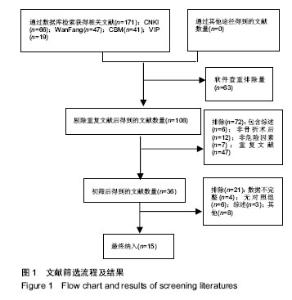
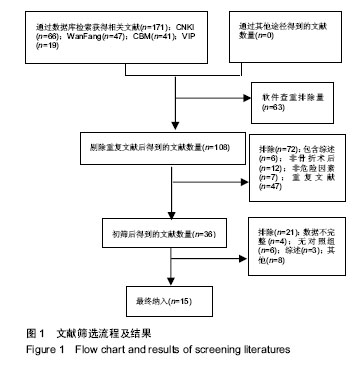
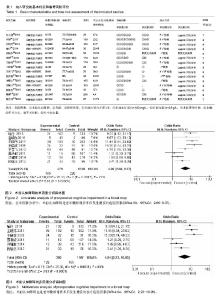
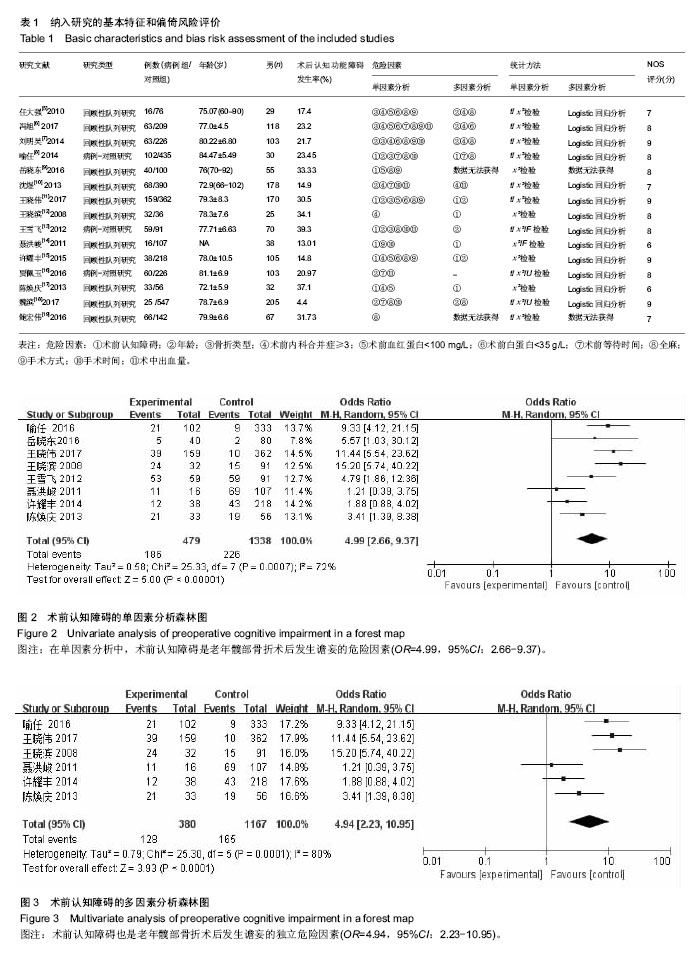
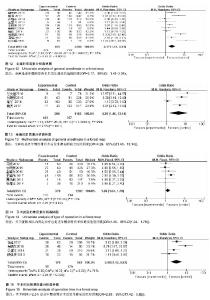
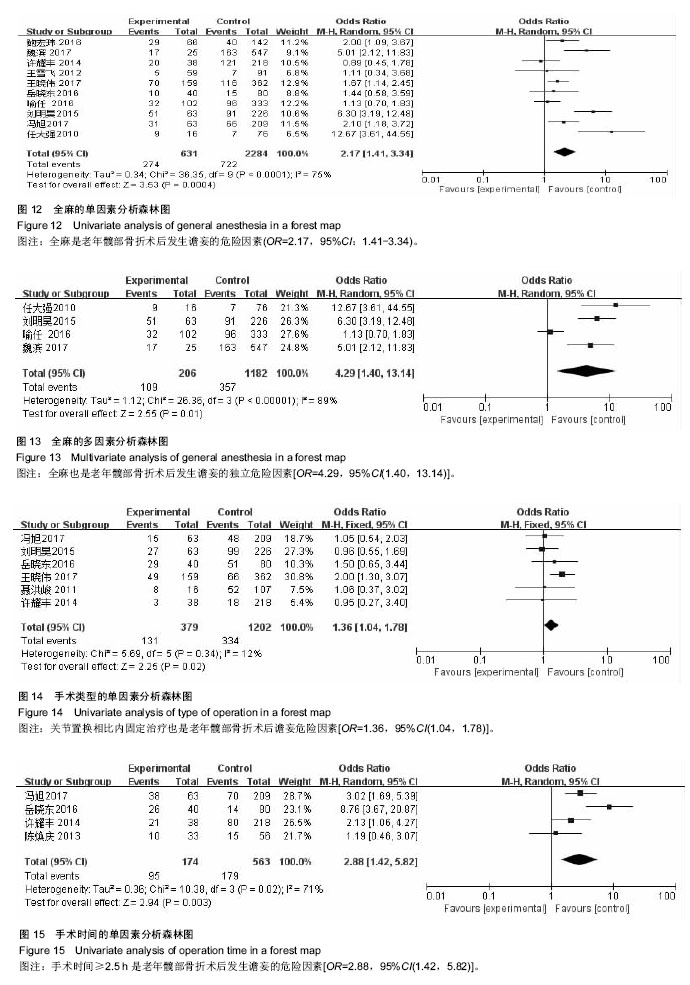
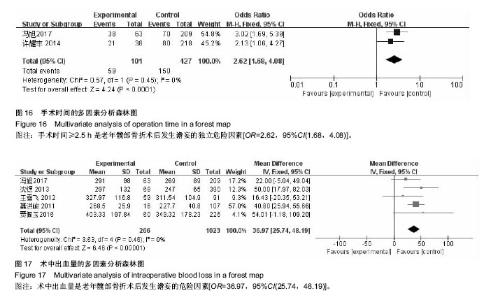
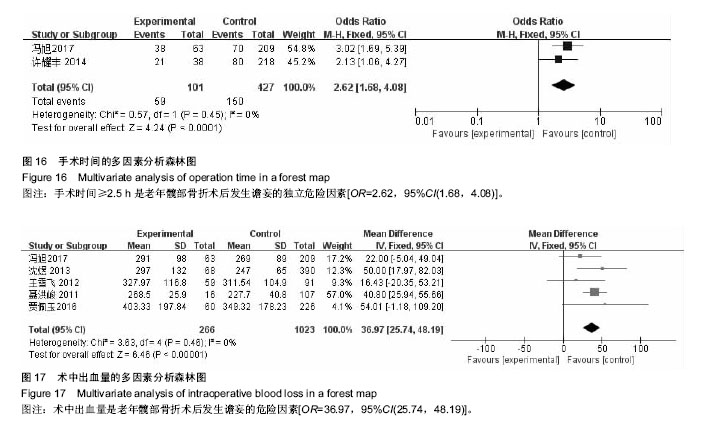
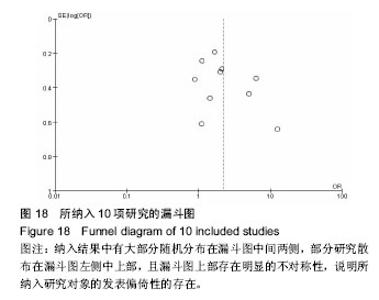
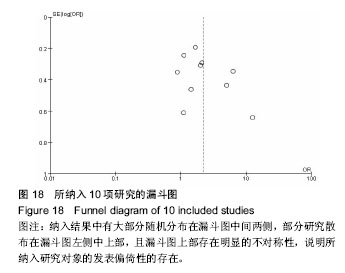
| [1] Rosso F,Dettoni F,Bonasia DE,et al.Prognostic factors for mortality after hipfracture:Operation within 48 hours ismandatory.Injury. 2016;47Suppl4: S91-S97.[2] Jones CA,Jhangri GS,Feeny DH,et al.Cognitive status at hospital admission: postoperative trajectory of functional recovery for hip fracture.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017;72(1):61-67.[3] Association AP.Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Washington DC: American Psychiatric, 2013.[4] Stang A.Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses.Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603-605.[5] 任大强.老年髋部骨折术后认知功能障碍的相关因素分析[D].山西医科大学, 2010.[6] 冯旭,陈辉,蔡宁宇,等.老年髋部骨折患者术后谵妄发生的危险因素分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(2):113-116.[7] 刘明昊.老年髋部骨折患者术后谵妄的相关危险因素及并发症分析[D].河北医科大学,2015.[8] 喻任,陆纯德,程艳,等.高龄髋部骨折患者术后谵妄危险因素调查[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(4):341-344.[9] 岳晓东,孟亚强,贾金鹏.高龄髋部骨折术后认知功能障碍的特点及防治康复措施[J].武警医学,2016,27(9):910-912.[10] 沈煜,沈惠良,张文博,等.老年髋部骨折术后谵妄状态的临床危险因素分析[J]. 中华医学杂志,2013,93(41):3276-3279.[11] 王晓伟,刘智,张建政,等.老年髋部骨折术后发生谵妄危险因素分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2017,33(6):505-509.[12] 王晓滨,苗卫红,黄公怡.老年髋部骨折患者手术后谵妄的临床研究[J].中华老年医学杂志,2008,27(2):99-102.[13] 王雪飞,韩莹,杨莉,等.老年髋部骨折术后血容量改变与谵妄的相关分析[J].中国综合临床,2012,28(9):910-913.[14] 聂洪峻,赵滨,张云强,等.123例老年髋部骨折患者术后谵妄发生的危险因素分析[J]. 贵州医药,2011,35(8):743-746.[15] 许耀丰,姜宏,李晓春,等.老年股骨转子间骨折术后并发谵妄的危险因素分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2015,31(2):143-147.[16] 贾佩玉,郭勇,王学敏,等.老年患者髋部骨折术后谵妄的危险因素分析[J].上海医学,2016,39(8):477-481.[17] 陈焕庆.老年患者髋部骨折术后谵妄的危险因素研究[J].中国乡村医药, 2013, 20(14):11-12.[18] 魏滨,张华,徐懋,等.髋部骨折老年患者发生严重术后谵妄的多因素分析[J].中国微创外科杂志,2017,17(1):38-41.[19] 鲍宏玮,严力生,陈红梅,等.麻醉选择对老年人髋部骨折术后谵妄的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(4):393-394.[20] 余雨.老年患者骨科手术后谵妄的危险因素研究[D].重庆医科大学,2013.[21] Watne LO,Torbergsen AC,Conroy S,et al.The effect of a pre and postoperative orthogeriatric service on cognitive function in patients with hip fracture: randomized controlled trial (Oslo Orthogeriatric Trial).BMC Med. 2014;12:63.[22] Bickel H, Gradinger R, Kochs E, et al.Incidence and risk factors of delirium after hip surgery]. Psychiatr Prax. 2004;31(7):360-365.[23] Lee HB, Mears SC, Rosenberg PB, et al.Predisposing factors for postoperative delirium after hip fracture repair in individuals with and without dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(12):2306-2313.[24] Siempos II,Ntaidou TK,Samonis G.The art of providing resuscitation in Greek mythology. Anesth Analg. 2014;119(6):1336-1341.[25] Goldenberg G, Kiselev P, Bharathan T. Predicting post-operative delirium in elderly patients undergoing surgery for hip fracture. Psychogeriatrics. 2006; 6(2):43-48.[26] 牛连信,闫国富. 多发性骨折后脂肪栓塞综合征的早期诊治[J].中华实用中西医杂志, 2005,18(11):1604-1605. |