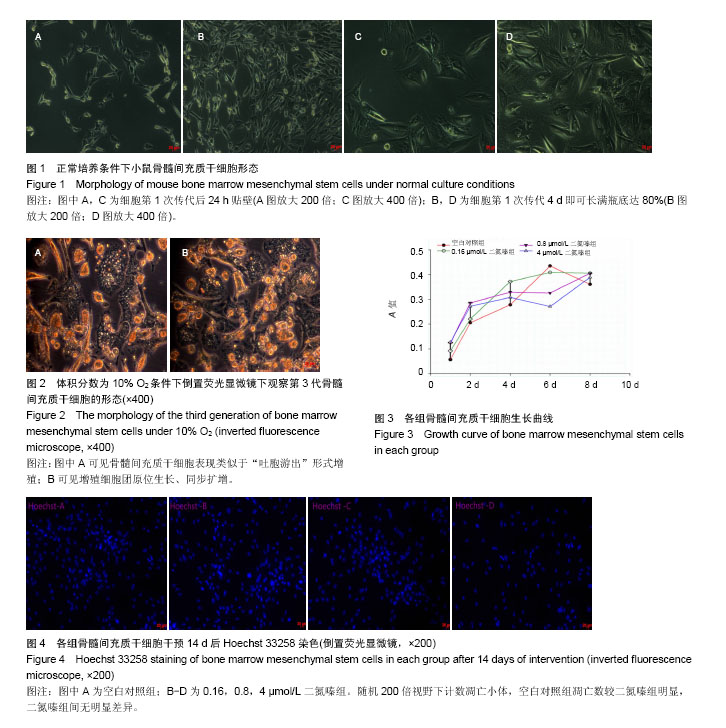
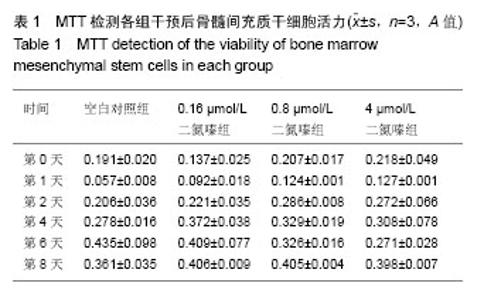
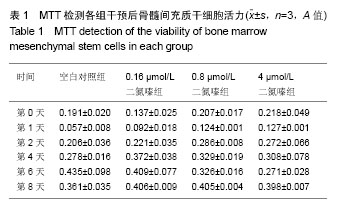
| [1] Schofield R. The relationship between the spleen colony-forming cell and the haemopoietic stem cell. Blood Cells. 1978;4(1-2):7-25.[2] Ivanova NB, Dimos JT, Schaniel C, et al. A stem cell molecular signature. Science. 2002;298(5593):601-604.[3] Solis MA, Chen YH, Wong TY, et al. Hyaluronan regulates cell behavior: a potential niche matrix for stem cells. Biochem Res Int. 2012;2012:346972.[4] Singh SR. Stem cell niche in tissue homeostasis, aging and cancer. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(35):5965-5974.[5] Mohyeldin A, Garzón-Muvdi T, Quiñones-Hinojosa A. Oxygen in stem cell biology: a critical component of the stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7(2):150-161.[6] Zhang W, Carreño FR, Cunningham JT, et al. Chronic sustained and intermittent hypoxia reduce function of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in nucleus of the solitary tract. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008;295(5): R1555-1562.[7] Merceron C, Vinatier C, Portron S, et al. Differential effects of hypoxia on osteochondrogenic potential of human adipose-derived stem cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010;298(2):C355-364.[8] Han XB, Zhang YL, Li HY, et al. Differentiation of Human Ligamentum Flavum Stem Cells Toward Nucleus Pulposus-Like Cells Induced by Coculture System and Hypoxia. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(12):E665-674. [9] Imanirad P, Dzierzak E. Hypoxia and HIFs in regulating the development of the hematopoietic system. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2013;51(4):256-263.[10] Chacko SM, Khan M, Kuppusamy ML, et al. Myocardial oxygenation and functional recovery in infarct rat hearts transplanted with mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009;296(5):H1263-273. [11] Ohnishi S, Yasuda T, Kitamura S, et al. Effect of hypoxia on gene expression of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and mononuclear cells. Stem Cells. 2007;25(5): 1166-1177.[12] Coetzee WA. Multiplicity of effectors of the cardioprotective agent, diazoxide. Pharmacol Ther. 2013;140(2):167-175.[13] Han JS, Wang HS, Yan DM, et al. Myocardial ischaemic and diazoxide preconditioning both increase PGC-1alpha and reduce mitochondrial damage. Acta Cardiol. 2010;65(6): 639-644.[14] Rüedi TP, Buckley RE, Moran CG.AO Principles of Fracture Management.Ao Principles of Fracture Management. 2007; 101(3) :1529.[15] Arinzeh TL, Peter SJ, Archambault MP, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells regenerate bone in a critical-sized canine segmental defect. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A (10):1927-1935.[16] Bohner M, Loosli Y, Baroud G, et al. Commentary: Deciphering the link between architecture and biological response of a bone graft substitute. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(2): 478-484.[17] Maslov LN, Podoksenov IuK, Portnichenko AG, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning of stem cells as a new approach to increase the efficacy of cell therapy for myocardial infarction. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2013;(12):16-25. [18] Arany PR, Cho A, Hunt TD, et al. Photoactivation of endogenous latent transforming growth factor-β1 directs dental stem cell differentiation for regeneration. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(238):238ra69.[19] 王立维,黄文,赵渝,等. 低氧培养对间充质干细胞生物学的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(23):4329-4333.[20] 黄莹,张建,陈兵,等. 低氧有助于小鼠骨髓源间充质干细胞的定向分化[J]. 首都医科大学学报,2015,36(1):18-21.[21] 邬波,马旭,朱大木,等. 胰岛素样生长因子1对骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化及基质金属蛋白酶表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(19):3421-3429.[22] Moyse E, Segura S, Liard O, et al. Microenvironmental determinants of adult neural stem cell proliferation and lineage commitment in the healthy and injured central nervous system. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2008;3(3): 163-184.[23] Sun D, Bullock MR, McGinn MJ, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor-enhanced neurogenesis contributes to cognitive recovery in rats following traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2009;216(1):56-65. [24] Weiss S, Reynolds BA, Vescovi AL, et al. Is there a neural stem cell in the mammalian forebrain. Trends Neurosci. 1996; 19(9):387-393.[25] 黄建锋,黄继锋,张伟才. 两种细胞因子联合诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向神经样细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(6): 829-834.[26] 王静,赵绍云,李明哲,等. Let-7c 慢病毒载体对骨髓间充质干细胞体外诱导分化为神经细胞的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(1):20-25.[27] 雷栓虎,岳海源,汪静,等.骨髓间充质干细胞诱导分化成骨方法的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(6):1101-1106.[28] Naumann A, Dennis J, Staudenmaier R, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells--a new pathway for tissue engineering in reconstructive surgery. Laryngorhinootologie. 2002;81(7): 521-527. [29] Reiser J, Zhang XY, Hemenway CS, et al. Potential of mesenchymal stem cells in gene therapy approaches for inherited and acquired diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005; 5(12):1571-1584.[30] Beyer Nardi N, da Silva Meirelles L. Mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, in vitro expansion and characterization. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006;(174):249-282.[31] 赵勤鹏. 定向诱导分化环境下骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨及成脂细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(32):5103-5107.[32] Wen Z, Zheng S, Zhou C, et al. Repair mechanisms of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in myocardial infarction. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(5):1032-1043. [33] Govoni M, Lotti F, Biagiotti L,et al. An innovative stand-alone bioreactor for the highly reproducible transfer of cyclic mechanical stretch to stem cells cultured in a 3D scaffold. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2014;8(10):787-793.[34] Malda J, Klein TJ, Upton Z. The roles of hypoxia in the in vitro engineering of tissues.Tissue Eng. 2007;13(9):2153-2162. |