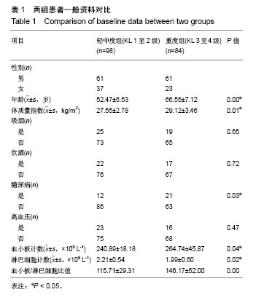
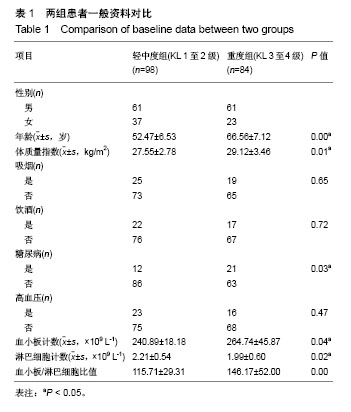
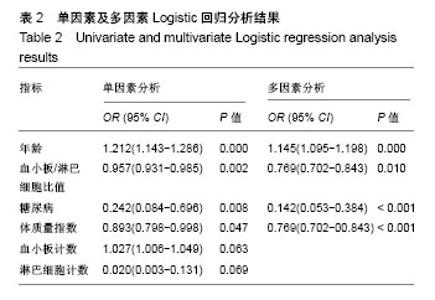
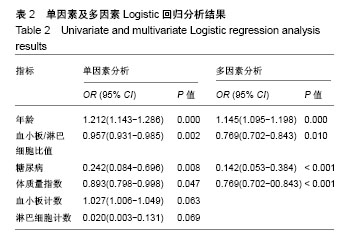
| [1] Berenbaum F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):16-21.[2] Orlowsky EW, Kraus VB. The role of innate immunity in osteoarthritis: when our first line of defense goes on the offensive. J Rheumatol. 2015;42(3): 363-371. [3] Scanzello CR. Chemokines and inflammation in osteoarthritis: insights from patients and animal models. J Orthop Res. 2017; 35(4):735-739.[4] Avcil S. Evaluation of the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, platelet/ lymphocyte ratio, and mean platelet volume as inflammatory markers in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2018. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12659.[5] Balta S, Dem?rkol S, Kucuk U. The platelet lymphocyte ratio may be useful inflammatory indicator in clinical practice. Hemodial Int. 2013;17(4):668-669.[6] Uslu AU, Küçük A, ?ahin A, et al. Two new inflammatory markers associated with Disease Activity Score-28 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015;18(7):731-735. [7] Furuncuo?lu Y, Tulgar S, Dogan AN, et al. How obesity affects the neutrophil/lymphocyte and platelet/lymphocyte ratio, systemic immune-inflammatory index and platelet indices: a retrospective study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016;20(7):1300-1306.[8] Yang W, Wang X, Zhang W, et al. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio are 2 new inflammatory markers associated with pulmonary involvement and disease activity in patients with dermatomyositis. Clin Chim Acta. 2017;465:11-16. [9] Fu H, Qin B, Hu Z, et al. Neutrophil-and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios are correlated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Lab. 2015;61(3-4):269-273.[10] Kim DS, Shin D, Lee MS, et al. Assessments of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in Korean patients with psoriasis vulgaris and psoriatic arthritis. J Dermatol. 2016;43(3):305-310.[11] Kwon HC, Kim SH, Oh SY, et al. Clinical significance of preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte versus platelet-lymphocyte ratio in patients with operable colorectal cancer. Biomarkers. 2012;17(3):216-222.[12] Kellegren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957;16(4):494-501.[13] Hagiwara S, Oshima K, Aoki M, et al. Usefulness of fibrin degradation products and d-dimer levels as biomarkers that reflect the severity of trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013; 74(5):1275-1278.[14] Schreiber MA, Differding J, Thorborg P, et al. Hypercoagulability is most prevalent early after injury and in female patients. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2005;58(3):475-481.[15] Luo X, Zhou L. Prognostic significance of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a meta-analysis. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2018;477:7-12. [16] Wang L, Liang D, Xu X, et al. The prognostic value of neutrophil to lymphocyte and platelet to lymphocyte ratios for patients with lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 2017;14(6):6449-6456. [17] Ta?o?lu Ö, ?ahin A, Karata? G, et al. Blood mean platelet volume and platelet lymphocyte ratio as new predictors of hip osteoarthritis severity. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(6):e6073. |