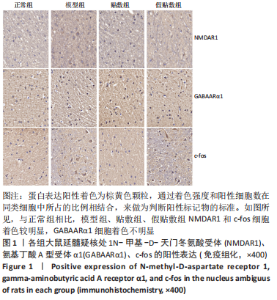
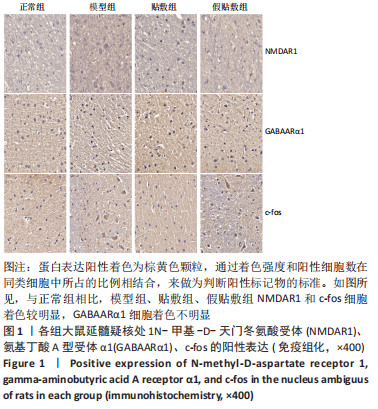
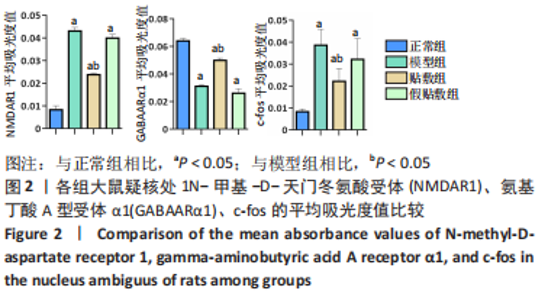
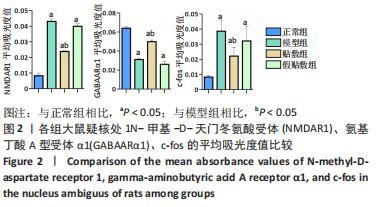
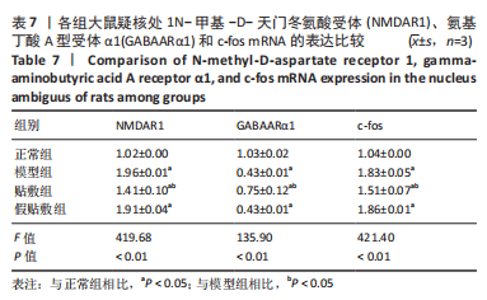
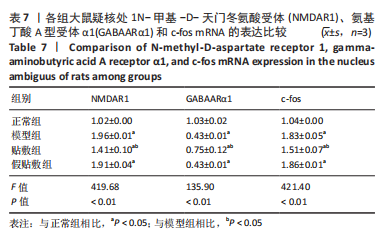
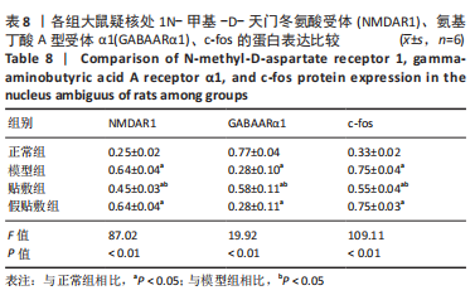
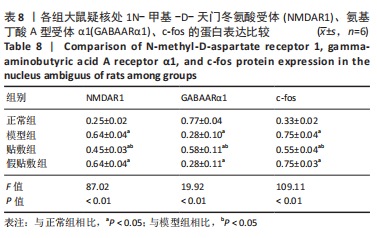
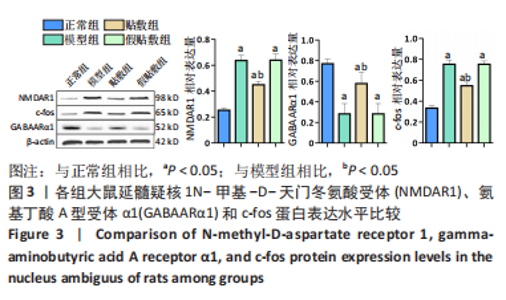
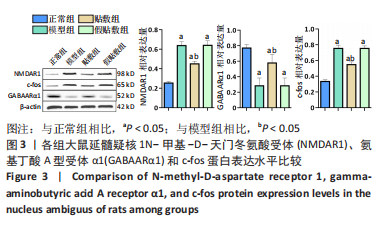
[1] 中国吞咽障碍康复评估与治疗专家共识组.中国吞咽障碍评估与治疗专家共识(2017年版)第一部分 评估篇[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2017,39(12):881-892.
[2] SURA L, MADHAVAN A, CARNABY G, et al. Dysphagia in the elderly: management and nutritional considerations. Clin Interv Aging. 2012;7: 287-298.
[3] NEWMAN R, VILARDELL N, CLAVÉ P, et al. Effect of Bolus Viscosity on the Safety and Efficacy of Swallowing and the Kinematics of the Swallow Response in Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: White Paper by the European Society for Swallowing Disorders (ESSD). Dysphagia. 2016;31(2):232-249.
[4] 李洪艳,朱茜,陈伟,等.多学科管理在脑卒中吞咽障碍患者中的应用[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2021,43(3):259-261.
[5] 陈清棠.临床神经病学[M].北京:北京科学技术出版社,2000:113.
[6] Li L, ZHANG LH, XU WP, et al. Risk assessment of ischemic stroke associated pneumonia. World J Emerg Med. 2014;5(3):209-213.
[7] 胡玉.针刺配合穴位贴敷治疗中风偏瘫64例临床观察[J].内蒙古中医药,2014,33(25):43-44.
[8] 胡琳丽.穴位贴敷联合吞咽训练在脑卒中后吞咽障碍患者中的应用效果研究[J].中国全科医学,2019,22(S1):176-179.
[9] 贺艳萍,肖小芹,邓桂明,等.中药穴位贴敷作用机理研究概况[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2017,24(3):134-136.
[10] 卫小梅,窦祖林,兰月,等.吞咽障碍干预的中枢神经通路调控机制[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2013,35(12):934-937.
[11] 华晓琼,李彦杰,金小琴,等.卒中后吞咽障碍的分子生物学研究进展[J].中国卒中杂志,2022,17(3):318-323.
[12] YE Q, LIU C, SHI J, et al. Effect of electro-acupuncture on regulating the swallowing by activating the interneuron in ventrolateral medulla (VLM). Brain Res Bull. 2019;144:132-139.
[13] 郭威.GAD67-GFP基因敲入小鼠谷氨酸能、5-HT能和SP能终末与三叉神经中脑核神经元联系的形态学研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2008.
[14] CHEN Z, HU Q, XIE Q, et al. Effects of Treadmill Exercise on Motor and Cognitive Function Recovery of MCAO Mice Through the Caveolin-1/VEGF Signaling Pathway in Ischemic Penumbra. Neurochem Res. 2019; 44(4):930-946.
[15] 孟肖蒙,刘晓亭.中药贴敷双侧“天枢”穴对功能性便秘大鼠结肠肌间神经丛血管活性肠肽、P物质的影响[J].针刺研究,2019,44(12): 906-910.
[16] 郭义,方剑乔.实验针灸学实验指导[M].北京:中国中医药出版社, 2012:46-49.
[17] LONGA EZ, WEINSTEIN PR, CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.
[18] GEORGE PAXINOS, CHARLES WATSON.大鼠脑立体定位图谱[M].诸葛启钏主译.北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:64-148.
[19] GBD 2016 NEUROLOGY COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(5): 459-480.
[20] LOSURDO A, BRUNETTI V, BROCCOLINI A, et al. Dysphagia and Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Acute, First-Ever, Ischemic Stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018;27(3):539-546.
[21] CABIB C, NASCIMENTO W, ROFES L, et al. Neurophysiological and Biomechanical Evaluation of the Mechanisms Which Impair Safety of Swallow in Chronic Post-stroke Patients. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;11(1):16-28.
[22] 王清任.医林改错[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:44-45.
[23] 刘未艾,叶德宝.穴位贴敷疗法透皮给药的研究进展[J].中医药通报,2004,3(4):59-62.
[24] 张艳宏.穴位贴敷疗法的理论基础及目前应用现状[J].甘肃中医, 2007,20(2):1-3.
[25] 董莉莉,林婷,江月卿.穴位贴敷联合康复护理对卒中后吞咽障碍患者吞咽功能及营养状况的影响[J].慢性病学杂志,2021,22(4): 575-577.
[26] 顾冬梅.中药穴位敷贴治疗功能性便秘对相关胃肠调节肽影响的研究[J].护理研究,2016,30(34):4325-4327.
[27] 赖燕新.中药穴位贴敷对脑卒中吞咽障碍患者康复的影响[J].中医中药,2015,7(3):53-54.
[28] 赵瑞瑞,周帅.穴位贴敷疗法的临床应用进展[J].国医论坛,2017, 32(1):68-70.
[29] 于书翔,周鸿飞.中医外治法治疗吞咽困难研究进展[J].临床军医杂志,2017,45(3):328-329.
[30] 伍碧贞,刘庆,廖贤静.穴位贴敷联合吞咽训练对脑卒中后吞咽障碍患者营养状况的影响[J].中国实用医药,2021,16(16):163-165.
[31] 马静丽,李彦杰,孟毅,等.祛痰治呛方穴位贴敷治疗卒中后吞咽障碍的疗效观察[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(7):4364-4367.
[32] DOELTGEN SH, HUCKABEE ML. Swallowing neurorehabilitation: from the research laboratory to routine clinical application. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;93(2):207-213.
[33] HUANG PL, WANG SJ, SUN RF, et al. Increased activation of the caudate nucleus and parahippocampal gyrus in Parkinson’s disease patients with dysphagia after repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: a case-control study. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(5):1051-1058.
[34] FURNESS JB. The enteric nervous system and neurogastroenterology. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;9(5):286-294.
[35] 叶秋平.电针廉泉穴对大鼠延髓腹外侧区吞咽神经元的影响研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2018.
[36] GIELEN M, BARILONE N, CORRINGER PJ. The desensitization pathway of GABAA receptors, one subunit at a time. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1): 5369.
[37] ZHANG M, CLARKE K, ZHONG H, et al. Postsynaptic action of GABA in modulating sensory transmission in co-cultures of rat carotid body via GABA(A) receptors. J Physiol. 2009;587(2):329-344.
[38] 郭威. GAD67-GFP基因敲入小鼠谷氨酸能、5-HT能和SP能终末与三叉神经中脑核神经元联系的形态学研究[D]. 西安:第四军医大学,2008.
[39] 史俊恒.电针廉泉、风府穴对大鼠脑干吞咽运动神经元疑核的影响[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2018.
[40] 彭会珍,张振香.水通道蛋白在急性缺血性脑卒中后脑水肿发生机制中的研究进展[J].重庆医学,2015,44(24):3436-3438.
[41] 石德志,张宝珍,刘霞.高压氧与康复综合治疗对急性脑卒中吞咽功能障碍的疗效观察[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2010,13(9):1318-1319.
|