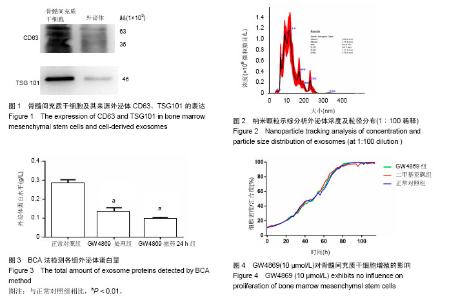
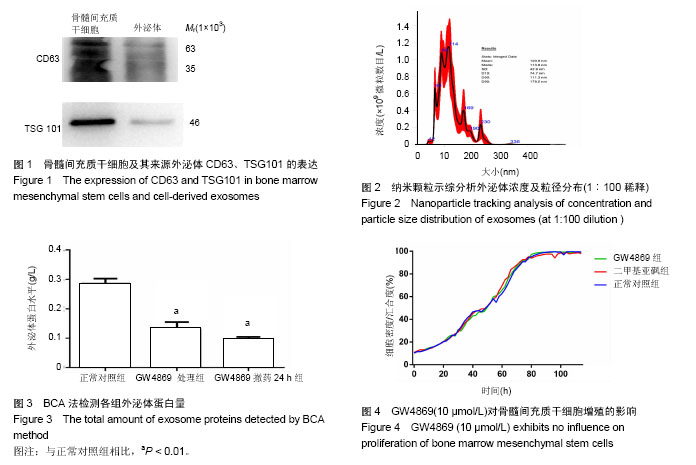
| [1] Tkach M, Théry C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go.Cell. 2016;164(6): 1226-1232.[2] Rashed M, Bayraktar E, Helal G, et al. Exosomes: From Garbage Bins to Promising Therapeutic Targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3): E538.[3] Chen B, Li Q, Zhao B, et al. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Potential Therapeutic Tool for Tissue Repair. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(9):1753-1758.[4] Lou G, Chen Z, Zheng M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(6):e346.[5] Crompot E, Van Damme M, Pieters K, et al. Extracellular vesicles of bone marrow stromal cells rescue chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from apoptosis, enhance their migration and induce gene expression modifications. Haematologica. 2017;102(9):1594-1604.[6] Colombo M, Moita C, van Niel G, et al. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(Pt 24):5553-5565.[7] Essandoh K, Yang L, Wang X, et al. Blockade of exosome generation with GW4869 dampens the sepsis-induced inflammation and cardiac dysfunction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1852(11):2362-2371.[8] Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S, et al. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science. 2008;319(5867):1244-1247.[9] Lang JK, Young RF, Ashraf H, et al. Inhibiting Extracellular Vesicle Release from Human Cardiosphere Derived Cells with Lentiviral Knockdown of nSMase2 Differentially Effects Proliferation and Apoptosis in Cardiomyocytes, Fibroblasts and Endothelial Cells In Vitro. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0165926.[10] Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;Chapter 3: Unit 3.22.[11] Gardiner C, Di Vizio D, Sahoo S, et al. Techniques used for the isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles: results of a worldwide survey. J Extracell Vesicles. 2016;5: 32945.[12] Pan BT, Teng K, Wu C, et al. Electron microscopic evidence for externalization of the transferrin receptor in vesicular form in sheep reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1985;101(3):942-948.[13] Raposo G, Nijman HW, Stoorvogel W, et al. Blymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 1996;183(3): 1161-1172.[14] Jia S, Zhang R, Li Z, et al. Clinical and biological significance of circulating tumor cells, circulating tumor DNA, and exosomes as biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(33):55632-55645.[15] Li P, Kaslan M, Lee SH, et al. Progress in Exosome Isolation Techniques. Theranostics. 2017;7(3):789-804.[16] Mincheva-Nilsson L, Baranov V, Nagaeva O, et al. Isolation and Characterization of Exosomes from Cultures of Tissue Explants and Cell Lines. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2016;115: 14.42.1-14.42.21.[17] Xu R, Greening DW, Zhu HJ, et al. Extracellular vesicle isolation and characterization: toward clinical application. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(4):1152-1162.[18] Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Yoshioka Y, et al. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(23):17442-17452.[19] Yuyama K, Sun H, Mitsutake S, et al. Sphingolipid-modulated exosome secretion promotes clearance of amyloid-β by microglia. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(14):10977-10989.[20] Essandoh K, Yang L, Wang X, et al. Blockade of exosome generation with GW4869 dampens the sepsis-induced inflammation and cardiac dysfunction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1852(11):2362-2371.[21] Phuyal S, Hessvik NP, Skotland T, et al. Regulation of exosome release by glycosphingolipids and flotillins. FEBS J. 2014;281(9):2214-2227..[22] 曹娟,吕琪,丁辉,等.大鼠活体内Luciferase 标记骨髓间充质干细胞生物发光示踪监测[J].中华灾害救援医学,2016, 4(1): 12-16.[23] 宋美娟,吕琪,丁辉,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗急性肺损伤的机制研究[J].中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志,2015,10(5):489-492.[24] 李嫣, 樊毫军,侯世科,等.人脐带间充质干细胞治疗热烟雾致急性肺损伤的实验研究[J]. 中华急诊医学, 2014,23(9): 1001-1005.[25] 申坤灵,樊毫军,丁辉,等.β-catenin慢病毒载体转染大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的实验研究[J].武警后勤学院学报:医学版, 2014, 23(6):461-464.[26] 王娜,樊毫军.经气管注入人MSCs对热烟雾吸入性肺损伤大鼠的作用[J].中国医学工程, 2012,20(5):126-128.[27] Song M, Lv Q, Zhang X, et al. Dynamic Tracking Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Tropism following Smoke Inhalation Injury in NOD/SCID Mice. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1691856.[28] Cao J, Hou S, Ding H, et al. In Vivo Tracking of Systemically Administered Allogeneic Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Normal Rats through Bioluminescence Imaging. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:3970942.[29] Zhu YG, Feng XM, Abbott J, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles for treatment of Escherichia coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cells. 2014;32(1):116-25.[30] Hu L, Wang J, Zhou X, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32993.[31] Ti D, Hao H, Fu X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNAs contribute to wound inflammation. Sci China Life Sci. 2016;59(12):1305-1312.[32] Zhang J, Guan J, Niu X, et al. Exosomes released from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived MSCs facilitate cutaneous wound healing by promoting collagen synthesis and angiogenesis. J Transl Med. 2015;13:49.[33] Toh WS, Lai RC, Hui JHP, et al. MSC exosome as a cell-free MSC therapy for cartilage regeneration: Implications for osteoarthritis treatment. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;67:56-64.[34] Merino-González C, Zuñiga FA, Escudero C, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Angiogenesis: Potencial Clinical Application. Front Physiol. 2016;7:24.[35] Lai RC, Arslan F, Lee MM, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):214-222.[36] Kosaka N, Yoshioka Y, Fujita Y, et al. Versatile roles of extracellular vesicles in cancer. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(4): 1163-1172.[37] Lobb RJ, van Amerongen R, Wiegmans A, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal non-small cell lung cancer cells promote chemoresistance. Int J Cancer. 2017;141(3): 614-620.[38] Li X, Wang S, Zhu R, et al. Lung tumor exosomes induce a pro-inflammatory phenotype in mesenchymal stem cells via NFκB-TLR signaling pathway. J Hematol Oncol. 2016;9:42.[39] Phinney DG, Pittenger MF. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4): 851-858. |