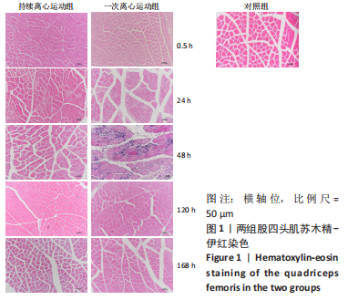
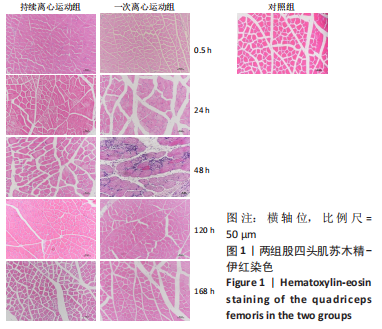
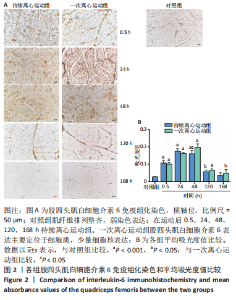
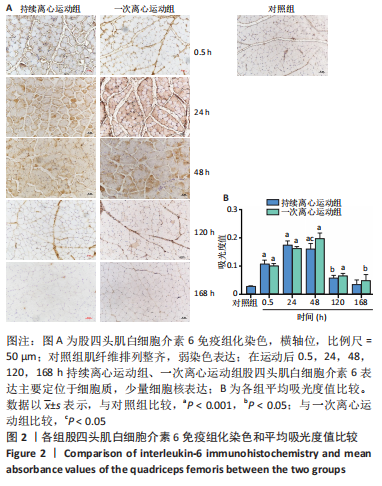
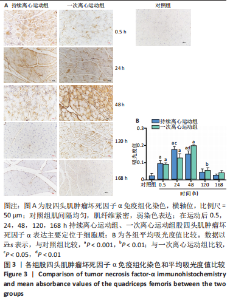
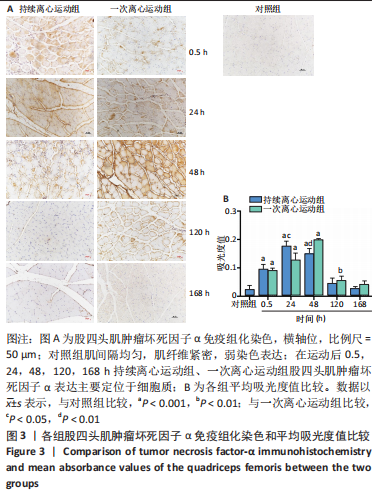
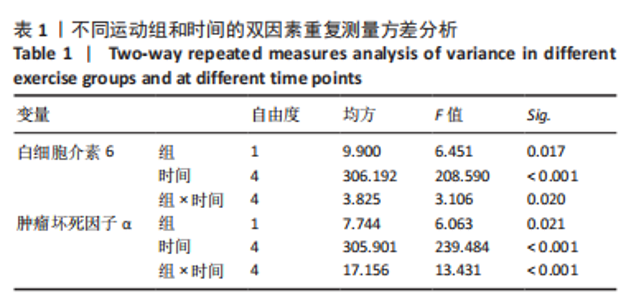
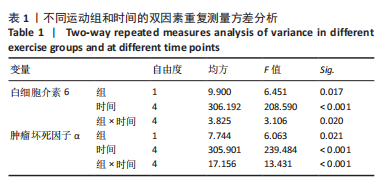
[1] BAI RJ, ZHANG HB, ZHAN HL, et al. Sports injury-related fingers and thumb deformity due to tendon or ligament rupture. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(9):1051-1058.
[2] SUN X, LAM WK, ZHANG X, et al. Systematic review of the role of footwear constructions in running biomechanics: implications for running-related injury and performance. J Sports Sci Med. 2020;19(1): 20-37.
[3] QU C, WU Z, XU M, et al. Cryotherapy models and timing-sequence recovery of exercise-induced muscle damage in middle- and long-distance runners. J Athl Train. 2020;55(4):329-335.
[4] BONTEMPS B, VERCRUYSSEN F, GRUET M, et al. Downhill running: What are the effects and how can we adapt? A narrative review. Sports Med. 2020;50(12):2083-2110.
[5] 吕晓虹,高月,刘强,等.运动性肌肉损伤:机制、磁共振定量评价及治疗研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2280-2286.
[6] MARKUS I, CONSTANTINI K, HOFFMAN JR, et al. Exercise-induced muscle damage: mechanism, assessment and nutritional factors to accelerate recovery. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2021;121(4):969-992.
[7] ORTEGA DR, LÓPEZ AM, AMAYA HM, et al. Tart cherry and pomegranate supplementations enhance recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage: a systematic review. Biol Sport. 2021;38(1):97-111.
[8] KYRIAKIDOU Y, WOOD C, FERRIER C, et al. The effect of Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation on exercise-induced muscle damage. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021;18(1):9.
[9] PAN SN, LYU XH, LIU Q, et al. Pay attention to the imaging study of sport injury and illness in Winter Olympics Sports. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(9):1013-1015.
[10] ARCK PC. When 3 Rs meet a forth R: Replacement, reduction and refinement of animals in research on reproduction. J Reprod Immunol. 2019; 132:54-59.
[11] 魏源,方春露,李良鸣,等.延迟性肌肉酸痛动物模型的建立及组织形态学观察(英文)[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(29):4645-4651.
[12] FU C, XIA Y, MENG F, et al. MRI quantitative analysis of eccentric exercise-induced skeletal muscle injury in rats. Acad Radiol. 2020;27(4): e72-e79.
[13] HODY S, CROISIER JL, BURY T, et al. Eccentric muscle contractions: Risks and Benefits. Front Physiol. 2019; 10:536-554.
[14] YOON SY, KIM YW, SHIN IS, et al. The beneficial effects of eccentric exercise in the management of lateral elbow tendinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med. 2021;10(17):3968.
[15] LYU X, GAO Y, LIU Q, et al. Exercise-induced muscle damage: multi-parametric MRI quantitative assessment. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):239.
[16] MINARI ALA, THOMATIELI-SANTOS RV. From skeletal muscle damage and regeneration to the hypertrophy induced by exercise: what is the role of different macrophage subsets. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022;322(1):R41-R54.
[17] ARMSTRONG RB, WARREN GL, WARREN JA. Mechanisms of exercise-induced muscle fibre injury. Sport Med. 1991;12(3):184-207.
[18] HYZEWICZ J, TANIHATA J, KURAOKA M, et al. Low-intensity training and the C5a complement antagonist NOX-D21 rescue the mdx phenotype through modulation of inflammation. Am J Pathol. 2017;187(5):1147-1161.
[19] SIDKY SR, INGALLS CP, LOWE DA, et al. Membrane proteins increase with the repeated bout effect. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2022;54(1):57-66.
[20] PINCHEIRA PA, HOFFMAN BW, CRESSWELL AG, et al. The repeated bout effect can occur without mechanical and neuromuscular changes after a bout of eccentric exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018;28(10): 2123-2134.
[21] NAUSHEEN S, MOIZ JA, RAZA S, et al. Preconditioning by light-load eccentric exercise is equally effective as low-level laser therapy in attenuating exercise-induced muscle damage in collegiate men. J Pain Res. 2017;10:2213-2221.
[22] HOPPELER H. Molecular networks in skeletal muscle plasticity. J Exp Biol. 2016;219(Pt 2):205-213.
[23] HYLDAHL RD, CHEN TC, NOSAKA K. Mechanisms and mediators of the skeletal muscle repeated bout effect. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2017; 45(1):24-33.
[24] JANNAS-VELA S, BUSTAMANTE A, ZBINDEN-FONCEA H, et al. Plasma α-Actin as an Early Marker of Muscle Damage After Repeated Bouts of Eccentric Cycling. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2022. doi: 10.1080/02701367.2022.2060926.
[25] HEDAYATPOUR N, FALLA D. Non-uniform muscle adaptations to eccentric exercise and the implications for training and sport. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2012;22(3):329-333.
[26] EBISUZAKI BT, RIEMEN ND, BETTENCOURT KM, et al. No Change in executive function or stress hormones following a bout of moderate treadmill exercise in preadolescent children. Int J Exerc Sci. 2020;13(5): 1650-1666.
[27] BURGOS J, VIRIBAY A, CALLEJA-GONZÁLEZ J, et al. Long-term combined effects of citrulline and nitrate-rich beetroot extract supplementation on recovery status in trained male triathletes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Biology(Basel). 2022;11(1):75.
[28] ZWOLSKI C, QUATMAN-YATES C, PATERNO MV. Resistance training in youth: laying the foundation for injury prevention and physical literacy. Sports Health. 2017;9(5):436-443.
[29] BONGIOVANNI T, GENOVESI F, NEMMER M, et al. Nutritional interventions for reducing the signs and symptoms of exercise-induced muscle damage and accelerate recovery in athletes: current knowledge, practical application and future perspectives. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020;120(9):1965-1996.
[30] MOHAMMADI H, AFZALPOUR ME, IEVARY SHA. Response of creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase enzymes to rest interval between sets and set-repetition configuration during bouts of eccentric exercise. Interv Med Appl Sci. 2018;10(2):83-86.
[31] DOUGLAS J, PEARSON S, ROSS A, et al. Chronic adaptations to eccentric training: a systematic review. Sports Med. 2017;47(5):917-941.
[32] MCNEILL C, BEAVEN CM, MCMASTER DT, et al. Survey of eccentric-based strength and conditioning practices in sport. J Strength Cond Res. 2020; 34(10):2769-2675. |