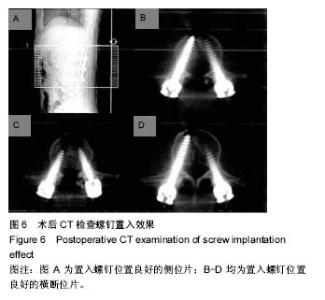
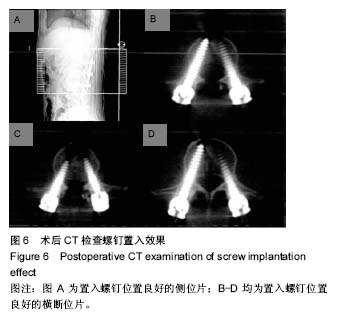
| [1] Amiot L, Lang KM, Zippel H, et al. Comparative results between conventional and computer-assisted pedicle screw installation in the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spine . Spine. 2000;25(5):606-614.
[2] 靳安民,姚伟涛,张辉,等. 腰椎内固定翻修术的初步研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2004, 24(9):525-529.
[3] Scuderi GR, Fallaha M, Masse V, et al. Total knee arthroplasty with a novel navigation system within the surgical field. Orthop Clin North Am. 2014;45(2):167.
[4] 李小丽,马剑雄,李萍,等. 3D打印技术及应用趋势[J].自动化仪表, 2014,35(1):1-5.
[5] 周伟民,闵国全,李小丽. 3D打印医学[J]. 组织工程与重建外科, 2014,4(3):58-62.
[6] Scuderi GR, Fallaha M, Masse V, et al. Total knee arthroplasty with a novel navigation system within the surgical field. Orthop Clin North Am. 2014;45(2):167.
[7] Zein NN, Hanouneh IA, Bishop PD, et al. Three-dimensional print of a liver for preoperative planning in living donor liver transplantation. Liver Trans. 2013;19(12):1304.
[8] Nakada T, Akiba T, Inagaki T, et al. Thoracoscopic anatomical subsegmentectomy of the right S2b + S3 using a 3D printing model with rapid prototyping. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2014;19(4):696-698.
[9] Tam MD, Laycock SD, Brown JR, et al. 3D printing of an aortic aneurysm to facilitate decision making and device selection for endovascular aneurysm repair in complex neck anatomy. J Endovasc Ther. 2013;20(6):863-867.
[10] Liu YF, Xu LW, Zhu HY, et al. Technical procedures for template-guided surgery for mandibular reconstruction based on digital design and manufacturing. Bio Med Eng. 2014; 13(1):63.
[11] Rankin TM, Mailey B, Cucher D, et al. Use of 3D printing for auricular template molds in first stage microtia. Plast Reconstruct Surg. 2014;134(1):16-17.
[12] Frame M, Leach W. DIY 3D printing of custom orthopaedic implants: a proof of concept study. Surg Technol Int. 2014; 24:314-317.
[13] 王忠宏,李扬帆,张曼茵. 中国3D打印产业的现状及发展思路[J]. 经济纵横, 2013,(1):90-93.
[14] Lu S, Xu YQ, Zhang YZ, et al. Rapid prototyping drill guide template for lumbar pedicle screw placement. Chin J Traumatol. 2009;12(3):177-180.
[15] Lu S, Xu YQ, Zhang YZ, et al. A novel computer-assisted drill guide template for lumbar pedicle screw placement: a cadaveric and clinical study. Int J Med Robot. 2009;5(2): 184-191.
[16] 陈玉兵,陆声,徐永清,等. 个体化导航模板辅助腰椎椎弓根螺钉置钉准确性实验研究[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2009, 19(8): 623-626.
[17] 唐雷. 数字医学技术与精准外科手术[J]. 中国实用妇科与产科杂志, 2012, 28(1):7-9.
[18] 夏锋,韦邦福.精准医疗的理念及其技术体系[J]. 医学与哲学(临床决策论坛版),2010,31(11):1-17.
[19] 龙晓宇,乔杰. 精准医疗在生殖医学临床中的应用[J]. 实用妇产科杂志, 2017, 33(6):407-408.
[20] 马丁. 精准医疗在宫颈癌防治中的应用[J]. 实用妇产科杂志, 2017, 33(6):404-407.
[21] 王红强,顾康生. 肿瘤精准医疗中的个性化药效评估(预测)方法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2017, 30(2):117-126.
[22] 刘晓晴,曲莉莉. 精准医疗时代肺癌分子靶向治疗选择[J]. 医学研究生学报, 2017, 30(11):1140-1145.
[23] 惠汝太,宋雷,胡盛寿. 心血管疾病的精准医疗时代已经到来?[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2017,45(6):471-475.
[24] 薛文,刘舒娆,管晓鹂,等. 微创经皮与传统开放椎弓根螺钉置入固定胸腰椎骨折的文献荟萃[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(13):1961-1969.
[25] 张强,李瑞龙,杨刘柱,等. 经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定修复单节段胸腰椎骨折:活动度改善12个月随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(9):1242-1248.
[26] 朱劲松,杨民,徐祝军,等. 后路经椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折治疗失败原因分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2016, 18(3): 253-256.
[27] 肖斌,李健,蔡厚洪,等. 经后路单侧伤椎固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床应用[J]. 重庆医学, 2016,45(22):3049-3051.
[28] 朱立帆,曾金才,朱晓东,等. 胸腰椎骨折三种不同内固定方式的疗效比较[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2016,26(10):893-898.
[29] 闫廷飞,史建刚,史国栋. 胸腰椎骨折伴脊髓神经损伤的治疗进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(6):552-555.
[30] 毛克亚,王岩,张永刚,等. 胸椎椎弓根螺钉置入位置的CT评价[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2005,15(4):222-224.
[31] 王娟,周义成,胡宁,等. MSCT三维重建指导椎弓根螺钉置入的体外应用研究[J]. 放射学实践, 2004,19(5):323-326.
[32] 胡勇,谢辉,徐荣明,等. 青少年脊柱侧凸患者胸椎椎弓根螺钉置入的准确性和安全性评价[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(11): 820-824.
[33] 谭明生,张光铂,移平,等. 管道疏通法行颈椎弓根螺钉置入的研究[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2002,12(6):405-410.
[34] 章莹,李宝丰,王新宇,等. 术前3D打印技术模拟复杂骨盆骨折手术提高疗效的可行性研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2015,17(1): 29-33.
[35] 邓爱文,熊日波,何伟明,等. 髋臼骨折中应用3D打印技术术后的康复策略[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014,34(4):591-593.
[36] 戎帅,滕勇,乌日开西•艾依提,等. 基于3D打印技术的腰椎多节段峡部裂个性化手术治疗[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2013, 21(21): 2222-2226.
[37] 李涛,陈卓夫,龚辉,等. 3D打印技术在复杂髋臼骨折术中的初步临床应用[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2016, 31(4):387-388.
[38] 章凯,陈育岳,夏虹,等. 3D打印技术辅助复杂性寰枢椎脱位手术临床应用[J]. 中国数字医学, 2013,8(10):58-60.
[39] 唐盛辉,孙永建,赵汉民,等. 3D打印技术辅助治疗高能量Pilon骨折的临床应用[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2015, 23(22): 2042-2046.
[40] 李新春,康麟,庞渊. 3D打印技术在Pilon骨折手术治疗中的应用[J]. 新疆医科大学学报, 2015,38(4):471-473. |