Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (1): 13-19.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0404
Previous Articles Next Articles
Titanium surface modification by acidic oxidation treatment activates the Wnt signaling pathway in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Wang Wei, Du Yuan-hong
- Department of Stomatology, the 463rd Hospital of PLA, Shenyang 110042, Liaoning Province, China
-
Revised:2017-10-15Online:2018-01-08Published:2018-01-08 -
Contact:Du Yuan-hong, Department of Stomatology, the 463rd Hospital of PLA, Shenyang 110042, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Wei, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Stomatology, the 463rd Hospital of PLA, Shenyang 110042, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Wei, Du Yuan-hong. Titanium surface modification by acidic oxidation treatment activates the Wnt signaling pathway in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(1): 13-19.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
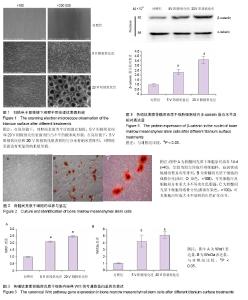
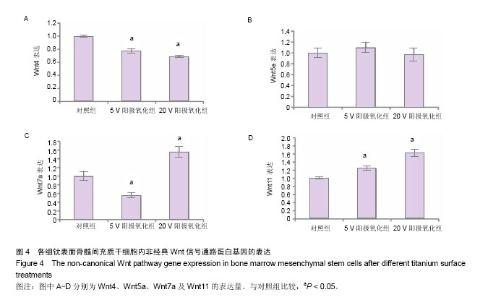
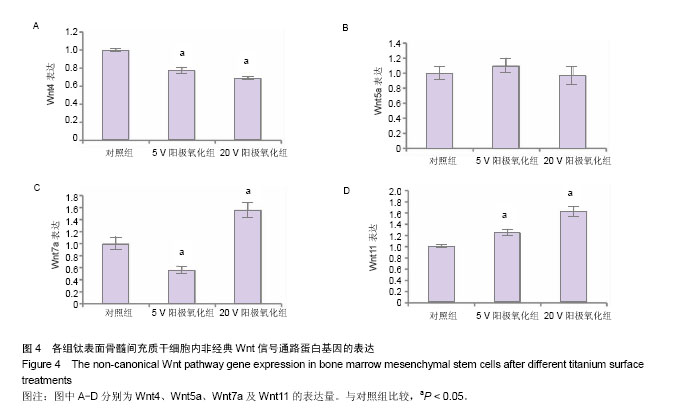
2.1 钛表面形貌观察 在低倍镜下,对照组表面为平行的抛光划痕,5 V阳极氧化组和20 V阳极氧化组表面为凹凸不平的微米坑形貌。在高倍数显微镜下,5 V阳极氧化组和20 V阳极氧化组表面均匀分布着纳米管阵列,5 V阳极氧化组表面纳米管直径约为30 nm,20 V阳极氧化组表面纳米管直径约为100 nm,对照组表面没有明显的纳米级形貌(图1)。 2.2 骨髓间充质干细胞的形态及生长情况观察 在骨髓间充质干细胞培养过程中,采用倒置显微镜观察细胞生长情况及形态,并拍照记录。细胞培养14 d后,骨髓间充质干细胞紧贴培养瓶生长,呈较为均匀的成纤维细胞样,旋涡状或辐射状整齐有序排列(图2A)。使用成脂诱导液诱导成脂分化10 d后,油红O染色可见细胞内及细胞间分布着大小不等的红色脂滴(图2B)。使用成骨诱导液成骨诱导 21 d后,经茜素红染色后可见细胞内形成大小不规则的红色矿化结节(图2C)。 2.3 微米纳米形貌表面骨髓间充质干细胞内经典Wnt信号通路蛋白表达水平 骨髓间充质干细胞在3组材料表面培养3 d后,5 V阳极氧化组和20 V阳极氧化组细胞内Wnt1和Wnt3a表达量较对照组明显增高(P < 0.05),且20 V阳极氧化组表面表达量最高(图3)。5 V阳极氧化组和20 V阳极氧化组Wnt1表达量分别为对照组的2.1和2.5倍,Wnt3a表达量分别为对照组的4.2和5.1倍。 2.4 微米纳米形貌表面骨髓间充质干细胞内非经典Wnt信号通路蛋白表达水平 3组材料表面骨髓间充质干细胞的非经典Wnt信号蛋白表达没有明显规律。与对照组相比,5 V阳极氧化组和20 V阳极氧化组细胞内Wnt4表达量下降(P < 0.05),分别为对照组的77%和69%;3组细胞内Wnt5a表达无明显差别。与对照组比较,5 V阳极氧化组细胞内Wnt7a表达量下降44%(P < 0.05);20 V阳极氧化组细胞内Wnt7a表达量升高,为对照组的1.56倍(P < 0.05)。5 V阳极氧化组和20 V阳极氧化组细胞内Wnt11表达水平升高(P < 0.05),分别是对照组的1.25倍和1.625倍(图4)。 2.5 微米纳米形貌表面骨髓间充质干细胞细胞核内β-catenin蛋白表达水平 骨髓间充质干细胞在3组材料表面培养7 d后,5 V阳极氧化组和20 V阳极氧化组细胞核内β-catenin的表达量高于对照组(P < 0.05)。条带灰度半定量分析显示与对照组相比,5 V阳极氧化组表达量升高2.3倍,20 V阳极氧化组升高3.6倍(图5)。"

| [1] Fraioli R,Rechenmacher F,Neubauer S,et al.Mimicking bone extracellular matrix: integrin-binding peptidomimetics enhance osteoblast-like cells adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation on titanium.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;128:191-200. [2] Gittens RA,Olivares-Navarrete R,Hyzy SL,et al.Superposition of nanostructures on microrough titanium-aluminum- vanadium alloy surfaces results in an altered integrin expression profile in osteoblasts.Connect Tissue Res.2014; 55 Suppl 1:164-8.[3] Wang X,Schwartz Z,Gittens RA,et al.Role of integrin alpha2 beta1 in mediating osteoblastic differentiation on three-dimensional titanium scaffolds with submicron-scale texture.J Biomed Mater Res A.2015;103(6):1907-1918.[4] Ryabenkova Y,Pinnock A,Quadros PA,et al.The relationship between particle morphology and rheological properties in injectable nano-hydroxyapatite bone graft substitutes.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;75:1083-1090.[5] Huang Y,Wang J,Yang F,et al.Modification and evaluation of micro-nano structured porous bacterial cellulose scaffold for bone tissue engineering.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;75:1034-1041. [6] Xing J,Mei T,Luo K,et al.A nano-scaled and multi-layered recombinant fibronectin/cadherin chimera composite selectively concentrates osteogenesis-related cells and factors to aid bone repair.Acta Biomater.2017;53:470-482. [7] Wang W,Zhao L,Wu K,et al.The role of integrin-linked kinase/beta-catenin pathway in the enhanced MG63 differentiation by micro/nano-textured topography. Biomaterials.2013;34:631-640.[8] Zhao L,Liu L,Wu Z,et al.Effects of micropitted/nanotubular titania topographies on bone mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation.Biomaterials.2012;33:2629-2641.[9] Stoddart A,Wang J,Hu C,et al.Inhibition of WNT signaling in the bone marrow niche prevents the development of MDS in the Apcdel/+ MDS mouse model.Blood. 2017;129(22): 2959-2970. [10] Lerner UH,Ohlsson C.The WNT system: background and its role in bone.J Intern Med.2015;277:630-649.[11] Buckland J.Bone: Anabolic Wnt/beta-catenin signalling: osteocytes are key.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(3):128.[12] Leucht P,Helms JA.Wnt signaling: an emerging target for bone regeneration.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(1): 67-68.[13] Jacobsen CM,Schwartz MA,Roberts HJ,et al.Enhanced Wnt signaling improves bone mass and strength, but not brittleness, in the Col1a1(+/mov13) mouse model of type I Osteogenesis Imperfecta.Bone. 2016;90:127-32.[14] Janeczek AA,Tare RS,Scarpa E,et al.Transient Canonical Wnt Stimulation Enriches Human Bone Marrow Mononuclear Cell Isolates for Osteoprogenitors.Stem cells. 2016;34:418-430.[15] Yang G,Fang W,Liu T,et al.Gene expression profiling of bone marrow-derived stromal cells seeded onto a sandblasted, large-grit, acid-etched-treated titanium implant surface: The role of the Wnt pathway.Arch of Oral Biol. 2016;61:71-78.[16] Shou K,Niu Y,Zheng X,et al.Enhancement of Bone-Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Angiogenic Capacity by NPWT for a Combinatorial Therapy to Promote Wound Healing with Large Defect. Biomed Res Int. 2017; 2017:7920265.[17] Frasca S,Norol F,Le Visage C,et al.Calcium-phosphate ceramics and polysaccharide-based hydrogel scaffolds combined with mesenchymal stem cell differently support bone repair in rats.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2017;28(2):35.[18] Heiden M,Huang S,Nauman E,et al.Nanoporous metals for biodegradable implants: Initial bone mesenchymal stem cell adhesion and degradation behavior.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(7):1747-1758. [19] Li G,Song Y,Shi M,et al.Mechanisms of Cdc42-mediated rat MSC differentiation on micro/nano-textured topography.Acta Biomaterialia.2017;49:235-246.[20] Fang H,Song P,Shen C,et al.Bone mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium induces the upregulation of Smad6, which inhibits the BMP-4/Smad1/5/8 signaling pathway. Neurol Res.2016;38:965-972.[21] Ho SS,Vollmer NL,Refaat MI,et al.Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Promotes Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Survival and Resultant Bone Formation When Entrapped in Photocrosslinked Alginate Hydrogels.Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(19):2501-2509. [22] Dubon MJ,Yu J,Choi S,et al.Transforming Growth Factor beta Induces Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration via Noncanonical Signals and N-cadherin.J Cell Physiol. 2018; 233(1):201-213. [23] Cong Q,Jia H,Li P,et al.p38alpha MAPK regulates proliferation and differentiation of osteoclast progenitors and bone remodeling in an aging-dependent manner.Sci Rep. 2017;7:45964.[24] Wang Y,Liu X,Dou C,et al.Staphylococcal protein A promotes osteoclastogenesis through MAPK signaling during bone infection.J Cell Physiol.2017;232(9):2396-2406.[25] Zhdanov VV,Miroshnichenko LA,Udut EV,et al.Role of PI3K, MAPK/ERK 1/2, and p38 in Production of Erythropoietic Activity by Bone Marrow Cells after Blood Loss.Bull Exp Biol Med. 016;162(1):51-55.[26] Zhao C,Li Y,Wang X,et al.The Effect of Uniaxial Mechanical Stretch on Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway in Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells.J Craniofac Surg.2017;28(1):113-117.[27] Wolski H,Drweska-Matelska N,Seremak-Mrozikiewicz A,et al.The role of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and LRP5 protein in metabolism of bone tissue and osteoporosis etiology.Ginekol Pol.2015;86:311-314.[28] Sun X,Wang H,Huang W,et al.Inhibition of bone formation in rats by aluminum exposure via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Chemosphere.2017;176:1-7.[29] Sandsmark E,Hansen AF,Selnaes KM,et al.A novel non-canonical Wnt signature for prostate cancer aggressiveness.Oncotarget.2017;8:9572-9586.[30] Famili F,Perez LG,Naber BA,et al.The non-canonical Wnt receptor Ryk regulates hematopoietic stem cell repopulation in part by controlling proliferation and apoptosis.Cell Death Dis.2016;7(11):e2479.[31] Franco CA,Jones ML,Bernabeu MO,et al.Non-canonical Wnt signalling modulates the endothelial shear stress flow sensor in vascular remodelling.Elife.2016;5:e07727. [32] Ruan W,Xue Y,Zong Y,et al.Effect of BMPs and Wnt3a co-expression on the osteogenetic capacity of osteoblasts.Mol Med Rep.2016;14(5):4328-4334.[33] Zhang Y,Huang X,Yuan Y.MicroRNA-410 promotes chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through down-regulating Wnt3a.Am J Transl Res.2017;9(1):136-145. [34] Li L,Peng X,Qin Y,et al.Acceleration of bone regeneration by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway via lithium released from lithium chloride/calcium phosphate cement in osteoporosis. Sci Rep.2017;7:45204.[35] Hendrickx G,Boudin E,Steenackers E,et al.Genetic Screening of WNT4 and WNT5B in Two Populations with Deviating Bone Mineral Densities.Calcif Tissue Int. 2017;100(3): 244-249.[36] Thiele S,Rachner TD,Rauner M,et al.WNT5A and Its Receptors in the Bone-Cancer Dialogue.J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(8):1488-1496.[37] He X,Wang H,Jin T,et al.TLR4 Activation Promotes Bone Marrow MSC Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation via Wnt3a and Wnt5a Signaling.PloS One.2016;11:e0149876.[38] Li J,Bao Q,Chen S,et al.Different bone remodeling levels of trabecular and cortical bone in response to changes in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in mice.J Orthop Res. 2017;35(4): 812-819.[39] Pflug T,Huynh-Do U,Rudloff S. Reduced beta-catenin expression affects patterning of bone primordia, but not bone maturation.Biol Open.2017;6(5):582-588. [40] Vega OA,Lucero CM,Araya HF,et al.Wnt/beta-catenin Signaling Activates Expression of the Bone-related Transcription Factor RUNX2 in Select Human Osteosarcoma Cell Types.J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(11):3662-3674. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [8] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [9] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [10] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [11] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [12] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [13] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [14] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [15] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||