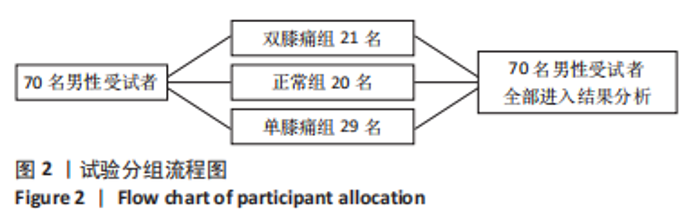
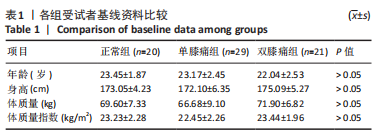
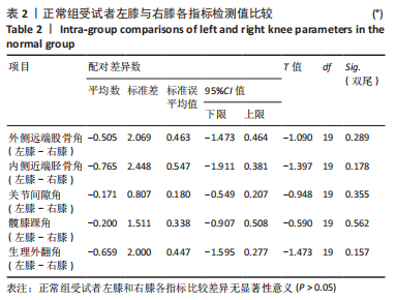
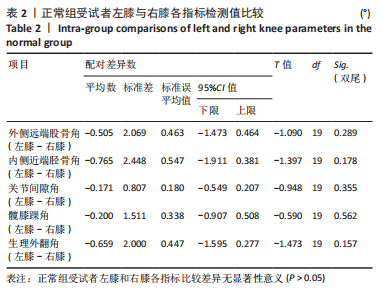
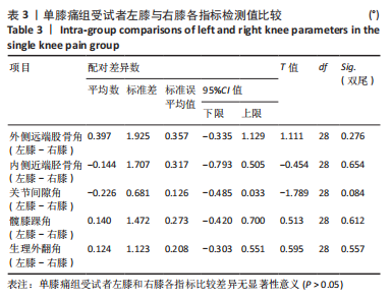
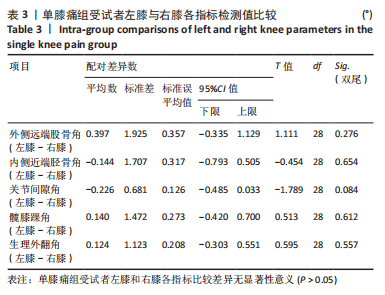
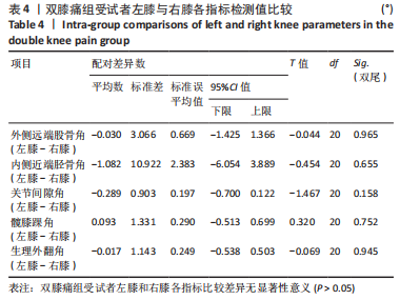
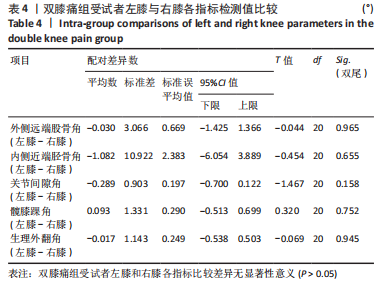
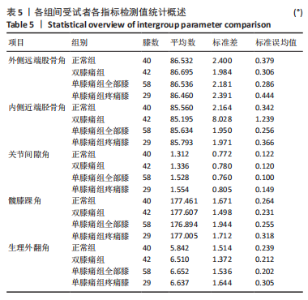
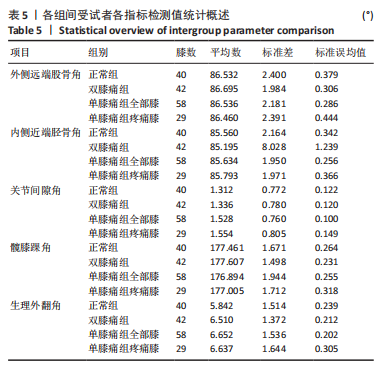
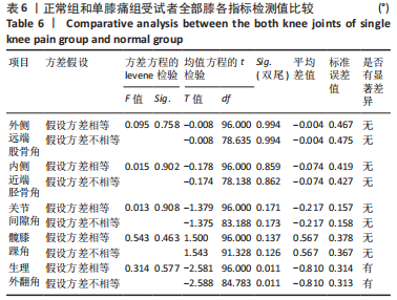
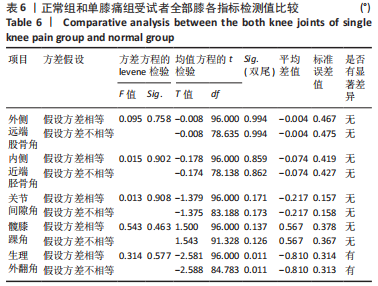
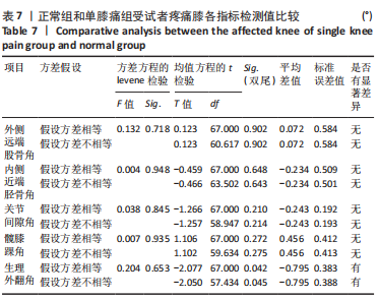
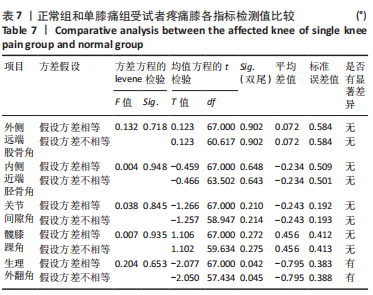
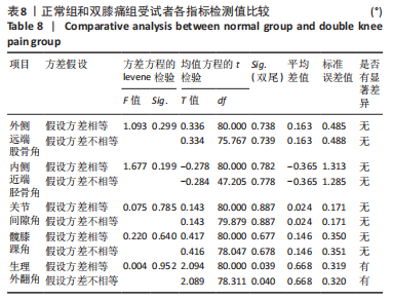
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (8): 1211-1216.doi: 10.12307/2023.858
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation between lower limb alignment and risk factors of patellofemoral pain syndrome in young men
Han Bing, Liu Hongbin, Wang Hehong, Zhao Hanqing, Zhao Riguang, Sun Yiyan, Zhang Yu
- Department of Orthopedics, 71 Group Army Hospital, Xuzhou 221004, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2022-10-18Accepted:2022-12-09Online:2024-03-18Published:2023-07-18 -
Contact:Liu Hongbin, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, 71 Group Army Hospital, Xuzhou 221004, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Han Bing, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, 71 Group Army Hospital, Xuzhou 221004, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Bing, Liu Hongbin, Wang Hehong, Zhao Hanqing, Zhao Riguang, Sun Yiyan, Zhang Yu. Correlation between lower limb alignment and risk factors of patellofemoral pain syndrome in young men[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1211-1216.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] CROSSLEY KM, STEFANIK JJ, SELFE J, et al. 2016 Patellofemoral pain consensus statement from the 4th International Patellofemoral Pain Research Retreat, Manchester. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(14):839-843. [2] BOLING M, PADUA D, MARSHALL S, et al. Gender differences in the incidence and prevalence of patellofemoral pain syndrome. Scand J Med Science Sports. 2010;20:725-730. [3] WITVROUW E, CALLAGHAN MJ, STEFANIK JJ, et al. Patellofemoral pain: consensus statement from the 3rd International Patellofemoral Pain Research Retreat held in Vancouver, September 2013. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48:411-414. [4] STATHOPULU E, BAILDAM E. Anterior knee pain: a long-term follow-up. Rheumatology. 2003;42:380-382. [5] PRICE AJ, JONES J, ALLUM R. Chronic traumatic anterior knee pain. Injury. 2000; 31:373-378. [6] SANDOW MJ, GOODFELLOW JW. The natural history of anterior knee pain in adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985;67:36-38. [7] THOMAS M, WOOD L, SELFE J, et al. Anterior knee pain in younger adults as a precursor to subsequent patellofemoral osteoarthritis: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010;11:201. [8] CROSSLEY KM. Is patellofemoral osteoarthritis a common sequela of patellofemoral pain? Br J Sports Med. 2014;48:409-410. [9] 许杰,周文琪,罗小兵.髌股疼痛综合征研究热点与内容的可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(12):1877-1887. [10] 孙茂淋,何锐,张颖,等.健康人群下肢力线测量在全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(8):584-588. [11] 吴伟,郭万首.下肢全长X线检查的临床应用及其精准性的研究进展[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2017,10(1):84-87. [12] POST WR, DYE SF. Patellofemoral Pain: An Enigma Explained by Homeostasis and Common Sense. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2017;46(2):92-100. [13] DAVIS IS, POWERS CM. Patellofemoral pain syndrome: proximal, distal, and local factors, an international retreat, April 30-May 2, 2009, Fells Point, Baltimore, MD. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2010;40:A1-16. [14] POWERS C, BOLGLA L, CALLAGHAN M, et al. Patellofemoral Research Retreat, Ghent, Belgium, patellofemoral pain: proximal, distal, and local factors. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012;42:A1-54. [15] GILES LS, WEBSTER KE, MCCLELLAND JA, et al. Does quadriceps atrophy exist in individuals with patellofemoral pain? A systematic literature review with meta-analysis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2013;43:766-776. [16] VAN TIGGELEN D, WITVROUW E, COOREVITS P, et al. Analysis of isokinetic parameters in the development of anterior knee pain syndrome: a prospective study in a military setting. Isokinet Exerc Sci. 2004;12:223-228. [17] WARYASZ GR, MCDERMOTT AY. Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS): a systematic review of anatomy and potential risk factors. Dyn Med. 2008;7:9. [18] WITVROUW E, LYSENS R, BELLEMANS J, et al. Vanderstraeten G. Intrinsic risk factors for the development of anterior knee pain in an athletic population. A two-year prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28:480-489. [19] MUCHA MD, CALDWELL W, SCHLUETER EL, et al. Hip abductor strength and lower extremity running related injury in distance runners: a systematic review. J Sci Med Sport. 2017;20:349-355. [20] SEMCIW A, NEATE R, PIZZARI T. Running related gluteus medius function in health and injury: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2016; 30:98-110. [21] RATHLEFF MS, RATHLEFF CR, CROSSLEY KM, et al. Is hip strength a risk factor for patellofemoral pain? A systematic review and metaanalysis. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48:1088. [22] CARLSON VR, BODEN BP, SHEN A, et al. The tibial tubercle–trochlear groove distance is greater in patients with patellofemoral pain: implications for the origin of pain and clinical interventions. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45:1110-1116. [23] AYSIN IK, ASKIN A, METE BD, et al. Investigation of the relationship between anterior knee pain and chondromalacia patellae and patellofemoral malalignment. Eurasian J Med. 2018;50:28-33. [24] ERDOGANOGLU Y, PEPE M, KAYA D, et al. Lower extremity alignment due to patellofemoral syndrome and dynamic postural balance. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2020;28(1):2309499019900819. [25] CITAKER S, KAYA D, YUKSEL I, et al. Static balance in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome. Sports Health. 2011;3(6):524-527. [26] NGUYEN AD, SHULTZ SJ. Identifying relationships among lower extremity alignment characteristics. J Athl Train. 2009;44(5):511-518. [27] LANKHORST NE, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA SMA, VAN MIDDELKOOP M. Risk factors for patellofemoral pain syndrome: A systematic review. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012;42(2):81-94. [28] PARK SK, STEFANYSHYN DJ. Greater Q angle may not be a risk factor of patellofemoral pain syndrome. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2011;26(4):392-396. [29] 凡廷旭,黄伟,胡宁,等.女性下肢力线旋转与髌股关节疼痛的临床研究[J].重庆医学,2014,43(32):4272-4279. [30] BOLING MC, NGUYEN AD, PADUA DA, et al. Gender-Specific Risk Factor Profiles for Patellofemoral Pain. Clin J Sport Med. 2021;31(1):49-56. [31] SELFE J, JANSSEN J, CALLAGHAN M, et al. Are there three main subgroups within the patellofemoral pain population? A detailed characterisation study of 127 patients to help develop targeted intervention (TIPPs). Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(14):873-880. [32] SELFE J, CALLAGAN M, WITVROUW E, et al. Targeted interventions for patellofemoral pain syndrome (TIPPS):classification of clinical subgroups. BMJ Open. 2013;3(9):e003795. [33] SELHORST M, RICE W, DEGENHART T, et al. Evaluation of a treatment algorithm for patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome: a pilot study. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2015;10:178-188. [34] CITAKER S, KAYA D, YUKSEL I, et al. Static balance in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome. Sports Health. 2011;3(6):524-527. |
| [1] | Liu Guangluan, Guo Zonglei, Ge Jin, Huang Dong, Wang Yehua. Anatomic risk factors for medial meniscus posterior root tears combined with anterior cruciate ligament injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 663-668. |
| [2] | Shen Lianwei, Zhu Hongliu, Wang Wei. Risk factor analysis of metabolic syndrome and construction of a nomogram prediction model in middle-aged and elderly people [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 657-662. |
| [3] | Yu Jian, Zhou Bingqian, Wang Zhao, Li Yue, Chang Yaru, Cao Hong. Comparison of random forest model and logistic regression model in predicting the prolonged length of stay of hip fracture patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5413-5420. |
| [4] | Meng Xiangli, Lyu Xiaohong. Effects of eccentric exercise patterns on exercise-induced muscle damage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5132-5136. |
| [5] | Yuan Haibo, Li Dongya, Pan Bin, Guan Kai, Chen Feng, Yuan Feng, Wu Jibin. Sagittal related factors of upper lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4984-4989. |
| [6] | Wang Kaiyu, Hu Peng, Wei Zairong, Huang Guangtao, Zhou Jian, He Guijia, Nie Kaiyu. Use of expanders and implants in breast reconstruction complicated with infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 461-469. |
| [7] | Zhang Qian, Bian Minjie, He Qin, Huang Dongfeng. Predicting vascular mild cognitive impairment based on vascular risk factors: construction and application of a support vector machine model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 287-292. |
| [8] | Weng Youlin, Cai Yu, Li Zutao, Guo Bin, Xu Jiangbo. Construction and validation of a model for predicting postoperative severe complications of intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2915-2920. |
| [9] | Wu Qian, Liu Lingfeng, Li Lisong, Lu Yingjie, Zhou Liyu, Xu Wu, Huang Lixin, Jiang Dinghua. Deep vein thrombosis distribution and risk factors after total knee arthroplasty during enhanced recovery after surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 2044-2050. |
| [10] | Wu Liang, Wang Qiang, Wang Wenbo, Xin Tianwen, Xi Kun, Tang Jincheng, Xu Jingzhi, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Risk factors for traumatic central cord syndrome underlying with cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1388-1394. |
| [11] | He Shiping, Jia Dazhou, Li Xiaolei, Wang Qiang. Establishment of prediction model of blood transfusion after proximal femoral nail anti-rotation fixation of femoral intertrochanteric fracture in elderly adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 929-933. |
| [12] | Rong Yi, Yu Hao, Yang Junfeng, Wang Lan, Zhang Jiannan, Shao Yang. Risk factor analysis and prediction of deep venous thrombosis of lower extremity in elderly patients with hip fracture after operation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5357-5363. |
| [13] | Zhou Shicheng, Han Hongguang, Ji Fang, Xu Liying, Zhang Xiaohui, Sun Chang. Effect and histocompatibility of expended polytetrafluoroethylene in modified Blalock-Taussig shunt [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3394-3400. |
| [14] | Liu Chen, Hu Chengzhe, Yin Xun, Yu Ziheng, Yang Jiandong. Risk factors of residual pain after percutaneous vertebral augmentation for osteoporotic thoracolumbar compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2900-2905. |
| [15] | Xu Jie, Zhou Wenqi, Luo Xiaobing. Visual analysis of patellofemoral pain syndrome research hotspots and content [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1877-1887. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||