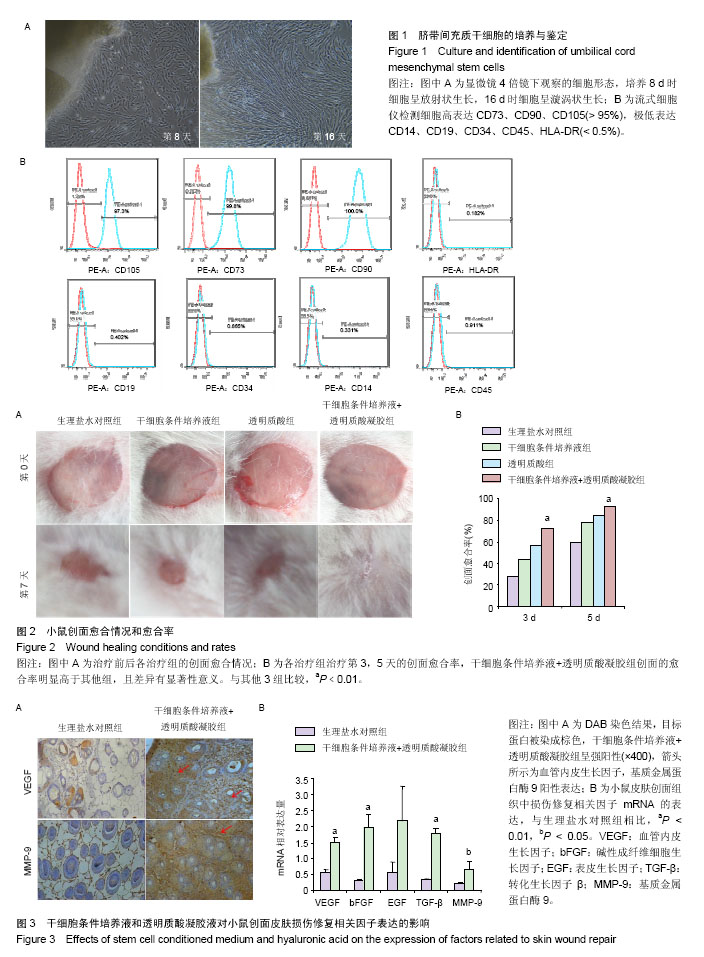
| [1] 武艳, 袁晓环, 杨岚,等. 间充质干细胞条件培养液对正常成纤维细胞及瘢痕成纤维细胞转化生长因子β产生和信号通路的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(29):4349-4354.[2] Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centred approach. Update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetologia. 2015;58(3):429-442.[3] 彭希亮, 张玉红, 倪文琼. 脂肪组织来源干细胞构建皮肤复合组织修复创面缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(1):8-12.[4] Zhong SP, Zhang YZ, Lim CT. Tissue scaffolds for skin wound healing and dermal reconstruction. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2010;2(5):510-525.[5] Xia G, Hong X, Chen X, et al. Intracerebral transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord blood alleviates hypoxic ischemic brain injury in rat neonates. J Perinat Med. 2010;38(2):215-221.[6] Nagamura-Inoue T, He H. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Their advantages and potential clinical utility. World J Stem Cells. 2014;6(2):195-202.[7] Wang Y, Chen X, Cao W, et al. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation: pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(11):1009-1016.[8] Sharma RR, Pollock K, Hubel A, et al. Mesenchymal stem or stromal cells: a review of clinical applications and manufacturing practices. Transfusion. 2014;54(5):1418-1437.[9] Chen L, Tredget EE, Wu PY, et al. Paracrine factors of mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages and endothelial lineage cells and enhance wound healing. PLoS One. 2008; 3(4):e1886.[10] Wu Y, Chen L, Scott PG, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing through differentiation and angiogenesis. Stem Cells. 2007;25(10):2648-2659.[11] 管峰,金嘉长,赵华国,等.海豚链球菌诱变发酵法制备透明质酸及其在动物皮肤修复中的应用[J]. 生物工程学报, 2016, 32(8): 1104-1114.[12] Weissmann B, Meyer K. The Structure of Hyalobiuronic Acid and of Hyaluronic Acid from Umbilical Cord. J Am Chem Soc. 1954; 76(7):1753-1757.[13] 谭荣,胡冬梅,胡坤娥.透明质酸治疗复发性口腔溃疡的临床疗效观察[J].中国美容医学杂志, 2012, 21(14):420-421.[14] Manuskiatti W, Maibach HI. Hyaluronic acid and skin: wound healing and aging. Int J Dermatol. 1996;35(8):539-544.[15] Neuman MG, Nanau RM, Oruña-Sanchez L, et al. Hyaluronic acid and wound healing. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2015;18(1): 53-60.[16] Song HF, Chai JK, Lin ZH, et al. Expression of hyaluronic acid and its receptor in the process of wound healing in different skin tissues and its significance. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2003;83(12):1070-1074.[17] Su Z, Ma H, Wu Z, et al. Enhancement of skin wound healing with decellularized scaffolds loaded with hyaluronic acid and epidermal growth factor. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;44:440-448.[18] Zhong SP, Zhang YZ, Lim CT. Tissue scaffolds for skin wound healing and dermal reconstruction. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2010;2(5):510-525.[19] Wang S, Yang H, Tang Z, et al. Wound Dressing Model of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Alginates Complex Promotes Skin Wound Healing by Paracrine Signaling. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:3269267.[20] Dimarino AM, Caplan AI, Bonfield TL. Mesenchymal stem cells in tissue repair. Front Immunol. 2013;4:201.[21] Shohara R, Yamamoto A, Takikawa S, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly accelerate wound healing by paracrine mechanisms. Cytotherapy. 2012;14(10):1171-1181.[22] Zhang Y, Hao H, Liu J, et al. Repair and regeneration of skin injury by transplanting microparticles mixed with Wharton's jelly and MSCs from the human umbilical cord. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2012;11(4):264-270.[23] Shen C, Lie P, Miao T, et al. Conditioned medium from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells induces migration and angiogenesis. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(1):20-30.[24] Arno AI, Amini-Nik S, Blit PH, et al. Human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells promote skin wound healing through paracrine signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(1):28.[25] Rodero MP, Khosrotehrani K. Skin wound healing modulation by macrophages. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2010;3(7):643-653.[26] Nan W, Liu R, Chen H, et al. Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Combined With a Collagenfibrin Double-layered Membrane Accelerates Wound Healing. Wounds. 2015; 27(5):134-140.[27] 陈泽林,周青,粟永萍,等. 小鼠皮肤创伤后创面局部真皮干细胞参与修复过程[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2013,35(9):886-891.[28] Wu Y, Chen L, Scott PG, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing through differentiation and angiogenesis. Stem Cells. 2007;25(10):2648-2659.[29] Shrestha C, Zhao L, Chen K, et al. Enhanced healing of diabetic wounds by subcutaneous administration of human umbilical cord derived stem cells and their conditioned media. Int J Endocrinol. 2013;2013:592454.[30] 杨化超,李茂,黄文.人脐带间充质干细胞对小鼠皮肤创面愈合及VEGF表达的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2016,38(5):456-462.[31] Hoeben A, Landuyt B, Highley MS, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rev. 2004; 56(4): 549-580.[32] 夏鹏,童文祥,喻永敏,等.大鼠皮肤切创愈合过程中VEGF, TGF-β1蛋白的表达[J].重庆医科大学学报, 2010, 35(8): 1167-1171. |