Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 189-195.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and biological properties of TiN/Ag composite coating on pure titanium surface
- 1The Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300211, China; 2Tianjin Institute of Urological Surgery, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300211, China
-
Received:2018-09-28Online:2018-01-18Published:2018-01-18 -
Contact:Peng Cheng, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, the Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300211, China -
About author:Ma Ming, Studying for master’s degree, the Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300211, China -
Supported by:the National High-Tech Research and Development Program of China (863 Program), No. 2015AA034702; the National Key Research and Development Program of China, No. 2016YFC1100302; the Applied Basic and Cutting-Edge Technology Research Program of Tianjin, No. 15JCZDJC38200; the Scientific Research Foundation of the Health and Family Planning Commission of Tianjin, No. 2015KZ094
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Ming, Wan Rong-xin, Lv Xiao-fei, Chu Shan-shan, Li Li-jun, Gu Han-qing, Peng Cheng.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
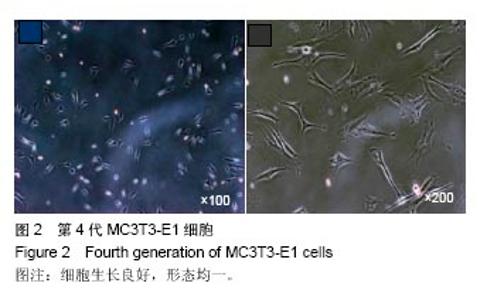
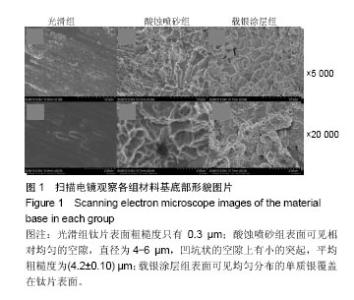
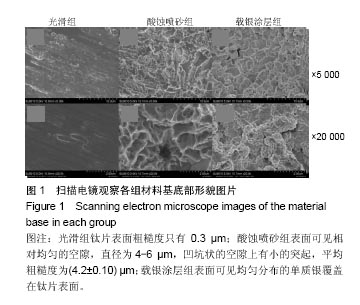
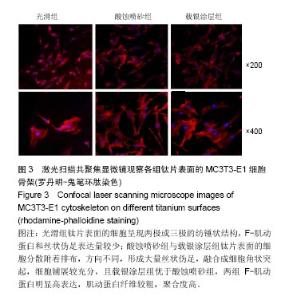
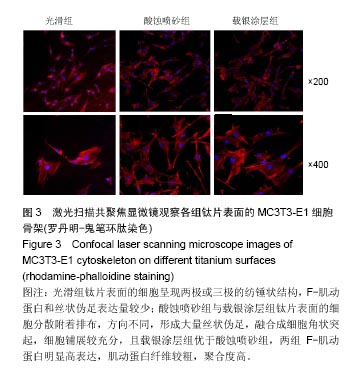
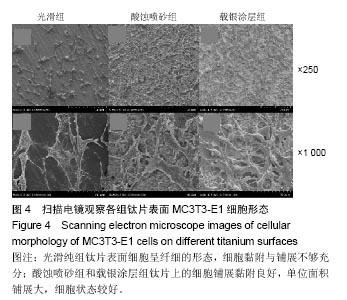
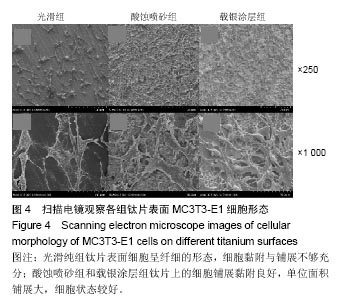
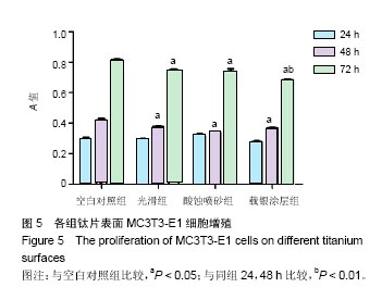
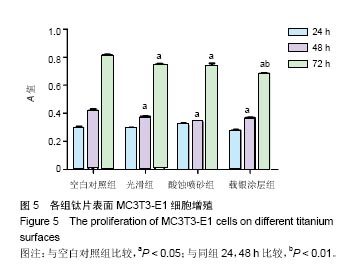
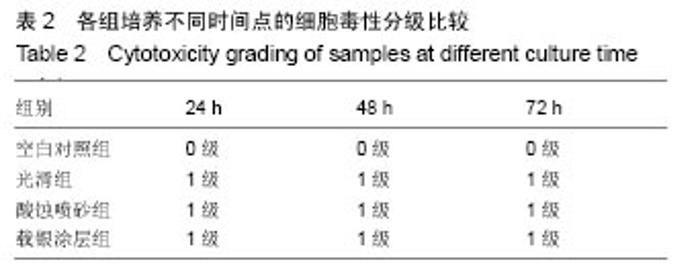
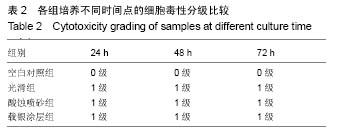
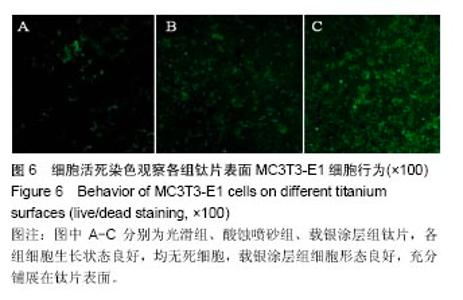
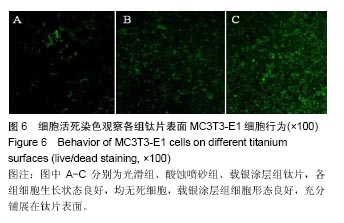
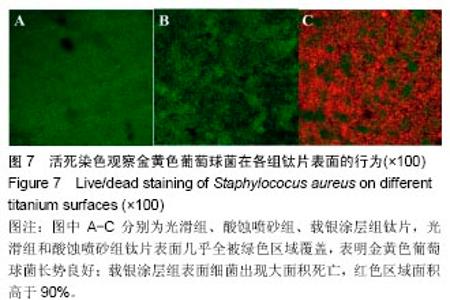
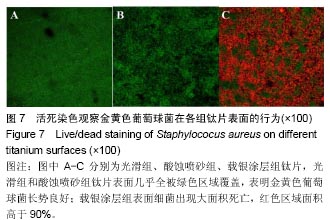
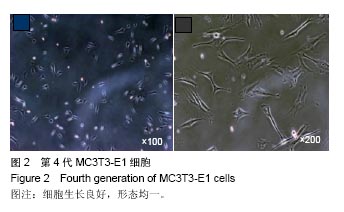
2.2 激光共聚焦下观察钛片表面细胞骨架形态、黏附及铺展展情况 第4代MC3T3-E1细胞生长良好,形态均一,可用于后续实验研究,见图2。 荧光显微镜观察显示,光滑组钛片表面的MC3T3-E1细胞呈现两极或三极的纺锤状结构,F-肌动蛋白和丝状伪足表达量较少,类似于正常生长的成纤维细胞;与光滑组不同,酸蚀喷砂组与载银涂层组钛片表面的MC3T3-E1细胞分散附着排布,方向不同,形成大量丝状伪足,相互交织融合在一起,形成细胞角状突起,两组钛片上的细胞铺展都比较充分,且载银涂层组优于酸蚀喷砂组,酸蚀喷砂组与载银涂层组的F-肌动蛋白明显高表达,肌动蛋白纤维较粗,聚合度高,说明酸蚀喷砂组与载银涂层组钛片上的细胞黏附优于光滑组(图3)。"
| [1]杨晓丰,刘帆,刘奕,等.医用钛材料表面改性研究进展[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2016,32(9):569-571.[2]焦艳军,王珏,潘福勤,等.纯钛种植体的2种表面处理对细菌黏附能力的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2009, 25(2):166-169.[3]Besinis A,Hadi SD,Le H.R,et al.Antibacterial activity and biofilm inhibition by surface modified titanium alloy medical implants following application of silver, titanium dioxide and hydroxyapatite nanocoatings.Nanotoxicology. 2017;11(3):327-338.[4]Zhao L,Chu PK,Zhang Y,et al.Antibacterial coatings on titanium implants.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009;91(1): 470-480.[5]Vimbela GV,Ngo SM,Fraze C,et al.Antibacterial properties and toxicity from metallic nanomaterials. Int J Nanomedicine.2017;12:3941-3965.[6]Rossi MC,Bezerra FJB,Silva RA,et al.Titanium-released from dental implant enhances pre-osteoblast adhesion by ROS modulating crucial intracellular pathways.J Biomed Mater Res A.2017;105(11):2968-2976. [7]Fernandes GV,Cavagis AD,Ferreira CV,et al.Osteoblast adhesion dynamics: a possible role for ROS and LMW-PTP.J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(6):1063-1069.[8]Arita S,Suzuki, M,Kazama-Koide M,et al.Shear bond strengths of tooth coating materials including the experimental materials contained various amounts of multi-ion releasing fillers and their effects for preventing dentin demineralization.Odontology.2017.doi: 10.1007/s10266-016-0290-1.[Epub ahead of print][9]才学敏,刘桐,唐慧琴,等.离子束辅助沉积TiN_Ag多层膜的抗菌性和抗腐蚀性[J].核技术,2007,30(12):1028-1032.[10]党超群,白雪冰,李金龙,等.TiSiN/Ag纳米多层涂层的抗菌及摩擦学性能研究[J].摩擦学学报,2017,37(1):1-10.[11]黄美东,李云珂,王萌萌,等.多弧离子镀沉积TiAlN_TiN多层膜的结构与性能[J].天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2015,35(1):26-29.[12]姜雪峰,刘清才,王海波.多弧离子镀技术及其应用[J].重庆大学学报(自然科学版),2006,29(10):55-57,68.[13]杜娟,姜焕焕,莫嘉骥,等.钛表面形貌和亲水性表面对成骨细胞增殖分化的影响[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2012,10(3):182-187.[14]Wu P,Gao H,Sun J,et al.Biosorptive dehydration of tert-butyl alcohol using a starch-based adsorbent: characterization and thermodynamics.Bioresour Technol.2012;107:437-443.[15]Tomankova K,Horakova J,Harvanova M,et al.Cytotoxicity, cell uptake and microscopic analysis of titanium dioxide and silver nanoparticles in vitro.Food Chem Toxicol.2015;82:106-115.[16]Abbas HK,Yoshizawa T,Shier WT.Cytotoxicity and phytotoxicity of trichothecene mycotoxins produced by Fusarium spp.Toxicon. 2013;74:68-75.[17]Miao X,Wang D,Xu L,et al.The response of human osteoblasts, epithelial cells, fibroblasts, macrophages and oral bacteria to nanostructured titanium surfaces: a systematic study.Int J Nanomedicine.2017;12:1415-1430.[18]Qin H,Cao H,Zhao Y,et al.In vitro and in vivo anti-biofilm effects of silver nanoparticles immobilized on titanium.Biomaterials.2014; 35(33):9114-9125.[19]Ye L.Current dental implant design and its clinical importance. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi.2017;35 (1):18-28.[20]邵磊,赵宝红.钛种植体骨结合界面组织学研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2014,7(7):440-445.[21]Ma Z,Li M,Liu R,et al.In vitro study on an antibacterial Ti-5Cu alloy for medical application.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2016;27(5):91.[22]Vahabzadeh S,Roy M,Bandyopadhyay A,et al.Phase stability and biological property evaluation of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings for orthopedic and dental applications.Acta Biomater. 2015;17: 47-55.[23]莫尊理,胡惹惹,王雅雯,等.抗菌材料及其抗菌机理[J].材料导报, 2014,28(1):50-52,90.[24]Qin H,Zhu C,An Z,et al.Silver nanoparticles promote osteogenic differentiation of human urine-derived stem cells at noncytotoxic concentrations.Int J Nanomedicine.2014;9:2469-2478.[25]Roy M,Pompella A,Kubacki J,et al.Photofunctionalization of dental zirconia oxide: Surface modification to improve bio-integration preserving crystal stability.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;156: 194-202.[26]Okazaki Y,Doi K,Oki Y,et al.Enhanced Osseointegration of a Modified Titanium Implant with Bound Phospho-Threonine: A Preliminary In Vivo Study.J Funct Biomater.2017;8(2).pii: E16. doi: 10.3390/jfb8020016.[27]Meng HW,Chien EY,Chien HH.Dental implant bioactive surface modifications and their effects on osseointegration: a review. Biomark Res.2016;4:24.[28]胡敏,刘莹,赖珍荃,等.磁控溅射TiN薄膜的工艺及电学性能研究[J].功能材料,2009,40(2):222-225.[29]袁建鹏.钛合金表面多弧离子镀TiAlN薄膜微观组织结构及性能研究[J].热喷涂技术,2012,4(3):84-88.[30]赵时璐,张钧,刘常升.多弧离子镀(Ti,Al,Zr,Cr)N多组元氮化物膜的研究[J].真空科学与技术学报,2009,29(6):707-711.[31]Qiao S,Cao H,Zhao X,et al.Ag-plasma modification enhances bone apposition around titanium dental implants: an animal study in Labrador dogs.Int J Nanomedicine.2015;10:653-664.[32]汤京龙,王硕,刘丽,等.纳米银颗粒的细胞毒性作用及机制初探[J].北京生物医学工程,2013,32(5):485-489.[33]刘泉,黄文,熊颖铭,等.纳米银改性钛片细胞生物毒性实验研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2014,28(4):214-217.[34]Dong F,Mohd Zaidi NF,Valsami-Jones E,et al.Time-resolved toxicity study reveals the dynamic interactions between uncoated silver nanoparticles and bacteria.Nanotoxicology.2017;11(5):637-646.[35]Dong F,Valsami-Jones E,Kreft JU.New,rapid method to measure dissolved silver concentration in silver nanoparticle suspensions by aggregation combined with centrifugation.J Nanopart Res. 2016;18(9):259.[36]刘玉,尹伟,史春.20-40nm银的体外生物安全性研究[J].口腔医学研究,2015,31(2):120-122.[37]Bouallegui Y,Ben Younes R,Turki F,et al.Effect of exposure time, particle size and uptake pathways in immune cell lysosomal cytotoxicity of mussels exposed to silver nanoparticles.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2017:1-6.[38]Foldbjerg R,Dang DA,Autrup H.Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in the human lung cancer cell line,A549.Arch Toxicol.2011;85(7):743-750.[39]Umeda H,Mano T,Harada K,et al.Appearance of cell-adhesion factor in osteoblast proliferation and differentiation of apatite coating titanium by blast coating method.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2017;28(8): 112.[40]于卫强,徐玲,张富强.TiO_2纳米管对MC3T3-E1前成骨细胞骨功能基因表达变化的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2011,27(2):101-104. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Zhao Qiao, Chen Shuo, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and properties of copper-loaded antibacterial functional film on titanium surface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [7] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [8] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [9] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [11] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [12] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [13] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||