[1] SAFIRI S, KOLAHI AA, SMITH E, et al. Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990-2017: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):819-828.
[2] HAWKER GA. Osteoarthritis is a serious disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 120(5):3-6.
[3] SHARMA L. Osteoarthritis of the Knee. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(1):51-59.
[4] 许铛瀚,林煜翔,韦佳,等.调和阴阳针刀治疗膝关节骨关节炎:随机对照试验[J].中国针灸,2022,42(12):1351-1356.
[5] 王超,李迎春,朱俊琛,等.“矫筋正骨法”针刀治疗膝骨关节炎临床疗效观察[J].安徽中医药大学学报,2022,41(5):80-84.
[6] 陈帅,严海霞,宫大伟,等.针刀松解联合关节镜治疗早中期膝骨关节炎顽固性疼痛疗效[J].中国老年学杂志,2022,42(20):4990-4994.
[7] YANG YH, LIU TH, ZHANG LD, et al. Role of the PERK-eIF2alpha-CHOP Signaling Pathway in the Effect of Needle Knife Therapy on Knee Joint Chondrocyte Apoptosis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019; 2019:7164916.
[8] 伍闲,宋小鸽,卢曼,等.基于lncRNA/miRNA/NF-κB通路探讨针刀对膝骨关节炎兔的软骨保护作用机制[J].北京中医药大学学报, 2022,45(6): 603-611.
[9] 卢曼,黄小双,孟德鸿,等.针刀对膝关节骨关节炎大鼠mTOR/Atg/ULK1/Beclin-1轴及软骨细胞自噬的影响[J].中国针灸,2022,42(1): 59-65.
[10] 陈倩,黄小双,杨永晖,等.针刀调节Ca2+抑制膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨细胞凋亡的实验研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2022,28(10): 1616-1623.
[11] PARK DR, KIM J, KIM GM, et al. Osteoclast-associated receptor blockade prevents articular cartilage destruction via chondrocyte apoptosis regulation. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1): 4343.
[12] 段文秀,汪宗保,张浩,等.木瓜蛋白酶诱导早期膝骨关节炎模型大鼠软骨超微结构的动态变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(18): 2789-2793.
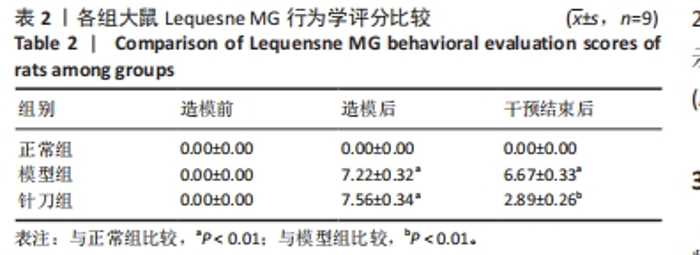
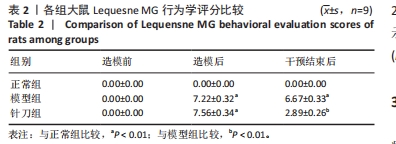
[13] LEQUESNE MG, SAMSON M. Indices of severity in osteoarthritis for weight bearing joints. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1991:27:16-18.
[14] 朱汉章.针刀医学体系概论[J].中国工程科学,2006(7):1-15.
[15] 张义,郭长青.针刀医学的学科属性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(28):5297-5300.
[16] XU X, LAI Y, HUA ZC. Apoptosis and apoptotic body: disease message and therapeutic target potentials. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(1):BSR20180992.
[17] HWANG HS, KIM HA. Chondrocyte Apoptosis in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(11):26035-26054.
[18] SALUCCI S, FALCIERI E, BATTISTELLI M. Chondrocyte death involvement in osteoarthritis. Cell Tissue Res. 2022;389(2):159-170.
[19] KIM N, TAKAMI M, RHO J, et al. A novel member of the leukocyte receptor complex regulates osteoclast differentiation. J Exp Med. 2002; 195(2):201-209.
[20] NEDEVA IR, VITALE M, ELSON A, et al. Role of OSCAR Signaling in Osteoclastogenesis and Bone Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:641162.
[21] ANDERSSON MK, LUNDBERG P, OHLIN A, et al. Effects on osteoclast and osteoblast activities in cultured mouse calvarial bones by synovial fluids from patients with a loose joint prosthesis and from osteoarthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(1):R18.
[22] CROTTI TN, DHARMAPATNI AA, ALIAS E, et al. The immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) -related factors are increased in synovial tissue and vasculature of rheumatoid arthritic joints. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(6):R245.
[23] CARDOSO AL, CORAZZA N, MICHEAU O, et al. The multifaceted role of TRAIL signaling in cancer and immunity. FEBS J. 2021;288(19):5530-5554.
[24] HOPE JM, LOPEZ-CAVESTANY M, WANG W, et al. Activation of Piezo1 sensitizes cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through mitochondrial outer membrane permeability. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(11):837.
[25] YANG Y, WANG Y, KONG Y, et al. Moderate Mechanical Stimulation Protects Rats against Osteoarthritis through the Regulation of TRAIL via the NF-kappaB/NLRP3 Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020: 6196398.
[26] LEE SW, LEE HJ, CHUNG WT, et al. TRAIL induces apoptosis of chondrocytes and influences the pathogenesis of experimentally induced rat osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(2):534-542.
[27] LEE SW, LEE HJ, MOON JB, et al. Purified extract from Clematis mandshurica prevents adenoviral-TRAIL induced apoptosis on rat articular chondrocytes. Am J Chin Med. 2008;36(2):399-410.
[28] LIU Y, GE J, CHEN D, et al. Osteoprotegerin deficiency leads to deformation of the articular cartilage in femoral head. J Mol Histol. 2016;47(5):475-483.
[29] CORALLINI F, CELEGHINI C, RIMONDI E, et al. Trail down-regulates the release of osteoprotegerin (OPG) by primary stromal cells. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226(9):2279-2286.
[30] DELIGIORGI MV, PANAYIOTIDIS MI, GRINIATSOS J, et al. Harnessing the versatile role of OPG in bone oncology: counterbalancing RANKL and TRAIL signaling and beyond. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020;37(1): 13-30.
[31] CHEN D, LIU Y, LIU Z, et al. OPG is Required for the Postnatal Maintenance of Condylar Cartilage. Calcif Tissue Int. 2019;104(4):461-474.
|