[1] 张岱年,方立天,程宜山,等.中华的智慧[M].北京:中华书局, 2017:3-501.
[2] 童瑶.中医基础理论[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,1999:1-580.
[3] 杨学鹏,张维波,李守力.中医阴阳学说导论[M].天津:学龄出版社,2019:4-122.
[4] CYRANOSKI D. Why Chinese medicine is heading for clinics around the world. Nature. 2018;561(7724):448-450.
[5] CHAN KW, WONG VT, TANG SCW. COVID-19: An Update on the Epidemiological, Clinical, Preventive and Therapeutic Evidence and Guidelines of Integrative Chinese-Western Medicine for the Management of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease. Am J Chin Med. 2020;48(3):737-762.
[6] 斯洛特·迈克尔.阴阳的哲学[M].北京:商务出版社,2018:41-477.
[7] ZHENG BJ, HUANG D, LI DY, et al. Some scale-free networks could be robust under selective node attacks. Europhys Lett. 2011;94(2):28010.
[8] FITZGERALD G, BOTSTEIN D, CALIFF R, et al. The future of humans as model organisms. Science. 2018;361(6402):552-553.
[9] MCKINNEY SM, SIENIEK M, GODBOLE V, et al. International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature. 2020; 577(7788):89-94.
[10] 贺来. “关系理性”与真实的“共同体”[J].中国社会科学,2015(6):22-44.
[11] TANG L, DING W, LIU C. Scaling Invariance of Sports Sex Gap. Front Physiol. 2020;11:606769.
[12] 张雨,刘芳.一种度量细胞网络结构的方法[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(1):83-86.
[13] NEWBERRY MG, SAVAGE VM. Self-Similar Processes Follow a Power Law in Discrete Logarithmic Space. Phys Rev Lett. 2019;122(15):158303.
[14] BIGELOW J. A Discourse on Self-Limited Diseases (1835). Montana: Kessinger Publishing LLC, 1999:35-400.
[15] SCHIFF GD, GALANTER WL, DUHIG J, et al. Principles of conservative prescribing. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171(16):1433-1440.
[16] DIESENDRUCK CE, SOTTOS NR, MOORE JS, et al. Biomimetic Self-Healing. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015;54(36):10428-10447.
[17] 张启明.未病测评学原理[M].北京:中医古籍出版社,2019:165-208.
[18] MOLOTKOV SN . On the relationship between: L Boltzmann entropy, M Planck distribution, C Shannon information and the principle of particles indistinguishability. Laser Physics Letters. 2020;17(11):1115202.
[19] LIU CY, WU DF, ZHU L, et al. Microenvironment Dependent Photobiomodulation on Function-Specific Signal Transduction Pathways. Int J Photoenergy. 2014;1:1-8.
[20] BURTSCHER M. A breath of fresh air for mitochondria in exercise physiology. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020;229(3):e13490.
[21] 刘承宜,朱玲,李方晖,等.自相似常数与定量差异及其在体育科学中的应用[J].体育学刊,2017,24(6):72-78.
[22] SUN S, HU C, PAN J, et al. Trait Mindfulness Is Associated With the Self-Similarity of Heart Rate Variability. Front Psychol. 2019;10:314.
[23] 汪志胜,郑滔,刘承宜.我国中小学生超重、肥胖检出率变化趋势的拓扑学特征[J].体育学刊,2020,27(1):139-144.
[24] UCCELLI S, PISU V, BRUNO N. Precision in grasping: Consistent with Weber’s law, but constrained by “safety margins”. Neuropsychologia. 2021;163:108088.
[25] MARTIUS F. Das Amdt-Schulz Grandgesetz. Munch Med Wschr. 1923; 70:1005-1006.
[26] ALGOM D. The Weber-Fechner law: A misnomer that persists but that should go away. Psychol Rev. 2021;128(4):757-765.
[27] DITZ HM, NIEDER A. Numerosity representations in crows obey the Weber-Fechner law. Proc Biol Sci. 2016;283(1827):20160083.
[28] STEVENS SS. To Honor Fechner and Repeal His Law: A power function, not a log function, describes the operating characteristic of a sensory system. Science. 1961;133(3446):80-86.
[29] 刘长林.阴阳的认识论意义[J].中国社会科学院研究生院学报, 2006(5):25-32.
[30] KONANGI S, PALAKURTHI NK, GHIA U, et al. von Neumann stability analysis of first-order accurate discretization schemes for one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D) fluid flow equations. Comput Math with Appl. 2018;75(2):643-665.
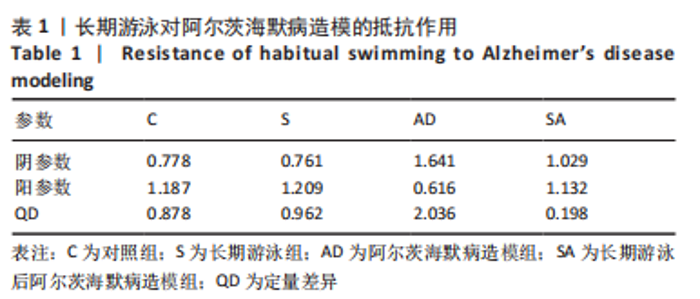
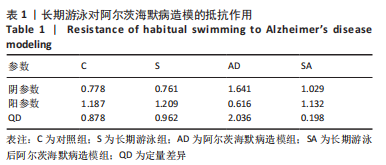
[31] WU C, YANG L, TUCKER D, et al. Beneficial Effects of Exercise Pretreatment in a Sporadic Alzheimer’s Rat Model. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(5):945-956.
[32] 刘力红.思考中医[M].桂林:广西师范大学出版社,2001:3-68.
|