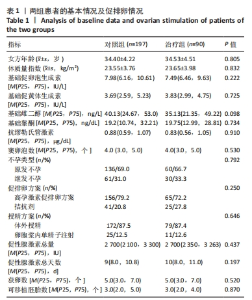
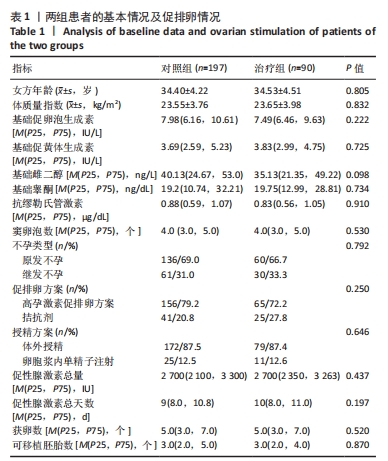
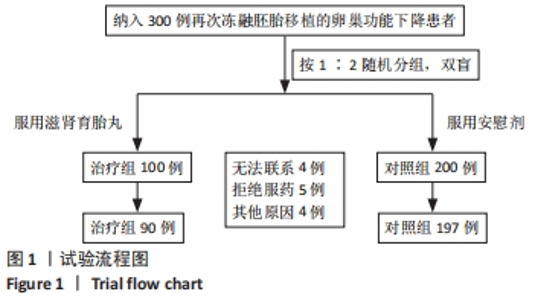
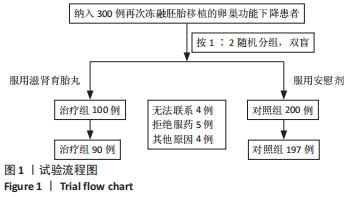
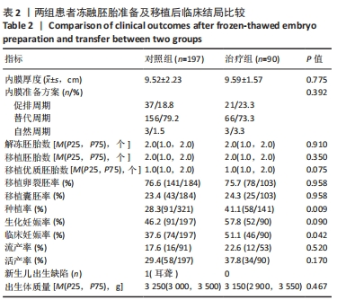
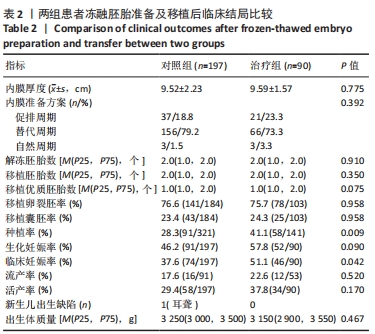
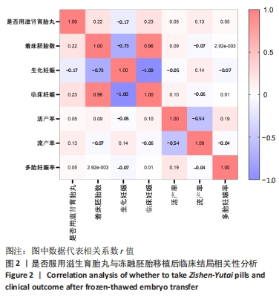
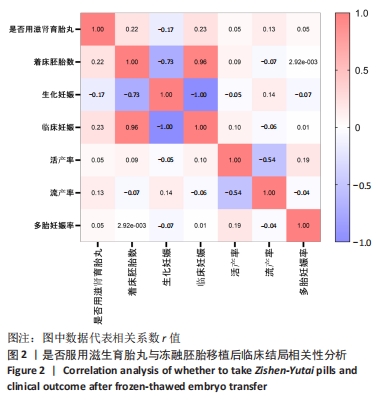
[1] ZHANG QL, LEI YL, DENG Y, et al. Treatment Progress in Diminished Ovarian Reserve: Western and Chinese Medicine. Chin J Integr Med. 2023;29(4):361-367.
[2] 张丽娜,孙克,纪亚忠.卵巢功能下降的评估标准及其诊治进展[J].第二军医大学学报,2019,40(6):659-663.
[3] 贾紫千,冯晓玲,赵颜,等.针药结合治疗卵巢储备功能下降的研究进展[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(3):1124-1127.
[4] 周琳,任梦雪,秦瑜玲,等.基于“气血理论”论治卵巢储备功能下降性不孕[J].中国临床医生杂志,2023,51(3):371-373.
[5] 李建茹,舒蒙蒙,方育恩,等.资癸益冲方对卵巢储备功能下降大鼠卵巢组织铁代谢及凋亡的影响[J].中成药,2023,45(2):399-405.
[6] 王悦竹,刘雁峰,曹一鸣,等.补肾疏肝方治疗卵巢储备功能减退70例临床观察[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(11):5883-5886.
[7] 刘思诗.滋肾育胎丸对肾虚型再次IVF-ET女性的临床观察及对子宫内膜容受性研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2015.
[8] 陈晓莉,杨冬梓.滋肾育胎丸对比安慰剂在进行新鲜胚胎移植周期的妇女中提高活产率的作用一项随机对照临床试验[J].中华生殖与避孕杂志,2022,42(10):1065-1074.
[9] 柏海燕,王婷,刘晓娟.滋肾育胎丸在体外受精-胚胎移植中效果的研究[J].世界中医药,2018,13(3):658-661.
[10] 胡晓文,潘巧玲.滋肾育胎丸联合针灸治疗卵巢储备功能减退临床观察[J].实用中医药杂志,2022,38(12):2056-2058.
[11] 高琦,王松峰,田海清,等.不同疗程滋肾育胎丸对体外受精-胚胎移植的疗效影响[J].新疆医科大学学报,2015,38(3):320-324.
[12] 朱文杰,李雪梅,陈秀敏,等.滋肾育胎丸对体外受精-胚胎移植患者胚胎种植率的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2002,22(10):729-730,737.
[13] 曹霁雯,刘华美,孙佳.滋肾育胎丸联合曲普瑞林对体外受精-胚胎移植患者妊娠结局的影响[J].中国药业,2021,30(3):66-68.
[14] 姚春玲.滋肾育胎丸在体外受精-胚胎移植中的功效[J].检验医学与临床,2017,14(11):372-373.
[15] 李佳,刘逸超,于洋,等.滋肾育胎丸对反复失败肾虚型IVF-ET患者子宫内膜容受性影响的临床观察[J].天津中医药大学学报,2019, 38(4):369-372.
[16] 马丹丽,习元堂,蒋凯林,等.滋肾育胎丸联合孕激素治疗先兆流产的Meta分析和间接比较[J].广州中医药大学学报,2018,35(4): 751-757.
[17] 闫晓彤.滋肾育胎丸临床应用及作用机制研究进展[J].上海中医药杂志,2016,50(8):98-100.
[18] 杨润雨,张杨,冯晓玲.卵巢储备功能下降所致不孕症中西医机制及治疗进展探析[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2019,21(9):189-192.
[19] 解小慧,刘鹏飞,张兵,等.中西医治疗卵巢储备功能下降型不孕症的研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2022,31(11):1573-1576, 1582.
[20] 姜智瑞,夏天.中医治疗卵巢储备功能下降的临床研究进展[J].天津中医药大学学报,2014,33(4):249-252.
[21] 郑蕾蕾,丁辉,李焕,等.卵巢储备功能下降研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2022,24(7):202-208.
[22] GURTCHEFF SE, KLEIN NA. Diminished ovarian reserve and infertility. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2011;54(4):666-674.
[23] ZHANG C, XU X. Advancement in the treatment of diminished ovarian reserve by traditional Chinese and Western medicine. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(4):1173-1176.
[24] 陈素珍,赵颖,张玉珍.滋癸益经汤联合滋肾育胎丸治疗卵巢早衰的研究[J].广州中医药大学学报,2020,37(1):41-45.
[25] 王月娇,徐莲薇,刘小菲,等.卵巢储备功能下降的中医研究进展[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2021,27(6):1047-1050.
[26] 李晓晓,齐丽红,仝瑞晓,等.卵巢储备功能下降病因及治疗的中西医研究进展[J].医学综述,2021,27(13):2612-2618.
[27] 许小凤,谈勇.卵巢储备功能下降及卵巢早衰动物模型研究进展[J].中国实验动物学报,2008,16(4):309-312.
[28] 高琦,田海清,王松峰,等.滋肾育胎丸对促排卵小鼠不同着床期子宫内膜HOXA10及下游基因EMX2表达的调控作用[J].广州中医药大学学报,2017,34(4):570-575.
[29] 陈晓莉,彭晓青,刘风华,等.中成药滋肾育胎丸临床应用新进展[J].今日药学,2022,32(8):573-577,582.
[30] 董燕,赵颖.补肾健脾中药安胎后对子代智力和体格发育的影响[J].新乡医学院学报,2007,24(5):477-479.
|