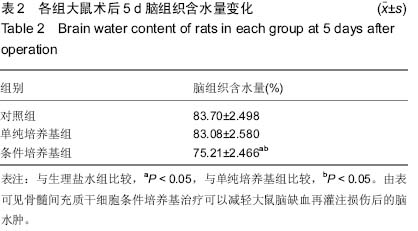
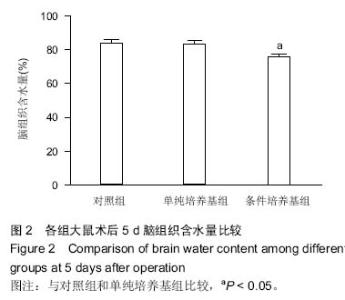
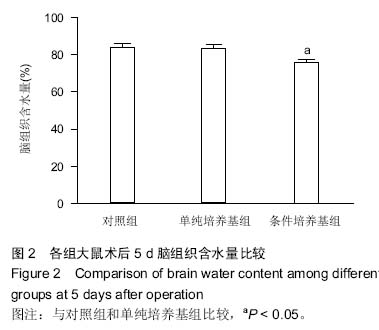
| [1] Ye X, Chopp M, Cui X, et al. Niaspan enhances vascular remodeling after stroke in type 1 diabetic rats. Exp Neurol. 2011;232(2):299-308.
[2] Friedman HS. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(21):1405.
[3] Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(13):1317-1329.
[4] Seo JH, Cho SR. Neurorestoration induced by mesenchymal stem cells: potential therapeutic mechanisms for clinical trials. Yonsei Med J. 2012;53(6):1059-1067.
[5] Chopp M, Li Y. Treatment of neural injury with marrow stromal cells. Lancet Neurol. 2002;1(2):92-100.
[6] Hu X, Zhang M, Leak RK, et al. Delivery of neurotherapeutics across the blood brain barrier in stroke. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(25):3704-3720.
[7] Kawamata T, Speliotes EK, Finklestein SP. The role of polypeptide growth factors in recovery from stroke. Adv Neurol. 1997;73:377-382.
[8] Cui X, Chen J, Zacharek A, et al. Nitric oxide donor upregulation of stromal cell-derived factor-1/chemokine (CXC motif) receptor 4 enhances bone marrow stromal cell migration into ischemic brain after stroke. Stem Cells. 2007; 25(11):2777-2785.
[9] Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, et al. Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 2001;32(4):1005-1011.
[10] Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, et al. Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats. Stroke. 2001;32(11):2682-2688.
[11] Lu SS, Liu S, Zu QQ, et al. In vivo MR imaging of intraarterially delivered magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells in a canine stroke model. PLoS One. 2013;8(2): e54963.
[12] Yu YL, Chou RH, Shyu WC, et al. Smurf2-mediated degradation of EZH2 enhances neuron differentiation and improves functional recovery after ischaemic stroke. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5(4):531-547.
[13] Komatsu K, Honmou O, Suzuki J, et al. Therapeutic time window of mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow after cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2010;1334:84-92.
[14] Cantinieaux D, Quertainmont R, Blacher S, et al. Conditioned medium from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves recovery after spinal cord injury in rats: an original strategy to avoid cell transplantation. PLoS One. 2013;8(8): e69515.
[15] Chen X, Katakowski M, Li Y, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cell cultures conditioned by traumatic brain tissue extracts: growth factor production. J Neurosci Res. 2002; 69(5):687-691.
[16] Skaper SD. The biology of neurotrophins, signalling pathways, and functional peptide mimetics of neurotrophins and their receptors. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008;7(1):46-62.
[17] Nakano N, Nakai Y, Seo TB, et al. Characterization of conditioned medium of cultured bone marrow stromal cells. Neurosci Lett. 2010;483(1):57-61.
[18] Endres M, Fan G, Hirt L, et al. Ischemic brain damage in mice after selectively modifying BDNF or NT4 gene expression. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20(1):139-144.
[19] Ferrara N, Chen H, Davis-Smyth T, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is essential for corpus luteum angiogenesis. Nat Med. 1998;4(3):336-340.
[20] Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor. Eur J Cancer. 1996;32A(14):2413-2422.
[21] Hawkins BT, Davis TP. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57(2):173- 185.
[22] Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, et al. Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell. 1996;87(7):1171-1180.
[23] Thurston G, Rudge JS, Ioffe E, et al. Angiopoietin-1 protects the adult vasculature against plasma leakage. Nat Med. 2000; 6(4):460-463.
[24] 沈丽萍,王帅帅,董丽果,等.经鼻给脐血间充质干细胞条件培养基治疗脑缺血再灌注损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(45): 7891-7897.
[25] Dray C, Rougon G, Debarbieux F. Quantitative analysis by in vivo imaging of the dynamics of vascular and axonal networks in injured mouse spinal cord. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106(23):9459-9464. |