Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (26): 4208-4213.doi: 10.12307/2023.525
Previous Articles Next Articles
Detection technology of mechanical properties of the arterial wall
Jiang Songsong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu
- The Fifth Affiliated (Zhuhai) Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zhuhai 519100, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2022-07-23Accepted:2022-09-19Online:2023-09-18Published:2023-01-28 -
Contact:Chen Shijiu, The Fifth Affiliated (Zhuhai) Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zhuhai 519100, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Jiang Songsong, Master candidate, The Fifth Affiliated (Zhuhai) Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zhuhai 519100, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960842 (to WC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Songsong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Detection technology of mechanical properties of the arterial wall[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4208-4213.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

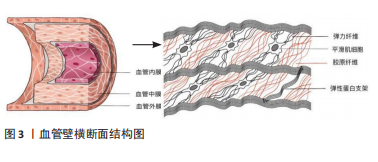
2.1 血管壁结构 根据细胞组织学的不同,动脉可分为两种截然不同的类型:弹力型和肌型。弹性(或传导)动脉位于心脏和其他器官附近,由许多层穿孔的弹性膜组成,因此这种结构特别适用于大量血液的流动;肌性动脉的功能是确保血液快速和完整地分配到所有器官和组织。此篇综述将集中在大而有弹性的动脉模型上。 大动脉壁由3层组成:内膜、中层和外膜,每一层都有不同的结构特征和与其功能严格相关的不同成分。内膜由2个亚层组成:最里面的一层主要由内皮细胞、薄的基底膜、富含蛋白多糖的基质和少量的胶原纤维组成[1],它构成管腔,因此具有与血液直接接触的功能,但它在决定动脉壁的弹性性质方面仅仅起着微不足道的作用;最外层主要由弹性蛋白纤维和单个血管平滑肌细胞(vascular smooth muscle cells,VSMCs)组成。实验结果证明,至少在健康的动脉中,由于其厚度有限,内膜对动脉壁力学的影响可以忽略不计。中层主要由VSMCs、弹性蛋白及胶原纤维组成[1-3]。整个中层呈同心结构单元组织,即整个厚度重复的内侧板层单元,由片状弹性板层和层间空间交替组成的,板层间隙是由VSMCs、胶原纤维、弹性蛋白支架和板层间弹性蛋白纤维组成的复杂结构。具体地说,板层间弹性蛋白纤维(占总弹性蛋白含量的27%)形成弹性层与VSMCs之间的连接,其相对于圆周方向具有约19°(圆周-径向平面)的倾角和在纵向-圆周平面中的圆周取向[4-5]。VSMCs的特征是与板层间弹性蛋白纤维的倾斜角相同的延长的椭圆形核,似乎既与胶原纤维又与弹性蛋白片层相互作用[4,6]。弹性蛋白支柱(占总弹性蛋白含量的2%)在相邻的弹性蛋白片层之间形成连接。VSMCs被波浪状的胶原纤维包围,就体积分数而言,胶原纤维代表了板层间隙的主要成分。内、外弹力板分别将中膜与内膜和外膜分开。外膜是动脉壁的最外层,是相对无细胞的,主要由胶原组成[7],与中膜相比,外膜中胶原纤维呈更复杂的角度分布,有研究发现胶原纤维的方向性随着外膜厚度的变化而变化[8]。血管壁横断面结构见图3。"

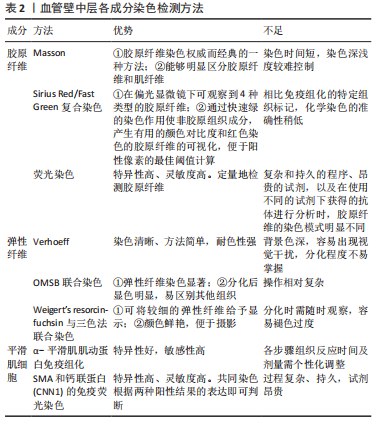
大动脉的3层结构及复杂的成分,使其具有非线性、各向异性的材料特性,并且这些特性随年龄、主动脉的离心距离、血管种类和病理条件而变化[9]。例如:在对主动脉的研究中发现,随着年龄的增大血管壁中弹性纤维的比例减少、胶原纤维的比例增加,导致血管顺应性下降[10-11];不同解剖部位的弹性动脉,其每层细胞含量有所差异,比如升主动脉到降主动脉的这段距离,从纵向微观结构来看,弹性蛋白占比呈明显下降趋势,力学试验角度观察,相比降主动脉,升主动脉每单位面积需要更高的能量[12-13]。但FERRUZZI等[14]学者通过双轴拉力试验等力学性能检测,认为随着年龄变化,5个血管区域(升、降低主动脉、肾上和肾下腹主动脉以及颈总动脉)之间的管壁结构和机械功能从弹性能量存储能力丧失等方面观察,变化几乎是一致的。动脉是一种分层的复合材料,具有不同的性质,但许多模型假设动脉壁是均匀的,这样有利于构建物理模型,对血管力学性能进行预测,但由于血管的复杂性,根据模型所计算出的结果往往与实际值存在偏差,实际应用中可能需要同时使用多层模型才能再现整个主动脉[15],或者将血管各层分离出来单独研究,例如,BOGUNOVIC等[16]将血管中的平滑肌细胞分离出来,利用电子细胞基质阻抗判断进行反复多次实验,得出较为精准的模型,用来预测血管平滑肌与血管动脉瘤之间的联系。机械驱动的血管壁重塑,通常假设动脉处于稳态应力状态,并且动脉壁中的几何、生物和化学变化是动脉试图恢复到稳态状态的结果[17-18]。想要得到血管材料的准确模型,往往需要将动脉壁的生物微结构与机械力学结合起来,进行综合分析[19]。 2.2 血管壁机械力学性能检测 血管壁不同于各种同性弹性体,它是更为复杂且异向性的,普遍认同其应力-应变关系为非线性关系。由于血管壁具有3层结构和多种成分,将其认为是一种具备特殊力学性质的复合材料,这种特性使得其在进行力学检测时,常常出现松弛及蠕变现象[20],需要通过相应的物理模型及函数关系进行校正,应用模型能更好地贴合实验数据,可以用来预测各种加载条件下的力学行为。众多学者通过不断的实验,逐渐将血管力学区分为主动力学和被动力学,便于描述及分析,例如通过进行弹性蛋白或胶原降解后的组织学研究和力学实验,为单个细胞外基质成分如何参与被动动脉机械提供了线索。现在普遍认为,VSMCs在动脉的主动机械反应中起着关键作用,胶原蛋白和弹性蛋白决定了被动力学,其中弹性蛋白通常被认为是各向同性和线性的,而胶原则被认为是各向异性和非线性的[2]。 2.2.1 血管单轴力学性能检测 单轴拉伸实验是研究材料机械性能的最基本、应用最广泛的实验,通过不同实验方案的设计,能够对血管进行拉伸性能、拉伸强度与变形率、拉断力、抗撕裂性能、剥离试验、压缩试验、弯曲试验、剪切试验等检测。在单轴拉伸实验中,常将获取到的血管进行修整,取其中轴向或周向的条状组织进行拉伸,或是直接将整段血管条夹持进行拉伸,记录力-伸长率之间的关系并建模,来研究血管单轴方向的力学性质,通常描述为杨氏模量或刚性[21-22],反复多次的单轴拉伸实验数据可被用于佐证物理模型的有效性[22]。通过对血管的不同角度在不同的拉伸速率下分别进行单轴测试实验,可用于分析血管不同方向的力学变化[23]。 2.2.2 血管双轴力学性能检测 双轴拉力试验与单轴拉力试验相比,其设备更加昂贵,且需要更加严格控制材料的大小、环境温度、湿度、材料固定角度等,所以目前国内开展应用较少。平面双轴拉力试验允许二维(2D)应力状态,用来完全表征它们的三维(3D)机械性能,可以更好地对生物组织复杂的力学行为进行模型构建和分析,这在传统的弹性本构模型中是不容易的。DEPLANO等[24]进行了双轴拉伸试验,并实施了立体数字图像来测量产生的位移的三维分量,这样更便于量化血管壁的力学指标,从而能更加准确地比较新鲜血管与处理后血管的差异。NIESTRAWSKA等[25]学者通过进行双轴拉伸实验分别对人类腹主动脉的周向和纵向进行研究,得到应力与拉伸比的曲线证明了动脉血管壁的各向异性和非线性。 2.2.3 血管压力爆破试验力学性能检测 对于血管移植物的机械强度,国际标准化组织(International Organization for Standardization,ISO)中标准7198描述的压力爆破测试是一种常用的血管移植物测试方法,对血管段进行插管,并以一定的速度用PBS液加压,直到失败,结合计算机记录相关数据进行统计,这种爆破压力测试可以模拟体内环境,并与新鲜血管做比对,结合相应的物理模型预测,从而探讨其是否合格进行体内移植[26]。但是压力爆破试验对血管口径及长短有一定的要求,对于长度较短、直径较大的移植物则不太可行,SYEDAIN等[27]在进行压力爆破测试的同时,尝试加入探头穿刺试验,阐明了测试参数的重要性,并为血管移植物的破裂强度提供了理论预测。 2.2.4 血管超声波成像定量力学性能检测 除了体外进行的力学测试,脉搏波速度(pulse wave velocity,PWV)也可以提供对动脉壁杨氏模量的估计,脉搏波本质上是在血液中传播的压缩压力波,但受到边界性质的影响,如杨氏模量E、半径R、厚度h和动脉壁密度r。最早学者们通过使用连接在皮肤上的2个或更多压力传感器测量相隔已知距离的2个动脉部位之间脉搏的传播时间,可以直接估计PWV。虽然这种方法是稳健的,并给出了动脉树一部分PWV的平均(或全局)估计,但由于2个测量点之间的距离存在误差,弹性模量无法准确估计。为了获得PWV的局部估计,减少传输波束数量的实时超声成像,即脉冲波成像技术被提出。但是这些技术都假定动脉壁的黏弹性性质在心动周期中是不变的,要获得局部、瞬时和定量的硬度测量,不能简单地依靠动脉脉搏产生的纵波,这时需要另一种被称为剪切波的机械波,可以用于每秒数次地感知动脉壁。为了产生这些机械波,需要一个独立的机械激励源,并且可以由聚焦的超声束的声辐射力来提供。有研究者结合剪切波及以前的技术,将提出的超声剪切成像(supersonic shear imaging,SSI)概念应用于血管壁,认为该技术可以作为一种非侵入性的定量测量动脉硬度的方法[28]。LOU等[29]学者通过临床试验后认为超声弹性成像技术与力学测试具有很好的一致性,可以稳定地评估颈动脉斑块的杨氏模量。机械力学检测方法的总结,见表1。"
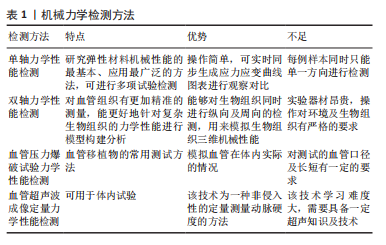

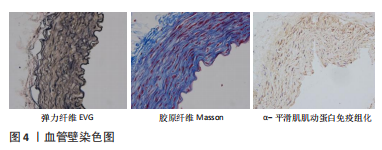
2.3 血管壁的微观结构检测 血管壁承担主要拉力的部分在于中膜,由弹性纤维、胶原蛋白、平滑肌构成,为了在微结构连接的本构模型中联系各个成分对血管壁的力学贡献,应用合理的成像方法进行观察,评判冻存处理后血管与新鲜血管的差异,便于找出理想的冻存方案。传统上,血管壁结构的定量是用生化和体视学方法来完成的,随着显微技术的发展,现今则是结合数字图像分析和处理技术。数字图像分析可以比目视定性方法更客观、更灵敏、更准确地进行定量评估。这些技术被应用于图像以提高其质量、解释或提供从中提取信息的工具[30]。图像分割方法提供了基于形态特征的感兴趣结构的初始近似,例如大小、形状、颜色等,然后是这些元素的量化[31]。 2.3.1 血管胶原纤维成像 动脉壁有3种类型的胶原蛋白:Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型,属于纤维亚家族;Ⅳ型,形成网状结构。胶原的交联度是胶原组织机械性能的关键决定因素,它的改变在病理学和衰老方面显著改变了动脉的行为[32]。微结构组织的属性和适当的数学描述可能会因动脉类型、种类、纵向位置和穿过管壁的径向位置而异[12],利用共焦显微镜[1]、偏振光显微镜[33]、多光子显微镜[34]、小角光散射及线性偏振光等[35-36],成像与机械测试相结合,便于研究微结构如何随载荷变化[37]。单纯的光学显微镜观察还需配合精准的特殊染色,例如:CAO等[38-39]学者通过Masson、Sirius Red等特异性染色来观察血管壁中胶原纤维的形态、数量等。SEGNANI等[40]通过实验证明了与单独的Sirius Red相比,Sirius Red/Fast Green这种复合染色的方法对胶原纤维的定性和定量评估都是最敏感的。免疫组织学实验显示CNA35探针与Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原抗体共定位,与现有的胶原蛋白可视化方法相比,这种荧光探针具有重要的优势[41]。 2.3.2 血管弹性纤维成像 弹性纤维的在血管壁的占比变化同上所述,此处不再赘述。弹性蛋白构成了90%的弹性纤维,是血管壁细胞外基质的重要组成部分,在没有能量输入的情况下允许长范围的变形和被动反冲。弹性蛋白在微观层面上呈现螺旋结构,这被认为是其弹性特性背后的原因之一[42];在分子水平上,解释弹性蛋白弹性的合理机制是提供弹性回弹力的熵变化,如在橡胶弹性的经典理论中看到的那样,以及弹性蛋白疏水区域的高度动态行为[43-44]。在组织学的研究中,弹性蛋白特殊染色技术有Orcein、Verhoef、Weigert’s resorcin-fuchsin以及Aldehyde-fuchsin等染色方法。Weigert’s resorcin-fuchsin染色法可与伊红或三色染色方法(如van Gieson)相结合,以增加染色结构的数量[45]。GAJDA等[46]在通过对小鼠头臂干动脉的粥样硬化斑块进行研究时,将orcein和martius scarlet blue(OMSB)联合起来对其进行染色,发现这种联合染色的新方法使弹性纤维能在复杂的血管壁成分中显著出来,并同时使胶原纤维着色,进行更好地定性定量分析。 2.3.3 血管平滑肌细胞成像 平滑肌细胞是周向的,利用与细胞外基质的连接来调节机械性能,通过这种收缩特性调节主动脉中的血流和脉压[47]。VSMC的功能及结构完整与主动脉瘤的形成息息相关,VSMC数量的减少、活性氧升高、自噬缺陷等都有助于腹主动脉瘤的形成[48]。在VSMC的研究中发现,平滑肌细胞内皮细胞富含的与迁移/分化相关的长链非编码RNA (smooth muscle and endothelial cell-enriched migration/differentiation associated long non-coding RNA,LncRNA SENCR)作为腹主动脉瘤治疗靶点的潜力,SENCR的过表达通过抑制VSMC细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解来抑制腹主动脉瘤的形成[49];抑制转录因子叉头盒O3a(forkhead box O3a,FoxO3a)过表达会激活VSMC自噬反应,通过降低FoxO3a有可能降低主动脉瘤形成[50]。在这些研究中,通过对α平滑肌肌动蛋白进行免疫组化,来观察血管平滑肌在血管壁中的含量,是比较常见的处理方法[51]。钙联蛋白(calnexin1,CNN1)是成熟平滑肌细胞的收缩标志,且CNN1和SMA的共同表达表明发育成熟,故对切片进行SMA和CNN1的免疫荧光染色,便于对处理后的血管移植物与新鲜血管的成熟平滑肌细胞进行比较[52]。 血管壁染色图见图4。血管壁中层各成分染色检测方法见表2。"
| [1] CHEN H, KASSAB GS. Microstructure-based constitutive model of coronary artery with active smooth muscle contraction. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):9339. [2] HOLZAPFEL GA, OGDEN RW. Biomechanical relevance of the microstructure in artery walls with a focus on passive and active components. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018;315(3):H540-H549. [3] CHEN H, KASSAB GS. Microstructure-based biomechanics of coronary arteries in health and disease. J Biomech. 2016;49(12):2548-2559. [4] CAVINATO C, HELFENSTEIN-DIDIER C, OLIVIER T, et al. Biaxial loading of arterial tissues with 3D in situ observations of adventitia fibrous microstructure: A method coupling multi-photon confocal microscopy and bulge inflation test. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;74:488-498. [5] SUGITA S, MATSUMOTO T. Multiphoton microscopy observations of 3D elastin and collagen fiber microstructure changes during pressurization in aortic media. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2017;16(3):763-773. [6] 王静,李逸明,刘丹,等.人主动脉平滑肌细胞体外分离及培养[J].临床军医杂志,2021,49(10):1117-1121,1126. [7] LUO T, CHEN H, KASSAB GS. Resliced image space construction for coronary artery collagen fibers. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0184972. [8] GIUDICI A, KHIR AW, SZAFRON JM, et al. From Uniaxial Testing of Isolated Layers to a Tri-Layered Arterial Wall: A Novel Constitutive Modelling Framework. Ann Biomed Eng. 2021;49(9):2454-2467. [9] SHERIFOVA S, HOLZAPFEL GA. Biomechanics of aortic wall failure with a focus on dissection and aneurysm: A review. Acta Biomater. 2019;99:1-17. [10] MOSTACO-GUIDOLIN LB, SMITH MSD, HEWKO M, et al. Fractal dimension and directional analysis of elastic and collagen fiber arrangement in unsectioned arterial tissues affected by atherosclerosis and aging. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(3):638-646. [11] JADIDI M, HABIBNEZHAD M, ANTTILA E, et al. Mechanical and structural changes in human thoracic aortas with age. Acta Biomater. 2020;103:172-188. [12] PENA JA, CORRAL V, MARTINEZ MA, et al. Over length quantification of the multiaxial mechanical properties of the ascending, descending and abdominal aorta using Digital Image Correlation. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;77:434-445. [13] MYNENI M, RAO A, JIANG M, et al. Segmental Variations in the Peel Characteristics of the Porcine Thoracic Aorta. Ann Biomed Eng. 2020; 48(6):1751-1767. [14] FERRUZZI J, MADZIVA D, CAULK AW, et al. Compromised mechanical homeostasis in arterial aging and associated cardiovascular consequences. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2018;17(5):1281-1295. [15] DIAZ C, PENA JA, MARTINEZ MA, et al. Unraveling the multilayer mechanical response of aorta using layer-specific residual stresses and experimental properties. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;113: 104070. [16] BOGUNOVIC N, MEEKEL JP, MICHA D, et al. Impaired smooth muscle cell contractility as a novel concept of abdominal aortic aneurysm pathophysiology. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):6837. [17] EICHINGER JF, HAEUSEL LJ, PAUKNER D, et al. Mechanical homeostasis in tissue equivalents: a review. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021; 20(3):833-850. [18] HUMPHREY JD, SCHWARTZ MA. Vascular Mechanobiology: Homeostasis, Adaptation, and Disease. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2021;23:1-27. [19] 孟鑫,王小峰,黄敏杰,等.猪动脉血管的力学性能分析[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(4):411-416. [20] 冯韵迪,吴昊,霍云龙.动脉血管壁主动和被动力学性能实验测量和建模分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2020,37(6):939-947. [21] KORENCZUK CE, DHUME RY, LIAO K, et al. Ex Vivo Mechanical Tests and Multiscale Computational Modeling Highlight the Importance of Intramural Shear Stress in Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms. J Biomech Eng. 2019;141(12):121010-121010-11. [22] SCHROEDER F, POLZER S, SLAZANSKY M, et al. Predictive capabilities of various constitutive models for arterial tissue. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;78:369-380. [23] JIA Y, QIAO Y, RICARDO ARGUETA-MORALES I, et al. Experimental Study of Anisotropic Stress/Strain Relationships of Aortic and Pulmonary Artery Homografts and Synthetic Vascular Grafts. J Biomech Eng. 2017; 139(10). doi: 10.1115/1.4037400. [24] DEPLANO V, BOUFI M, BOIRON O, et al. Biaxial tensile tests of the porcine ascending aorta. J Biomech. 2016;49(10):2031-2037. [25] NIESTRAWSKA JA, REGITNIG P, VIERTLER C, et al. The role of tissue remodeling in mechanics and pathogenesis of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Acta Biomater. 2019;88:149-161. [26] CASTILLO-CRUZ O, PEREZ-ARANDA C, GAMBOA F, et al. Prediction of circumferential compliance and burst strength of polymeric vascular grafts. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;79:332-340. [27] SYEDAIN ZH, PRUNTY A, LI J, et al. Evaluation of the probe burst test as a measure of strength for a biologically-engineered vascular graft. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;119:104527. [28] PALMERI ML, MILKOWSKI A, BARR R, et al. Radiological Society of North America/Quantitative Imaging Biomarker Alliance Shear Wave Speed Bias Quantification in Elastic and Viscoelastic Phantoms. J Ultrasound Med. 2021;40(3):569-581. [29] LOU Z, YANG J, TANG L, et al. Shear Wave Elastography Imaging for the Features of Symptomatic Carotid Plaques: A Feasibility Study. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36(6):1213-1223. [30] ARGANDA-CARRERAS I, ANDREY P. Designing Image Analysis Pipelines in Light Microscopy: A Rational Approach. Methods Mol Biol. 2017; 1563:185-207. [31] JACKSON N, ASSAD M, VOLLMER D, et al. Histopathological Evaluation of Orthopedic Medical Devices: The State-of-the-art in Animal Models, Imaging, and Histomorphometry Techniques. Toxicologic Pathology. 2019;47(3):280-296. [32] PIERCE GL, COUTINHO TA, DUBOSE LE, et al. Is It Good to Have a Stiff Aorta with Aging? Causes and Consequences. Physiology (Bethesda). 2022;37(3):154-173. [33] SÁEZ P, GARCÍA A, PEÑA E, et al. Microstructural quantification of collagen fiber orientations and its integration in constitutive modeling of the porcine carotid artery. Acta Biomater. 2016;33:183-193. [34] CAVINATO C, MURTADA SI, ROJAS A, et al. Evolving structure-function relations during aortic maturation and aging revealed by multiphoton microscopy. Mech Ageing Dev. 2021;196:111471. [35] BIANCHI F, HOFMANN F, SMITH AJ, et al. Probing multi-scale mechanical damage in connective tissues using X-ray diffraction. Acta Biomater. 2016;45:321-327. [36] GREINER C, GRAINGER S, FARROW S, et al. Robust quantitative assessment of collagen fibers with picrosirius red stain and linearly polarized light as demonstrated on atherosclerotic plaque samples. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0248068. [37] BLOKSGAARD M, LEURGANS TM, SPRONCK B, et al. Imaging and modeling of acute pressure-induced changes of collagen and elastin microarchitectures in pig and human resistance arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017;313(1):H164-H178. [38] CHEN SH, GAN L, ZHUANG M, et al. Overwork Affects Extracellular Matrix of Arterial Vessel Wall in Rats. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2022;44(2):262-269. [39] CAO S, DENG Q, TAN T, et al. Transthoracic ultrasound-guided percutaneous intramyocardial injection combined with ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-mediated angiogenin 1 gene therapy in canine myocardial infarction model. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2021;11(6):1190-1205. [40] SEGNANI C, IPPOLITO C, ANTONIOLI L, et al. Histochemical Detection of Collagen Fibers by Sirius Red/Fast Green Is More Sensitive than van Gieson or Sirius Red Alone in Normal and Inflamed Rat Colon. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0144630. [41] MOHAMMADKHAH M, SIMMS CK, MURPHY P. Visualisation of Collagen in fixed skeletal muscle tissue using fluorescently tagged Collagen binding protein CNA35. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;66: 37-44. [42] XIAO Y, LING S, PEI Y. Structure of Elastin. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2347: 27-33. [43] HEDTKE T, SCHRADER CU, HEINZ A, et al. A comprehensive map of human elastin cross-linking during elastogenesis. FEBS J. 2019;286(18): 3594-3610. [44] REICHHELD SE, MUIZNIEKS LD, KEELEY FW, et al. Direct observation of structure and dynamics during phase separation of an elastomeric protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(22):E4408-E4415. [45] HERNANDEZ-MORERA P, TRAVIESO-GONZALEZ CM, CASTANO-GONZALEZ I, et al. Segmentation of elastic fibres in images of vessel wall sections stained with Weigert’s resorcin-fuchsin. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2017;142:43-54. [46] GAJDA M, JASZTAL A, BANASIK T, et al. Combined orcein and martius scarlet blue (OMSB) staining for qualitative and quantitative analyses of atherosclerotic plaques in brachiocephalic arteries in apoE/LDLR(-/-) mice. Histochem Cell Biol. 2017;147(6):671-681. [47] GIUDICI A, WILKINSON I B, KHIR AW. Review of the Techniques Used for Investigating the Role Elastin and Collagen Play in Arterial Wall Mechanics. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2021;14:256-269. [48] LU H, DU W, REN L, et al. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Aortic Aneurysm: From Genetics to Mechanisms. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021; 10(24):e023601. [49] CAI Z, HUANG J, YANG J, et al. LncRNA SENCR suppresses abdominal aortic aneurysm formation by inhibiting smooth muscle cells apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2021;21(3):323-330. [50] LU W, ZHOU Y, ZENG S, et al. Loss of FoxO3a prevents aortic aneurysm formation through maintenance of VSMC homeostasis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(4):378. [51] GUO Y, ZHU F, ZHANG X, et al. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibition prevents venous adaptive remodeling via regulation of Eph-B4. Vascular. 2022;30(1):120-129. [52] KIRKTON RD, SANTIAGO-MAYSONET M, LAWSON JH, et al. Bioengineered human acellular vessels recellularize and evolve into living blood vessels after human implantation. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(485):eaau6934. [53] DE BEAUFORT HWL, FERRARA A, CONTI M, et al. Comparative Analysis of Porcine and Human Thoracic Aortic Stiffness. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2018;55(4):560-566. [54] RAFUSE M, XU X, STENMARK K, et al. Layer-specific arterial micromechanics and microstructure: Influences of age, anatomical location, and processing technique. J Biomech. 2019;88:113-121. |
| [1] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [2] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [4] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [6] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [7] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [8] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [9] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [10] | Chen Shisong, Liu Xiaohong, Xu Zhiyun. Current status and prospects of bioprosthetic heart valves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1096-1102. |
| [11] | Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Early thrombosis and prevention of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [12] | Tang Haotian, Liao Rongdong, Tian Jing. Application and design of piezoelectric materials for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [13] | Bai Siqi, Xiao Zhen, Liu Jing. Application potential of adipose-derived stem cells in female pelvic floor dysfunction diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 921-927. |
| [14] | Zhang Qijian, Xu Ximing. Acquisition and application of ectodermal mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| [15] | Xiong Juan, Guan Yalin, Yang Yutong, Wang Fan, Liu Zhongshan. Application of stem cells to skin anti-aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 948-954. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||