Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (16): 2560-2565.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1169
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects and influencing factors of neurophysiological monitoring on reducing the risk of nerve injury in spine surgery
Li Manglai1, Yang Xuejun2
- 1Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Thoracolumbar Spine Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2019-06-08Published:2019-06-08 -
Contact:Yang Xuejun, Master, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Thoracolumbar Spine Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Li Manglai, Master candidate, Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Manglai, Yang Xuejun. Effects and influencing factors of neurophysiological monitoring on reducing the risk of nerve injury in spine surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(16): 2560-2565.
share this article
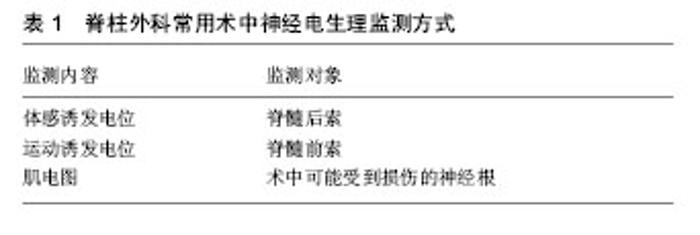
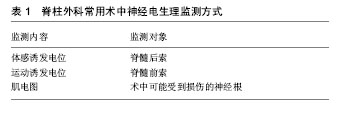
2.1 监测机制 2.1.1 解剖学基础 各种神经、神经通路、结缔组织及它们的血液供应都集中在脊椎相对狭小的骨性结构区域即椎管内,其中包含了脊髓、神经根、保护脊髓的软组织膜性结构(硬脑膜、蛛网膜和硬膜外脂肪)、脑脊液和血液供应系统。在行脊柱外科手术切除椎板、黄韧带及置钉和截骨的过程中,若操作不慎,较易损伤脊髓,导致不良后果。脊髓的各个节段与脊柱相比较短,并在第一腰椎的上方随着脊髓圆锥而终止,但神经根走行于各节段椎体的椎间孔。因此在第一腰椎以下进行手术时,即使不会损伤脊髓,但对于神经根损伤的风险仍然是存在的。术中神经电生理监测可以提示脊髓或神经根是否受损,监测节段应根据手术时的进行操作范围进行改动[6]。 传导功能和反射功能是脊髓的2个主要功能。传导功能包括上行传导束和下行传导束,感觉冲动由上行传导束通过脊髓白质传到脑,而后者将脑的神经冲动通过脊髓传到效应器,从而产生各种感觉和运动功能。神经电生理监测技术就是以此为依据,使用体感诱发电位监测脊髓上行传导束,以运动诱发电位监测脊髓的下行传导束。 2.1.2 监测方式 本体感觉由脊髓后索向上传递,此处通常由体感诱发电位监测。压迫脊髓、神经根或马尾神经,会导致体感诱发电位出现异常[7]。体感诱发电位目前在国际上尚未形成诊断的统一标准,一般情况下,体感诱发电位波幅下降超过50%和(或)潜伏期延长超过10%,即可视为预警标准[8]。Nuwer等[9]对51 263例脊柱侧弯矫形手术的患者进行了体感诱发电位的监测,在研究中,体感诱发电位敏感度为92%,特异度为98%。但体感诱发电位只能监测脊髓后索的感觉通路,而对通过前索传递的运动通路无法进行监测[10]。该电位监测机制为非实时监测,而是需对波形进行叠加,得出平均波形,至少要叠加100-200次来观察波形潜伏期及波幅改变,因此具有一定的滞后性。但单一的体感诱发电位监测仅仅能评价感觉神经的功能与完整性,存在较高的假阴性率和假阳性率,因此在术中监测时具有一定的局限性[11-12]。 运动诱发电位是通过脊髓前索向下传递,而目前最常用的监测脊髓前索的方法为经颅磁刺激的运动诱发电位监测。相比于体感诱发电位监测时需要观察所获得的叠加波形与基线值比较波幅和潜伏期,当运动诱发 电位的波幅下降大于80%时,即可视为一个有价值的报警[13]。在一项1 543例样本的研究中,运动诱发电位监测用于术中脊髓损伤监测的敏感性和特异性分别为100%和99.6%,总体假阳性率为0.33%,对术后新发神经功能障碍运动诱发电位监测的阳性预计值为84.4%[14]。运动诱发电位通过增加对损伤节段运动神经冲动传导路径的监测,可以使监护的假阴性率明显降低,显著降低术后运动障碍的风险[14-15]。尽管其影响因素较多,但仍可提醒手术医师尽早处理出现的可能存在的问题,以此来降低不可逆性损伤的发生率。 术中可能受到损伤的神经根是肌电图监测的主要对象,见表1。肌肉由多个肌纤维和终板组成,当运动神经冲动传至肌肉时,运动终板被激活,相对应的肌纤维产生收缩活动,即肌肉收缩。如果手术操作不当,牵拉或压迫到神经根时,相应神经根支配的肌肉会出现肌电图波异常形态,但也有可能是其他方式刺激到神经 根[16]。谭海涛等[17]的研究表明,自发肌电图监测在脊柱外科手术中的灵敏度为82.35%, 特异度为93.10%。其监测的敏感度及特异度要高于体感诱发电位和运动诱发电位[18-19]。肌电图监测对钝器械刺激和/或运动神经损伤较为敏感,但在急性神经横断时可能会出现假阴性的情况。此外,在急性神经横断后,机械刺激和电刺激仍然可以激活损伤部分的神经末梢[20]。在脊柱外科手术中,自发性肌电图监测提供的指标更为安全客观,手术的安全性通过在术中使用自发肌电图监测可以得到很大的提高[21]。"

2.2 监测影响因素 2.2.1 麻醉药物 许多临床报道显示,麻醉药物是在进行术中神经电生理监测时,诱发电位出现异常信号重要原因之一[3,22-24],尤其是吸入麻醉对运动诱发电位的监测结果潜在着混淆的可能性[22]。吸入麻醉药主要作用于突触前后的NMDA受体,进而发挥作用;而静脉麻醉药如丙泊酚主要通过作用于GABAa受体,从而增强GABA活性而产生作用[25-26]。但麻醉药物对神经电生理监测的影响机制目前仍不确定,可能是对神经元有着直接抑制作用[27]。 目前在临床上,单一的吸入麻醉或者全凭静脉麻醉使用较少,麻醉医生多采取使用多种药物的静-吸复合麻醉。一般多采用短效静脉麻醉药,如丙泊酚等烷基酸类药物,以及舒芬太尼、瑞芬太尼等阿片受体激动剂联合应用。在一项临床研究中,使用丙泊酚麻醉时,诱发电位对于其药物剂量的变化存在着滞后效应,即当药物剂量增加时,诱发电位的延迟期均明显缩短,且运动诱发电位对丙泊酚剂量的变化更为敏感。 α2-肾上腺素受体激动剂作为行全身麻醉时气管插管和机械通气的镇静药物也广泛应用于临床。代表药物为右旋美托咪定。研究表明,在行成人胸椎肿瘤手术时,丙泊酚-瑞芬太尼麻醉合并使用右旋美托咪定,并不会对诱发电位的监测有着不利影响[28]。 2.2.2 肌松剂 N2胆碱受体阻滞剂为目前临床最常用的肌松剂,又称骨骼肌松弛药(skeletal muscular relaxants),作用机制为选择性地作用于运动神经终板膜上的N2受体,而使传向骨骼肌的神经冲动受到阻断,进而导致肌肉松弛。目前在临床上较常使用非去极化肌松药,包括阿曲库铵、苯磺顺阿曲库铵、罗库溴铵等。在产生运动诱发电位的过程中有突触参与,肌松药物对该传递抑制作用的敏感性非常高。肌松水平对体感诱发电位影响不大,但对运动诱发电位有相对较大的影响。研究认为顺式阿曲库铵较适宜的麻醉诱导剂量为3倍ED95(95%有效率),此时可以获得较理想的肌松效果且不会影响运动诱发电位的引出[29]。 运动诱发电位在脊柱外科手术中具有令人满意的敏感度和特异度,并且能为术中决策提供重要的信 息[30]。但肌松药物对于运动诱发电位的影响较大,在脊柱外科术中行神经电生理监测时,应谨慎使用该类药物。 2.2.3 其他因素 血供和体温对于机体组织的意义重大,血流量减少以及温度的降低均会降低机体的基础代谢率,对神经冲动的传导尤为严重。在行脊柱外科手术时,术中操作可能会损伤重要的血管,导致脊髓血供不足,而且侧支循环无法完全代偿。此外术中患者的血压过低也可能会造成脊髓缺血,进而导致脊髓损伤。尤其是7-11肋间后动脉双侧损伤时,对于脊髓的影响更为严重[31]。因此,脊髓缺血对于神经电生理监测的影响也是不可忽视的。 在脊柱外科的手术中,有时会因手术时间较长、切口过大而导致患者的体温降低,进而使神经电生理监测结果出现异常。在一项前瞻性研究中,相比于低体温的患者,正常体温患者的运动神经传导速度要快,且远端感觉冲动的传导时间明缩短[32]。有学者认为,术中患者体温降低至32 ℃时并不会引起体感诱发电位波幅的改变[33]。目前较长时间的脊柱外科手术均已应用加温毯,这对维持患者体温有着重要的作用。 除血压和体温外,出现报警常见原因还包括冲洗时生理盐水温度过低、患者呼吸功能受抑制、截骨过程中截骨面靠拢、术中电磁场干扰等[5,34]。此外,安置心脏起搏器也是监测运动诱发电位的禁忌证。"

| [1] 朱士广,杨树源. 脊髓手术中的神经电生理监测[J]. 临床神经电生理学杂志,2006,15(2):99-102.[2] Holdefer RN, MacDonald DB, Skinner SA. Somatosensory and motor evoked potentials as biomarkers for post-operative neurological status.Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;126:857-865. [3] 林国中,王振宇. 神经电生理监测在脊髓手术中的应用[J]. 临床神经外科杂志,2012,9(2):117-119.[4] Thirumala PD, Huang J, Thiagarajan K, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of combined multimodality somatosensory evoked potential and transcranial motor evoked potential intraoperative monitoring in patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2016;41(19):E1177-1184.[5] 张玉新,何帆,王珏.多模式神经电生理监测在脊柱手术中报警因素分析[J].现代电生理学杂志,2014,21(4):199-203.[6] Rabai F, Sessions R, Seubert CN. Neurophysiological monitoring and spinal cord integrity. Best Pract Res Clin Anesthesiol. 2016; 30(1):53-68.[7] Roy MW, Gilmore R, Walsh JW. Evaluation of children and young adults with tethered spinal cord syndrome. Utility of spinal and scalp recorded somatosensory evoked potentials. Surg Neurol. 1986;26(3):241-248.[8] Devlin VJ, Anderson PA, Schwartz DM, et al. Intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring: focus on cervical myelopathy and related issues. Spine J. 2006; 6(6):S212-S224.[9] Nuwer MR, Dawson EG, Carlson LG, et al. Somatosensory evoked potential spinal cord monitoringreduces neurologic deficits after scoliosis surgery: results of alarge multicenter survey. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol.1995;96(1):6-11.[10] Ginsburg HH, Shetter AG, Raudzens PA. Postoperative paraplegia with preserved intraoperative somatosensory evoked potentials. J Neurosurg.1985;63(2):296-300. [11] Guerit JM. Neuromonitoring in the operation room: why, when and how to monitor . Electrocephalogr Clin Neurophysiol.1998;106(1): 1-21.[12] Storm SA, Kraft GH. The clinical use of dermatomal somatosensory evoked potentials in lumbosacral spinal stenosis. PhysMed Rehabil Clin N Am. 2004;15(4): 107-115.[13] Langeloo DD, Lelivelt A, Louis JH, et al. Transcranial electrical motor-evoked potential monitoring during surgery for spinal deformity: a study of 145 patients. Spine. 2003;28(10):1043-1050.[14] 庄乾宇,王树杰,仉建国,等.经颅电刺激运动诱发电位监测标准化方案在1543例脊柱畸形矫形手术中的应用[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2015,8(1):27-31.[15] Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, et al. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58(10): 982-990.[16] 邱勇,刘兴勇.神经电生理监测在脊柱外科的应用现状[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(7):670-672.[17] 谭海涛,江建中,谢兆林,等.肌电图监测在极外侧入路椎间融合术联合经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定术中的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015, 25(7):618-624.[18] Haghighi SS, Blaskiewicz DJ, Ramirez B, et al. Can intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring during cervical spine decompression predict post-operative segmental C5 palsy? J Spine Surg. 2016; 2(3):167-172.[19] Kimura J. Peripheral Nerve Diseases. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2006: 621-630.[20] Holland NR. Intraoperative electromyography. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2002;19(5):444-453.[21] 胡楷,熊梅,王言,等.神经电生理监测在经皮内窥镜下腰椎间盘切除术中的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(7):602-606.[22] Tamkus AA, Rice KS, Kim HL. Differential rates of false-positive findings in transcranial electric motor evoked potential monitoring when using inhalational anesthesia versus total intravenous anesthesia during spine surgeries. Spine J. 2014; 14(8): 1440-1446.[23] 陈炎春,卫法泉,孔飞娟.脊柱侧弯矫形术中七氟烷联合丙泊酚静吸复合麻醉对SEP及MEP的影响[J].中华全科医学, 2017,15(3): 418-420+527.[24] 汪露,角述兰,杨娟,等.地氟醚和七氟醚对术中运动诱发电位监测的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2015,31(3):253-256.[25] Kopp LA, Yost CS, Kindler CH. Anaesthetic mechanisms: update on the challenge of unravelling the mystery of anaesthesia. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2009;26(10):807-820.[26] Campagna JA, Miller KW, Forman SA. Mechanisms of actions of inhaled anesthetics. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348(21):909-910. [27] Bonhomme V, Boveroux P, Hans P, et al. Influence of anesthesia on cerebral blood flow, cerebral metabolic rate, and brain functional connectivity. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2011;24(5): 474-479.[28] Li Y, Meng L, Peng Y, et al. Effects of Dexmedetomidine on motor- and somatosensory-evoked potentials in patients with thoracic spinal cord tumor: a randomized controlled trial. Bmc Anesthesiol. 2015;16(1):51-58.[29] 张园园,董江涛,代志刚,等.不同剂量顺式阿曲库铵对神经外科手术运动诱发电位的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志, 2017,33(2):129-132.[30] Zhuang Q, Wang S, Zhang J, et al. How to make the best use of intraoperative motor evoked potential monitoring? experience in 1162 consecutive spinal deformity surgical procedures. Spine. 2014;39(24):1425-1432.[31] 戴景兴,原林,周志涛,等.结扎数支肋间后动脉对胸腰段脊髓血供影响[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2003,21(6):575-577.[32] 曲瑶, 于高起, 韩伟,等. 低体温对患者体感诱发电位的影响[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2011, 31(1):13-16.[33] Kottenberg-Assenmacher E, Armbruster W, Bornfeld N, et al. Hypothermia does not alter somatosensory evoked potential amplitude and global cerebral oxygen extraction during marked sodium nitroprusside-induced arterial hypotension. Anesthesiology. 2003; 98(5):1112-1118.[34] 陈裕光,万勇,郑召民,等.脊柱侧凸手术中TES-MEP、CSEP阳性与手术操作相关原因分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2010,8(2):86-89.[35] Noonan KJ, Walker T, Feinberg JR, et al. Factors related to false- versus true-positive neuromonitoring changes in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgery. Spine. 2002;27(8):825-830.[36] Dawson EG, Sherman JE, Kanim LE, et al. Spinal cord monitoring. results of the scoliosis research society and the european spinal deformity society survey. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).1991;16:S361-364.[37] Neurophysiological Monitoring of Spinal Cord Function During Spinal Deformity Surgery. in: Scoliosis Research Society, 2009.[38] Nuwer MR. PW6-1 IONM techniques useful in assessing spinal cord function in scoliosis surgery. Clin Neurophysiol. 2010;121 (10):S89-S89.[39] Schwartz DM, Auerbach JD, Dormans JP, et al. Neurophysiological detection of impending spinal cord injury during scoliosis surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(11): 2440-2449.[40] Tamaki T, Kubota S. History of the development of intraoperative spinal cord monitoring. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(2):140-146.[41] Hickey R, Albin MS, Bunegin L, et al. Autoregulation of spinal cord blood flow: is the cord a microcosm of the brain? Stroke. 1986; 17(6): 1183-1189.[42] Gonzalez AA, Jeyanandarajan D, Hansen C, et al. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring during spine surgery: a review. Neurosurg Focus. 2009;27(4):E6.[43] Sutter M, Eggspuehler A, Muller A, et al. Multimodal intraoperative monitoring: an overview and proposal of methodology based on 1017 cases. Eur Spine J. 2007; 16(Suppl 2): S153-S161.[44] Sloan TB, Mongan P, Lyda C, et al. Lidocaine infusion adjunct to total intravenous anesthesia reduces the total dose of propofol during intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring. J Clin Monit Comput. 2014;28(2):139-147.[45] Jou IM, Chern TC, Chen TY, et al. Effects of desflurane on spinal somatosensory-evoked potentials and conductive spinal cord evoked potential. Spine. 2003;28(16):1845-1850.[46] Hasan MS, Tan JK, Chan CYW, et al. Comparison between effect of desflurane/remifentanil and propofol/remifentanil anesthesia on somatosensory evoked potential monitoring during scoliosis surgery—A randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Surg. 2018; 26(3):1-7.[47] 严彬,黄晓虹,吴元珏,等.右美托咪定对颈椎前路手术运动诱发电位监测的影响[J].实用骨科杂志,2018,24(3):223-225.[48] Kuizenga K, Wierda JM, Kalkman CJ. Biphasic EEG changes in relation to loss of consciousness during induction with thiopental, propofol, etomidate, midazolam or sevoflurane. Br J Anaesthesia. 2001; 86(3):354-360.[49] 于琳琳,王军,马越,等.不同肌松水平对术中脊髓神经电生理监测的影响[J].首都医科大学学报,2017,38(3):357-360.[50] 李传翔,宋伏虎,王怡,等.不同肌松程度对脊柱外科手术经颅电刺激运动诱发电位监测的临床观察[J].南方医科大学学报,2010,30(12): 2686-2688.[51] 孙麟,罗超,宋跃明,等.重度脊柱侧弯患者术中血压变化对体感诱发电位的影响及处理方法[J].华西医学,2014,29(1):19-22.[52] 齐宗华,西永明,刘勇,等.颈胸椎手术中体感诱发电位监护的影响因素分析及准确性观察[J].中华外科杂志,2007,45(4):240-242. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [3] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [4] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [5] | Ma Binxiang, He Wanqing, Zhou Guangchao, Guan Yonglin. Triptolide improves motor dysfunction in rats following spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 701-706. |
| [6] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [7] | Yan Peng, Ma Yufei, Cui Jingfu, Hao Shaofei, Liu Jinhui, Guan Chunlei, Wang Xiaoran, Yang Xiaoyu. Mechanism of anodic block electrical stimulation of sacral nerve root to reconstruct bladder function [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3684-3689. |
| [8] | Xu Weilong, Zuo Yuan, Xin Daqi, He Chenyang, Zhao Peng, Shi Ming, Zhou Boyuan, Liu Yating, Zhao Yan. Selection of modeling methods for acute compressive spinal cord injury: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3767-3772. |
| [9] | Tian Ting, Li Xiaoguang. Problems and challenges in regeneration and repair of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3039-3048. |
| [10] | Ren Bingkai, Zheng Yibin, Huang Leiwen, Wu Fanhui, Yang Dong . Value of respiratory tract management and fiberoptic bronchoscopy in traumatic cervical spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2902-2907. |
| [11] | Chen Xingying, Hao Fei, Gao Yudan, Zhao Wen, Duan Hongmei, Yang Chaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Rehabilitation training combined with neurotrophin 3-chitosan scaffolds enhanced skeletal muscle morphology and functional recovery in rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2514-2520. |
| [12] | Wu Cunshu, Zhan Xiaoxuan, Zhao Siyi, Huang Fan, Zhang Yue, Qiu Mingwang, Xia Jingxian, Lu Xiaobo. Gait training for spinal cord injury based on radar plotting: an overview of systematic reviews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2287-2296. |
| [13] | Qian Nannan, Zhang Qian, Yang Rui, Ao Jun, Zhang Tao. Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury: cell therapy and combination of new drugs and biomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2114-2120. |
| [14] | Fang Chao, Sun Jian, Wei Laifu, Gao Fei, Qian Jun . Oscillating field stimulation inhibits neuroinflammatory response and promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1717-1722. |
| [15] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Spinal cord injury repaired by using nano tissue-engineered spinal cord [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1550-1554. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||