Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (22): 3445-3450.doi: 10.12307/2024.538
Comparison of initial stability of mandibular first molar repaired with different threaded implants under immediate loading
Li Xinru, Zhao Wenbo, Ji Yan, Teng Weiwei, Wang Yiming, Zhou Libo
- Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Jiamusi University, Heilongjiang Key Lab of Oral Biomedicine Materials and Clinical Application, Experimental Center for Stomatology Engineering, Jiamusi 154000, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2023-10-25Accepted:2023-11-27Online:2024-08-08Published:2024-01-19 -
Contact:Zhou Libo, Attending physician, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Jiamusi University, Heilongjiang Key Lab of Oral Biomedicine Materials and Clinical Application, Experimental Center for Stomatology Engineering, Jiamusi 154000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Li Xinru, Master candidate, Physician, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Jiamusi University, Heilongjiang Key Lab of Oral Biomedicine Materials and Clinical Application, Experimental Center for Stomatology Engineering, Jiamusi 154000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation Project of Heilongjiang Province, No. LH2021H108 (to ZLB); Training Program for Young Innovative Talents in General Higher Education Institution of Heilongjiang Province, No. UNPYSCT-2020057 (to ZLB); Heilongjiang Province Higher Education Teaching Reform Project, No. SJGZ20220124 (to ZLB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Xinru, Zhao Wenbo, Ji Yan, Teng Weiwei, Wang Yiming, Zhou Libo. Comparison of initial stability of mandibular first molar repaired with different threaded implants under immediate loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3445-3450.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
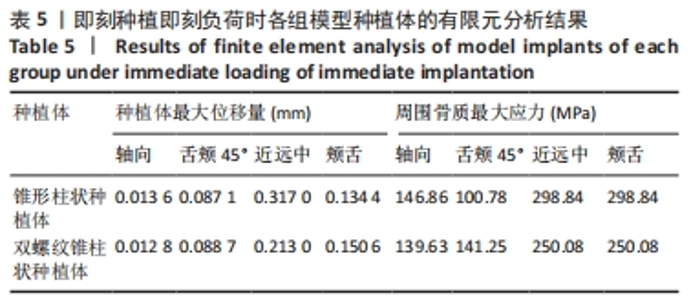
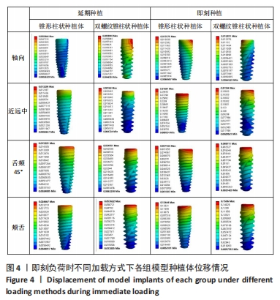
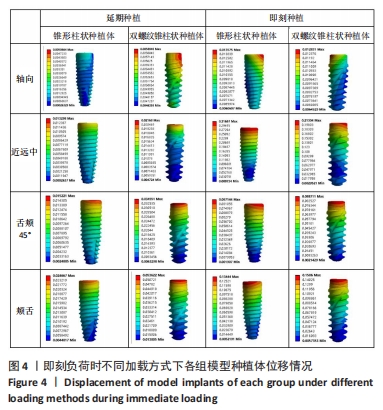
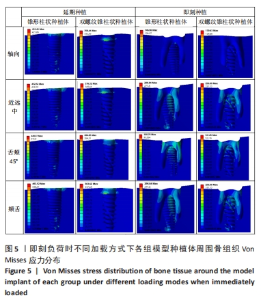
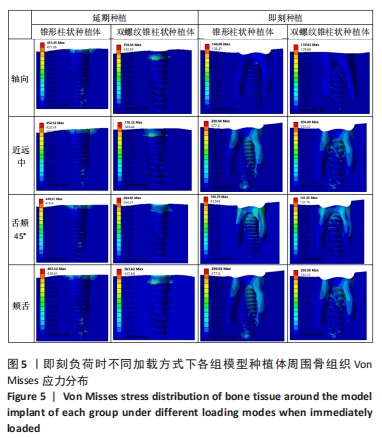
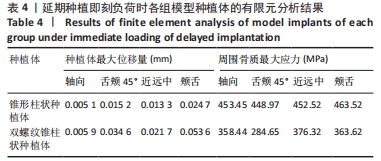
在延期种植即刻负荷模型中4个方向上施加载荷时,双螺纹锥柱状种植体周围骨质最大应力值均小于锥形柱状种植体围骨质最大应力值;在颊舌向加载载荷时,两种种植体的位移量均最大但相差较小,最大位移量均小于0.06 mm;在颊舌向加载载荷时,种植体周围骨质的应力最大,应力集中在种植体窝的颈部,锥形柱状种植体周围骨质最大应力为463.52 MPa,显著大于双螺纹锥柱状种植体周围骨质最大应力(376.32 MPa);舌颊45°加载载荷时,两种种植体周围骨质最大应力最小,双螺纹锥柱状种植体周围骨质最大应力为284.65 MPa,显著低于锥形柱状种植体周围骨质最大应力(448.97 MPa)。 2.1.2 即刻种植即刻负荷时各模型种植体位移和周围骨质应力分布 即刻种植即刻负荷时两种种植体的位移情况和周围骨质应力分布,见图4,5及表5。"
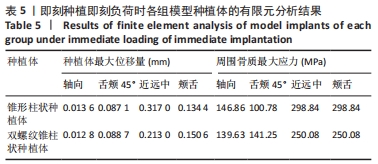
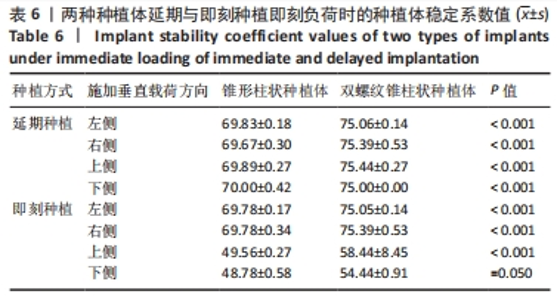
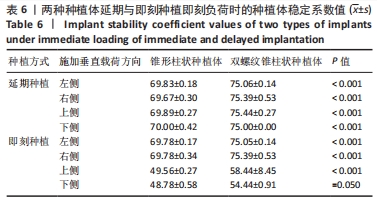
在即刻种植即刻负荷中4个方向上施加载荷时,双螺纹锥柱状种植体周围骨质最大应力值在3个方向上小于锥形柱状种植体周围骨质最大应力值,仅在舌颊45°时双螺纹锥柱状种植体周围骨质最大应力值大于锥形柱状种植体围骨质最大应力值;在近远中向加载载荷时,锥形柱状种植体位移量达到了0.31 mm、周围骨质最大应力值为298.84 MPa,双螺纹锥柱状种植体位移量和周围骨质最大应力值分别为 0.21 mm和250.08 MPa。由表5可以看出,在进行即刻种植即刻负荷时,轴向施加载荷时两种植体的最大位移量最小,均为0.01 mm左右;锥形柱状种植体周围骨质最大应力值出现在近远中与颊舌方向施加载荷时(298.84 MPa),双螺纹锥柱状种植体周围骨质最大应力值出现在近远中与颊舌方向施加载荷时(250.08 MPa)。 2.2 体外实验验证结果 在延期种植即刻负荷时,双螺纹锥柱状种植体各个方向的种植体稳定系数值均大于锥形柱状种植体(P < 0.001);在即刻种植即刻负荷时,双螺纹锥柱状种植体各个方向的种植体稳定系数值均大于锥形柱状种植体(P≤0.05),见表6。"
| [1] BRIZUELA-VELASCO A, CHAVARRI-PRADO D. The functional loading of implants increases their stability: A retrospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21(1):122-129. [2] OSTMAN PO, HELLMAN M, SENNERBY L. Direct implant loading in the edentulous maxilla using a bone density-adapted surgical protocol and primary implant stability criteria for inclusion. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2005;7 Suppl 1:S60-S69. [3] RYU HS, NAMGUNG C, LEE JH, et al. The influence of thread geometry on implant osseointegration under immediate loading: a literature review. J Adv Prosthodont. 2014;6(6):547-554. [4] CHEN J, CAI M, YANG J, et al. Immediate versus early or conventional loading dental implants with fixed prostheses: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. J Prosthet Dent. 2019;122(6):516-536. [5] IOANNIDOU E, DOUFEXI A. Does loading time affect implant survival? A meta-analysis of 1,266 implants. J Periodontol. 2005;76(8):1252-1258. [6] KIM HS, CHO HA, KIM YY, et al. Implant survival and patient satisfaction in completely edentulous patients with immediate placement of implants: a retrospective study. BMC Oral Health. 2018;18(1):219. [7] ELLIS R, CHEN S, DAVIES H, et al. Primary stability and healing outcomes of apically tapered and straight implants placed into fresh extraction sockets. A pre-clinical in vivo study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2020;31(8):705-714. [8] IBRAHIM A, HEITZER M, BOCK A, et al. Relationship between Implant Geometry and Primary Stability in Different Bony Defects and Variant Bone Densities: An In Vitro Study. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(19):4349. [9] IMAI M, OGINO Y, TANAKA H, et al. Primary stability of different implant macrodesigns in a sinus floor elevation simulated model: an ex vivo study. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):332. [10] MESNARD M, RAMOS A, SIMOES JA. Influences of implant condyle geometry on bone and screw strains in a temporomandibular implant. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42(3):194-200. [11] 高文波,马宗民,李淑娴,等.有限元分析不同骨质下种植体长度及直径对初期稳定性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(6): 875-880. [12] 施梦汝,谢伟丽,施武阁,等.柱形锥形种植体在不同种植深度的三维有限元研究[J].口腔医学,2019,39(7):577-580. [13] 孙江伟,王俊祥,白布加甫•叶力思,等.不同光滑颈圈种植体修复时应力分布的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(7):1004-1011. [14] 赵楚翘,徐一驰,刘定坤,等.髓腔固位冠及桩核冠修复下颌第一磨牙大面积缺损的生物力学分析[J]. 口腔医学研究,2018,34(5): 513-517. [15] KANG N, WU YY, GONG P, et al. A study of force distribution of loading stresses on implant-bone interface on short implant length using 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2014;118(5):519-523. [16] KIM YK, LEE JH, LEE JY, et al. A randomized controlled clinical trial of two types of tapered implants on immediate loading in the posterior maxilla and mandible. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(6):1602-1611. [17] 周宏志,张可,王学玲,等.不同形态种植体在两种骨质内以不同角度植入的应力分析[J].口腔医学研究,2022,38(2):138-143. [18] ATIEH MA, ALSABEEHA NH, DUNCAN WJ, et al. Immediate single implant restorations in mandibular molar extraction sockets: a controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013;24(5):484-496. [19] GAO Y, LUO D, YUAN M, et al. Immediate implant placement in single mandibular molar with chronic periapical periodontitis. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023;124(6S):101545. [20] RAMAKRISHNAN HS, SUNDAR P, HALDER S, et al. Graftless Immediate Dual Implant Anatomic Placement With Immediate Provisional Passive Loading and Definitive Hybrid Crown for the Restoration of Mandibular Molar: A Clinical Report. Cureus. 2023;15(5):e38654. [21] AVILA G, GALINDO P, RIOS H, et al. Immediate implant loading: current status from available literature. Implant Dent. 2007;16(3):235-245. [22] JIANG X, ZHOU W, WU Y, et al. Clinical Outcomes of Immediate Implant Loading with Fixed Prostheses in Edentulous Maxillae: A Systematic Review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2021;36(3):503-519. [23] LEVIN BP, CHU SJ, SAITO H, et al. A Novel Implant Design for Immediate Extraction Sites: Determining Primary Stability. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2021;41(3):357-364. [24] RAGUCCI GM, ELNAYEF B, CRIADO-CAMARA E, et al. Immediate implant placement in molar extraction sockets: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Implant Dent. 2020;6(1):40. [25] UNSAL GS. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of Different Implant Configurations in Enlarged First Molar Areas. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2020;35(4):675-683. [26] AYALI A, ALTAGAR M, OZAN O, et al. Biomechanical comparison of the All-on-4, M-4, and V-4 techniques in an atrophic maxilla: A 3D finite element analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2020;123:103880. [27] BAVETTA G, BAVETTA G, RANDAZZO V, et al. A Retrospective Study on Insertion Torque and Implant Stability Quotient (ISQ) as Stability Parameters for Immediate Loading of Implants in Fresh Extraction Sockets. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:9720419. [28] LEKHOLM U. Immediate/early loading of oral implants in compromised patients. Periodontol 2000. 2003;33:194-203. [29] PAMMER D. Evaluation of postoperative dental implant primary stability using 3D finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(3):280-287. [30] THANASRISUEBWONG P, PIMKHAOKHAM A, JIRAJARIYAVEJ B, et al. Influence of the Residual Ridge Widths and Implant Thread Designs on Implant Positioning Using Static Implant Guided Surgery. J Prosthodont. 2023;32(4):340-346. [31] VALENTE ML, DE CASTRO DT, SHIMANO AC, et al. Analysis of the influence of implant shape on primary stability using the correlation of multiple methods. Clin Oral Investig. 2015;19(8):1861-1866. [32] KARL M, IRASTORZA-LANDA A. Does implant design affect primary stability in extraction sites? Quintessence Int. 2017;48(3):219-224. [33] LEBLEBICIOĞLU KI, KILIC K, BAL B, et al. Finite Element Analysis of the Stress Distribution Associated With Different Implant Designs for Different Bone Densities. J Prosthodont. 2022;31(7):614-622. [34] BRUNSKI JB. Avoid pitfalls of overloading and micromotion of intraosseous implants. Dent Implantol Update. 1993;4(10):77-81. [35] AL-SAWAI AA, LABIB H. Success of immediate loading implants compared to conventionally-loaded implants: a literature review. J Investig Clin Dent. 2016;7(3):217-224. [36] SMITH RB, TARNOW DP. Classification of molar extraction sites for immediate dental implant placement: technical note. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(3):911-916. [37] ATALAY S, CAKMAK G, DONMEZ MB, et al. Effect of implant location and operator on the accuracy of implant scans using a combined healing abutment-scan body system. J Dent. 2021;115:103855. |
| [1] | Kong Dai, Wang Xinkai, Zhang Wenhui, Pei Xiaohang, Lian Cheng, Niu Xiaona, Guo Honggang, Niu Junwei, Zhu Zunmin, Liu Zhongwen. Oral Herombopag Olamine and subcutaneous recombinant human thrombopoietin after haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 1-7. |
| [2] | Liang Cheng, Zhang Linqi, Wang Guan, Li Wen, Duan Ke, Li Zhong, Lu Xiaobo, Zhuo Naiqiang. Finite element and biomechanical analysis of different implants in repair for unilateral unstable pelvic posterior ring injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1336-1341. |
| [3] | Xiaheida·Yilaerjiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun, Reyila·Kuerban, Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Chen Xin. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the distribution pattern of stress in bone tissues with different characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1277-1282. |
| [4] | Wei Yuanbiao, Lin Zhan, Chen Yanmei, Yang Tenghui, Zhao Xiao, Chen Yangsheng, Zhou Yanhui, Yang Minchao, Huang Feiqi. Finite element analysis of effects of sagittal cervical manipulation on intervertebral disc and facet joints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 827-832. |
| [5] | Dai Huijuan, Wang Zhaoxin, Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Sun Jiangwei, Gulizainu·Yibulayin, Nijiati·Tuerxun. Biomechanical difference between resin ceramic crown and zirconia all-ceramic crown implant restorations in three occlusal relationships [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 657-663. |
| [6] | Yin Kaiwen, Li Yunfeng. Application of metal-organic frameworks in implant surface modification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 783-788. |
| [7] | Wang Jiani, Chen Junyu. Angiogenesis mechanism of metal ions and their application in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [8] | Zhang Qianlong, Maihemuti•Yakufu, Song Chenhui, Liu Xiuxin, Ren Zheng, Liu Yuzhe, Muyashaer•Abudushalamu, Sajidan•Aikebaier, Ran Jian. Finite element analysis of the effect of the distribution position and content of bone cement on the stress and displacement of reverse femoral intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 336-340. |
| [9] | Dai Jing, Liu Shasha, Shen Mingjing. Exosome-loaded injectable hydrogel for repairing bone defects around implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 347-354. |
| [10] | Chen Yuanyuan, Wang Wei, Zhao Lu, Annikaer·Aniwaer, Nijati·Turson. Finite element analysis of the influence of scaffold materials on the fixed restoration of edentulous maxillary implants under two designs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 411-418. |
| [11] | Tan Junjie, Du Jiaheng, Wen Zhenyu, Yan Jiyuan, He Kui, Duan Ke, Yin Yiran, Li Zhong. Antibacterial magnesium oxide-calcium phosphate composite coating prepared by combining electrodeposition and sol-gel impregnation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(29): 4663-4670. |
| [12] | Wang Zhaofei, He Guoyun, Tian Fangcan, Li Guangfeng, Cao Zhonghua, Liu Xiangfei. Antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticle-coated stainless steel prepared via active screen plasma surface modification in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3464-3471. |
| [13] | Lu Jing, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Wang Huan, Shu Jiayu, Li Wenjie, Luo Yuncai, Dong Qiang. Biomechanical characteristics of “All-on-4” concept analyzed by three-dimensional finite element method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3591-3596. |
| [14] | Zhang Jinghua, Bai Lijing, Yu Chunmei. Effect of Zishen-Yutai pills on refrozen-thawed embryo transfer in patients with diminished ovarian reserve [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 3037-3041. |
| [15] | Chen Jiawen, Luo Siyang, Liu Yin, Chen Guangneng, Zuo Yuwen, He Xianyu, Ma Minxian. Finite element analysis of the effect of bone on occlusal adjustment of right upper first molar implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2579-2586. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||