Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (5): 664-668.doi: 10.12307/2024.251
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and properties of selective laser melting of porous titanium at a low energy density
Cheng Jinhui, Wu Quan, Peng Min, Huang Changli, Tian Huimin, Li Yang
- School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2023-01-12Accepted:2023-02-14Online:2024-02-18Published:2023-08-16 -
Contact:Wu Quan, MD, Associate professor, School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Cheng Jinhui, Master candidate, School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Guizhou Provincial Department of Education Serves the “Four New” and “Four Modernizations” Science and Technology Research Project, No. Qianjiaoji [2022]005 (to WQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cheng Jinhui, Wu Quan, Peng Min, Huang Changli, Tian Huimin, Li Yang. Preparation and properties of selective laser melting of porous titanium at a low energy density[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 664-668.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
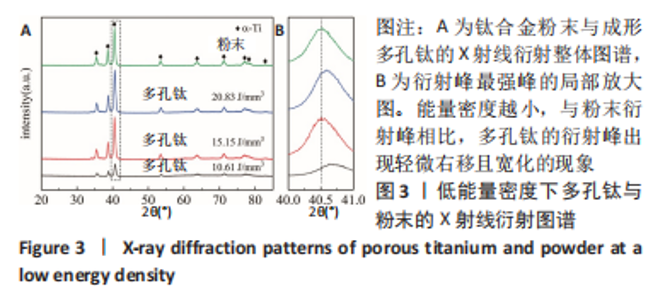
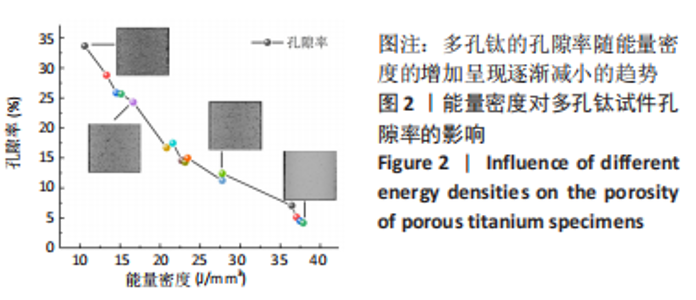
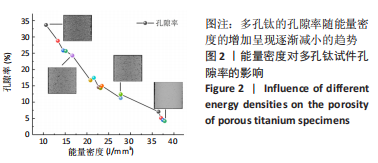
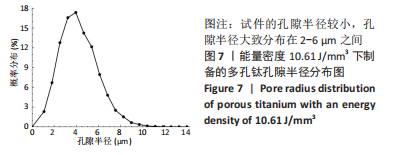
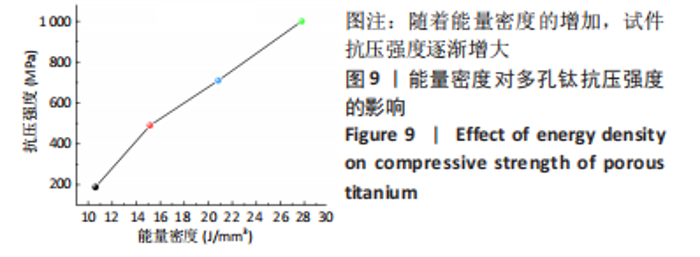
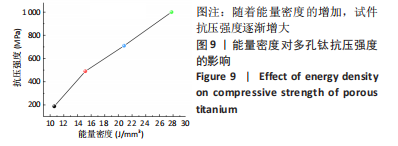
随着能量密度的增加,试件的孔隙率逐渐降低,在10.61-37.88 J/mm3范围内,选区激光熔化成形试件的孔隙率在4.16%-33.67%之间。将表1参数设计值与图2结果结合分析,可将成形试件按能量密度大致分为成形多孔和成形较为致密2个区域。在能量密度10.61-27.78 J/mm3区间下,能成形孔隙率11.23%-33.67%的多孔试件,该区间下能量输入不足,合金内部熔池流动性较差,无法形成良好的重叠,形成较大孔隙。同时,熔深不足造成的润湿不良也使得层与层之间出现未熔合层间孔隙[31-32]。在能量密度27.78-37.88 J/mm3区间下,随着能量密度的增加,熔池流动性提高,粉末颗粒熔化为连续熔道[33-34],试件的孔隙率降低,该区间下成形试件较为致密,孔隙率较小。 2.2 成形件物相分析 图3显示了在不同能量密度下成形的多孔钛的X射线衍射图谱。由图3A可知,Ti-6Al-4V合金粉末与成形多孔试件主要由密排六方α钛组成,β相的含量很少,可能原因为:β相晶粒非常细小,散布于α相晶界间,难以生成明显的特定β相晶面指数的衍射峰[35]。同时,与Ti-6Al-4V合金粉末X射线衍射峰相比,多孔试件的衍射峰出现轻微右移现象。这是因为小能量密度下热输入减少,加快了试件冷却速度,致使Al、V元素固溶于相结构中,又因为Al、V的原子半径小于Ti(Al:0.143 nm,V:0.134 nm,Ti:0.145 nm)[36-37],α相及β相的晶格常数降低,衍射峰右移。"
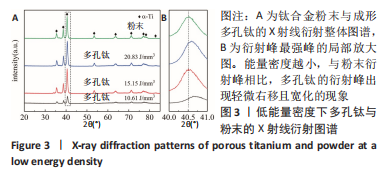

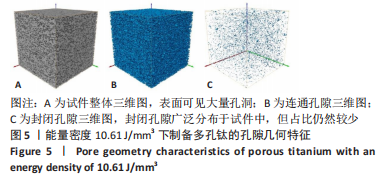
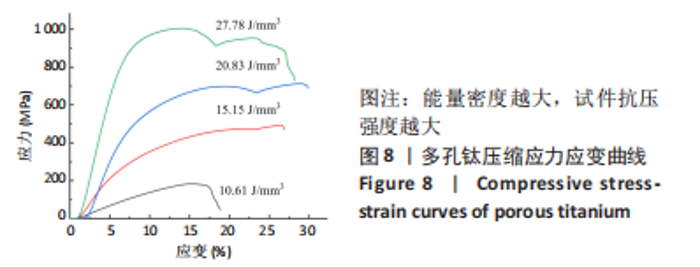
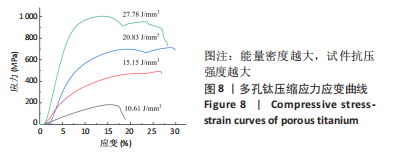
对图3A中衍射角40°-41°进行局部放大,得到图3B。由图3B可知,衍射峰最强峰的强度随着能量密度的减小逐渐降低并出现宽化现象,这是因为激光能量输入不足导致试样结晶度较差,从而造成衍射峰峰值降低且宽化的现象。 2.3 成形件微观形貌演变 图4为不同能量密度下成形的多孔钛断面微观形貌,可以发现,试件断面出现未完全熔化球形粉末颗粒,且随着能量密度的增加,颗粒数目越来越少。图4A为能量密度10.61 J/mm3下制备的试件,断面出现大量表面微熔化的球形粉末颗粒,颗粒之间轻微连接,形成烧结颈。该阶段处于典型的烧结早期烧结颈长大阶段,该阶段下原子向颗粒结合面的大量迁移使得烧结颈扩大,颗粒间距离缩小,形成具有大量连通孔隙、高比表面积的多孔钛[38-39]。图4B是图4A的放大倍数图,可清晰看到轻微连接的烧结颈及不规则条状连通孔隙,封闭孔较少,熔化的粉末颗粒间形成的小孔与球形颗粒烧结模型中烧结颈长大阶段描述一致。图4C是能量密度15.15 J/mm3下制备的试件,此时,粉末颗粒熔化程度加剧,烧结颈较图4A中长大,粉末之间熔化成团聚状,形成轻微熔道,但仍有部分粉末颗粒未完全熔化,孔隙尺寸较之前变小,不规则连通孔仍然是该能量密度下的主要孔隙组成。能量密度的增加主要表现为烧结颈和孔隙尺寸的变化。图4D是能量密度20.83 J/mm3下制备的试件,该能量密度下粉末熔化程度加剧,能清晰看到层与层之间的熔道,但仍有未完全熔化的粉末颗粒,出现近球形封闭孔隙,该阶段下孔隙以连通孔和近球形封闭孔为主。"

| [1] WANG ZM, JIA YF, ZHANG XC, et al. Effects of different mechanical surface enhancement techniques on surface integrity and fatigue properties of Ti-6Al-4V: a review. Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci. 2019;44(6):445-469. [2] WANG F, WANG JJ, LI QS, et al. Analysis and research of the high-cycle fatigue fracture mode based on stress ratio and residual stress of Ti-6Al-4V. Adv Mater Sci Eng. 2022;2022:1-9. [3] KALANTARI K, SALEH B, WEBSTER TJ. Biological applications of severely plastically deformed nano-grained medical devices: a review. Nanomaterials. 2021;11(3):748. [4] JOSKA L, FOJT J, MESTEK O, et al. The effect of a DLC coating adhesion layer on the corrosion behavior of titanium and the Ti6Al4V alloy for dental implants. Surf Coat Technol. 2012;206(23):4899-4906. [5] MARIN E, FUSI S, PRESSACCO M, et al. Characterization of cellular solids in Ti6Al4V for orthopaedic implant applications: trabecular titanium. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2010;3(5):373-381. [6] LIU S, SHIN YC. Additive manufacturing of Ti6Al4V alloy: a review. Mater Des. 2019;164:107552. [7] 王建忠,敖庆波,荆鹏,等.多孔钛的制备及应用[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2022,51(5):1907-1918. [8] 赵立杰,张芳,彭军,等.多孔金属材料的制备工艺研究进展及应用[J].粉末冶金工业,2022,32(5):110-116. [9] 肖健,邱贵宝.大孔径高孔隙率烧结泡沫钛的造孔剂研究述评[J].中国材料进展,2018,37(5):372-378. [10] 刘永宁,王智祥,刘锦平,等.造孔剂法制备泡沫钛的研究现状与进展[J].粉末冶金技术,2019,37(4):306-311. [11] SHI MJ, LIU SF, WANG QG, et al. Preparation and properties of titanium obtained by spark plasma sintering of a Ti powder-fiber mixture. Materials. 2018;11(12): 2510. [12] ZHANG LC, CHEN LY. A review on biomedical titanium alloys: recent progress and prospect. Adv Eng Mater. 2019;21(4):1801215. [13] 高祥熙,杨平华,乔海燕,等.基于μCT表征的SLM成形GH3536高温合金缺陷特征[J].材料工程,2022,50(10):63-72. [14] 廉艳平,王潘丁,高杰,等.金属增材制造若干关键力学问题研究进展[J].力学进展,2021,51(3):648-701. [15] SHIPLEY H, MCDONNELL D, CULLETON M, et al. Optimisation of process parameters to address fundamental challenges during selective laser melting of Ti-6Al-4V: a review. Int J Mach Tools Manuf. 2018;128:1-20. [16] 高芮宁,熊胤泽,张航,等.SLM制备径向梯度多孔钛/钽的力学性能及生物相容性[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2021,50(1):249-254. [17] CHANG C, HUANG J, YAN XC, et al. Microstructure and mechanical deformation behavior of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V ELI alloy porous structures. Mater Lett. 2020;277:128366. [18] HAO MZ, WEI CJ, LIU X, et al. Quantitative evaluation on mechanical characterization of Ti6Al4V porous scaffold designed based on Weaire-Phelan structure via experimental and numerical analysis methods. J Alloy Compd. 2021;885:160234. [19] 吴先哲,刘红旗,王富友,等.激光选区熔化技术制造医用多孔金属材料研究现状[J].激光杂志,2018,39(11):8-17. [20] GOTOH R, FURST BI, ROBERTS SN, et al. Experimental and analytical investigations of AlSi10Mg, stainless steel, Inconel 625 and Ti-6Al-4V porous materials printed via powder bed fusion. Prog Addit Manuf. 2022;7(5):943-955. [21] SHI CL, LU NN, QIN YR, et al. Study on mechanical properties and permeability of elliptical porous scaffold based on the SLM manufactured medical Ti6Al4V. Plos One. 2021;16(3):e0247764. [22] LIAO BO, XU C, LI W, et al. Bionic mechanical design and SLM manufacture of porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds for load-bearing cancellous bone implants. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2021;23(3):97-107. [23] BARTOLOMEU F, COSTA MM, ALVES N, et al. Selective Laser Melting of Ti6Al4V sub-millimetric cellular structures: prediction of dimensional deviations and mechanical performance. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;113:104123. [24] RAN QC, YANG WH, HU Y, et al. Osteogenesis of 3D printed porous Ti6Al4V implants with different pore sizes. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;84:1-11. [25] DU Y,LIANG HX,XIE DQ,et al.Design and statistical analysis of irregular porous scaffolds for orthopedic reconstruction based on voronoi tessellation and fabricated via selective laser melting (SLM). Mater Chem Phys. 2020;239:121968. [26] GE JG, HUANG J, LEI YP, et al. Microstructural features and compressive properties of SLM Ti6Al4V lattice structures. Surf Coat Technol. 2020;403:126419. [27] JING YL, WANG P, YAN XL. Effect of process parameters and layer thickness on the quality and performance of Ti-6Al-4V fabricated by selective laser melting. Coatings. 2021;11(11):1323. [28] JIANG HZ, LI ZY, FENG T, et al. Effect of process parameters on defects, melt pool shape, microstructure, and tensile behavior of 316L stainless steel produced by selective laser melting. Acta Metall Sin(Engl Lett). 2021;34:495-510. [29] 孙靖,吴俊,朱忠良,等.激光能量密度对选区激光熔化成形Al_4SiC_4/AlSi10Mg复合材料显微组织的影响[J].机械工程材料,2022,46(8):68-74. [30] COSMA C, KESSLER J, GEBHARDT A, et al. Improving the mechanical strength of dental applications and lattice structures SLM processed. Materials. 2020;13(4):905. [31] 尹浜兆,秦瑜,温鹏,等.激光粉末床熔融制备金属骨植入物[J].中国激光, 2020,47(11):8-25. [32] 姚讯杰,王佳玮,杨雁程,等.金属构件激光增材制造缺陷产生机理及控制机制探究[J].中国激光,2022,49(14):286-296. [33] ZHOU YS, LIU YD, SUN XH, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the formed specimen of TC4 titanium alloy by selective laser melting variable parameter forming process. Appl Phys A. 2022;128(10):917. [34] FOTOVVATI B, RAUNIYAR S, ARNOLD JA, et al. Experimental, computational, and data-driven study of the effects of selective laser melting (SLM) process parameters on single-layer surface characteristics. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2022; 123(1-2):119-144. [35] 毛江虹,罗斌莉,杨晓康.空冷条件下医用TC4合金的组织与相转变[J].热加工工艺,2021,50(22):153-158. [36] 时国浩.激光熔化沉积工艺参数对Ti6Al4V合金组织与性能影响的研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2021. [37] 毛新华,刘辛,谢焕文,等.制备方法对3D打印用Ti-6Al-4V合金粉体特性的影响[J].材料研究与应用,2017,11(1):13-18. [38] 杨建明,曹赛男,王永宽,等.水基粘结剂3DP法三维打印多孔316L不锈钢的研究[J].热加工工艺,2022,51(2):60-64. [39] 黄培云.粉末冶金原理[M].北京:冶金工业出版社,1997:1-2. |
| [1] | Wang Jianchun, Yang Shuqing, Su Xin, Wang Hongyuan. Different contents of B2O3 affect mechanical properties and bioactivity of bioactive glass scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 712-716. |
| [2] | Lan Weiwei, Yu Yaodong, Huang Di, Chen Weiyi. In vitro degradation behavior of Mg-Zn-Ca alloys [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 717-723. |
| [3] | Wei Yuxue, Wang Di, Liu Xiaoqiu. Design, synthesis and properties of oral composite resin monomers with different photoinitiators [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 731-735. |
| [4] | Zhang Yihai, Shang Peng, Ma Benyuan, Hou Guanghui, Cui Lunxu, Song Wanzhen, Qi Dexuan, Liu Yancheng. Structural design and mechanical property analysis of trabecular scaffold of triply periodic minimal surface with a radial gradient [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 741-746. |
| [5] | Xu Rong, Wang Haojie, Geng Mengxiang, Meng Kai, Wang Hui, Zhang Keqin, Zhao Huijing. Research advance in preparation and functional modification of porous polytetrafluoroethylene artificial blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 759-765. |
| [6] | Xu Xiaodong, Zhou Jiping, Zhang Qi, Feng Chen, Zhu Mianshun, Shi Hongcan. 3D printing process of gelatin/oxidized nanocellulose skin scaffold with high elastic modulus and high porosity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 398-403. |
| [7] | He Yinhao, Li Xiaosheng, Chen Hongwen, Chen Tiezhu. 3D printed porous tantalum metal in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: current status and application prospect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1455-1461. |
| [8] | Zhong Yizheng, Huang Peizhen, Cai Qunbin, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Dong Hang. Microstructural indexes that determine the trabecular bone maximum stress of micro-finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1313-1318. |
| [9] | Wang Shuxiang, Wu Quan, Zhou Xiaosong, Kuang Xiantao. Selective laser melting forming process and deformation experiment of titanium alloy full crown [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1012-1016. |
| [10] | Wang Mingsheng, Cui Huanxi, Cui Hongkai, Pei Guanhui, Li Daoguang, Yan Haiqing, Zhang Ping. Ngn2 effects on brain microstructure and keratinocyte activity in cerebral ischemia rats via regulating Nrf2/HO-1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5298-5303. |
| [11] | Guo Chao, Li Qiyi, Cui Jinghong, Wang Hui, Tang Yanfeng. Effects of Yiqi Huoxue Tongluo Decoction on synovial cell apoptosis and ADAMTS-5 protein expression in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4193-4199. |
| [12] | Jiang Songsong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Detection technology of mechanical properties of the arterial wall [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4208-4213. |
| [13] | Deng Moyuan, Peng Kun. Role and regulation of macrophages in biomaterial-mediated fibrosis formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 4085-4092. |
| [14] | Lyu Jiayi, Yao Qingqiang, Zhu Yishen. Role and advantages of carbon nanotubes for tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 4093-4100. |
| [15] | Chen Jianquan, Chen Maoshui, Lyu Zhouming, Chen Rongbin, Yu Zhaoyu, Liu Wanpeng, Lin Xinyuan, Lin Dingkun. Biomechanical properties of cortical bone trajectory combined with pedicle screw fixation on vertebral body motion unit: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3457-3462. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||