Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (21): 3394-3400.doi: 10.12307/2022.650
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect and histocompatibility of expended polytetrafluoroethylene in modified Blalock-Taussig shunt
Zhou Shicheng1, Han Hongguang2, Ji Fang3, Xu Liying2, Zhang Xiaohui2, Sun Chang2
- 1Graduate School, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, China Medical University, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, 3Medical Management Division, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2021-10-12Accepted:2021-11-19Online:2022-07-28Published:2022-01-28 -
Contact:Han Hongguang, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zhou Shicheng, Master candidate, Physician, Graduate School, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, China Medical University, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:The 2020 Shenyang Science and Technology Plan Project, No. 20-205-4-016 (to HHG); the Top-Notch Military Medical Science and Technology Youth Training Program, No. 20QNPY090 (to HHG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Shicheng, Han Hongguang, Ji Fang, Xu Liying, Zhang Xiaohui, Sun Chang. Effect and histocompatibility of expended polytetrafluoroethylene in modified Blalock-Taussig shunt[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3394-3400.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
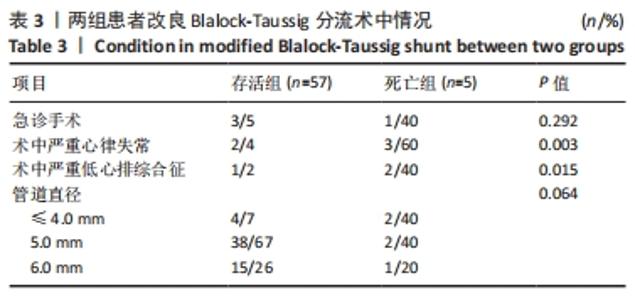
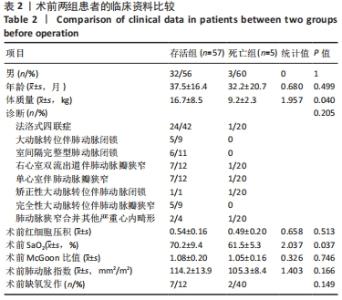
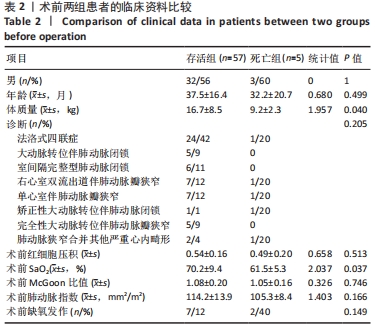
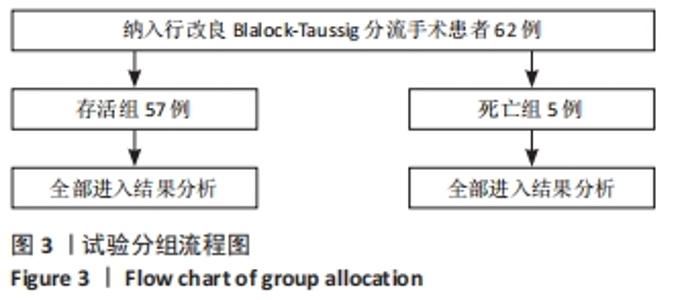
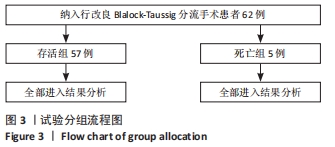
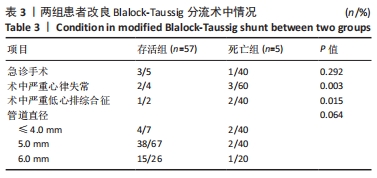
2.4 两组患者手术效果与结局分析 2.4.1 术中概况 部分患者因严重缺氧发作进入监护室紧急行气管插管并随后急诊手术,生存组有6例行术前插管(11%),3例行急诊手术(5%);死亡组有2例行术前插管(40%),1例行急诊手术(20%)。术中发生不良事件(严重低术中严重低心排综合征和心律失常)5例(8%),积极静脉应用抗心律失常药物及血管活性药物,即刻进行血气分析,纠正电解质紊乱,纠治后血压及心律均较为平稳。存活组中4例选用≤4.0 mm管道,38例患者选用5.0 mm管道,15例选用6 mm管道;死亡组中2例选用≤4.0 mm管道,2例选用5.0 mm管道,1例选用6 mm管道。两组患者术中情况,见表3。"
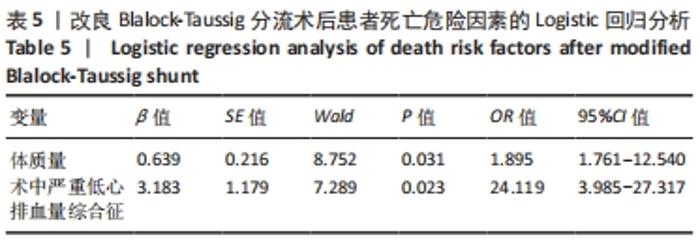
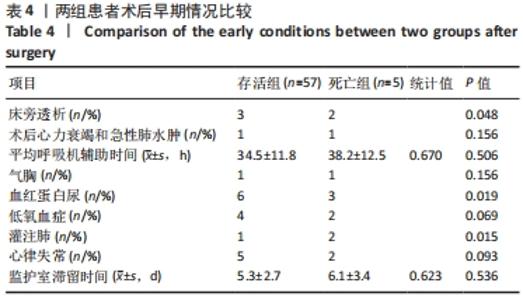
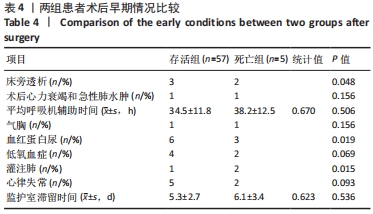
62例中术后早期死亡5例(8%),其中术后心力衰竭和急性肺水肿2例(3%),表现为突然的心跳、血压、SaO2迅速下降,即刻床旁心肺复苏无效后死亡;术后3例(5%)发生严重低心排综合征。术后由于存在人工管道分流作用,肺循环血流、心内分流明显增加,从而导致体循环血流减少,脉压差增加。血流动力学改变加重心脏负荷的同时也影响冠状动脉的灌注。因此,获得足够的舒张压以期保证冠脉灌注,适当给予血管活性药物将血压维持在较高水平。 改良Blalock-Taussig分流手术监护成功的关键是术前准确把握手术指征,术后严格控制肺循环血流。术后监护过程中若出现下述情况,应积极处理:①低SaO2、低血压:考虑纠治低血容量、贫血、术后低心排血量综合征等进行综合救治;②人工管道分流失效:尽早提高血压,满足各脏器灌注,必要时应用肺血管靶向药物来降低肺血管阻力;③血氧饱和度过高和高血压:适当减少分钟通气量,增加呼吸末正压,加强心血管收缩以及增加心室舒张期在心动周期中的占比,增加肺血管阻力;④难以纠治的低SaO2和体循环休克:积极处理后若无明显改善,则应及时与外科医生沟通协调,进一步诊治。 2.5 二元Logistic回归结果分析 二元Logistic逐步回归分析结果显示,术后患者低体质量、术中严重低心排血量综合征是改良Blalock-Taussig分流术后患者死亡的危险因素,见表5。"
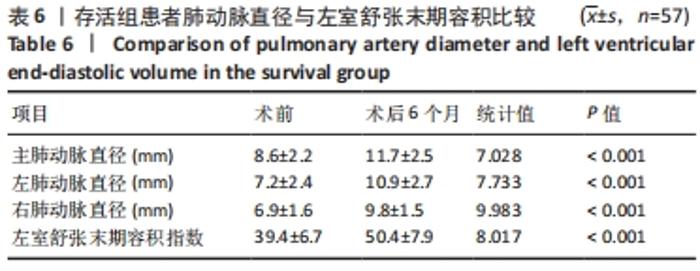
2.6 存活组患者术后随访情况 改良Blalock-Taussig分流术后进行严密随访尤为重要,主要观察人工血管通畅情况及主肺动脉、左右肺动脉的发育情况,选择适当时机后行二期矫治术。 57例患者术后均有不同程度好转并顺利出院,获得术后随访。术后定期随访时行动脉血气分析、胸部正侧位X射线检查、彩色多普勒超声心动图及体表心电图检查。术后复查,患者发绀症状消失,营养状态明显好转,体质量增加。彩超复查记录的肺动脉内径及左心室内径变化,同时观察人工管道的血流和通畅情况,未发现患者分流管堵塞,人工管道通畅率良好。随访肺动脉内径及左心室内径变化与术前记录进行比较,发现改良Blalock-Taussig分流手术使患者左心室和肺动脉发育均明显改善(P < 0.05),见表6,表明改良Blalock-Taussig分流术后都可以促进肺血管和左心室的发育。同时57例患者术后12个月随访期间无不良反应发生,人工血管与组织相容性较好。"
| [1] 胡盛寿.《先天性心脏病外科治疗中国专家共识》述评[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2021,28(1):1-3. [2] 宋晓琪,杜欣为,王顺民,等.基于回归分析和机器学习的先天性心脏病患儿术后住院死亡预测模型的建立—单中心12年大数据汇总分析[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2020,36(2):65-73. [3] 葛同开,陈寄梅,庄建,等.改良Blalock-Taussig分流术治疗新生儿期紫绀型先天性心脏病的疗效分析[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2020,27(7):737-741. [4] YUAN SM, SHINFELD A, RAANANI E. The Blalock-Taussig shunt. J Card Surg. 2009;24(2):101-108. [5] BREDY C, MINISTERI M, KEMPNY A, et al. New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification in adults with congenital heart disease: relation to objective measures of exercise and outcome. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes. 2018;4(1):51-58. [6] 刘玉洁,徐卓明,朱丽敏,等.新生儿改良Blalock-Taussing分流术后疗效的影响因素[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2018,34(10):577-580. [7] 严拓,刘雅文,吴灿,等.人工血管研究现状与应用优势[J].中国组织工程究,2018,22(30):4849-4854. [8] 单亚平,张惠锋,叶明,等.生物修饰ePTFE促进内皮化的研究[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2018,39(3):219-224. [9] POLLMANN AS, LEWIS DR, GUPTA RR. Structural integrity of intraocular lenses with eyelets in a model of transscleral fixation with the Gore-Tex suture. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2020;46(4):617-621. [10] 何艳平,马德春,李磊,等.人工血管材料血液相容性及表面改性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(8):1272-1276. [11] 杨柳,姜南,徐扬阳,等.膨体聚四氟乙烯与人脂肪干细胞的体外生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(12):1932-1937. [12] HAGDORN QAJ, BERGER RMF. Setting the stage for increasing diversity in congenital cardiology: let’s celebrate the 75th anniversary of the Blalock-Thomas-Taussig shunt. Cardiol Young. 2020;30(3):446-447. [13] DAVE HH. Modified Blalock-Taussig shunt: simple but unpredictable. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016;50(1):178-179. [14] ZURAKOWSKI D, JONAS RA. The many factors leading to resurgence of the Blalock shunt for tetralogy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;161(2): 396-399. [15] 张本,龚德军,张锡武,等.磷酰胆碱表面改性增强聚四氟乙烯心脏瓣膜材料的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(34): 5509-5514. [16] 陈宝林.王东安.用于心血管医疗装置的聚合物材料表面构建与生物相容性评价:聚合物生物材料表面的内皮细胞组织工程化改性[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(30):4515-4523. [17] MUMTAZ MA, ROSENTHAL G, QURESHI A, et al. Melbourne shunt promotes growth of diminutive central pulmonary arteries in patients with pulmonary atresia, ventricular septal defect, and systemic-to-pulmonary collateral arteries. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85(6):2079-2084. [18] LI D, WANG Y, LIN K, et al. Modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt: A Single-Center Experience and Follow-Up. Heart Surg Forum. 2020;23(1): E53-E57. [19] CAO JY, PHAN K, AYER J, et al. Long term survival of hypoplastic left heart syndrome infants: Meta-analysis comparing outcomes from the modified Blalock-Taussig shunt and the right ventricle to pulmonary artery shunt. Int J Cardiol. 2018;254:107-116. [20] 孙阳雪,闫军.改良Blalock-Taussig分流术分流管道选择策略研究进展[J].临床军医杂志,2020,48(4):472-474. [21] 朱耀斌,张雅娉,李志强,等.先天性心脏病改良Blalock-Taussig管道闭塞的危险因素分析[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2020,34(2): 125-127. [22] MOOFUVONG M, TANASANSUTTIPORN J, WASINWONG W, et al. Predictors of death after receiving a modified Blalock-Taussig shunt in cyanotic heart children: A competing risk analysis. PLoS One. 2021; 16(1):e245754. [23] CHITTITHAVORN V, DUANGPAKDEE P, RERGKLIANG C, et al. Risk factors for in-hospital shunt thrombosis and mortality in patients weighing less than 3 kg with functionally univentricular heart undergoing a modified Blalock-Taussig shunt. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2017;25(3): 407-413. [24] 姜正明,陈魁,胡彩娜.聚四氟乙烯人工血管对血小板聚集的影响及细胞相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(47):7064-7069. [25] MOUSAVI SR, MOATAMEDI MR, AKBARI-MM. Comparing frozen saphenous vein with Gore-tex in vascular access for chronic hemodialysis. Hemodial Int. 2011;15(4):559-562. [26] 李建民.膨体聚四氟乙烯假体隆鼻整形的效果:随机对照临床试验方案[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(6):980-984. [27] 侯亮,张扬,孙轶峰,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞复合两种填充材料体外生物相容性的比较[J].中国美容医学,2017,26(7):48-52. [28] GEDICKE M, MORGAN G, PARRY A, et al. Risk factors for acute shunt blockage in children after modified Blalock-Taussig shunt operations. Heart Vessels. 2010;25(5):405-409. [29] 李丹,王旭,李霞,等.先天性心脏病体-肺分流术后管道梗阻的早中期结果及危险因素分析[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2019, 35(3):145-149. [30] AHMAD U, FATIMI SH, NAQVI I, et al. Modified Blalock-Taussig shunt: immediate and short-term follow-up results in neonates. Heart Lung Circ. 2008;17(1):54-58. [31] SAHOO M, SAHU M, KALE S, et al. Serous fluid leakage following modified Blalock-Taussig operation using PTFE grafts. Indian Heart J. 2001;53(3):328-331. [32] ZHU Y, ZHANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Study on the correlation of modified Blalock Taussig duct occlusion and platelet parameters in congenital heart disease. Asian J Surg. 2019;42(5):599-603. [33] WELLS WJ, YU RJ, BATRA AS, et al. Obstruction in modified Blalock shunts: a quantitative analysis with clinical correlation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79(6):2072-2076. [34] MOHAMMADI S, BENHAMEID O, CAMPBELL A, et al. Could we still improve early and interim outcome after prosthetic systemic-pulmonary shunt? A risk factors analysis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;34(3):545-549. [35] ZHOU T, WANG Y, LIU J, et al. Pulmonary artery growth after Modified Blalock-Taussig shunt: A single center experience. Asian J Surg. 2020; 43(2):428-437. [36] ABDELMASSIH AF, MENSHAWEY R, MENSHAWEY E, et al. Blalock-Taussig Shunt versus Ductal Stent in the Palliation of Duct Dependent Pulmonary Circulation; A Systematic Review and Metanalysis. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2021;100885. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2021.100885. [37] BOUMA BJ, MULDER BJ. Changing Landscape of Congenital Heart Disease. Circ Res. 2017;120(6):908-922. [38] MOUSAVI SR, MOATAMEDI MR, AKBARI MM. Comparing frozen saphenous vein with Gore-tex in vascular access for chronic hemodialysis. Hemodial Int. 2011;15(4):559-562. [39] WILLIAMS JA, BANSAL AK, KIM BJ, et al. Two thousand Blalock-Taussig shunts: a six-decade experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84(6):2070-2075. [40] LI JS, YOW E,BEREZNY KY, et al. Clinical outcomes of palliative surgery including a systemic-to-pulmonary artery shunt in infants with cyanotic congenital heart disease: does aspirin make a difference? Circulation. 2007;116(3):293-297. [41] ALSAGHEIR A, KOZIARZ A, MAKHDOUM A, et al. Duct stenting versus modified alock-Taussig shunt in neonates and infants with duct-dependent pulmonary blood flow: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;161(2):379-390. [42] GEDICKE M, MORGAN G, PARRY A, et al. Risk factors for acute shunt blockage in children after modified Blalock-Taussig shunt operations. Heart Vessels. 2010;25(5):405-409. [43] SANTORO G, CAPOZZI G, CAIANIELLO G, et al. Pulmonary artery growth after palliation of congenital heart disease with duct-dependent pulmonary circulation: arterial duct stenting versus surgical shunt. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(23):2180-2186. [44] ARNAZ A, PIŞKIN S, OĞUZ GN, et al.Effect of modified Blalock-Taussig shunt anastomosis angle and pulmonary artery diameter on pulmonary flow. Anatol J Cardiol. 2018;20(1):2-8. [45] AZBOY D, TEMIZTÜRK Z. Clinical Outcomes after Biologic Graft Use for the Creation of Blalock-Taussig Shunt in Critically Ill Patients with Thrombophilia. Heart Surgery Forum. 2020;23(6):E718-E724. [46] PEA-TRUJILLO V, GALLO-BERNAL S, MELO JFF. Cardiology in the Young Mediastinal mass after a Blalock-Taussig shunt: utility of CT angiography. Cardiology in the Young. 2020;30(5):722-723. [47] 张程,王鹏程,吴柯叶,等.新型国产生物源性胶原涂层涤纶血管抗血浆渗出及抗出血性能研究初探[J].中国体外循环杂志,2021, 19(4):235-238. |
| [1] | Wu Liang, Wang Qiang, Wang Wenbo, Xin Tianwen, Xi Kun, Tang Jincheng, Xu Jingzhi, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Risk factors for traumatic central cord syndrome underlying with cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1388-1394. |
| [2] | He Shiping, Jia Dazhou, Li Xiaolei, Wang Qiang. Establishment of prediction model of blood transfusion after proximal femoral nail anti-rotation fixation of femoral intertrochanteric fracture in elderly adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 929-933. |
| [3] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [4] | Yang Feng, Zhao Qian, Zhang Shixuan, Zhao Tienan, Feng Bo. Effectiveness and safety of rapamycin combined with CD133 antibody stent in preventing vascular restenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 579-584. |
| [5] | Jin Herong, Cui Jingbin, Shao Cang. Materials of interbody fusion cage: advantages and focus of clinical application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3592-3597. |
| [6] | Li Duchenhui, Tian Ai, Tang Zhenglong. Angiogenesis induced by bone bioscaffold materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3602-3608. |
| [7] | Liu Liang, Hu Gaoquan, Wei Zhao, Chen Lin, Hong Feng. Potential of bacterial nanocellulose/polydopamine composite tubes as small-diameter artificial blood vessel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3535-3542. |
| [8] | Guo Yangyan, Yu Zhengwen, Zhang Jian. Research hotspots of magnesium alloy biomaterials in an in vivo animal [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3556-3565. |
| [9] | Feng Le, Qiu Peng, Liu Min, Zhou Hui. Characterization of chitosan-modified polyetheretherketone and its effect on MC3T3-E1 cell adhesion and proliferation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3351-3356. |
| [10] | Gao Feifei, Du Bin, Liu Xin, Chen Hao, Chen Yang, Hou Wei. Advantage of mesoporous materials in bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3401-3409. |
| [11] | Li Wenle, Wang Haosheng, Ning Lijun, Zhang Wenshi, Gao Sen, Sun Lijun, Hu Zhaohui. Analysis of the risk for bone cement leakage after percutaneous vertebroplasty in osteoporosis patients and model verification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1477-1482. |
| [12] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [13] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [14] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [15] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||