Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (5): 815-820.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0456
Effects of extracellular matrix stiffness and thickness on cell growth
Li Shan1, 2, Liu Xiao-yi1, 2, Sun Yan1, 2, Zhao Feng1, He Jing-wen1
- 1School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China; 2State Key Laboratory of Transducer Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200050, China
-
Revised:2017-09-14Online:2018-02-18Published:2018-02-18 -
Contact:Yan, M.D., Master’s supervisor, Associate professor, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China; State Key Laboratory of Transducer Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200050, China -
About author:Li Shan, Studying for master’s degree, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China; State Key Laboratory of Transducer Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200050, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31470942; 111 Project 345, No. B13003
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Shan, Liu Xiao-yi, Sun Yan, Zhao Feng, He Jing-wen. Effects of extracellular matrix stiffness and thickness on cell growth[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(5): 815-820.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
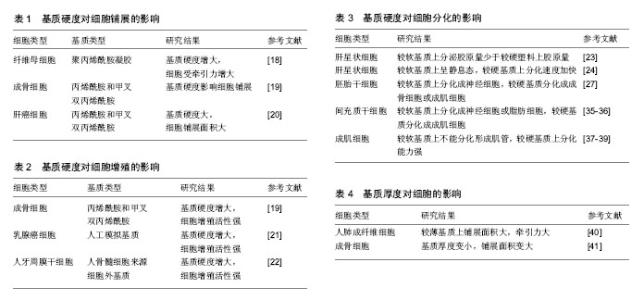
2.1 基质硬度对细胞的影响 目前有很多关于机械力对细胞作用的研究,其中研究比较多的是基质硬度对细胞的影响[9-10]。细胞对细胞外基质硬度变化的响应是一种对力学刺激,即牵引力的响应。通过把力学信号转化成生物信号来对细胞产生作用[11]。充分了解机械力的传导过程及对细胞的作用机制可以从细胞水平对疾病进行治疗,也有利于组织工程领域的进一步发展[12-14]。 2.1.1 基质硬度对细胞铺展的影响 细胞外基质可以维持细胞的正常结构和功能。在动物体中,若细胞外基质合成或者代谢出现了不稳定或者是不平衡就会引发细胞外基质硬度的变化[15],一旦基质硬度改变,细胞自身分泌的整合素及与其配体的结合就会受到影响,进而影响黏着斑的形成、细胞的黏附和一些其他相关功能的丧失,例如细胞发生形态改变。细胞自身能够通过调节肌动球蛋白收缩来不断适应外界环境。在细胞的生长过程中,通过调整细胞骨架大小和形态来适应细胞外基质的不断改变,基质所具有的张力与细胞受到的牵引力是相应变化的量[16]。来自细胞外基质的力可以通过细胞骨架来进行传递,最后传到细胞核表面。在较软基质上,细胞形成的应力纤维不能整合,从而产生很小的压力。细胞就会通过改变形状来适应细胞外基质的变化,实现细胞内压力的平衡[17]。 Yip等[18]在加入氮丙酰胺-6-氨基己酸(ACA)的聚丙烯酰胺凝胶膜上(硬度梯度为6-110 kPa)培养纤维母细胞,当基质硬度低于20 kPa时,随着基质变硬,细胞受到的张力降低;而当基质硬度较大时,随着到一定程度而后保持稳定。刘蕾等[19]通过调整丙烯酰胺和甲叉双丙烯酰胺的相对浓度制备出了较硬的凝胶(杨氏模量约为25 kPa)和相对较软的凝胶,当基质变硬,细胞受到的张力会增大(杨氏模量约为5 kPa)。在这两种凝胶上培养成骨细胞MC3T3。免疫荧光法检测发现MC3T3细胞形态随着凝胶基质弹性模量的降低,由梭形逐渐变成长条形,较硬胶和较软胶上培养的细胞铺展面积也存在显著差异。杨本艳姿等[20]采用上述相同方法对基质硬度进行改变,将人肝癌细胞培养在不同硬度的基质上,结果发现较硬的基底会更有利于肝癌细胞的铺展且会缩短肝癌细胞铺展所需时间。见表1。 上述实验均表明细胞骨架能直接受到基质硬度的调节,在较硬的基质上细胞铺展情况较好,形成更粗的应力纤维且较紧实,而在较软的基质上细胞会趋近于圆形。从上述不同硬度基质对细胞铺展的影响来看,越硬基质上生长的细胞感知到的牵引力会越大,细胞生长越分散,铺展面积也会越大。 2.1.2 基质硬度对细胞增殖的影响 细胞以分裂的方式来进行增殖。细胞增殖是生物体重要的生命特征,也是生物体生长、发育、繁殖的基础。现阶段检测细胞增殖情况最直接的方法即检测细胞中的DNA含量,最常用的检测手段为MTT比色法。一定细胞数范围之内,MTT结晶形成的量和细胞数成正比,此方法被广泛用于一些生物活性因子的检测、抗肿瘤药物筛选等。 陈莉等[21]将乳腺癌细胞接种至不同硬度(分别为1,20,40 kPa)的人工模拟基质上,3 d后进行观察并比较乳腺癌细胞的增殖活性。结果表明,在较硬的40 kPa的人工基质上,乳腺癌细胞增殖能力明显高于其他两个实验组,且差异有显著性意义。刘蕾等[19]通过改变丙烯酰胺和甲叉双丙烯酰胺的相对含量,制备出较硬的弹性模量约为25 kPa的凝胶和较软的弹性模量约为5 kPa的凝胶。在不同硬度的凝胶上培养成骨样细胞MC3T3,用MTT法检测不同硬度凝胶基质对细胞增殖的影响。结果显示,随着基质硬度的降低,MC3T3的增殖受到了抑制,从而可以得出较软细胞外基质对成骨样细胞增殖具有抑制作用这一结论。王阿娴等[22]建立了人颌骨骨髓来源的细胞外基质模型来模拟牙周微环境中的细胞基质微环境,发现人骨髓细胞来源的细胞外基质模型培养的人牙周膜干细胞的增殖能力明显优于普通培养条件。骨髓来源的细胞外基质硬度大于牙周膜细胞外基质,说明了基质硬度的增大能提高细胞的增殖能力。从上述研究中可以看出,不同来源细胞在硬度不同的基质上生长,细胞的增殖水平会随着基质硬度的增大,逐渐增强。见表2。 2.1.3 基质硬度对细胞分化的影响 生物体由受精卵经过分化形成形态、结构、功能有明显差异的各种细胞。正常情况下细胞分化是不可逆的,当细胞受到刺激后,就会向着一个固定的方向分化,引起细胞变化的刺激消失后,分化过程并不会停止。相关研究已经表明细胞外环境成分及性质的变化会影响细胞的分化。 Friedman等[23]把即时提取的肝星状细胞培养在一种取自于大鼠肿瘤的基底膜状的基质上,研究发现胶原的分泌量明显少于培养在塑料基底上培养的肝星状细胞。Sohara等[24]将活化后的肝星状细胞接种在弹性模量接近400 Pa的基质上,发现细胞变为静息态细胞。当基质硬度增加后,肝星状细胞的分化速度会不断增加。Yeung等[25]研究显示肝星状细胞在弹性模量为400 Pa的基质上培养1 d时的形态、含维生素A脂滴的量、蛋白的表达量均与静态细胞相似,而生长在弹性模量为8-22 kPa较硬的基质上时,细胞表现出转移分化。 哺乳动物细胞不仅能感受到施加在细胞上的外力,还能感知到外界环境中的机械特性,例如基质的硬度[26]。基质硬度对于细胞分化也有一定的影响,Engler等[27]通过实验证明生长在类似于脑组织的较软基质上的胚胎干细胞易分化形成神经细胞,相对来说在较硬的像骨组织或是肌肉组织的基质上生长则更容易分化形成成骨或成肌细胞。基质硬度能影响胚胎干细胞分化的主要原因是细胞在基质上形成的细胞骨架应力纤维[28]。研究表明随着基质硬度的不断增大,胚胎干细胞中E-钙黏素的表达量不断增加,细胞可以维持较高的分化潜能。因此通过提高细胞外基质硬度来人为干预细胞的分化方向为临床疾病的治疗提供了一个新的思路。 干细胞因具有多潜能性,在治疗人类疾病方面有巨大的应用前景[29-31]。干细胞的生长和分化除了受到生物化学信号的调节,也会受到微环境的生物物理性质的影响[32-34]。近年来很多研究表明在一定培养条件下模拟不同组织硬度的细胞外基质能诱导间充质干细胞分化形成不同类型的细胞。Tse等[35]制备了利用胶原蛋白进行表面修饰且硬度不同的聚酰胺凝胶,当间充质干细胞培养在类似脑组织硬度的聚酰胺凝胶(弹性模量为0.1-1.0 kPa)上时,间充质干细胞会长出神经细胞的分支,通过检测发现神经细胞的标志分子P-NFH有表达;当间充质干细胞培养于类似于肌肉组织硬度的聚酰胺凝胶(弹性模量为8-12 kPa)上时,细胞变成了梭形且成肌细胞的标志性蛋白MYOD的表达量增大。聚酰胺凝胶弹性模量增大至25-40 kPa时,类似于骨组织的硬度,接种后发现间充质细胞变为多角形,成骨细胞的标志分子RUNX2的表达水平不断上调。Winer等[36]研究发现不添加任何分化诱导因子,将间充质干细胞接种于模拟骨髓硬度的软基质上时,细胞既不增殖也不分化,而是处于静止状态。为了证明较软基质上的间充质干细胞仍然具有多向分化潜能,细胞培养2 d后,添加成脂诱导液, 形成了明显的脂滴,说明其仍具有分化潜能,并向脂肪细胞进行分化。以上实验说明了软基质能保持间充质干细胞处于静止状态,且能保持多向分化潜能,能感应到外界的各种刺激。 Levy-Meital等[37]将成肌细胞接种在不同硬度的PLLA/PLGA多孔支架上。通过调节PLLA和PLGA的比例来改变支架的硬度。结果显示当PLLA的含量由100%变为25%,成肌细胞分化形成肌管的过程受到影响。在不含PLLA的支架上不能分化形成肌管且细胞不能正常生长。以上结果说明太软的基质不能承受细胞力的作用,相反,如果基质的硬度太大,肌管则不能进行平行组装。Engler等[38]将成肌细胞培养在有条带状胶原的玻璃上,只有在类似于正常肌肉组织硬度的基质(弹性模量为12 kPa)上生长时肌球蛋白和肌动蛋白条带才会出现。在相对于肌肉组织来说更软或者更硬的基质上生长时,细胞不会发生延伸。在玻璃片上铺一层成肌细胞,细胞会分化形成肌管,接着再在肌管上铺一层成肌细胞,细胞也会分化形成肌管。当下层细胞不融合形成肌管,而是单个成肌细胞时,上层的细胞不会融合形成肌管。Boontheekul等[39]通过改变生物分子和氧化物的质量比来改变基质硬度,比较硬的基质(弹性模量在13-45 kPa)上成肌细胞的分化能力增强。见表3。 2.2 基质厚度对细胞的影响 Lin等[40]通过研究表明人肺成纤维细胞感受外部环境的程度与其水平尺寸有关。在较薄的基质上生长的细胞会有较大的铺展面积、较大的弹性模量和较大的牵引力,而当基质的厚度小于细胞的水平尺寸时,细胞会感觉更硬一些。基质的厚度超过细胞的水平尺寸后,细胞铺展面积、所受牵引力都逐渐减小,在细胞黏着斑附近的基质厚度则不会对细胞产生任何影响。细胞在黏着斑附近受到的力能反映出基质的厚度。 Mullen等[41]将聚酰胺凝胶做成楔形并在上面接种成骨细胞,通过研究细胞铺展面积来研究基质厚度对成骨细胞生长的影响。随着基质厚度的减小,细胞的铺展面积逐渐增大。聚酰胺凝胶的硬度增大等效于基质厚度的降低。当聚酰胺凝胶的厚度减小时就等效于基质的硬度增大。当凝胶的厚度减小,细胞感受到的剪切硬度增大。凝胶的厚度对细胞行为的影响程度主要取决于胶的构成材料。见表4。 2.3 基质厚度与硬度之间的关系 一些基质硬度对细胞生长影响的研究中往往将基质的厚度默认为未发生变化,这种假设存在一定的局限性,不能准确地说明基质硬度对细胞生命活动的影响。基质的硬度、厚度、几何形状、细胞距离基质边界的距离等因素都会影响到细胞的生长。当基质的厚度变小,就等效于基质的硬度增大,而当基质厚度增大,则等效于基质的硬度减小。若构成基质的材料有弹性,基质表面的位移和基质的厚度相比较很小时则可以不考虑基质厚度对细胞的影响,即当基质的厚度超过一定范围,细胞则感受不到基质的厚度,影响细胞的细胞外基质机械性质主要是基质的硬度及其交联程度等。"

| [1] Sen S, Engler AJ, Discher DE. Matrix strains induced by cells: Computing how far cells can feel. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2009; 2(1):39-48.[2] Boontheekul T, Hill EE, Kong HJ, et al. Regulating myoblast phenotype through controlled gel stiffness and degradation. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(7):1431-1442.[3] Pelham RJ Jr, Wang Y. Cell locomotion and focal adhesions are regulated by substrate flexibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(25):13661-13665.[4] Discher DE, Janmey P, Wang YL. Tissue cells feel and respond to the stiffness of their substrate. Science. 2005; 310(5751):1139-1143.[5] Engler AJ, Griffin MA, Sen S, et al. Myotubes differentiate optimally on substrates with tissue-like stiffness: pathological implications for soft or stiff microenvironments. J Cell Biol. 2004;166(6):877-887.[6] Lin YC, Tambe DT, Park CY, et al. Mechanosensing of substrate thickness. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2010;82(4 Pt 1):041918.[7] Butler JP, Toli?-Nørrelykke IM, Fabry B, et al. Traction fields, moments, and strain energy that cells exert on their surroundings. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;282(3): C595-605.[8] Lv H, Li L, Sun M, et al. Mechanism of regulation of stem cell differentiation by matrix stiffness. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015; 6:103.[9] Mullen CA, Haugh MG, Schaffler MB, et al. Osteocyte differentiation is regulated by extracellular matrix stiffness and intercellular separation. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2013; 28:183-194.[10] Palchesko RN, Zhang L, Sun Y, et al. Development of polydimethylsiloxane substrates with tunable elastic modulus to study cell mechanobiology in muscle and nerve. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51499.[11] Sazonova OV, Isenberg BC, Herrmann J, et al. Extracellular matrix presentation modulates vascular smooth muscle cell mechanotransduction. Matrix Biol. 2015;41:36-43.[12] Bonewald LF. The amazing osteocyte. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(2):229-238.[13] Papachroni KK, Karatzas DN, Papavassiliou KA, et al. Mechanotransduction in osteoblast regulation and bone disease. Trends Mol Med. 2009;15(5):208-216.[14] Santos A, Bakker AD, Klein-Nulend J. The role of osteocytes in bone mechanotransduction. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20(6): 1027-1031.[15] 王红兵,林雨,杨力,等.基质硬度和表面形貌对细胞生物学行为的影响[J].细胞生物学杂志,2009,31(5):608-614.[16] De R, Zemel A, Safran SA. Do cells sense stress or strain? Measurement of cellular orientation can provide a clue. Biophys J. 2008;94(5):L29-31.[17] Simon DN, Wilson KL. The nucleoskeleton as a genome-associated dynamic 'network of networks'. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12(11):695-708.[18] Yip AK, Iwasaki K, Ursekar C, et al. Cellular response to substrate rigidity is governed by either stress or strain. Biophys J. 2013;104(1):19-29.[19] 刘蕾,谈雯雯,杨团民,等.细胞外基质硬度对成骨细胞 MC3T3-E1形态、增殖及矿化能力的影响[J].陕西医学杂志, 2015,44(10):1300-1303.[20] 杨本艳姿,王红兵,谭乔燕,等. 不同基底硬度对人肝癌细胞黏附、铺展和迁移的影响[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(3):305-311.[21] 陈莉,李长樱,杨新华,等.基质硬度对乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞增殖能力的影响[J].中华乳腺病杂志:电子版,2008,2(2): 184-189.[22] 王阿娴,唐丽, 梁源,等.人骨髓来源细胞外基质对人牙周膜干细胞增殖的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(6):938-943.[23] Friedman SL, Roll FJ, Boyles J, et al. Maintenance of differentiated phenotype of cultured rat hepatic lipocytes by basement membrane matrix. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(18): 10756-10762.[24] Sohara N, Znoyko I, Levy MT, et al. Reversal of activation of human myofibroblast-like cells by culture on a basement membrane-like substrate. J Hepatol. 2002;37(2):214-221.[25] Yeung T, Georges PC, Flanagan LA, et al. Effects of substrate stiffness on cell morphology, cytoskeletal structure, and adhesion. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2005;60(1):24-34.[26] Discher DE, Janmey P, Wang YL. Tissue cells feel and respond to the stiffness of their substrate. Science. 2005;310 (5751):1139-1143.[27] Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, et al. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126(4):677-689.[28] Evans ND, Minelli C, Gentleman E, et al. Substrate stiffness affects early differentiation events in embryonic stem cells. Eur Cell Mater. 2009;18:1-14.[29] Das M, Sundell IB, Koka PS. Adult mesenchymal stem cells and their potency in the cell-based therapy. J Stem Cells. 2013;8(1):1-16.[30] Eirin A, Lerman LO. Mesenchymal stem cell treatment for chronic renal failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(4):83.[31] Zeng X, Couture LA. Pluripotent stem cells for Parkinson's disease: progress and challenges. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(2):25.[32] Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, et al. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126(4):677-689.[33] Zoldan J, Karagiannis ED, Lee CY, et al. The influence of scaffold elasticity on germ layer specification of human embryonic stem cells. Biomaterials. 2011;32(36):9612-9621.[34] Gilbert PM, Havenstrite KL, Magnusson KE, et al. Substrate elasticity regulates skeletal muscle stem cell self-renewal in culture. Science. 2010;329(5995):1078-1081.[35] Tse JR, Engler AJ. Stiffness gradients mimicking in vivo tissue variation regulate mesenchymal stem cell fate. PLoS One. 2011;6(1):e15978.[36] Winer JP, Janmey PA, McCormick ME, et al. Bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells become quiescent on soft substrates but remain responsive to chemical or mechanical stimuli. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009; 15(1):147-154.[37] Levy-Mishali M, Zoldan J, Levenberg S. Effect of scaffold stiffness on myoblast differentiation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(4):935-944.[38] Engler AJ, Griffin MA, Sen S, et al. Myotubes differentiate optimally on substrates with tissue-like stiffness: pathological implications for soft or stiff microenvironments. J Cell Biol. 2004;166(6):877-887.[39] Boontheekul T, Hill EE, Kong HJ, et al. Regulating myoblast phenotype through controlled gel stiffness and degradation. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(7):1431-1442.[40] Lin YC, Tambe DT, Park CY, et al. Mechanosensing of substrate thickness. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2010;82(4 Pt 1):041918.[41] Mullen CA, Vaughan TJ, Billiar KL, et al. The effect of substrate stiffness, thickness, and cross-linking density on osteogenic cell behavior. Biophys J. 2015;108(7):1604-1612.[42] Wan LQ, Ronaldson K, Park M, et al. Micropatterned mammalian cells exhibit phenotype-specific left-right asymmetry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(30): 12295-12300.[43] Gribova V, Gauthier-Rouvière C, Albigès-Rizo C, et al. Effect of RGD functionalization and stiffness modulation of polyelectrolyte multilayer films on muscle cell differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(5):6468-6480. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [3] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [6] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [7] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [8] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [9] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [10] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [11] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [12] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [13] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [14] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [15] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||