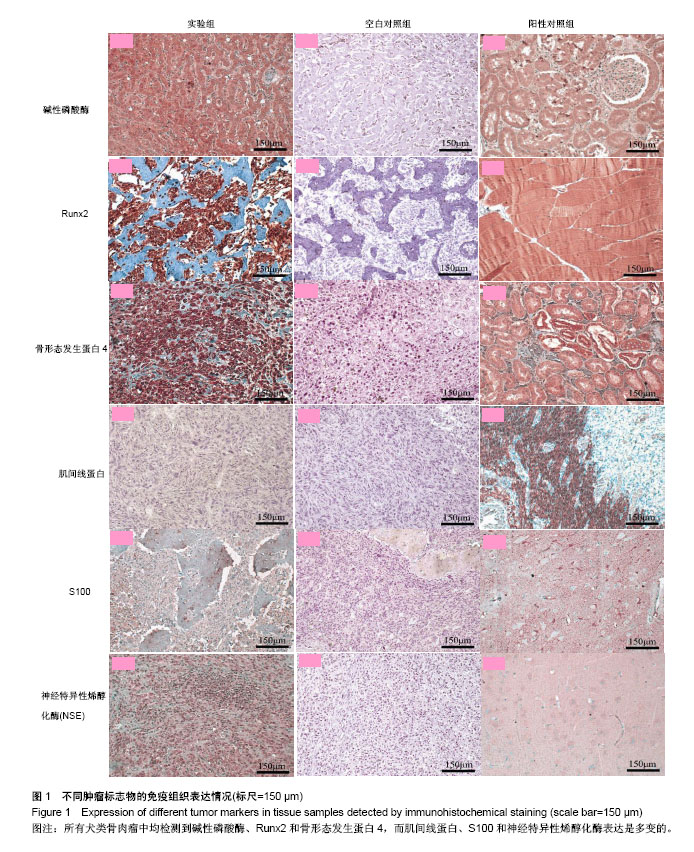
| [1] Brodey RS,Riser WH.Canine osteosarcoma: a clinicopathologic study of 194 cases. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research.1969;62(20):54-64.[2] Li B,Ye Z.Epigenetic alterations in osteosarcoma:promising targets. Molecular Biology Reports.2014;41(39):3303-3315.[3] Jongeward SJ.Primary bone tumors.Veterinary Clinics of North America: Small Animal Practice.1985;15(10):609-641.[4] Satelli A,Li S.Vimentin in cancer and its potential as a molecular target for cancer Therapy.Cell Mol Life Sci.2011; 68(18):3033-3046.[5] Gorlick R.Current concepts on the molecular biology of osteosarcoma.Cancer Treat Res. 2009;152:467-478.[6] Hewitt HB.The choice of animal tumors for experimental studies of cancer therapy. Adv Cancer Res.1978; 27(9): 149-200.[7] Herberman RB.Counterpoint: animal tumor models and their relevance to human tumor immunology. J Biol Response Mod. 1983;2(1):39-46.[8] Guil-Luna S,Millan Y,Sanchez-Cespedes R.Comparative aspects between canine and human mesenchymal tumors. Sarcoma Research International.2015;2(16):1011-1013.[9] Owen LN.Comparative aspects of bone tumours in man and dog. Proc R Soc Med. 1967 Dec;60(12):1309-1310.[10] Owen LN,Bostock DE,Betton GR,et al.The role of spontaneous canine tumours in the evaluation of the aetiology and therapy of human cancer. J Small Anim Pract. 1975;16(3):155-162.[11] Paoloni M, Davis S, Lana S, et al.Canine tumor cross-species genomics uncovers targets linked to osteosarcoma progression. BioMed Central Genomics.2009;10(73): 1-13.[12] Trihia H,Valavanis C.Histopathology and molecular pathology of bone and extraskeletal osteosarcomas.//Osteosarcoma, M Agarwal, Ed., InTech, Rijeka.2012;21(50):3-40.[13] Rosier RN, Bukata SV.Sarcomas of bone.//Oncology: An Evidence-based Approach to Sarcomas of Bone,AE Chang, PA Ganz, DF Hayes,et al.Eds.Springer.New York.2007;34(8): 1025-1038.[14] Rosenberg AE.Bone tumours.//Diagnostic Immunopathology, 2nd Edit.RB Colvin,AK Bhan,RT McCluskey,Eds.Raven Press.New York.1995;41(6): 633-649.[15] Taylor CR,Shi S.Techniques of immunohistochemistry: principles, pitfalls and standardization.//Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry: Theranostic and Genomic Applications, 4th Edit.DJ Dabbs,Ed.,Elsevier, Philadelphia. 2014;9(37):1-38.[16] Coffin CM,Belchis D.Immunohistology of pediatric neoplasms.//Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry,2nd Edit.,DJ Dabbs, Ed.,Elsevier,Philadelphia. 2016;57(31):611-636.[17] Egshatyan L,Kashtanova D,Popenko A,et al.Gut microbiota and diet in patients with different glucose tolerance.Endocrine Connections.2016;5(7):1-9. [18] Gebhard C,Gabriel C,Walter I.Morphological and immunohistochemical characterization of canine osteosarcoma spheroid cell cultures. Embryologia. 2016;45(75):219-230.[19] Barger A,Graca R,Bailey K,et al.Use of alkaline phosphatase staining to differentiate canine osteosarcoma from other vimentinpositive tumors. Veterinary Pathology. 2005;42(13): 161-165.[20] Nagamine E, Hirayama K, Matsuda K, et al. Diversity of histologic patterns and expression of cytoskeletal proteins in canine skeletal osteosarcoma.Veterinary Pathology.2015; 52(29):977-984.[21] Ueda T, Araki N, Mano M, Myoui A, et al. Frequent expression of smooth muscle markers in malignant fibrous histiocytoma of bone. Journal of Clinical Pathology. 2002; 55(11): 853-858.[22] Hasegawa T, Hirose T, Kudo E,et al.Immunophenotypic heterogeneity in osteosarcomas. Human Pathology.1991; 22(43):583-590.[23] Mandal PK,Chatterjee S,Ray S,et al.Osteosarcoma: an immunophenotypic study for characterization and behavior.Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science.2014; 13(5):443-448.[24] Chano T,Matsumoto K,Ishizawa M,et al.Analysis of the presence of osteocalcin,S-100 protein, and proliferating cell nuclear antigen in cells of various types of osteosarcomas. Eur J Histochem. 1996;40(3):189-198.[25] Sharili AS,Allen S,Smith K,et al.Expression of Snail2 in long bone osteosarcomas correlates with tumour malignancy. Tumour Biology.2011;32(50):515-526.[26] Miyazono K,Kamiya Y,Morikawa M.Bone morphogenetic protein receptors and signal transduction.J Biochem. 2010; 147(1):35-51.[27] Yoshikawa H,Nakase T,Myoui A.Bone morphogenetic proteins in bone tumors.J Orthop Sci.2004;9(3):334-340.[28] Olstad K,Ostevik L,Carlson CS.Osteochondrosis can lead to formation of pseudocysts and true cysts in the subchondral bone of horses. Vet Pathol.2015;52(5):862-872. [29] Raval P,Hsu HH,Schneider DJ,et al.Expression of bone morphogenetic proteins by osteoinductive and non-osteoinductive human osteosarcoma cells.J Dent Res. 1996;75(7):1518-1523. |