Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (22): 3591-3596.doi: 10.12307/2024.481
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biomechanical characteristics of “All-on-4” concept analyzed by three-dimensional finite element method
Lu Jing, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Wang Huan, Shu Jiayu, Li Wenjie, Luo Yuncai, Dong Qiang
- School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2023-08-17Accepted:2023-09-14Online:2024-08-08Published:2024-01-20 -
Contact:Dong Qiang, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Lu Jing, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Jing, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Wang Huan, Shu Jiayu, Li Wenjie, Luo Yuncai, Dong Qiang. Biomechanical characteristics of “All-on-4” concept analyzed by three-dimensional finite element method[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3591-3596.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 植体直径对“All-on-4”应力分布的影响 “All-on-4”技术分别在侧切牙区植入2枚垂直种植体,在第一或第二前磨牙区植入2枚倾斜种植体,利用4枚种植体完成无牙颌种植修复,实现即刻负载。种植体的初期稳定性是即刻负载成功的关键条件。而种植体的初期稳定性与颌骨的质量、种植体的几何形状、长度及直径等多种因素有关。在一项人体体外研究中,SILVA等[7]研究证明,锥形植入物具有更高的初期稳定性。即使在Ⅲ型骨(Lekholm和Zarb分类)中锥形种植体也保持了较高的初期稳定性[8]。2018年ITI共识会议的临床建议指出[9],在可能损伤解剖结构或产生一些根尖开窗风险的情况下,可以考虑使用锥形种植体。经典“All-on-4”技术种植位点相对固定,为获得良好的初期稳定性及相对微创的完成治疗,目前临床上大都使用锥形或锥柱状种植体。不同种植体形状是否会影响“All-on-4”的应力分布,目前相关研究较少。 在骨宽度不足的情况下,窄直径种植体也越来越多地应用在临床中,作为替换标准种植体的一种选择。KLEIN等[10]根据前人的研究将窄直径种植体分为了3种类型:①< 3.0 mm种植体(“迷你种植体”);②3.0-3.25 mm种植体;③3.3-3.5 mm种植体。虽然在一些Meta分析中报道了窄直径种植体和标准直径种植体的生存率相当[11-12]。但在一项体外研究中显示,标准种植体在静态和循环载荷试验中均显示出更高的强度[13]。这可能是因为,随着直径的增加,种植体与邻近颌骨之间的接触面积增大,从而使传递到种植体周围组织的单位面积负荷减少,对周围骨的应力分布更有利。这也是为什么相较于直径更大的植体,窄直径植体存在更高超负荷风险的原因之一。 然而,以上研究都只针对单个的种植体而言,与“All-on-4”中使用窄直径种植体情况不同,由于夹板的作用,上部修复体在负载时,力的分布与单个种植体不同。有学者利用三维有限元方法分别评估了在上颌骨中不同种植体直径(3.0 mm,3.5 mm,4.3 mm)的单冠、三单位桥以及“All-on-4”支持的修复体在轴向和斜向加载下,种植体周围应力的变化和过载体积的大小,研究结果发现,对于单冠而言,虽然随着种植体直径的增加,种植体周围区域过载的体积减小[14];由3.0 mm直径种植体支持的三单位桥在种植体周围的平均应力和过载体积方面要低于3.5 mm种植体支持的单冠;将4枚窄直径种植体运用在“All-on-4” 中,当后牙区负载时,在3.0 mm与3.5 mm直径的“All-on-4”组模型中远中倾斜种植体周围的过载体积高于3.0 mm与3.5 mm种植体支持的单冠。MOREIRA DE MELO等[15]的研究显示,在“All-on-4”支持的丙烯酸树脂牙的设计中,2.9 mm直径的“All-on-4”模型与3.5 mm直径的“All-on-4”组模型在应力分布上是相似的,但3.5 mm模型组在轴向负荷下种植体周围骨丧失的风险降低了16%,斜向负荷下的风险降低了4%,就种植体与基台而言,在3.5 mm模型中观察到最高von Mises值,在直径2.9 mm的模型中,中央螺丝的应力峰值接近钛的屈服强度。综合上述研究结果发现,在后牙区加载时,倾斜种植体周围骨表现出较高的压应力。利用 “All-on-4”来进行治疗时,不可避免的会存在悬臂。悬臂的存在使得全牙列修复体在远中悬臂梁处有更高的超载风险[16]。 尽管窄直径种植体可以作为一种可选方案来解决水平骨量不足的问题,避免复杂的骨增量手术,但目前“All-on-4”技术中使用窄直径种植体的相关研究较少,虽然“All-on-4”技术的夹板作用可能会对应力的分布有积极影响,但目前的研究尚不能证明窄直径种植体应用于“All-on-4”中夹板作用的优势,尤其在后牙区。在应用于“All-on-4”技术时,需要谨慎考虑悬臂的影响以及窄直径种植体的强度是否能承受悬臂梁的超载风险。进一步的研究仍然需要探索窄直径种植体在“All-on-4”技术中的应用前景和潜在风险。此外,针对窄直径种植体和悬臂的问题,临床上还需要综合考虑患者的口腔状况、个体因素以及长期治疗效果等因素,做出全面的治疗决策。"

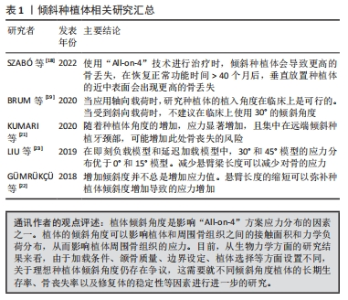
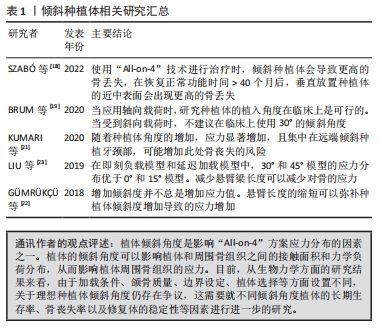
2.2 植体倾斜角度对“All-on-4”的应力分布的影响 与天然牙相比,种植体由于缺乏牙周韧带,对创伤性咬合力的耐受性较差,它们更容易受到非轴向力的影响。临床研究发现,倾斜种植体与轴向种植体有相似的留存率以及较为稳定的种植体边缘骨水平维持[17]。但也有研究认为,倾斜种植体在每个时间点,周围的骨丧失水平明显高于轴向种植体[18]。生物力学研究表明,当种植体倾斜时,邻近骨受到的应力增加[19]。 在“All-on-4”技术的实际应用中,远中使用倾斜种植体的临床优势就是可以在有限的剩余骨量中尽量使用较长的种植体,增大了种植体与骨的接触面积,能获得良好的初期稳定,增大AP(anterior/posterior)距,减少悬臂长度,从而改善力在颌骨中的传导分布。据报道,远端种植体的最大倾斜角度可达45°[20]。目前,对远中植体倾斜角度生物力学方面的研究结果并不一致,对理想的远中植体倾斜角度仍然存在争议。 KUMARI等[21]利用有限元方法评估了不同种植体角度(30°,40°,45°)在上颌骨中的应力分布,结果表明,在后牙负载时,倾斜种植体远中的颈部区域出现骨的最大应力值,并且,在45°模型中应力几乎是30°模型的2倍。GüMRüK?ü等[22]研究表明,当植体放置在相同位置时,在倾斜角度分别为0°,30°,45°的模型中,30°的模型中可以观察到骨应力的峰值。LIU等[23]的研究显示在后牙区植入的倾斜种植体中,0°模型的平均主拉应力最高,30°和45°模型都有着更好的应力分布,且平均主拉应力总是随倾角的增加而减小。 “All-on-4”技术通过倾斜远中种植体的方法,减少远中悬臂梁的长度。随着种植体的倾斜角度的增加,悬臂梁长度减小,可能会减少骨的应力分布。上述研究出现不同结果的原因是,研究因素受到悬臂与倾斜角度两者共同影响;除此之外,不同的颌骨质量也会影响应力分布的结果。综上所述,倾斜远中种植体的方法在降低远中悬臂梁长度、减少骨应力分布方面具有潜在的优势,远中植体倾斜30°还是45°也取决于解剖结构与颌骨的质量。随后的研究需要综合考虑悬臂、倾斜角度以及颌骨质量等因素的共同影响,进一步确定理想的角度范围。此外通过长期临床随访研究,可以评估不同倾斜角度下“All-on-4”治疗的生物力学效果和长期稳定性,这有助于验证理论研究。在实际临床应用中,医生的临床经验和对患者个体情况的评估也对长期的治疗效果起着重要的作用。文章总结了目前对倾斜种植体相关研究进展,见表1。"

2.3 悬臂梁长度对“All-on-4”应力分布的影响 临床研究发现,种植修复体断裂的地方一般多位于远中悬臂处[24]。悬臂梁的存在,使修复体在行使咀嚼功能时,后牙区的咀嚼压力,会通过悬臂梁传递到种植体,形成了以远中种植体为支点的杠杆,这种杠杆作用会对前部区域种植体周围的骨界面应力产生不良的影响。第五次欧洲骨结合协会(EAO)共识大会指出,当悬臂梁平均长度不超过2个牙位时,无牙颌患者种植修复仍有较高的成功率,但5-10年的修复并发症发生率较高[25]。MALó等[26]在5-13年的随访期间,发现有58.8%的临时修复体和7.3%的最终修复体发生机械并发症。另一项长达10年的回顾性队列研究报道中也显示,有27.1%的患者出现机械并发症[27]。 HORITA等[28]的研究发现,即刻负重时,压力峰值在有无悬臂梁情况下分别升高 26.4%-39.0%和24.0%-35.8%,而负重部位明显影响应力分布,无悬臂梁者应力峰值较有悬臂梁者低45.3%-52.6%。在一项体外实验研究和有限元研究中发现,随着载荷向远端磨牙区域移动,骨内的应力和应变显著增加[29]。当载荷靠近后部倾斜种植体并位于修复体悬臂上时,骨的应力和应变明显高于相同的加载条件下没有悬臂梁的应力与应变。SHETTY等[30]研究结果表明,无论使用何种材料,悬臂梁长度和咬合力的增加都会导致所有种植体周围的应力增加。悬臂载荷对种植体周围的骨应力和应变有很大影响。较高的骨应力和应变可能会增加骨丧失的风险。由于上颌牙槽骨密度较疏松,尤其是在上颌后牙区,因此,有学者建议上颌种植修复体悬臂梁长度应控制在10-12 mm [31]。DRAGO[32]的4年临床回顾性分析表明,临时修复体悬臂长度不应超过一个牙齿大小,而最终修复体的悬臂长度/AP距比必须小于1。当比值保持在0.9时,修复体并发症发生率低于1%。 悬臂长度会影响种植体-骨界面的应力以及种植体和修复组件的应力分布[33]。选择适当的悬臂梁长度以延长种植体及义齿的生存率,是临床面临的一个重要问题。如果没有充分规划悬臂长度将会导致植体、颌骨、修复体及其组件应力的增加,从而导致中央螺丝松动、中央螺丝断裂、修复体的断裂、种植体折断。悬臂的长度也受到牙弓形态的影响,因为悬臂不仅出现在后牙区,在前牙也会出现悬臂,尖圆形和卵圆形牙弓较方圆形牙弓更有利于AP距扩散,从而影响应力的分布。目前,关于“All-on-4”技术中理想悬臂长度的选择主要基于临床经验性建议,但缺乏高水平的循证证据来支持,这意味着在实践中的悬臂长度选择需要结合医生的临床经验。首先应尽量避免悬臂的存在,尤其是在临时修复体中和低质量的骨中;当悬臂无法避免时,应尽量缩短悬臂长度,或增加种植体数目,总之需要综合考虑患者的骨质状况、修复体的设计、种植体的数量和位置,以及患者的口腔功能需求等因素进行合理的设计,尽量降低机械并发症发生的概率。"


2.4 上部结构材料对“All-on-4”的应力分布的影响 用于修复体上部结构的支架材料特性对修复治疗的成功起着重要的作用。钛、氧化锆、碳纤维等材料一直以来都是被用来制作支架的主要材料。近年来,一种名为聚醚醚酮[poly (ether-ether-ketone),PEEK]的新材料被引入,该材料具有优异的力学性能,并被用来制作为种植体的基台及支架等,这种材料的弹性模量接近于人类骨骼,使其像骨骼一样有弹性[34]。而PEEK和聚醚酮酮[(poly(ether-ketone-ketone),PEKK]之间存在一些差异,PEKK具有更多的酮基,增加热稳定性,提供更多的表面化学修饰选择,并比PEEK显示更好的物理和力学性能[35]。研究表明,与低刚性的材料相比,刚性材料在修复支架中表现出更高的应力值[36]。具有较高弹性模量的材料可以抵抗变形,从而增加应力浓度。弹性模量较低的支架材料可以降低咬合力,均匀分布载荷[37]。MALó等[38]的一项临床研究报道了在1年的随访期内,使用“All-on-4”技术治疗无牙颌并运用PEEK支架制作的修复体机械并发症发生率较低,在49列无牙颌弓中,有1例丙烯酸树脂牙折裂、1例PEEK支架折裂以及3例中央螺丝松动。 DAYAN等[39]的研究发现与钛和氧化锆相比,由PEKK和PEEK材料构建的支架具有相对较低的弹性模量,使得支架本身的应力较小,但对骨、种植体、基牙和中央螺丝的应力转移较高,它们将应力转移到种植体和更接近于加载部位相邻颌骨中。在另一些有限元研究中也证明与更刚性的材料相比,PEEK支架表现出最高的应力峰值[40]。HAROUN等[41]的研究也发现,使用低弹性模量的材料,如丙烯酸树脂和PEEK可以减少传递到颌骨的应力。TRIBST等[42]的研究发现,在距远中种植体2 mm的悬臂端垂直加载200 N力时,当悬臂长度不变时,氧化锆支架应力高于钴铬合金支架,在后者模型中,种植体、中央螺丝以及颌骨应力值高于氧化锆支架模型。KELKAR等[43]研究发现,在远中种植体轴向加载200 N力时,钛支架Von Mises值约为氧化锆支架的3倍;在悬臂端垂直加载时,钛支架与氧化锆支架的Von Mises值相近分别为56.05 MPa和55.91 MPa。而PEEK支架在轴向和斜向载荷下均具有最高的压缩应变值,而在3种不同材料的支架中氧化锆支架的斜载荷的拉伸应变最小。 因此从生物力学的角度上可以推断,在应用“All-on-4”治疗无牙颌时,由于悬臂的存在,使用钛及氧化锆等刚性较大的材料或许可以减少固定修复体中修复体组件、种植体和种植体周围骨的应力。在骨密度高的患者中,使用弹性模量低的材料(如某些聚合物材料)可以更好地平衡力的传递,减少骨与种植体或修复体之间的应力集中,但仍要警惕骨吸收的风险。在骨密度低的患者中,骨质状况较差,骨组织的强度可能相对较低,在这种情况下,使用弹性模量高的材料(如钛合金)可以提供更强的支持力,减少修复体与种植体或周围骨组织之间的应力集中,避免过度的应力对脆弱骨组织造成不利影响。此外,就上部修复组件而言,基台与种植体的连接方式不同,也会影响应力分布,目前涉及到基台与种植体的连接方式的相关研究较少,不同的连接方式是否会影响 “All-on-4”上部修复组件的应力分布,还需要更多的研究证实。文章总结了不同材料支架应力分布的汇总表见表2。"


2.5 不同设计方案对“All-on-4”的应力分布影响 经典的“All-on-4”无牙颌即刻种植修复技术,可以相对高效以及微创地完成种植修复,然而,该技术的使用仍存在一定的局限性。PAULO等[44]指出使用经典的 “All-on-4”治疗上颌骨的解剖纳入标准是:尖牙到尖牙的剩余牙槽嵴宽度≥ 4 mm,剩余骨高度≥10 mm。但在重度萎缩上颌无牙颌病例中,往往无法满足该条件。有研究发现,在面对重度萎缩上颌无牙颌的情况下,尽管上前牙区颌骨的骨量整体是严重不足的,但在上颌骨的中线、梨状窝外侧等解剖位置,其骨量相较于其他部位充足,且往往还有部分皮质骨[45]。因此,有研究提出了两种改良型“All-on-4”技术[46-47],一种M型结构,称为“M-4”,另一种结构称为“V-4”。AYALI等[48]在对“All-on-4”“M-4”和“V-4”治疗上颌无牙颌的应力分布的研究中并未发现三者的应力值有很大差异,但“M-4”和“V-4”技术的应力总体略低于标准“All-on-4”技术。有学者建议在治疗严重萎缩的无牙颌且不满足经典“All-on-4”适应证时,可以考虑使用“V-4”[49]。然而,目前对于“M-4”和“V-4”的研究较少,它们在生物力学上面的优势还需要进一步的研究。 随着种植体表面处理技术的不断改进,短植体也越来越多的应用到萎缩的无牙颌患者中。在一项Meta分析中显示:在12个月的随访后,超短的种植体与较长的种植体相比,生存率无显著差异[50]。而在另一项Meta分析中显示,短种植体在上颌骨内的存活率可能低于长种植体[51]。长种植体可以提供更大的表面积,获得更大的初期稳定性。BARIKANIE等[52]从一项体外研究中得出结论,初始稳定性随着种植体长度的增加而显著增加。HIMMLOVá 等[53]的研究表明,种植体长度对应力分布的影响很小。有研究表明在后牙区使用7 mm短植体的改良“All-on-4”与经典的“All-on-4”相比,改良组在上颌骨表现出更为理想的von-Mises应力分布[54]。在另一项在前牙区使用7 mm短植体改良“All-on-4”与经典的“All-on-4”的对比研究中,显示两者应力值相似[55]。 根据目前的生物力学研究结果来看,短植体和改良的“All-on-4”技术在“All-on-4”治疗中可能成为备选方案,以避开经典“All-on-4”技术的一些敏感性,其中包括“M-4”和“V-4”等改良技术。这些改良技术利用上颌骨中线和梨状窝外侧的皮质骨,甚至可以形成双皮层骨固定,从理论上来看,可以实现即刻负载。然而,目前针对这类改良技术的临床病例较少,长期有效性尚不能得到充分评估。此外,不同颌骨质量、植体分布位置以及上部修复体材料对这类技术都会有影响。因此,在制定治疗方案时,需要根据每个病例的具体情况进行个性化设计,并综合考虑患者的局部和全身因素、医生的技术和技能等,从而为患者制定一个长期有效的治疗方案。 2.6 不同咬合设计对“All-on-4”的应力分布的影响 影响种植治疗成功与否的一个关键因素就是咬合的设计[56]。由于缺乏牙周韧带,种植修复体更易发生过载,种植体周围应力增加,导致种植体周骨组织的丧失,促进各种机械并发症的发生,如修复体的折断、中央螺丝的松动及崩瓷等,最终导致种植失败。“All-on-4”仅仅只用4枚种植体来支撑一个10-12个牙位的修复体,其在功能运动中受到的载荷将由这4枚种植体传递到相邻的颌骨中。研究证明咬合过载与治疗成功率相关[57]。因此,正确的咬合设计是至关重要的。 有研究建议“All-on-4”的咬合设计除了遵循一般义齿修复的原则外,还有以下要点:①避免早接触,过早的接触会使种植体承受过大咬合负荷。②避免牙合干扰,建立稳定的咬合关系,牙齿轻接触,前伸和侧方运动均无牙合干扰。③后牙减径,降低牙尖斜度[58]。④修复体牙齿排列的弓形,应与患者颌弓的形状以及种植基牙的位置相协调。马斐斐等[59]用T-scan Ⅲ咬合系统测量了13例无牙颌“All-on-4”种植修复患者的咬合力,结果显示牙尖交错位时咬合力相对集中于前磨牙区;在种植体前牙区、尖牙区及游离端悬臂梁区域咬合力分布较小且较均匀。 ABDUO等[60]报道了尖牙引导牙合和组牙功能牙合在修复体的寿命方面没有差异。而张雪洋等[61]也认为,与天然牙相比,种植体无论是对菌斑的敏感性还是牙合力的承载力都更薄弱,所以更应选择尖牙引导牙合。MIRALLES[62]指出,在恢复咬合时尖牙引导牙合和组牙功能牙合二者之间并无差异。TüRKER等[63]的研究发现,在对颌也采用“All-on-4”来进行治疗时,在尖牙引导牙合中可以观察到最低的应力值。而该学者在之后的一项研究中却发现,在对颌同样也采用“All-on-4”来进行治疗时,种植体支持的修复体却在尖牙引导牙合时观察到较高的应力[64]。在3种不同的咬合设计中,组牙功能牙合的应力值普遍较低。 尖牙引导牙合在侧方运动时,靠尖牙引导,其他所有牙不接触,减少了后牙区种植体受力情况。种植牙由于缺乏牙周膜的保护,对牙合力的承载更弱,而种植体直接将力传递到周围骨中,从理论上来说,在无牙颌种植固定修复中,尖牙引导牙合可能是较好的选择。但影响咬合的因素有很多,除了关节和肌肉之外,对颌牙弓的形态、覆牙合覆盖的情况,以及余留牙的情况、不同类型的修复体、患者自身的咬合习惯等,都会对咬合设计产生影响,因此目前的研究尚不能判断哪种咬合设计是最好的。有限元研究可以通过人为设置需改变的因素,保持其他因素不变来进行研究。但需要注意的是,口腔的咀嚼过程是一个重复的过程,咬合负荷在颌骨的功能运动过程中不断形成,并不同于实验中的单次加载。因此,在进一步研究理想的咬合设计时需要细化实验设计,并进行大量的临床研究来探索不同情况下的最佳咬合设计。"

| [1] CORDARO M, DONNO S, AUSENDA F, et al. Influence of bone anatomy on implant placement procedures in edentulous arches of elderly individuals: a cross-sectional study on computed tomography images. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2020;35(5):995-1004. [2] MALÓ P, RANGERT B, NOBRE M. “All-on-Four” immediate-function concept with Brånemark System implants for completely edentulous mandibles: a retrospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003;5 Suppl 1:2-9. [3] CHAN MH, NUDELL YA. All-on-4 Concept Update. Dent Clin North Am. 2021;65(1):211-227. [4] DO TA, LE HS, SHEN YW, et al. Risk factors related to late failure of dental implant-a systematic review of recent studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(11):3931. [5] MARCIÁN P, WOLFF J, HORÁČKOVÁ L, et al. Micro finite element analysis of dental implants under different loading conditions. Comput Biol Med. 2018;96:157-165. [6] NIMBALKAR S, DHATRAK P, GHERDE C, et al. A review article on factors affecting bone loss in dental implants. Mater Today Proc. 2020;43(2):970-976. [7] SILVA GAF, FAOT F, POSSEBON APDR, et al. Effect of macrogeometry and bone type on insertion torque, primary stability, surface topography damage and titanium release of dental implants during surgical insertion into artificial bone. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;119:104515. [8] JAVED F, AHMED HB, CRESPI R, et al. Role of primary stability for successful osseointegration of dental implants: factors of influence and evaluation. Interv Med Appl Sci. 2013;5(4):162-167. [9] JUNG RE, AL-NAWAS B, ARAUJO M, et al. Group 1 ITI consensus report: the influence of implant length and design and medications on clinical and patient-reported outcomes. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29 Suppl 16:69-77. [10] KLEIN MO, SCHIEGNITZ E, AL-NAWAS B. Systematic review on success of narrow-diameter dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014;29 Suppl 1:43-54. [11] SCHIEGNITZ E, AL-NAWAS B. Narrow-diameter implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29 Suppl 16:21-40. [12] GONZÁLEZ-VALLS G, ROCA-MILLAN E, CÉSPEDES-SÁNCHEZ JM, et al. Narrow diameter dental implants as an alternative treatment for atrophic alveolar ridges. systematic review and meta-analysis. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(12):3234. [13] SONG SY, LEE JY, SHIN SW. Effect of implant diameter on fatigue strength. Implant Dent. 2017; 26(1):59-65. [14] VALERA-JIMÉNEZ JF, BURGUEÑO-BARRIS G, GÓMEZ-GONZÁLEZ S, et al. Finite element analysis of narrow dental implants. Dent Mater. 2020;36(7):927-935. [15] MOREIRA DE MELO EJ JR, FRANCISCHONE CE. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of two angled narrow-diameter implant designs for an all-on-4 prosthesis. J Prosthet Dent. 2020;124(4):477-484. [16] CENKOGLU BG, BALCIOGLU NB, OZDEMIR T, et al. The effect of the length and distribution of implants for fixed prosthetic reconstructions in the atrophic posterior maxilla: a finite element analysis. Materials (Basel). 2019;12(16):2556. [17] 姚立敏,王娟,童昕.比较All-on-4种植修复中倾斜种植体与轴向种植体临床效果的5年回顾性研究[J].口腔医学,2021,41(3):242-246,283. [18] SZABÓ ÁL, NAGY ÁL, LÁSZLÓFY C, et al. Distally tilted implants according to the all-on-four® treatment concept for the rehabilitation of complete edentulism: a 3.5-year retrospective radiographic study of clinical outcomes and marginal bone level changes. Dent J (Basel). 2022;10(5):82. [19] BRUM JR, MACEDO FR, OLIVEIRA MB, et al. Assessment of the stresses produced on the bone implant/tissue interface to the different insertion angulations of the implant - a three-dimensional analysis by the finite elements method. J Clin Exp Dent. 2020;12(10):e930-e937. [20] MALÓ P, RANGERT B, NOBRE M. All-on-4 immediate-function concept with Brånemark System implants for completely edentulous maxillae: a 1-year retrospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2005;7 Suppl 1:S88-S94. [21] KUMARI A, MALHOTRA P, PHOGAT S, et al. A finite element analysis to study the stress distribution on distal implants in an all-on-four situation in atrophic maxilla as affected by the tilt of the implants and varying cantilever lengths. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2020;20(4):409-416. [22] GÜMRÜKÇÜ Z, KORKMAZ YT. Influence of implant number, length, and tilting degree on stress distribution in atrophic maxilla: a finite element study. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;56(6):979-989. [23] LIU T, MU Z, YU T, et al. Biomechanical comparison of implant inclinations and load times with the all-on-4 treatment concept: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(6):585-594. [24] DRAGO C, HOWELL K. Concepts for designing and fabricating metal implant frameworks for hybrid implant prostheses. J Prosthodont. 2012;21(5):413-424. [25] HÄMMERLE CHF,CORDARO L, ALCCAYHUAMAN KAA, et al. Biomechanical aspects: Summary and consensus statements of group 4. The 5th EAO Consensus Conference 2018. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29 Suppl 18:326-331. [26] MALÓ P, DE ARAÚJO NOBRE M, LOPES A, et al. The All-on-4 concept for full-arch rehabilitation of the edentulous maxillae: a longitudinal study with 5-13 years of follow-up. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21(4):538-549. [27] GRANDI T, SIGNORINI L. Rehabilitation of the completely edentulous mandible by all-on-four treatment concept: a retrospective cohort study with up to 10 years follow-up. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;58(1):10. [28] HORITA S, SUGIURA T, YAMAMOTO K, et al. Biomechanical analysis of immediately loaded implants according to the “All-on-Four” concept. J Prosthodont Res. 2017;61(2):123-132. [29] WU AY, HSU JT, FUH LJ, et al. Biomechanical effect of implant design on four implants supporting mandibular full-arch fixed dentures: in vitro test and finite element analysis. J Formos Med Assoc. 2020;119(10):1514-1523. [30] SHETTY R, SINGH I, SUMAYLI HA, et al. Effect of prosthetic framework material, cantilever length and opposing arch on peri-implant strain in an all-on-four implant prostheses. Niger J Clin Pract. 2021;24(6):866-873. [31] GREENSTEIN G, CAVALLARO JJR. Cantilevers extending from unilateral implant-supported fixed prostheses: a review of the literature and presentation of practical guidelines. J Am Dent Assoc. 2010;141(10):1221-1230. [32] DRAGO C. Ratios of cantilever lengths and anterior-posterior spreads of definitive hybrid full-arch, screw-retained prostheses: results of a clinical study. J Prosthodont. 2018;27(5):402-408. [33] SALEH SABER F, GHASEMI S, KOODARYAN R, et al. The comparison of stress distribution with different implant numbers and inclination angles in all-on-four and conventional methods in maxilla: a finite element analysis. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2015;9(4):246-253. [34] AL-RABAB’AH M, HAMADNEH W, ALSALEM I, et al. Use of high performance polymers as dental implant abutments and frameworks: a case series report. J Prosthodont. 2019;28(4):365-372. [35] KEWEKORDES T, WILLE S, KERN M. Wear of polyetherketoneketones - Influence of titanium dioxide content and antagonistic material. Dent Mater. 2018;34(3):560-567. [36] TRIBST JPM, DE MORAIS DC, ALONSO AA, et al. Comparative three-dimensional finite element analysis of implant-supported fixed complete arch mandibular prostheses in two materials. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2017;17(3):255-260. [37] BHERING CL, MESQUITA MF, KEMMOKU DT, et al. Comparison between all-on-four and all-on-six treatment concepts and framework material on stress distribution in atrophic maxilla: a prototyping guided 3D-FEA study. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;69:715-725. [38] MALÓ P, DE ARAÚJO NOBRE M, MOURA GUEDES C, et al. Short-term report of an ongoing prospective cohort study evaluating the outcome of full-arch implant-supported fixed hybrid polyetheretherketone-acrylic resin prostheses and the All-on-Four concept. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018;20(5):692-702. [39] DAYAN SC, GECKILI O. The influence of framework material on stress distribution in maxillary complete-arch fixed prostheses supported by four dental implants: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021;24(14):1606-1617. [40] VILLEFORT RF, TRIBST JPM, DAL PIVA AMO, et al. Stress distribution on different bar materials in implant-retained palatal obturator. PLoS One. 2020;15(10):e0241589. [41] HAROUN F, OZAN O. Evaluation of Stresses on implant, bone, and restorative materials caused by different opposing arch materials in hybrid prosthetic restorations using the all-on-4 technique. Mat(Basel). 2021;14(15):4308. [42] TRIBST JPM, CAMPANELLI DE MORAIS D, MELO DE MATOS JD, et al. Influence of framework material and posterior implant angulation in full-arch all-on-4 implant-supported prosthesis stress concentration. Dent J (Basel). 2022;10(1):12. [43] KELKAR KC, BHAT V, HEGDE C. Finite element analysis of the effect of framework materials at the bone-implant interface in the all-on-four implant system. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2021;18:1. [44] PAULO M, MIGUEL NAD, ARMANDO L. An overview of the All-on-4™ implant philosophy. Fac Dent J. 2012;3(1):20-27. [45] JENSEN OT. Complete arch site classification for all-on-4 immediate function. J Prosthet Dent. 2014;112(4):741-751.e2. [46] JENSEN OT, ADAMS MW. The maxillary M-4: a technical and biomechanical note for all-on-4 management of severe maxillary atrophy--report of 3 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 67(8):1739-1744. [47] JENSEN OT, ADAMS MW, BUTURA C, et al. Maxillary V-4: Four implant treatment for maxillary atrophy with dental implants fixed apically at the vomer-nasal crest, lateral pyriform rim, and zygoma for immediate function. Report on 44 patients followed from 1 to 3 years. J Prosthet Dent. 2015;114(6):810-817. [48] AYALI A, ALTAGAR M, OZAN O, et al. Biomechanical comparison of the All-on-4, M-4, and V-4 techniques in an atrophic maxilla: a 3D finite element analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2020; 123:103880. [49] JENSEN TO, ADAMS WM, COTTAM RJ, et al. The All-on-4 shelf: maxilla. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010,68(10):2520-2527. [50] MORASCHINI V, MOURÃO CFAB, MONTEMEZZI P, et al. Clinical comparation of extra-short (4 mm) and long (>8 mm) dental implants placed in mandibular bone: a systematic review and metanalysis. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9(3):315. [51] XU X, HUANG J, FU X, et al. Short implants versus longer implants in the posterior alveolar region after an observation period of at least five years: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent. 2020;100:103386. [52] BARIKANI H, RASHTAK S, AKBARI S, et al. The effect of shape, length and diameter of implants on primary stability based on resonance frequency analysis. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2014;11(1):87-91. [53] HIMMLOVÁ L, DOSTÁLOVÁ T, KÁCOVSKÝ A, et al. Influence of implant length and diameter on stress distribution: a finite element analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2004;91(1):20-25. [54] 木志翔,刘婷,陈陶,等.两种上颌无牙颌种植固定修复方案的有限元分析[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(10):931-935. [55] BOZYEL D, TAŞAR FARUK S. Biomechanical behavior of All-on-4 and M-4 configurations in an atrophic maxilla: a 3D finite element method. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e929908. [56] TARUNA M, CHITTARANJAN B, SUDHEER N, et al. Prosthodontic perspective to all-on-4® concept for dental implants. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(10):ZE16-ZE19. [57] STOICHKOV B, KIROV D. Analysis of the causes of dental implant fracture: a retrospective clinical study. Quintessence Int. 2018;49(4):279-286. [58] 庞丽娇,杨海萍,胡婷姿,等.All-on-4种植固定修复的咬合设计[J].口腔医学,2021,41(8):765-768. [59] 马斐斐,林野,邸萍,等.T-ScanⅢ咬合分析系统测量无牙颌All-on-4种植修复后力分布初探[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2016,51(9):517-520. [60] ABDUO J, TENNANT M. Impact of lateral occlusion schemes: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2015;114(2):193-204. [61] 张雪洋,黄雁红,陈沛,等.无牙颌种植义齿的咬合设计[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2018,36(1):1-3. [62] MIRALLES R. Canine-guide occlusion and group function occlusion are equally acceptable when restoring the dentition. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2016;16(1):41-43. [63] TÜRKER N, BÜYÜKKAPLAN US, SADOWSKY SJ, et al. Finite element stress analysis of applied forces to implants and supporting tissues using the “All-on-Four” concept with different occlusal schemes. J Prosthodont. 2019;28(2):185-194. [64] TÜRKER N, ALKIŞ HT, SADOWSKY SJ, et al. Effects of occlusal scheme on all-on-four abutments, screws, and prostheses: a three-dimensional finite element study. J Oral Implantol. 2021;47(1):18-24. [65] KAYABAŞI O, YÜZBASIOĞLU E, ERZINCANLI F. Static, dynamic and fatigue behaviors of dental implant using finite element method. Adv Eng Soft. 2006;37(10):649-658. |
| [1] | Li Zhifei, Yang Yin, Chen Hualong, Liang Qinqiu, Zhong Yuanming, Zhang Yisheng. Finite element analysis of the correlation between tilt angle of titanium cage and postoperative subsidence of titanium cage after anterior subtotal cervical corpectomy, decompression and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1313-1319. |
| [2] | Ouyang Beiping, Ma Xiangyang, Luo Chunshan, Zou Xiaobao, Lu Tingsheng, Chen Qiling. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new horizontal screw-screw crosslink in posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1320-1324. |
| [3] | Chen Mengmeng, Bao Li, Chen Hao, Jia Pu, Feng Fei, Shi Guan, Tang Hai. Biomechanical characteristics of a novel interspinous distraction fusion device BacFuse for the repair of lumbar degenerative disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1325-1329. |
| [4] | Liang Cheng, Zhang Linqi, Wang Guan, Li Wen, Duan Ke, Li Zhong, Lu Xiaobo, Zhuo Naiqiang. Finite element and biomechanical analysis of different implants in repair for unilateral unstable pelvic posterior ring injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1336-1341. |
| [5] | Guo Sutong, Feng Dehong, Guo Yu, Wang Ling, Ding Yujian, Liu Yi, Qian Zhengying, Li Mingyang. Construction and finite element analysis of normal and osteoporotic hip models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1342-1346. |
| [6] | Yang Junliang, Lu Tan, Xu Biao, Jiang Yaqiong, Wang Fucheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of effects of partial anterior cruciate ligament rupture on knee joint stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1347-1353. |
| [7] | Li Chaojie, Gulati•Maitirouzi, Aierxiding•Abulaiti, Zheng Hui, Tu Hudi. Finite element analysis of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction at different flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1359-1364. |
| [8] | Weng Rui, Lin Dongxin, Guo Haiwei, Zhang Wensheng, Song Yuke, Lin Hongheng, Li Wenchao, Ye Linqiang. Abnormal types of intervertebral disc structure and related mechanical loading with biomechanical factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1436-1442. |
| [9] | Xiaheida·Yilaerjiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun, Reyila·Kuerban, Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Chen Xin. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the distribution pattern of stress in bone tissues with different characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1277-1282. |
| [10] | Wang Qiang, Li Shiyun, Xiong Ying, Li Tiantian. Biomechanical changes of the cervical spine in internal fixation with different anterior cervical interbody fusion systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 821-826. |
| [11] | Wei Yuanbiao, Lin Zhan, Chen Yanmei, Yang Tenghui, Zhao Xiao, Chen Yangsheng, Zhou Yanhui, Yang Minchao, Huang Feiqi. Finite element analysis of effects of sagittal cervical manipulation on intervertebral disc and facet joints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 827-832. |
| [12] | Zhang Rui, Wang Kun, Shen Zicong, Mao Lu, Wu Xiaotao. Effects of endoscopic foraminoplasty and laminoplasty on biomechanical properties of intervertebral disc and isthmus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 833-839. |
| [13] | Kang Zhijie, Cao Zhenhua, Xu Yangyang, Zhang Yunfeng, Jin Feng, Su Baoke, Wang Lidong, Tong Ling, Liu Qinghua, Fang Yuan, Sha Lirong, Liang Liang, Li Mengmeng, Du Yifei, Lin Lin, Wang Haiyan, Li Xiaohe, Li Zhijun. Finite element model establishment and stress analysis of lumbar-sacral intervertebral disc in ankylosing spondylitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 840-846. |
| [14] | Zhang Min, Peng Jing, Zhang Qiang, Chen Dewang. Mechanical properties of L3/4 laminar decompression and intervertebral fusion in elderly osteoporosis patients analyzed by finite element method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 847-851. |
| [15] | Xue Xiaofeng, Wei Yongkang, Qiao Xiaohong, Du Yuyong, Niu Jianjun, Ren Lixin, Yang Huifeng, Zhang Zhimin, Guo Yuan, Chen Weiyi. Finite element analysis of osteoporosis in proximal femur after cannulated screw fixation for femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 862-867. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||