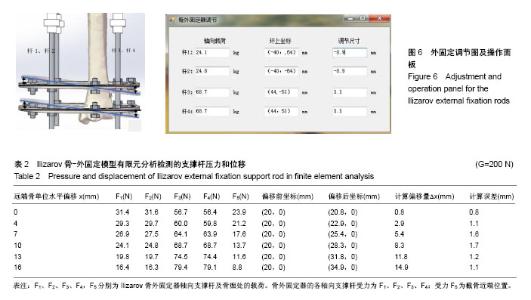
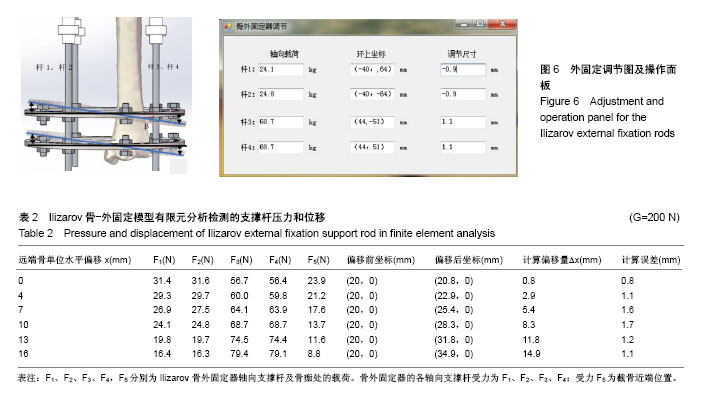
| [1] Alkenani NS, Alosfoor MA, Al-Araifi AK, et al. Ilizarov bone transport after massive tibial trauma: Case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016;28:101-106.[2] 马翔宇,王东. 开放性骨折修复:创面感染、植入物选择及预后评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(26):4258-4264.[3] 肖樵苏,张先文,叶俊武,等.应用骨搬运术同期治疗合并难治性软组织缺损的胫骨大段骨缺损[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2016, 30(8): 961-965.[4] Sadek AF, Laklok MA, Fouly EH, et al. Two stage reconstruction versus bone transport in management of resistant infected tibial diaphyseal nonunion with a gap. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(9): 1233-1241.[5] Yin P, Zhang Q, Mao Z, et al. The treatment of infected tibial nonunion by bone transport using the Ilizarov external fixator and a systematic review of infected tibial nonunion treated by Ilizarov methods. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica. 2014;80(3): 426-435.[6] 洪帆,谢加兵,丁国正.内固定植入物与外固定支架修复胫骨骨折骨不连的策略及辅助治疗[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(26): 3946-3952.[7] 赵玉峰,刘华渝,任永川,等. Ilizarov骨延长和骨搬移技术治疗下肢长骨创伤后慢性骨髓炎[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2015, 31(4): 294-298.[8] Spiegelberg B, Parratt T, Dheerendra SK, et al. Ilizarov principles of deformity correction. Ann Royal Coll Surg Eng. 2010;92(2): 101-105.[9] 闫秀中,王燕,焦绍锋,等. Ilizarov环形外固定架治疗胫腓骨开放骨折的临床研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2017, 25(4): 321-324.[10] 郭乾臣,张弢. Ilizarov牵张成骨在肢体延长中的临床应用及新进展[J]. 中华保健医学杂志, 2011,13(4):349-351.[11] 殷照阳,殷建,孙晓,等.Ilizarov骨搬移技术治疗胫骨感染性骨缺损合并软组织缺损[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2011,27(10): 901-904.[12] 蒲超,朱红,唐付林,等. 应用Ilizarov技术修复胫骨慢性骨髓炎并骨缺损[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(2):168-169.[13] Paley D. Problems, obstacles, and complications of limb lengthening by the Ilizarov technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;250(250): 81.[14] Burnei G, Vlad C, Gavriliu S, et al. Upper and lower limb length equalization: diagnosis, limb lengthening and curtailment, epiphysiodesis. Roman J Int Med. 2012;50(1): 43-59.[15] 陈育锋,陈晴,郑大伟,等.双下肢直立位全长X片在下肢矫畸中的应用[J]. 中国伤残医学,2015,23(19):86-88.[16] 夏和桃. 肢体延长的基础进展及临床有关问题[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(8):605-612.[17] 王波,胡海涛,潘健,等.膝关节骨性关节炎全膝关节置换术后下肢力线与早期临床效果关系的研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015,30(10):1044-1048.[18] 林汉文,温俊茂,黄超原,等.骨性关节炎患者下肢力线改变与疼痛部位的关系:影像学评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(7): 1110-1114.[19] Englund M. The role of biomechanics in the initiation and progression of OA of the knee. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010; 24(1): 39-46.[20] 刘彦士,张弢,马信龙,等. 轴向载荷分担比例评价骨愈合刚度及其指导骨外固定器安全拆除时机[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2016, 18(12): 1050-1056.[21] Mehboob A, Mehboob H, Kim J, et al. Influence of initial biomechanical environment provided by fibrous composite intramedullary nails on bone fracture healing. Comp Struct. 2017. [22] Siddiqui NA, Owen JM. Clinical advances in bone regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;8(3): 192-200.[23] Schuh R, Panotopoulos J, Puchner SE, et al. Vascularised or non-vascularised autologous fibular grafting for the reconstruction of a diaphyseal bone defect after resection of a musculoskeletal tumour. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(9): 1258-1263.[24] 张立超,张立敏,武丽珠. 全膝关节置换固定和旋转平台假体的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(39):5801-5806.[25] Inam M, Saeed M, Khan I, et al. Outcome of ilizarov fixator in tibial non-union. J Pak Med Assoc. 2015; 65(11 Suppl 3): S94-99.[26] Khan MS, Raza W, Ullah H, et al. Outcome of ilizarov fixator in complex non-union of long bones. J Pak Med Assoc. 2015; 65(11 Suppl 3): S147-151.[27] Peng J, Min L, Xiang Z, et al. Ilizarov bone transport combined with antibiotic cement spacer for infected tibial nonunion. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(6): 10058-10065.[28] Khan MS, Rashid H, Umer M, et al. Salvage of infected non-union of the tibia with an Ilizarov ring fixator. J Orthop Surgery (Hong Kong). 2015;23(1): 52-55.[29] 余凯,杨晶,杨广忠,等. Ilizarov牵拉架外固定治疗胫骨骨缺损的钢环参数选择[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(4): 577-582.[30] 田志刚,杜晓杰,林虹,等. 应用Ilizarov技术治疗儿童骨骺损伤后下肢短缩成角畸形[J]. 黑龙江医药, 2015, 28(3): 653-654.[31] 蒋守海,董长红,周立国,等. 应用Ilizarov技术修复胫骨长段骨髓炎骨缺损36例[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(18): 1699-1702.[32] In Y, Kim SJ, Kwon YJ. Patellar tendon lengthening for patella infera using the Ilizarov technique. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89(3): 398-400.[33] Henderson DJ, Rushbrook JL, Stewart TD, et al. What are the biomechanical effects of half-pin and fine-wire configurations on fracture site movement in circular frames? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(4): 1041-1049.[34] Simpson AL, Ma B, Slagel B, et al. Computer-assisted distraction osteogenesis by Ilizarov's method. Int J Med Robot. 2008;4(4):310-320.[35] 扈延龄,金丹,苏秀云,等. 基于三维CT数据的髋臼骨折计算机辅助虚拟手术设计[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(2):135-137.[36] Tresley J, Schoenleber SJ, Singer AD, et al. "Ilizarov" external fixation: what the radiologist needs to know. Skelet Radiol. 2015;44(2): 179-195. |