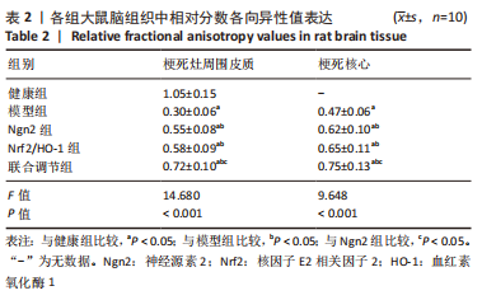
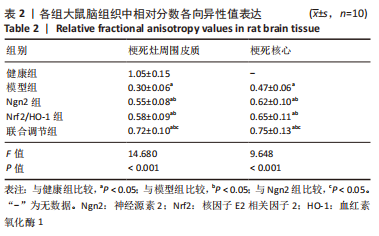
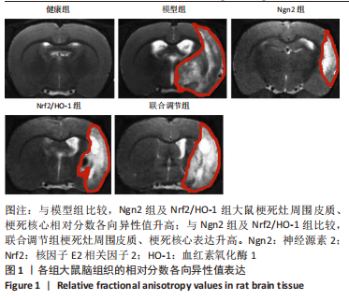
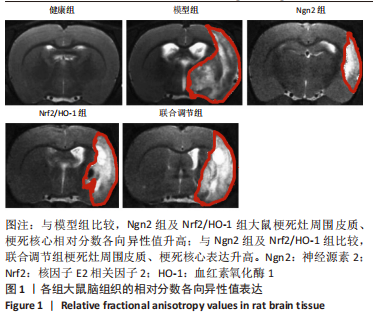
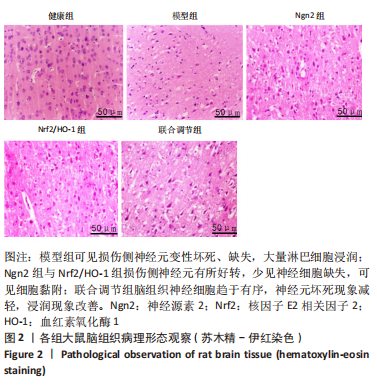
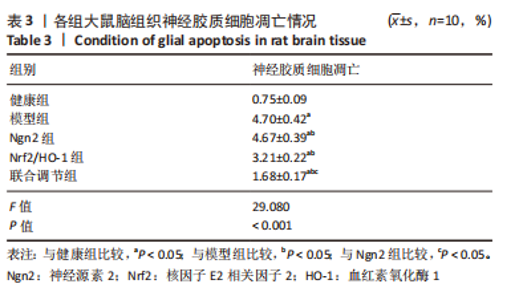
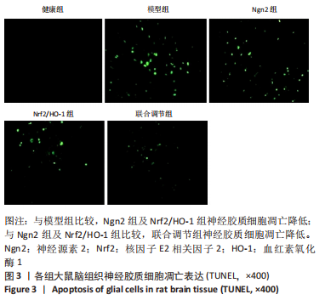
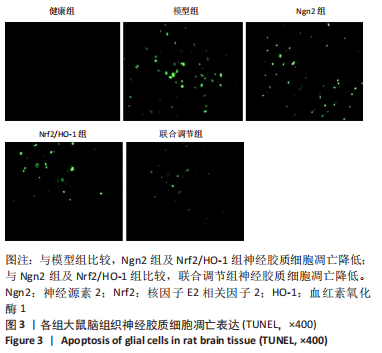
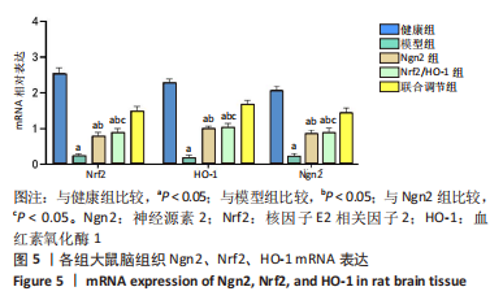
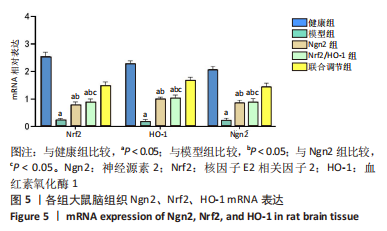
[1] 芦颖,韩化敏.缺血性脑卒中神经保护剂临床转化研究进展[J].中国新药杂志,2019,28(6):683-688.
[2] 李威,刘新峰.急性缺血性卒中治疗时间窗的研究进展[J].中国卒中杂志,2018,13(4):363-371.
[3] 付海龙.丁苯酞注射液对急性脑梗死患者静脉溶栓后缺血再灌注损伤保护作用的研究[J].中国实用医药,2018,13(30):98-99.
[4] 易耀兴,张杲黎,康丽丽,等.慢性脑缺血后脑组织AQP4的表达变化[J].重庆医科大学学报,2020,45(1):45-50.
[5] 郝怀勇,吴超,向金保,等.Ngn2基因诱导的神经潜能骨髓间充质干细胞移植联合Janus激酶信号转导及转录激活因子通路抑制剂治疗大鼠脑缺血[J].中华实验外科杂志,2021,38(9):1685-1689.
[6] 苏凡,申俊,刘娜娜,等.葡萄籽原花青素联合亚低温通过ERK/Nrf2/HO-1通路对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠的保护作用[J].现代药物与临床, 2020,35(3):426-432.
[7] 巩敏杰,安佳琪,吴锋,等.褪黑素通过Nrf2/HO-1信号通路减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2019,40(6): 857-863+876.
[8] MIAO ZY, XIA X, CHE L, et al. Genistein attenuates brain damage induced by transient cerebral ischemia through up-regulation of Nrf2 expression in ovariectomized rats. Neurol Res. 2018:40(8):689-695.
[9] 林斯革,陈皓,蔡雪峰,等.MiR-153通过调控Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路改善脑缺血再灌注后的炎症反应及保护神经元功能的研究[J].免疫学杂志,2020,36(9):737-747.
[10] 白登彦,张海军,袁治国,等.局部转染Ngn2基因对大鼠实验性急性脊髓损伤运动功能影响的研究[J].中国伤残医学,2013,21(9): 55-57.
[11] 李雪, 王浩,彭师嘉,等. Ghrelin抑制Aβ25-35诱导的BV-2细胞炎症反应及改善细胞线粒体功能的机制研究[J].免疫学杂志,2020, 36(7):562-571.
[12] BERECZKI D JR, BALLA J, BERECZKI D. Heme Oxygenase-1: Clinical Relevance in Ischemic Stroke. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(20):2229-2235.
[13] LU J, HUANG Q, ZHANG D, et al. The Protective Effect of DiDang Tang Against AlCl3-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in PC12 Cells Through the Activation of SIRT1-Mediated Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;15(11): 466.
[14] 叶胜,曹钰.Nrf2-HO1信号通路调控脑缺血-再灌注氧化应激损伤的研究进展[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2019,28(12):1571-1575.
[15] ZHAO Y, WANG J, DU J, et al. Apoptosis%brain-derived neurotrophic factor%global cerebral ischemia%neurogenin-2%transactivator of transcription domain. Front cell neurosci. 2018;14(12):475-475.
[16] JIANRONG S, YANJUN Z, CHEN Y, et al. DUSP14 rescues cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (IR) injury by reducing inflammation and apoptosis via the activation of Nrf-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;509(3):713-721.
[17] TURLOVA E, FENG ZP, SUN HS. The role of TRPM2 channels in neurons, glial cells and the blood-brain barrier in cerebral ischemia and hypoxia.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(5):713-721.
[18] WANG J, ISHFAQ M, XU L, et al. METTL3/m6A/miRNA-873-5p attenuated oxidative stress and apoptosis incolistin-induced kidney injury by modulating Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:517.
[19] ZHAO Y, WANG J, DU J, et al. TAT-Ngn2 Enhances Cognitive Function Recovery and Regulates Caspase-Dependent and Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathways After Experimental Stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:475.
[20] 刘宇彤,车楠,李莉,等.花青素通过Nrf-2/HO-1信号通路调控哮喘气道炎症[J].免疫学杂志,2019,35(1):36-41.
[21] HU Q, ZUO T, DENG L, et al. β-Caryophyllene Suppresses Ferroptosis Induced by Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion via Activation of the NRF2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in MCAO/R rats. Phytomedicine. 2022;102: 154112.
[22] PAK C, GRIEDER S, NAN Y, et al. Rapid generation of functional and homogeneous excitatory human forebrain neurons using Neurogenin-2(Ngn2).https://doi.org/10.1038/protex.2018.082.
|