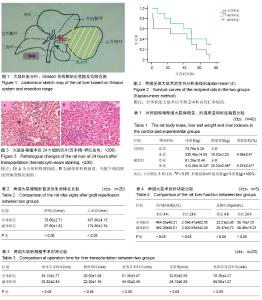
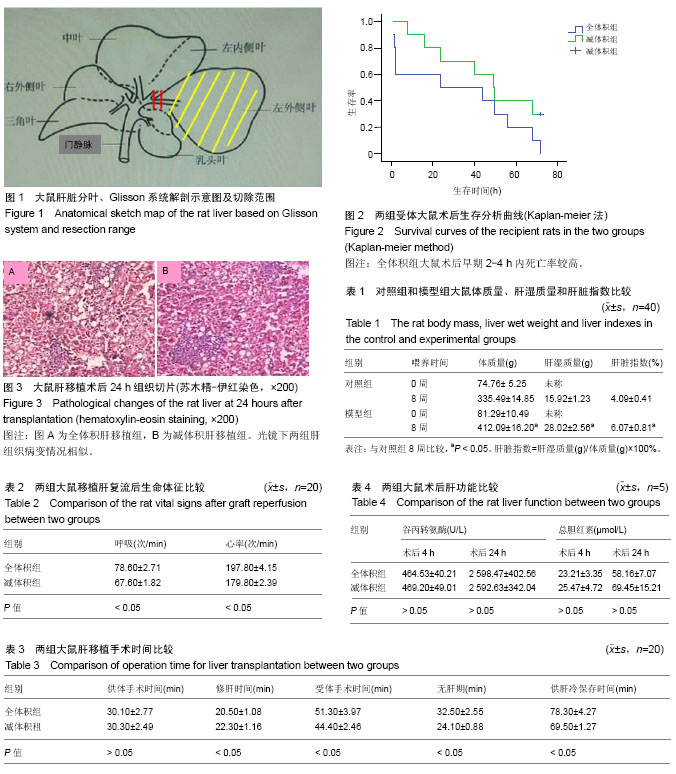
| [1] |
Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin.
Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339.
|
| [2] |
Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei.
In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141.
|
| [3] |
Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian.
The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812.
|
| [4] |
Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui.
Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569.
|
| [5] |
Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han.
Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606.
|
| [6] |
Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He.
Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620.
|
| [7] |
Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei.
Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631.
|
| [8] |
Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia.
Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643.
|
| [9] |
Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian.
Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650.
|
| [10] |
Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong.
Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430.
|
| [11] |
Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin.
Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465.
|
| [12] |
Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo.
Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478.
|
| [13] |
Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui.
Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486.
|
| [14] |
Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong.
Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516.
|
| [15] |
Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei.
Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533.
|