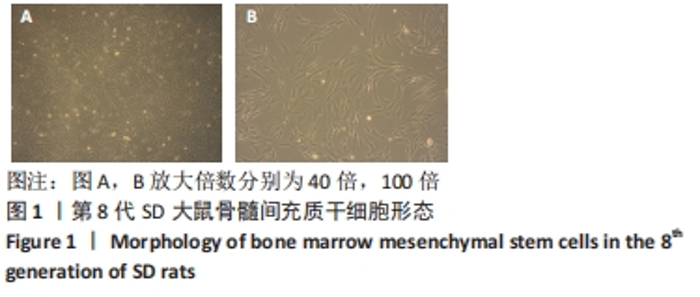
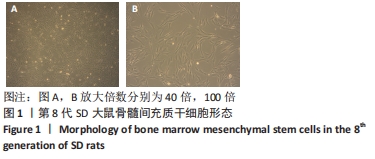
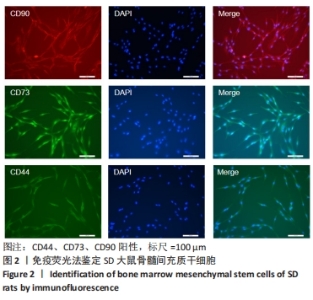
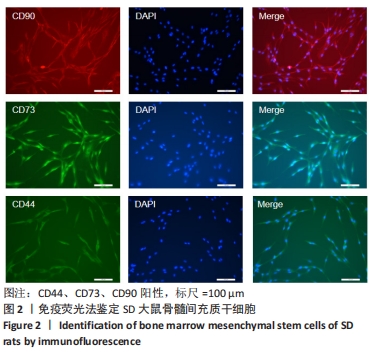
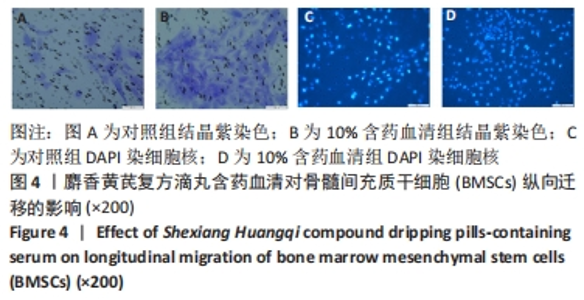
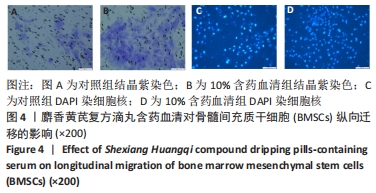
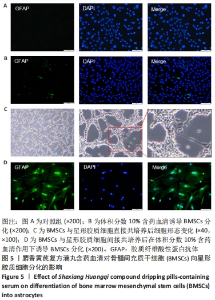
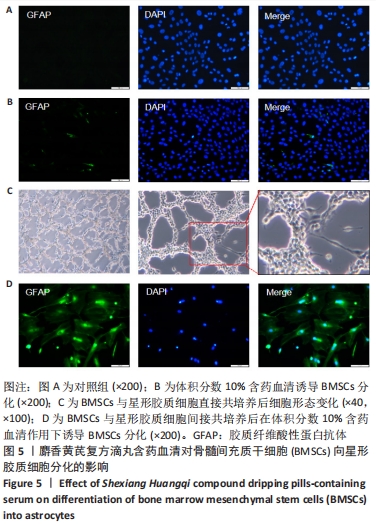
[1] SIFAT AE, VAIDYA B, ABBRUSCATO TJ. Blood-Brain Barrier Protection as a Therapeutic Strategy for Acute Ischemic Stroke. AAPS J. 2017; 19(4):957-972.
[2] LIU D, XU L, ZHANG X, et al. Snapshot: Implications for mTOR in Aging-related Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Aging Dis. 2019;10(1):116-133.
[3] LI Z, YE H, CAI X, et al. Bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells modulate microglial activation in the peri-infarct area in rats during the acute phase of stroke. Brain Res Bull. 2019;153:324-333.
[4] YU X, WU H, ZHAO Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells alleviate brain white matter injury via the enhanced proliferation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells in focal cerebral ischemic rats. Brain Res. 2018;1680:127-136.
[5] LI Y, HUANG J, WANG J, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation supplemented with curcumin improves the outcomes of ischemic stroke via AKT/GSK-3β/β-TrCP/Nrf2 axis. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):49.
[6] ANDRZEJEWSKA A, DABROWSKA S, LUKOMSKA B, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Neurological Disorders. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(7):2002944.
[7] SANMARCO LM, POLONIO CM, WHEELER MA, et al. Functional immune cell-astrocyte interactions. J Exp Med. 2021;218(9):e20202715.
[8] LIU LR, LIU JC, BAO JS, et al. Interaction of Microglia and Astrocytes in the Neurovascular Unit. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1024.
[9] 杨斌,王楠,谭睿,等.中药及其单体对骨髓间充质干细胞诱导分化的研究进展[J].中草药,2022,53(24):7915-7924.
[10] 王诗琦,张金生.中医药调控缺血缺氧微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及衰老的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(7):1129-1134.
[11] 武晓伟,郝艳艳,聂春霞,等.中药血清药物化学的方法学概述及应用领域研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(3):173-179.
[12] DELONG JH, OHASHI SN, O’CONNOR KC, et al. Inflammatory Responses After Ischemic Stroke. Semin Immunopathol. 2022;44(5):625-648.
[13] 张运克,车志英,李可.补阳还五汤联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植脑缺血再灌注大鼠脑组织紧密连接蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(1):55-60.
[14] 张运克,车志英,李可.补阳还五汤联合骨髓间充质干细胞对脑缺血大鼠血脑屏障通透性的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(7): 1548-1553.
[15] 张运克,杨俊红,高峰,等.补阳还五汤联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大脑中动脉栓塞模型整合素相关因子的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(5):724-729.
[16] 李东红,胥芷灵,徐翠珊,等.复方麝香黄芪滴丸的体外及体内血清化学成分分析[J].中国医院药学杂志,2022,42(6):582-589.
[17] 于丹,王莹,高原,等.补中益气汤含药血清对TGF-β介导的A549/DDP细胞Snail、E-cadherin表达的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2023, 43(7):1636-1639.
[18] 祝英杰,王强,韦斌,等.冠通方含药血清通过miR-223/NLRP3信号通路调控血管内皮细胞焦亡的作用及机制研究[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2023,21(6):1037-1041.
[19] 张伟,刘向哲,韩红艳,等.健脾补肾活血方含药血清调控PI3K/Akt信号通路影响大鼠内皮祖细胞功能的机制[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2023,25(1):227-234.
[20] LIU Z, WANG Z, ZHU Z, et al. Crocetin Regulates Functions of Neural Stem Cells to Generate New Neurons for Cerebral Ischemia Recovery. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023:e2203132. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202203132. Epub ahead of print.
[21] DENG Y, LI Z, SUN X, et al. TRIM29 (Tripartite Motif Containing 29) Alleviates NLRC4 (NLR Family CARD Domain Containing Protein 4) Inflammasome Related Cerebral Injury via Promoting Proteasomal Degradation of NLRC4 in Ischemic Stroke. Stroke. 2023;54(5):1377-1389.
[22] GUO X, LIU R, JIA M, et al. Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Induced Blood Brain Barrier Dysfunction and the Involved Molecular Mechanism. Neurochem Res. 2023 Apr 5. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-03923-x. Epub ahead of print.
[23] SHOJAEI F, RAHMATI S, BANITALEBI DEHKORDI M. A review on different methods to increase the efficiency of mesenchymal stem cell-based wound therapy. Wound Repair Regen. 2019;27(6):661-671.
[24] FU X, LIU G, HALIM A, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration and Tissue Repair. Cells. 2019;8(8):784.
[25] KASSIS I, VAKNIN-DEMBINSKY A, KARUSSIS D. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: agents of immunomodulation and neuroprotection. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011;6(1):63-68.
[26] NERI S. Genetic Stability of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Regenerative Medicine Applications: A Fundamental Biosafety Aspect. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2406.
[27] LEE S, CHOI E, CHA MJ, et al. Cell adhesion and long-term survival of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells: a prerequisite for cell therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:632902.
[28] JIANG CT, WU WF, DENG YH, et al. Modulators of microglia activation and polarization in ischemic stroke (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(5): 2006-2018.
[29] 杨浩东,谢兴文,李宁,等.中药调控骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成骨分化相关信号通路的研究进展[J/OL].中国实验方剂学杂志:1-10[2023-04-06].DOI:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.202202425.
[30] 朱余俊,吕浩,江渟.复方补肾活血颗粒对人骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及Wnt/PI3K-AKT信号通路相关蛋白表达的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2022,29(3):79-84.
[31] 刘燕,关永格,宋阳.归肾丸水提物干预SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及PI3K、AKT蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2020, 24(13):1983-1988.
[32] 朱俊朗,陈鸿泰,罗毅文,等.棕榈酸靶向调控趋化因子受体4促进骨髓间充质干细胞体外迁移的研究[J].时珍国医国药,2020, 31(3):562-566.
[33] 曲铁兵.川芎嗪预处理促进骨髓间充质干细胞迁移的体外研究[D].杭州:浙江中医药大学,2014.
[34] 刘永琦,李静雅,蔡玲,等.黄芪多糖诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分化的特性[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2014,21(6):60-64.
[35] SONG S, HUANG H, GUAN X, et al. Activation of endothelial Wnt/β-catenin signaling by protective astrocytes repairs BBB damage in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2021;199:101963.
[36] STOKOWSKA A, ASWENDT M, ZUCHA D, et al. Complement C3a treatment accelerates recovery after stroke via modulation of astrocyte reactivity and cortical connectivity. J Clin Invest. 2023; 133(10):e162253.
[37] 朱立坚,杜浩然,李海龙,等.益气活血类中成药治疗缺血性中风的网状Meta分析[J].中国中药杂志,2023,48(11):3097-3109.
[38] 李志更,岳利峰,马培,等.从“痰瘀互结”论治缺血性中风[J/OL].辽宁中医杂志:1-7[2023-04-06]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1128.R.20230216.1739.012.html
[39] 郑文旭,张保朝,李富慧,等.补阳还五汤对线栓大鼠模型脑损伤和血脑屏障通透性的影响[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2023,21(2):276-282.
[40] 杨璐平,孙红梅,盖聪,等.补阳还五汤及其拆方对缺血性中风气虚血瘀证大鼠脑血流及脂质代谢的影响[J].北京中医药大学学报, 2022,45(10):1029-1036.
[41] 毕芳芳,史敏,程微微,等.黄芪甲苷对缺血性卒中小鼠神经功能保护作用及机制研究[J].现代检验医学杂志,2023,38(1):89-93.
[42] 戚明珠,张铌雪,苏晓慧,等.黄芪甲苷治疗缺血性脑卒中的网络药理学[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(3):163-170.
[43] 甘红霞.黄芪甲苷调控RhoA通路促进神经突起生长的机制研究[D].恩施:湖北民族大学,2022.
[44] 刘晓丹,丁煌,邓常清.黄芪甲苷配伍三七总皂苷对OGD/R大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、凋亡、迁移及神经分化的影响[J].中草药,2019,50(23):5795-5801.
[45] 刘邦,詹锶楷,李克宁,等.基于网络药理学与体外实验探讨川芎活性成分治疗缺血性脑卒中的作用机制[J].中药新药与临床药理,2022,33(11):1536-1544.
[46] 于亚君.人工麝香对星形胶质细胞氧糖剥夺/复氧损伤后的保护作用及机制研究[D].天津:天津中医药大学,2020.
[47] 欧阳波,刘晓丹,杨筱倩,等.冰片配伍黄芪甲苷和三七总皂苷通过Notch信号通路对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤模型的神经保护作用[J].中草药,2020,51(23):5990-5997.
[48] 欧阳波,刘晓丹,杨筱倩,等.冰片配伍黄芪甲苷和三七总皂苷对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤神经元的保护作用[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2020,40(10):1210-1215.
[49] 张睿,倪敏,周春根,等.从中医“精气转化”探讨黄芪对间充质干细胞增殖及分化的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2020,38(10):146-149.
[50] 李建国,谢兴文,李鼎鹏,等.从BMSCs探讨“肾主骨生髓”理论指导下中医药治疗骨质疏松症的研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2022,28(8):1205-1207,1218. |