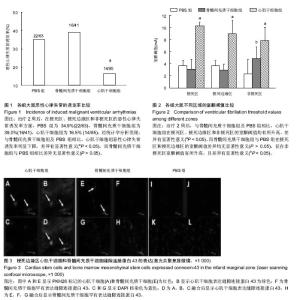
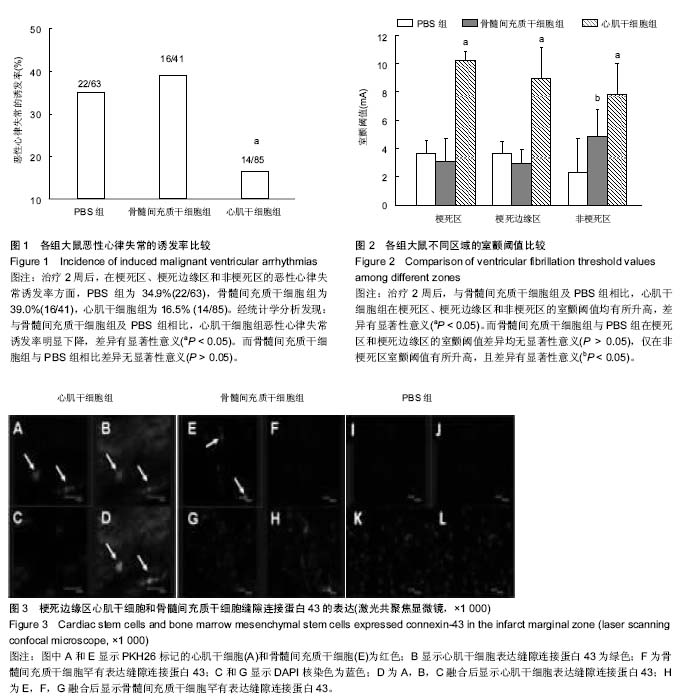
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Short-term efficacy of cardiac stem cells in improving the electrophysiological stability and ventricular fibrillation threshold after myocardial infarction
Zhong Ting-ting, Hou Jing-ying, Guo Tian-zhu, Zheng Shao-xin, Zhou Chang-qing, Long Hui-bao, Wu Quan-hua, Wu Hao, Wang Tong
- Department of Emergency, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2015-07-02Published:2015-07-02 -
Contact:Wang Tong, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Investigator, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Emergency, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital,S un Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhong Ting-ting, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Emergency, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81270213, 81070125; the Science and Technology Plan of Guangdong Province, No. 2010B031600032, 2014A020211002; the Fundamental Research Funds for Universities, No. 13ykzd16
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhong Ting-ting, Hou Jing-ying, Guo Tian-zhu, Zheng Shao-xin, Zhou Chang-qing, Long Hui-bao, Wu Quan-hua, Wu Hao, Wang Tong. Short-term efficacy of cardiac stem cells in improving the electrophysiological stability and ventricular fibrillation threshold after myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.28.020.
share this article
| [1] Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;129(3):e28-e292.
[2] Willerson JT. Stem cell therapy for cardiovascular diseases: a progressive journey. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2015;30(3):205-212.
[3] Macia E, Boyden PA. Stem cell therapy is proarrhythmic. Circulation. 2009;119(13):1814-1823.
[4] Menasché P. Stem cell therapy for heart failure: are arrhythmias a real safety concern. Circulation. 2009;119(20): 2735-2740.
[5] Liao SY, Liu Y, Siu CW, et al. Proarrhythmic risk of embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte transplantation in infarcted myocardium. Heart Rhythm. 2010;7(12):1852-1859.
[6] Ishii T, Pera RA, Greely HT. Ethical and legal issues arising in research on inducing human germ cells from pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;13(2):145-148.
[7] Yoshida Y, Yamanaka S. iPS cells: a source of cardiac regeneration. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;50(2):327-332.
[8] Yoshida Y, Yamanaka S. Recent stem cell advances: induced pluripotent stem cells for disease modeling and stem cell-based regeneration. Circulation. 2010;122(1):80-87.
[9] Marbán E, Cho HC, Cingolani E. Taking the cells out of cell therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(17):1707-1708.
[10] Narita T, Shintani Y, Ikebe C, et al. The use of cell-sheet technique eliminates arrhythmogenicity of skeletal myoblast-based therapy to the heart with enhanced therapeutic effects. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(1):261-269.
[11] Menasche P. Cardiac cell therapy: lessons from clinical trials. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;50(2):258-265.
[12] Askar SF, Ramkisoensing AA, Atsma DE, et al. Engraftment patterns of human adult mesenchymal stem cells expose electrotonic and paracrine proarrhythmic mechanisms in myocardial cell cultures. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013; 6(2):380-391.
[13] Hare JM, Fishman JE, Gerstenblith G, et al. Comparison of allogeneic vs autologous bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells delivered by transendocardial injection in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy: the POSEIDON randomized trial. JAMA. 20122;308(22):2369-2379.
[14] Hou J, Wang L, Jiang J, et al. Cardiac stem cells and their roles in myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Rev. 2013;9(3): 326-338.
[15] Malliaras K, Makkar RR, Smith RR, et al. Intracoronary cardiosphere-derived cells after myocardial infarction: evidence of therapeutic regeneration in the final 1-year results of the CADUCEUS trial (CArdiosphere-Derived aUtologous stem CElls to reverse ventricUlar dySfunction). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(2):110-122.
[16] Ye J, Yeghiazarians Y. Cardiac stem cell therapy: review of the native cardiac progenitor cells and future direction. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014;63(2):85-94.
[17] Zheng SX, Weng YL, Zhou CQ, et al. Comparison of cardiac stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on the cardiac electrophysiology in rats with myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Rev. 2013;9(3):339-349.
[18] Wang T, Tang W, Sun S, et al. Improved outcomes of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rats with myocardial infarction treated with allogenic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(3):833-839.
[19] Wang T, Sun S, Wan Z, et al. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Resuscitation. 2012;83(11):1391-1396.
[20] 王彤, 郑韶欣, 周长青, 等. 心肌干细胞移植可改进心力衰竭大鼠室颤阈值和电生理的稳定性[J]. 中国组织工程研究和临床康复, 2011, 15(36): 6753-6756.
[21] Chen J, Zheng S, Huang H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells enhanced cardiac nerve sprouting via nerve growth factor in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Curr Pharm Des. 2014; 20(12): 2023-2029.
[22] Wang T, Tang W, Sun S, et al. Intravenous infusion of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves myocardial function in a rat model of myocardial ischemia. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(11):2587-2593.
[23] Western D, Hanson B, Taggart P. Measurement bias in activation-recovery intervals from unipolar electrograms. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;308(4):H331-338.
[24] Wang H, Tang W, Ristagno G, et al. The potential mechanisms of reduced incidence of ventricular fibrillation as the presenting rhythm in sudden cardiac arrest. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(1):26-31.
[25] Eifling M, Razavi M, Massumi A. The evaluation and management of electrical storm. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(2): 111-121.
[26] Benito B, Josephson ME. Ventricular tachycardia in coronary artery disease. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2012;65(10):939- 955.
[27] Pokorný J, Staněk V, Vrána M. Sudden cardiac death thirty years ago and at present. The role of autonomic disturbances in acute myocardial infarction revisited. Physiol Res. 2011; 60(5): 715-728.
[28] Williams AR, Hatzistergos KE, Addicott B, et al. Enhanced effect of combining human cardiac stem cells and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to reduce infarct size and to restore cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2013;127(2):213-223.
[29] Williams AR, Suncion VY, McCall F, et al. Durable scar size reduction due to allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell therapy regulates whole-chamber remodeling. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013; 2(3):e000140.
[30] Hwang HJ, Chang W, Song BW, et al. Antiarrhythmic potential of mesenchymal stem cell is modulated by hypoxic environment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(17):1698-1706.
[31] Smart N, Bollini S, Dubé KN, et al. De novo cardiomyocytes from within the activated adult heart after injury. Nature. 2011; 474(7353):640-644.
[32] Makkar RR, Smith RR, Cheng K, et al. Intracoronary cardiosphere-derived cells for heart regeneration after myocardial infarction (CADUCEUS): a prospective, randomised phase 1 trial. Lancet. 2012;379(9819):895-904.
[33] Davis DR, Kizana E, Terrovitis J, et al. Isolation and expansion of functionally-competent cardiac progenitor cells directly from heart biopsies. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010;49(2): 312-321.
[34] Senyo SE, Steinhauser ML, Pizzimenti CL, et al. Mammalian heart renewal by pre-existing cardiomyocytes. Nature. 2013; 493(7432):433-436.
[35] Bolli R, Chugh AR, D'Amario D, et al. Cardiac stem cells in patients with ischaemic cardiomyopathy (SCIPIO): initial results of a randomised phase 1 trial. Lancet. 2011;378 (9806):18471857.
[36] Tang XL, Rokosh G, Sanganalmath SK, et al. Intracoronary administration of cardiac progenitor cells alleviates left ventricular dysfunction in rats with a 30-day-old infarction. Circulation. 2010;121(2):293-305.
[37] Ellison GM, Vicinanza C, Smith AJ, et al. Adult c-kit(pos) cardiac stem cells are necessary and sufficient for functional cardiac regeneration and repair. Cell. 2013;154(4):827-842.
[38] Zhao X, Huang L. Cardiac stem cells: A promising treatment option for heart failure. Exp Ther Med. 2013;5(2):379-383.
[39] Fontes MS, van Veen TA, de Bakker JM, et al. Functional consequences of abnormal Cx43 expression in the heart. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1818(8):2020-2029.
[40] Wu W, Li Y, Lu Z, et al. Increased susceptibility to ischemia-induced ventricular tachyarrhythmias in depressed rats: Involvement of reduction of connexin 43. Exp Ther Med. 2012;3(2):192-194. |
| [1] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [2] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [3] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [4] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [5] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [6] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [7] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [8] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [9] | Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun. The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 754-760. |
| [10] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [11] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [12] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [13] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [14] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [15] | Yi Meizhi, Luo Guanghua, Xiao Yawen, Hu Rong, Chen Xiaolong, Zhao Heng. MRI findings of anatomical variations of the talus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3888-3893. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||