Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (30): 4889-4895.doi: 10.12307/2024.639
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application and prospect of robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty
Wang Ruoyu1, Zhang Zhifeng2, Huang Jian2
- 1Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-01-06Accepted:2023-09-21Online:2024-10-28Published:2023-12-28 -
Contact:Huang Jian, Professor, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China Zhang Zhifeng, Associate professor, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Ruoyu, Master candidate, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. 2020MS08144 (to ZZF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Ruoyu, Zhang Zhifeng, Huang Jian. Application and prospect of robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4889-4895.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
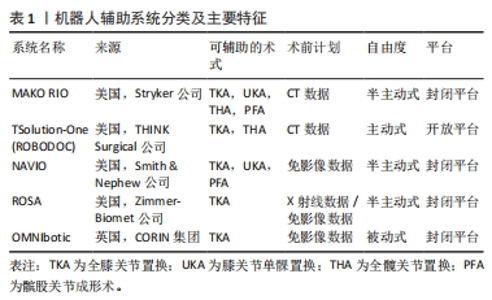
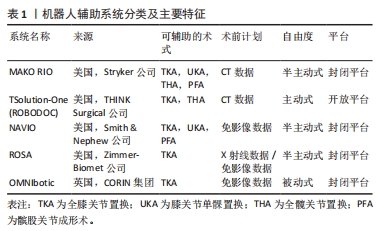
2.1 机器人辅助全膝关节置换系统 2.1.1 主动式、半主动式及被动式系统 根据机器人辅助全膝关节置换过程中机器人设备的自由度,机器人系统可分为主动式、半主动和被动式系统。被动式系统也被称为计算机辅助系统或导航系统,它仅为截骨摆锯提供正确、精准定位及截骨危险区监视,而并不独立地执行截骨操作,需要医生直接控制机器人完成全膝关节置换。与被动式系统相反,具有主动式系统的机器人可以自主地进行截骨等手术操作,所以人机交互的水平明显降低。半主动式系统结合了以上两种系统原理,也是目前使用最为广泛的系统,其主要特点是在半主动式系统机器人的监视下,主刀医生需要控制机器人的机械臂进行股骨侧和胫骨侧截骨,机器人系统可以提供术中触觉、听觉或视觉信号的实时反馈,以限制截骨范围,降低与术前手术计划的偏差,同时起到保护关节周围韧带和软组织的作用,因此也被称为“触觉”反馈系统[14-15]。 2.1.2 开放平台系统和封闭平台系统 近些年来,机器人辅助全膝关节置换的临床应用越来越广泛,在领域内有着极高的关注度,这促使着各大假体制造商大力投资该项技术,各种机器人的质量水平、竞争力、技术深度以及相关研究的数量也因此快速增长[16],但这也导致了不同品牌的机器人之间更为明显的技术屏障。封闭系统只与设计该系统的制造商提供的特定假体相兼容[17],这不仅迫使手术医生需要放弃使用自己更为熟悉和喜欢的膝关节假体,而封闭系统的特定假体是否真正适合需要行全膝关节置换的患者也成为一个不可避免的问题。相反,开放系统可与不同制造商的多种不同类型假体相兼容,而开放系统会因缺乏不同假体的详细生物力学数据[11],进而影响机器人辅助全膝关节置换的精准性。 2.1.3 需影像数据系统和免影像数据系统 需影像数据系统需要患者术前膝关节X射线平片或CT扫描数据,以创建虚拟3D膝关节计算机模型,作为术前规划和术中计划调整的参考。该系统仍需要手术医师在术中完成对膝关节骨性解剖结构的注册登记(向机器人系统反馈膝关节解剖结构参数),使其与术前影像参数完成配准,而该系统额外增加的影像成本和医源性辐射暴露也成为其潜在的缺点[18]。免影像数据系统虽减少了医源性辐射暴露,但其准确性仅依赖于手术医师在术中对骨性解剖标志进行注册登记的结果,而有明显膝关节畸形或骨缺损患者的解剖标志可能会发生改变,这无形中也提高了注册的难度。 2.1.4 现有具体的机器人辅助系统 MAKO RIO系统:在2006年,第一代 MAKO骨科机器人于美国佛罗里达州诞生,并成功实施了首例膝关节单髁置换手术。2013年史赛克(Stryker)公司收购了 MAKO外科公司,并于2015年推出了第三代即最新一代的 MAKO智能骨科机器人系统,次年完成了首例MAKO 机器人辅助全膝关节置换,MAKO智能骨科机器人也是现在使用最多的机器人设备。MAKO RIO (Robotic Arm Interactive Orthopaedic)系统是封闭平台、半主动式、需CT影像数据的机器人系统,基本原理是医生通过分析术前三维 CT数据,做出术前规划(最适合患者的人工膝关节尺寸及摆设位置),术中实时传送患者三维骨骼影像及膝关节运动参数,并可通过膝关节的活动范围来评估畸形和韧带松弛状况,让手术医师及时修改手术计划[17,19],完全依照患者膝关节解剖形态进行手术。 ROBODOC系统:该系统诞生于1992年,是最初用于全髋关节置换中股骨侧截骨操作的主动式机器人系统[20]。2014年,THINK Surgical公司(前Curexo科技公司)在ROBODOC系统的基础上逐步开发,并将其更名为TSolution-One系统。TSolution-One系统是一种开放平台、主动式的、需CT影像数据的机器人系统。患者术前膝关节的CT影像数据需要导入到名为TPLAN 3D的工作站进行数据处理,以制定术前计划,患者基于CT影像数据的术前计划需要进一步上传至TCAT(Think Computer Assisted Tool),TCAT最终通过与术前计划配准,限制自己的操作范围,在不需要医生操控的情况下,自主实施磨削截骨[11]。与其他机器人系统不同,TSolution-One系统不能调整手术计划,而只能执行预定计划[17]。TSolution-One系统也是目前技术较为成熟、应用最为广泛的开放平台的机器人系统。 NAVIO系统:该系统是一种封闭平台、半主动式、免影像数据的机器人系统[21],于2012年获得FDA批准用于全膝关节置换、单髁关节置换(Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty,UKA)、髌股关节成形术 (Patello-Femoral Arthroplasty,PFA)。NAVIO与其他免影像数据系统相同,不需要采集患者术前膝关节影像数据,而是利用自身光学导航和免影像数据系统通过手术医师在术中对胫骨和股骨的注册来采集骨性结构数据,从而创建膝关节的虚拟模型[22]。但当手术医师在操作轻便的半主动式手持截骨器突破截骨计划时,与常规的触觉反馈功能不同,它会通过降低摆锯速度和回缩刀头来避免错误发生[17]。 ROSA系统:该系统是一种封闭平台、半主动式、需X射线或免影像数据的只用于全膝关节置换的机器人系统。在对膝关节骨性标志进行注册并确认术中计划后,ROSA系统仍然允许手术医师根据每位患者膝关节结构和韧带张力实时调整手术计划,而不需要依据患者术前膝关节影像数据生成的3D模型[23]。该系统也只负责截骨导板的定位及安置,手术医师仍需要使用传统的截骨工具进行截骨操作[24]。 OMNIbotic系统:该系统是一种封闭平台、被动式、免影像数据的仅用于全膝关节置换的截骨导向系统。患者膝关节解剖结构数据均由手术医师在术中注册获得,其特点是具有评估韧带平衡的组件(BalanceBot),用于测量伸直、屈曲和整个膝关节运动范围内的韧带张力,旨在降低术后膝关节韧带不平衡的风险[13,25]。在截骨时,需要在股骨侧和胫骨侧固定OMNIbotic系统自带的截骨导板进行截骨,在对截骨结果验证后,仍可以调整计划继续截骨[26]。 近年来,膝关节置换中的机器人辅助系统正引发关节外科领域的革命性变革。这些系统根据主动性、半主动性和被动性进行划分,也可以依据平台的封闭性和开放性进行分类,而在影像数据方面,系统分为需影像数据和免影像数据2类,各有利弊。具体而言,MAKO RIO半主动式系统作为目前使用最为广泛的机器人系统,通过CT影像数据和实时反馈,让医生根据患者的解剖形态进行手术,而ROBODOC的TSolution-One系统则以开放平台为基础,实现主动式截骨操作。与此不同,NAVIO系统以免影像数据的光学导航技术为依托,提供准确的膝关节虚拟模型,来使手术更为精确。ROSA系统则在术中根据患者个体特征和韧带张力实时调整计划,为手术医生提供更大的自由度。而OMNIbotic系统则专注于被动式截骨导向,通过组件评估韧带平衡,减少手术后的不平衡风险,见表1。"
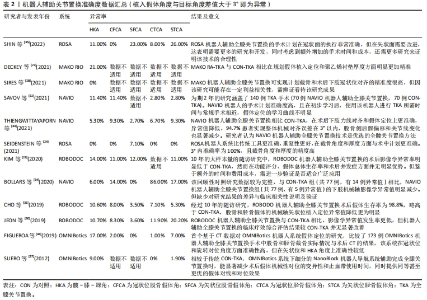
上述机器人辅助系统的涌现,标志着医疗技术正逐步实现个性化和精准化治疗。从封闭平台到开放平台,从影像数据到免影像数据,从主动式操作到被动式导向,每种系统都在不同程度上优化了手术流程,每一环节都呈现出创新的崭新面貌。这一技术进步也带来了新的挑战,例如如何在保持操作简便性的同时保障精确性,以及如何将这些系统更好地融入实际临床环境。总的来说,机器人辅助系统正在推进着膝关节置换手术的演变,为患者提供了一种新的治疗方式,将医疗领域推向了一个更加前沿的未来。 2.2 机器人辅助技术的主要优势——精准度的提高 每一位关节外科医生在全膝关节置换中都希望完成精准的假体植入,以重建一个平衡、稳定和耐用的膝关节,所以准确度和精密度是全膝关节置换的重中之重。准确度通常是指完成计划目标的能力,而精密度是指随着时间的推移重复出现相同结果的能力。与传统全膝关节置换相比,众多学者已证明机器人辅助技术能有效提高假体定位和下肢力线对齐的精准度[24,27-37]。尽管近些年提出了不同下肢力线对齐方式的理念,但机械轴对齐仍然是最常被使用的力线对齐方式,也被认为是最保险的方式[38]。通常认为术后冠状位下肢机械轴角度应在中立位,即0°±3°的范围内,若超出该范围则为影像学异常值[39]。由此可见,在治疗过程与随访的过程中分析,机器人辅助全膝关节置换系统具有很大的优势,在精准性和系统的应用上,机器人辅助全膝置换系统具有比人手更好的精密度,具体研究成果见表2。"
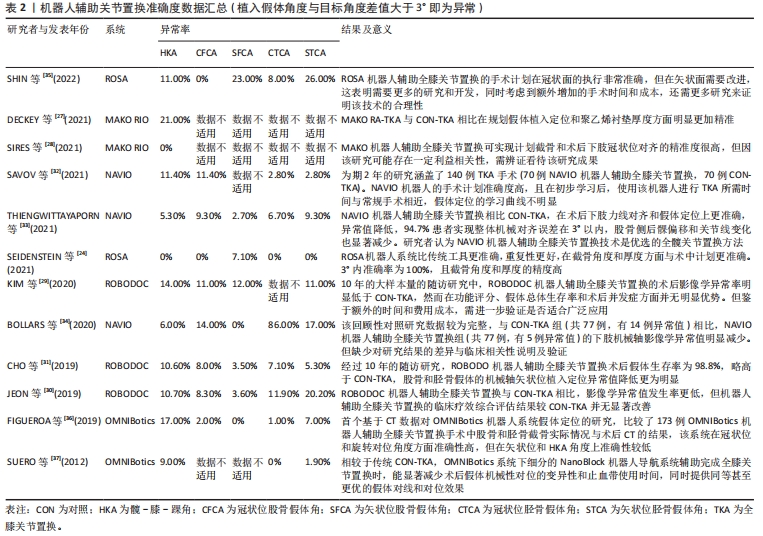
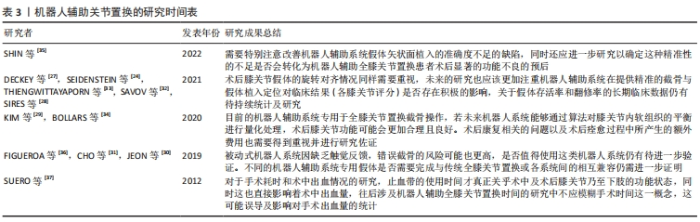
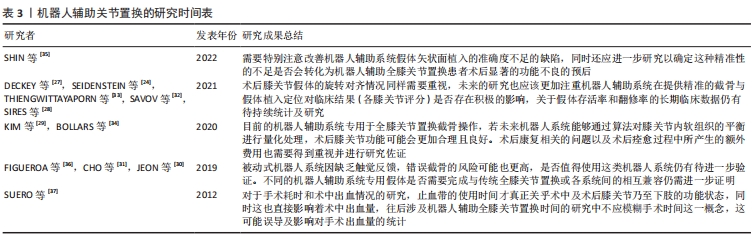
对于膝关节力线的重建,特别是对冠状位机械轴的纠正,机器人辅助全膝关节置换较传统全膝关节置换表现出更高的准确性。在术后关节线位置方面,机器人辅助全膝关节置换术后关节线高度较术前的平均变化更小,关节线异常值(关节线改变> 5 mm的偏差)发生率也更小,这说明机器人辅助全膝关节置换能更安全、准确地恢复关节生物力学状态[11,32-33]。机器人辅助全膝关节置换术后关节线高度较传统全膝关节置换也有所降低,而全膝关节置换术后关节线高度下降可能有助于降低患者膝关节不稳定的发生率,在一定程度上改善临床疗效[40]。同时机器人辅助全膝关节置换在术中计划执行方面更为精确,减小了股骨和胫骨假体植入位置与计划之间的差异,以及聚乙烯垫片厚度的不一致性[32]。但也有研究发现若设定与术中计划存在±3°误差为可接受的准确性结果,则矢状位的假体组件角的准确度较冠状位差12%-26%[35]。虽然有些研究已经证明机器人辅助全膝关节置换在手术完成的准确性方面显示出不俗的能力,但其如何影响临床疗效和患者满意度仍需进一步深入研究,未来的研究需要探讨机器人辅助全膝关节置换的潜在益处以及其在改善患者术后康复中的作用。 由此可见,一例全膝关节置换的成功并不只取决于精准度,假体的寿命和患者的术后满意度等都是必须重视的因素。随着机器人辅助全膝关节置换近些年飞速发展,机器人系统也迅速更新换代,多数较权威的中长期研究结果仍是悬而未决的,所以正确定义其未来前景和应用并不是一件易事,因此不同时期关于机器人辅助系统的研究所暴露出的问题更有助于对机器人辅助系统的升级进化和再次验证,见表3。"

2.3 机器人辅助技术的客观不足 2.3.1 学习曲线 手术时间延长是机器人辅助全膝关节置换的主要问题之一,因为较长时间的手术不仅会增加术后并发症的发生率,还会产生额外的手术成本。相关文献中报道的学习曲线结果不尽相同,且完成学习曲线所必需的病例数范围很广,从7例到43例不等[10,41]。KAYANI等[10]在其临床对照试验中分析得出MAKO机器人系统的学习曲线为7例,即手术医师通过使用MAKO机器人系统完成7例机器人辅助全膝关节置换的经验积累,可以达到与传统全膝关节置换相同的手术时间和手术团队的默契程度,而且即使未完成学习曲线也并不影响MAKO机器人系统假体定位的准确性。另一项涉及386例患者与6位手术医师的关于MAKO机器人系统的回顾性临床分析显示,MAKO 机器人辅助全膝关节置换的学习曲线11-43例,研究者推断这可能与不同手术医师的经验以及不同手术团队的默契程度有关,并且也发现MAKO 机器人辅助全膝关节置换的学习曲线并不影响其对假体植入的定位和屈伸间隙的平衡[41]。此外VANLOMMEL等[12]的同类型回顾性分析报道,使用免影像数据的ROSA系统的学习曲线为6-11例机器人辅助全膝关节置换。由于ROSA系统与MAKO系统都使用光学导航引导的机械臂进行截骨操作,因此与KAYANI等[10]报道的学习曲线例数相接近也是合理的。然而在对前10例机器人辅助全膝关节置换各个手术步骤耗时的分析后发现,ROSA系统的初始准备时间[(8.9±1.9) min vs.(14.0±4.3) min]和注册时间较MAKO系统更短,但ROSA系统的骨准备和假体植入试验的耗时更长。 THIENGWITTAYAPORN等[33]在完成超过150例全膝关节置换的随机对照试验后得到了另一种免影像数据的NAVIO系统的学习曲线结果。研究者们发现机器人辅助全膝关节置换组的平均手术时间明显长于传统全膝关节置换组(70.1 min vs. 61.9 min,P < 0.001),且机器人辅助全膝关节置换组前10例的平均手术时间较传统全膝关节置换组的更长(95.0 min vs. 61.9 min,P < 0.001)。试验结果还显示,在完成最初的7个机器人辅助全膝关节置换病例,手术时间出现了一个拐点,在拐点之前的部分为平均手术时间100 min的初始学习阶段和平均手术时间67 min的熟练阶段(P < 0.001)。SAVOV等[32]对两组各70例患者分别进行NAVIO机器人辅助全膝关节置换和传统全膝关节置换并分析了NAVIO机器人系统的学习曲线,当完成11例NAVIO 机器人辅助全膝关节置换后,两组手术时间便无显著性差异(机器人辅助全膝关节置换69 min vs. 传统全膝关节置换67 min;P=0.5)。但BELL等[9]的一项包括60例NAVIO 机器人辅助全膝关节置换的回顾性分析显示,对于接受过进修医生培训的资深外科医生来说,需要29例机器人辅助全膝关节置换来完成学习曲线。在整个学习曲线中,若将每10例机器人辅助全膝关节置换规定为一组,并将手术步骤进行划分后,平均关节置换时间从第一组的41.8 min减少到最后一组患者的31.1 min,总体手术时间减少了26%;而时间缩短最明显的手术步骤是“术中计划的回顾”,平均时间缩短2.1 min,且效率提高了73.3%。 一项对115例患者使用TSolution One机器人系统的多中心前瞻性研究结果显示, TSolution One 机器人辅助全膝关节置换的学习曲线为10-20例[42],但与BELL等[9]的研究以及大多数关于这一主题的研究相同,完成机器人辅助全膝关节置换的手术医师都是接受过进修医生培训的资深外科医生。所以为了评估普通骨科医生的机器人辅助全膝关节置换学习曲线情况,ALI等[43]回顾性分析了2名未接受过进修医生培训的骨科医生在分别完成60例机器人辅助全膝关节置换与20例传统全膝关节置换后,最终报道普通的骨科医生可以在前40个病例中完成机器人辅助全膝关节置换的学习曲线,换而言之,他们有可能在前40例手术内完成与传统全膝关节置换时间框架相近的机器人辅助全膝关节置换。 2.3.2 成本与效益 有研究显示机器人辅助系统需要昂贵的使用成本来支撑完成每一例全膝关节置换,其中包括术前影像采集、基础系统、一次性用品的消耗以及与术中操作相关的各类成本,且预估的初始启动成本可达到约80万美元之多,此外当每位患者决定并实施机器人辅助全膝关节置换后就会产生约1 500美元的固定费用,其对一次性用品消耗的成本为750-1 300美元[11,44]。对于需影像数据的机器人系统,术前患者影像学数据的采集工作十分关键,据研究报道这部分的成本至少为260美元,并且大多数此类机器人系统的年维护成本在4万-15万美元,除此之外对整个手术团队进行培训仍需要额外的成本消耗[45]。 VERMUE等[46]设计了一个马尔可夫(Markov)状态转移模型,来模拟平均年龄为67岁因原发性膝骨关节炎行全膝关节置换后20年间患者的术后状况并对其进行研究,最终报道从社会整体收益的角度来看,每台手术机器人每年需至少完成253例机器人辅助全膝关节置换才可能实现成本效益化,即因为新技术给整个社会带来的收益超过其使用成本,而机器人系统也主要通过降低全膝关节置换整体翻修率来实现这一点。另一项基于马尔可夫模型的对于全膝关节置换术后患者的终生结果研究显示,对于一个中等规模(每年可完成100例机器人辅助全膝关节置换)的医疗机构来说,只要每年的机器人辅助全膝关节置换的术后翻修率保持在1.6%以下,并且保证生活质量指数大于0.84,就可以实现成本效益化,否则不建议进行机器人辅助全膝关节置换[47],以避免不必要的医疗资源的消耗。 对于患者而言,目前接受机器人辅助全膝关节置换所需的花费仍然较传统全膝关节置换等其它手术方式的更多。STEFFENS等[48]比较了2018年10月至2019年6月间MAKO 机器人辅助全膝关节置换和计算机导航全膝关节置换的住院成本,并报道称若将前期手术设备的准备以及维护成本计入住院成本时,机器人辅助全膝关节置换的平均住院花销明显比计算机导航全膝关节置换更高(21 507.6美元 vs. 19 659.7美元,P=0.034)。 2.3.3 机器人系统的相关并发症 尽管机器人辅助系统的术后并发症并不常见,但机器人辅助全膝关节置换术中需在膝关节的骨性结构上植入定位螺钉和刚性参考架(需要与固定螺钉配合使用)以执行膝解剖结构注册和光学追踪。这些螺钉就会引起一些只与机器人辅助全膝关节置换相关的并发症,包括螺钉浅表部位的感染、钉道骨髓炎、螺钉部位的应力性骨折、血管损伤、血肿和骨化性肌炎等。为了降低螺钉处骨折的风险,BAEK等[49]在81例MAKO机器人辅助全膝关节置换患者中使用了单骨皮质螺钉,经过术后1年的随访,81例患者均未发现螺钉处出现骨折,这可能与螺钉与骨性结构的接触减少有关。而THOMAS 等[50]最近报道,在共7 336例机器人辅助导航全膝关节置换与机器人辅助全膝关节置换中,关于手术所用螺钉的总体并发症发生率为1.4%,术中及术后并发症的发生率分别为1.4%和1.1%,其中最常见的术中并发症是螺钉的脱位、断裂及松动(占所有术中并发症的40%),其最终可导致机器人辅助全膝关节置换与机器人辅助导航全膝关节置换的“流产”,不得不转而采用传统全膝关节置换。最常见的术后并发症是与螺钉造成的炎症相关的并发症(占所有术后并发症的 83%),其中包括皮肤浅表部位感染、蜂窝组织炎和螺钉处的刺激感,最终可能造成住院成本的增加甚至需要进行二次手术处理,这产生了不必要的经济负担。"

| [1] 边焱焱,程开源,常晓,等.2011至2019年中国人工髋膝关节置换手术量的初步统计与分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(21):1453-1460. [2] 邵宏翊,吴立东,曹光磊,等.国产机器人辅助全膝关节置换的精准性:一项多中心随机对照临床研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(4): 310-316. [3] ROBERTSSON O, DUNBAR M, PEHRSSON T, et al. Patient satisfaction after knee arthroplasty: a report on 27 372 knees operated on between 1981 and 1995 in Sweden. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(3):262-267. [4] SCOTT CE, HOWIE CR, MACDONALD D, et al. Predicting dissatisfaction following total knee replacement: a prospective study of 1217 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(9):1253-1258. [5] SIRES JD, WILSON CJ. CT validation of intraoperative implant position and knee alignment as determined by the MAKO total knee arthroplasty system. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(10):1133-1137. [6] SONG EK, SEON JK, YIM JH, et al. Robotic-assisted TKA reduces postoperative alignment outliers and improves gap balance compared to conventional TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):118-126. [7] SULTAN AA, SAMUEL LT, KHLOPAS A, et al. Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty more accurately restored the posterior condylar offset ratio and the insall-salvati index compared to the manual technique: a cohort-matched study. Surg Technol Int. 2019;34:409-413. [8] 李超,刘宇博,张帅,等.功能对线与限制性运动对线机器人辅助全膝关节置换短期临床研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(4):325-332. [9] BELL C, GRAU L, OROZCO F, et al. The successful implementation of the Navio robotic technology required 29 cases. J Robot Surg. 2022;16(3):495-499. [10] KAYANI B, KONAN S, HUQ SS, et al. Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty has a learning curve of seven cases for integration into the surgical workflow but no learning curve effect for accuracy of implant positioning. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(4):1132-1141. [11] LIOW MHL, CHIN PL, PANG HN, et al. THINK surgical TSolution-One(®) (Robodoc) total knee arthroplasty. SICOT J. 2017;3:63. [12] VANLOMMEL L, NEVEN E, ANDERSON M B, et al. The initial learning curve for the ROSA® Knee System can be achieved in 6-11 cases for operative time and has similar 90-day complication rates with improved implant alignment compared to manual instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. J Exp Orthop. 2021;8(1):119. [13] WAKELIN EA, SHALHOUB S, LAWRENCE JM, et al. Improved total knee arthroplasty pain outcome when joint gap targets are achieved throughout flexion. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(3):939-947. [14] KAYANI B, KONAN S, AYUOB A, et al. Robotic technology in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. EFORT Open Rev. 2019;4(10):611-617. [15] MANCINO F, CACCIOLA G, MALAHIAS M A, et al. What are the benefits of robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty over conventional manual total knee arthroplasty? A systematic review of comparative studies. Orthop Rev. 2020;12(Suppl 1):8657. [16] INNOCENTI B, BORI E. Robotics in orthopaedic surgery: why, what and how? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(12):2035-2042. [17] SOUSA PL, SCULCO PK, MAYMAN DJ, et al. Robots in the operating room during hip and knee arthroplasty. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020;13(3): 309-317. [18] SIDDIQI A, HARDAKER WM, EACHEMPATI KK, et al. Advances in computer-aided technology for total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2017;40(6):338-352. [19] MARCHAND R C, SODHI N, KHLOPAS A, et al. Patient satisfaction outcomes after robotic arm-assisted total knee arthroplasty: a short-term evaluation. J Knee Surg. 2017;30(9):849-853. [20] 冼达亨,赵晶,王英杰,等.机器人辅助全膝关节置换治疗合并关节外畸形的外翻膝1例报道及文献复习[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023, 16(4):367-371. [21] SIDDIQI A, MONT MA, KREBS VE, et al. Not all robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty are the same. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29(2):45-59. [22] JACOFSKY DJ, ALLEN M. Robotics in arthroplasty: a comprehensive review. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10):2353-2363. [23] PARRATTE S, PRICE AJ, JEYS LM, et al. Accuracy of a new robotically assisted technique for total knee arthroplasty: a cadaveric study. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(11):2799-2803. [24] SEIDENSTEIN A, BIRMINGHAM M, FORAN J, et al. Better accuracy and reproducibility of a new robotically-assisted system for total knee arthroplasty compared to conventional instrumentation: a cadaveric study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(3):859-866. [25] KEGGI JM, WAKELIN EA, KOENIG JA, et al. Impact of intra-operative predictive ligament balance on post-operative balance and patient outcome in TKA: a prospective multicenter study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(12):2165-2174. [26] BLUM CL, LEPKOWSKY E, HUSSEIN A, et al. Patient expectations and satisfaction in robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty: a prospective two-year outcome study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(12):2155-2164. [27] DECKEY DG, ROSENOW CS, VERHEY JT, et al. Robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty improves accuracy and precision compared to conventional techniques. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-b(6 Supple A):74-80. [28] SIRES JD, CRAIK JD, WILSON J. Accuracy of bone resection in MAKO total knee robotic-assisted surgery. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(7):745-748. [29] KIM YH, YOON SH, PARK JW. Does Robotic-assisted TKA result in better outcome scores or long-term survivorship than conventional TKA? A randomized, controlled trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020;478(2):266-275. [30] JEON SW, KIM KI, SONG SJ. Robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty does not improve long-term clinical and radiologic outcomes. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(8):1656-1661. [31] CHO KJ, SEON JK, JANG WY, et al. Robotic versus conventional primary total knee arthroplasty: clinical and radiological long-term results with a minimum follow-up of ten years. Int Orthop. 2019;43(6):1345-1354. [32] SAVOV P, TUECKING LR, WINDHAGEN H, et al. Imageless robotic handpiece-assisted total knee arthroplasty: a learning curve analysis of surgical time and alignment accuracy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(12): 2119-2128. [33] THIENGWITTAYAPORN S, UTHAITAS P, SENWIRUCH C, et al. Imageless robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty accurately restores the radiological alignment with a short learning curve: a randomized controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2021;45(11):2851-2858. [34] BOLLARS P, BOECKXSTAENS A, MIEVIS J, et al. Preliminary experience with an image-free handheld robot for total knee arthroplasty: 77 cases compared with a matched control group. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020;30(4):723-729. [35] SHIN C, CROVETTI C, HUO E, et al. Unsatisfactory accuracy of recent robotic assisting system ROSA for total knee arthroplasty. J Exp Orthop. 2022;9(1):82. [36] FIGUEROA F, WAKELIN E, TWIGGS J, et al. Comparison between navigated reported position and postoperative computed tomography to evaluate accuracy in a robotic navigation system in total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2019;26(4):869-875. [37] SUERO EM, PLASKOS C, DIXON PL, et al. Adjustable cutting blocks improve alignment and surgical time in computer-assisted total knee replacement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(9):1736-1741. [38] RIVIÈRE C, IRANPOUR F, AUVINET E, et al. Alignment options for total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017; 103(7):1047-1056. [39] KAZARIAN GS, HADDAD FS, DONALDSON MJ, et al. Implant malalignment may be a risk factor for poor patient-reported outcomes measures (PROMs) following total knee arthroplasty (TKA). J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(6s): S129-S133. [40] VAN LIESHOUT WAM, VALKERING KP, KOENRAADT KLM, et al. The negative effect of joint line elevation after total knee arthroplasty on outcome. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(5):1477-1486. [41] VERMUE H, LUYCKX T, WINNOCK DE GRAVE P, et al. Robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty is associated with a learning curve for surgical time but not for component alignment, limb alignment and gap balancing. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(2):593-602. [42] MAHURE SA, TEO GM, KISSIN YD, et al. Learning curve for active robotic total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(8): 2666-2676. [43] ALI M, PHILLIPS D, KAMSON A, et al. Learning curve of robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty for non-fellowship-trained orthopedic surgeons. Arthroplast Today. 2022;13:194-198. [44] ST MART JP, GOH EL. The current state of robotics in total knee arthroplasty. EFORT Open Rev. 2021;6(4):270-279. [45] MOSCHETTI WE, KONOPKA JF, RUBASH HE, et al. Can robot-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty be cost-effective? A markov decision analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(4):759-765. [46] VERMUE H, TACK P, GRYSON T, et al. Can robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty be a cost-effective procedure? A Markov decision analysis. Knee. 2021;29:345-352. [47] RAJAN PV, KHLOPAS A, KLIKA A, et al. The Cost-effectiveness of robotic-assisted versus manual total knee arthroplasty: a markov model-based evaluation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2022;30(4):168-176. [48] STEFFENS D, KARUNARATNE S, MCBRIDE K, et al. Implementation of robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty in the public health system: a comparative cost analysis. Int Orthop. 2022;46(3):481-488. [49] BAEK J H, LEE SC, KIM JH, et al. Distal femoral tracker pin placement prevents delayed pin tract-induced fracture in robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty: results of minimum 1-year follow-up. J Knee Surg. 2022; 36(10):1102-1104. [50] THOMAS TL, GOH GS, NGUYEN MK, et al. Pin-related complications in computer navigated and robotic-assisted knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(11):2291-2307. [51] ELLIOTT J, SHATROV J, FRITSCH B, et al. Robotic-assisted knee arthroplasty: an evolution in progress. A concise review of the available systems and the data supporting them. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(12):2099-2117. [52] SIDDIQI A, HORAN T, MOLLOY RM, et al. A clinical review of robotic navigation in total knee arthroplasty: historical systems to modern design. EFORT Open Rev. 2021;6(4):252-269. [53] AGARWAL N, TO K, MCDONNELL S, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes in robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(11):3393-3409. [54] KHLOPAS A, SODHI N, SULTAN AA, et al. Robotic arm-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(7):2002-2006. [55] MANCINO F, ROSSI SMP, SANGALETTI R, et al. A new robotically assisted technique can improve outcomes of total knee arthroplasty comparing to an imageless navigation system. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;143(5): 2701-2711. [56] DEFRANCE MJ, YAYAC MF, COURTNEY PM, et al. The impact of author financial conflicts on robotic-assisted joint arthroplasty research. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(4):1462-1469. [57] BATAILLER C, PARRATTE S. Assistive technologies in knee arthroplasty: fashion or evolution? Rate of publications and national registries prove the Scott Parabola wrong. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(12):2027-2034. [58] ROSSI SMP, MANCINO F, SANGALETTI R, et al. Augmented reality in orthopedic surgery and its application in total joint arthroplasty: a systematic review. Appl Sci. 2022;12(10):5278. [59] 许中华.机器人辅助技术降低全膝关节置换创伤效应的前瞻性、随机对照研究[D].重庆:中国人民解放军陆军军医大学,2022. [60] 邵小龙,杜天舒,闫昭,等.机器人辅助全膝关节置换的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2022,11(7):521-525. [61] 张子安,张海宁,李海燕,等.机器人辅助技术在全膝关节置换手术中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(11):937-941. [62] 赵晶,余沐洋,彭慧明,等.机器人辅助全膝关节置换流程优化及学习曲线研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(4):333-339. [63] 智信,平航宇,彭伟,等.鸿鹄机器人辅助全膝关节置换学习曲线初步研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(4):340-346. [64] 荣根祥,张金陵,张弘景,等.机器人辅助全膝关节置换治疗膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J]实用骨科杂志,2022,28(11):976-981. |
| [1] | Li Yongjie, Fu Shenyu, Xia Yuan, Zhang Dakuan, Liu Hongju. Correlation of knee extensor muscle strength and spatiotemporal gait parameters with peak knee flexion/adduction moment in female patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1354-1358. |
| [2] | Li Chaojie, Gulati•Maitirouzi, Aierxiding•Abulaiti, Zheng Hui, Tu Hudi. Finite element analysis of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction at different flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1359-1364. |
| [3] | Min Meipeng, Wu Jin, URBA RAFI, Zhang Wenjie, Gao Jia, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Fan Lei. Role and significance of artificial intelligence preoperative planning in total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1372-1377. |
| [4] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [5] | Du Changling, Shi Hui, Zhang Shoutao, Meng Tao, Liu Dong, Li Jian, Cao Heng, Xu Chuang. Efficacy and safety of different applications of tranexamic acid in high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1409-1413. |
| [6] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [7] | Lin Zeyu, Xu Lin. Research progress in gout-induced bone destruction mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| [8] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [9] | Zhao Garida, Ren Yizhong, Han Changxu, Kong Lingyue, Jia Yanbo. Mechanism of Mongolian Medicine Erden-uril on osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1193-1199. |
| [10] | Han Bing, Liu Hongbin, Wang Hehong, Zhao Hanqing, Zhao Riguang, Sun Yiyan, Zhang Yu. Correlation between lower limb alignment and risk factors of patellofemoral pain syndrome in young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1211-1216. |
| [11] | Li Rui, Zhang Guihong, Wang Tao, Fan Ping. Effect of ginseng polysaccharide on the expression of prostaglandin E2/6-keto-prostaglandin 1alpha in traumatic osteoarthritis model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1235-1240. |
| [12] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [13] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [14] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [15] | Li Jiaqi, Huang Yuanli, Li Yan, Wang Chunren, Han Qianqian. Mechanism and influencing factors in molecular weight degradation of non-cross-linked hyaluronic acid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 747-752. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||