Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (1): 139-146.doi: 10.12307/2023.743
Previous Articles Next Articles
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the heterogeneity of astrocytes
Long Qingxi1, Zhang Pingshu1, 2, Liu Qing1, Ou Ya1, 2, Zhang Lili1, 2, Yuan Xiaodong1, 2
- 1Department of Neurology, Kailuan General Hospital, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China; 2Hebei Key Laboratory of Neurobiology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2022-10-29Accepted:2022-12-09Online:2024-01-08Published:2023-06-29 -
Contact:Yuan Xiaodong, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Neurology, Kailuan General Hospital, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China; Hebei Key Laboratory of Neurobiology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Long Qingxi, Master candidate, Resident physician, Department of Neurology, Kailuan General Hospital, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:Hebei Provincial Innovation Capacity Improvement Plan in 2020 - Science and Technology Research and Development Platform and New Research and Development Organization Construction Project, No. 20567622H (to YXD); Tangshan Scientific and Technological Research and Development Plan in 2020 (The Fourth Batch), No. 20130210D (to YXD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Long Qingxi, Zhang Pingshu, Liu Qing, Ou Ya, Zhang Lili, Yuan Xiaodong. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the heterogeneity of astrocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 139-146.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
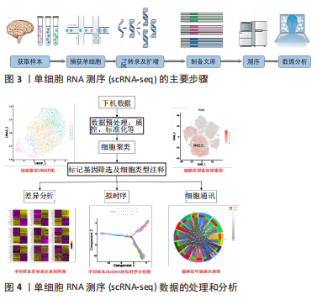
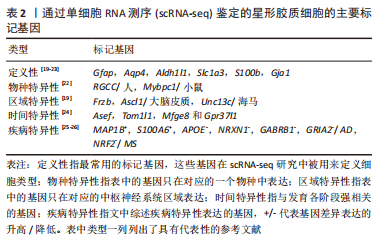
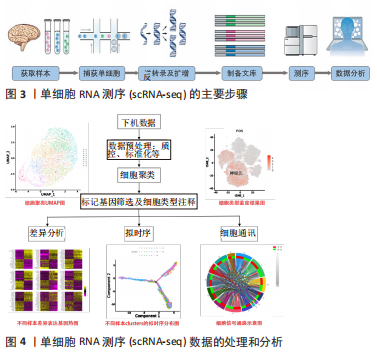
2.1 scRNA-seq技术 scRNA-seq通过高敏性及高通量技术从单细胞水平揭示全基因组的基因表达,是破译细胞异质性最先进的方法,能够增强细胞类型、谱系和状态的分辨,可以发现基因表达、细胞生物学和中枢神经系统功能之间的新联系,增加人们对细胞分子指纹的理解。scRNA-seq是将分离的单个细胞的全基因组 DNA扩增,获得完整基因组后进行高通量测序的一种组学技术[2]。这项技术最早在2009年由北京大学TANG等[3]开发,使高通量RNA测序首次成为可能,自此开辟了一条扩大细胞数量的新途径。随后越来越多改进的scRNA-seq技术涌现,2017年商业测序平台出现以后该技术被大规模运用,并呈指数级增长[4]。同年,伦敦召开的一场国际会议揭开了“人类细胞图谱”全球行动计划的序幕,而scRNA-seq研究是人类细胞图谱计划中的核心内容,星形胶质细胞的scRNA-seq研究则在绘制神经细胞谱中发挥了关键作用。 2.1.1 scRNA-seq技术的方法步骤 scRNA-seq主要包含以下3个主要步骤:①制备单细胞悬液,进行细胞捕获。目前最常见的单细胞分离和捕获技术包括流式细胞分选、荧光激活细胞分选、微流控系统和激光显微切割 [5-6]。②单细胞转录组的扩增和测序。从混悬液中分离出单个细胞产生互补cDNA,并通过PCR或体外转录进行扩增。PCR作为非线性扩增过程应用在Smart-seq,Drop-seq和10x Genomics等方法。体外转录是另一种线性扩增过程用于CEL-seq,MARS-Seq和inDrop-seq方法中。目前最常用的是Smart-seq技术。③测序数据的处理和分析。尽管尚无测序数据处理的指南或共识,但数据分析流程一般包括均一化、降维、聚类、Marker基因筛选、细胞分类和数据可视化几个步骤。一旦确定细胞类型,就可以应用差异基因表达、基因网络或假次分析等方法进一步表征细胞间的差异[7]。总之,单细胞转录组分析涵盖了基因水平和细胞水平的探索,它可以表征不同细胞亚群或同一细胞群体的异质性,也可以发现决定细胞命运的分支点(如通过拟时序分析在单细胞水平推断细胞轨迹),这有望发掘新的细胞类型、功能和细胞的隐蔽状态。 scRNA-seq的主要步骤和数据的处理和分析流程见图3,4。"

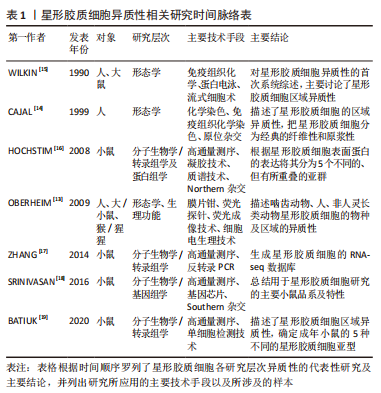
2.1.2 scRNA-seq技术在神经科学中的应用 在神经科学领域,物种间大脑差异的新发现是scRNA-seq应用的最新影响之一,特别是对人类大脑和动物模型中基因表达谱和细胞类型的研究。首先,哺乳动物之间许多发育机制是共享的,但某些编码信号通路、细胞膜阳离子通道及神经递质合成酶的基因,在人类祖细胞及神经细胞中出现了独特表达[8]。其次,最初scRNA-seq侧重于分析神经系统各个部分的细胞异质性,从而产生全面的细胞谱数据。然而早期的研究促使该领域认识到常用的谱系树可能过于简单,研究数据表明不同区域发育中的大脑都会产生更丰富的细胞异质性[9]。当解释细胞随时间变化的过程时,与固定的细胞类型不同,细胞状态变化的转录组特征会发生改变,出现细胞类型的暂时性相互转化,这模糊了细胞类型的边界从而分裂了发育进程[10]。scRNA-seq对于确定细胞随时间的变化如何影响神经发育、神经系统疾病以及物种差异的机制至关重要。最后,近几年scRNA-seq将一系列神经系统疾病的细胞进行分类,通过特定细胞群的发展预测疾病病因,研究发病机制。特定星形胶质细胞亚型激活与疾病进展和临床结局有关,测量和鉴定细胞类型差异的精细能力会对神经系统疾病的治疗和预防产生直接影响[11]。 目前大多数基于scRNA-seq的临床研究仍处于探索阶段,主要侧重于重新审视和更好地理解疾病过程,识别诊断和治疗标志物。尽管每个细胞的成本已经显著降低,但每个样本的成本(包括文库制备和测序)仍然很高,这仍然是使用scRNA-seq作为常规诊断工具的一个限制因素。 2.2 scRNA-seq分析揭示的星形胶质细胞的异质性 星形胶质细胞的异质性是指星形胶质细胞结构形态、胞质活性物质、膜受体、对创伤的反应以及细胞间的网络连接等存在一定程度的差异,这些异质性存在于物种、时间、空间及疾病中[12]。细胞异质性对于组织生物学和细胞功能的研究具有重要意义,既往研究者们通过显微成像、免疫组织化学染色、膜片钳、流式细胞检测及高通量测序分析等技术,在星形胶质细胞异质性形态学、基因组学及蛋白组学等方面都进行了相关探索。然而,这些方法的局限性在于只能实现对细胞群体的相对粗略标记,即使是高通量的测序技术(如全基因组测序)也只是对整体细胞群平均丰度的检测,不能准确反映细胞的异质性。文章根据研究层次对星形胶质细胞异质性研究进行了时间脉络的总结梳理[13-19],见表1。"
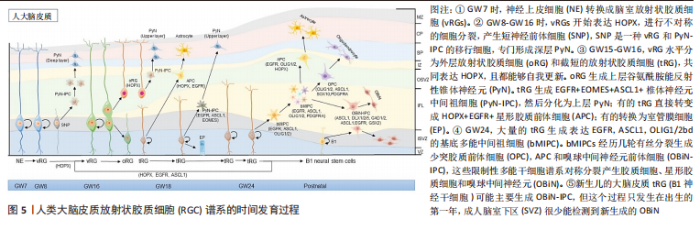
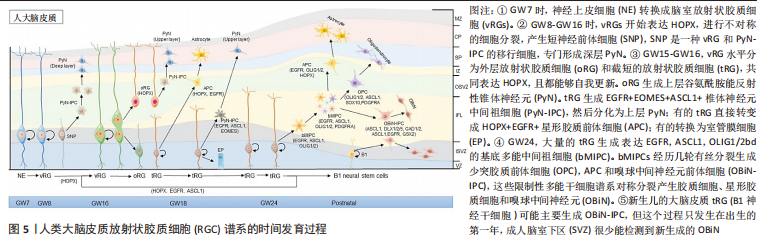
2.2.1 scRNA-seq对星形胶质细胞物种异质性的研究 生物医学研究进展常常依赖于动物模型的使用,尽管它们的基因和人类的基因高度保守,但细微差异的遗传后果不容忽视,有研究表明超过90%的临床前有效药物在临床试验中失败,即使对于相同的物种和疾病,队列之间的异质性也是普遍存在的,物种差异在转化中起关键作用[27]。啮齿动物是生物医学研究中使用最广泛的实验动物之一,不同研究里都观察到人类和小鼠神经胶质细胞(包括星形胶质细胞)的细胞亚型和转录图谱存在差异[28-29]。 人和小鼠星形胶质细胞之间转录组存在广泛的保守性,RNA-seq比较分析发现,人类星形胶质细胞在“防御反应”的基因中表达水平更高,有较高表达的枢纽基因是白细胞介素6和Tlr4;小鼠星形胶质细胞与代谢相关基因的表达水平更高,高表达呼吸链成分中的基因Ndufb7 [30]。此外,结合IP3受体并调节细胞内钙存储的蛋白质MRVI1在人类星形胶质细胞中特异性表达,位于内质网膜上的钙渗透性离子通道(ryanodine receptor 3, Ryr3)在人星形胶质细胞中高度表达,而小鼠中则不是[31]。这些发现与OBERHEIM等[13]对人类和小鼠星形胶质细胞网络之间钙瞬变传播差异的研究结果相一致。研究者利用scRNA-seq技术比较小鼠和人脑中几种常见神经胶质细胞包括星形胶质细胞的基因表达谱,观察到人和小鼠共有的细胞标记物存在差异表达[22]。Galatro实验组的另一项研究也发现,在衰老过程中,人类和小鼠胶质细胞标记基因(包括CX3CR1,P2ry12,CD11b,TLR,Fcγ和Siglec,以及增殖和细胞周期调节因子相关基因TAL1和IFI16)相同,但这些重叠基因在人类呈表达上调的趋势,小鼠中则不出现此现象[32]。在疾病相关研究中,人类星形胶质细胞比小鼠星形胶质细胞更容易受到氧化应激损伤,Ros解毒酶过氧化氢酶基因在小鼠星形胶质细胞中的表达水平是人星形胶质细胞的3-6倍;G6pd基因表达比人星形胶质细胞高2-10倍。PolyI:C和肿瘤坏死因子α在人星形胶质细胞中诱导抗原呈递基因,但在小鼠星形胶质细胞中不诱导抗原呈递基因,这一发现对临床药物的开发及治疗具有很大的意义[30]。除了小鼠,有研究利用单细胞转录组分析表征绒猴视觉皮质缺血性中风后的星形胶质细胞,发现非人灵长类动物中基因的表达模式更加细化,狨猴脑中风后的星形胶质细胞高表达RTN4A/NogoA基因,而在小鼠脑中风的星形胶质细胞中却不明显[33]。人脑卒中部位周围的胶质纤维酸性蛋白阳性反应性星形胶质细胞中RTN4A(NogoA)同样明显上调,在脑卒中后RTN4A(NogoA)的表达上调可能是灵长类动物特有的。 总之,上述研究证明了scRNA-seq在对比不同种属星形胶质细胞基因表达差异方面有极大的优势,人星形胶质细胞与研究模型间存在明显异质性。虽然比较多个模式生物的想法也已经被用于再生医学研究[34],然而在机制研究和药物筛选中,种属差异可能是导致临床转化困难的原因之一,应当进行充分的考虑,scRNA-seq技术的发展很大程度上解决了以上问题。 2.2.2 scRNA-seq对星形胶质细胞时间异质性的研究 细胞在发育过程中的异质性一直是科学研究的主要领域,阐明人类大脑星形胶质细胞发生的时间异质性是神经生物学领域内的重要问题之一,scRNA-seq研究为促进这一领域的发展做出了很大贡献。多年来的研究发现成熟星形胶质细胞池的更新有两条途径,一条是作为前体细胞的放射状胶质细胞(Radial glia cells,RGC)的分化,另一条是成熟星形胶质细胞通过自身分裂和分化进行自我更新[35-36]。虽然星形胶质细胞的生成、发育和成熟还没有明确的检查点,但研究者们发现,在前体细胞分化为星形胶质细胞的过程中,细胞谱系存在明显的时间异质性。从妊娠第7周,以脑室放射状胶质细胞(ventricular radial glial cells,vRG)为起点,经历多次转变及分裂后,在胚胎晚期,形成典型的星形胶质细胞(包括成熟和不成熟的星形胶质细胞)[37],见图5。"

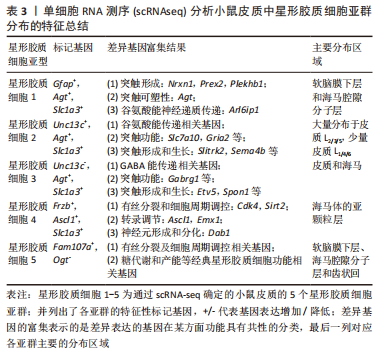
YANG等[38]对人类大脑皮质细胞进行 scRNA-seq分析结果表明,在GW17-GW18时,发育为星形胶质细胞的vRG,tRG和oRG是共存的,都表达了共同的神经胶质标记基因(Hopx,Fam107a,Lifr,Aldoc,Aqp4,Bcan,Gfap 和Tnc等),在GW21-GW26时人皮质tRG表达的50多个基因是星形胶质细胞谱系的标记基因,包括Aldoc,Aqp4,Dbi,Gfap,Glul,S100b,Slc1a2和Sox9等。 除了直接的人脑细胞研究,在小鼠脊髓发育的过程中,星形胶质细胞也表现出明显的时间异质性。早在 E12.5时期,星形胶质细胞就可以通过标记基因 Slc1a3,Aldh1l1和 NfiA的表达来划分[39]。随后,E13.5-E18.5小鼠脊髓星形胶质细胞中,Sox9通过调节 Nfe2l1表达促进 星形胶质细胞 的成熟[40]。而 ChaBoub对从 E12.5到P7的多个发育时间点样本的转录组测序发现,Asef,Tom1l1,Mfge8 和 Gpr37l1可以作为脊髓星形胶质细胞发育中期的新标记[24]。此外,BOISVERT等[41]分析了4月龄和24月龄小鼠星形胶质细胞的基因表达谱发现,衰老的星形胶质细胞表现出显著的分子差异,炎症和突触消除途径的基因表达增加。 星形胶质细胞在神经疾病中发生炎症转化,且各亚型具有明确的转录组图谱。 目前能够准确反映 星形胶质细胞在时间尺度上异质性的单细胞分辨率研究仍然较少,以上的scRNA-seq研究结果提示,星形胶质细胞不同发育阶段出现各自独立又相互联系的基因表达,表现出迥异的细胞亚型及转录学差异,可以深入研究星形胶质细胞的发育轨迹。而这些差异基因的表达是怎样调控星形胶质细胞的发育的,在每一个阶段是否存在共同的上游触发点,是未来需要进一步探索的重要方向。 2.2.3 scRNA-seq星形胶质细胞区域异质性的研究 星形胶质细胞存在于整个神经系统中,但不同的发育来源可能导致星形胶质细胞区域化。这种空间定位非常稳定,即使在神经损伤和衰老的情况下也不会发生变化[42]。早在Cajal时代,人们就发现星形胶质细胞的区域多态性:分布于白质的纤维性星形胶质细胞和分布于灰质的原浆性星形胶质细胞。美国加州大学Rowitch实验室一直从事星形胶质细胞异质性的研究,并通过RNAseq转录组分析,找到了不同层星形胶质细胞特异的基因标签(很多编码转录因子或离子通道蛋白),发现定位在特定区域的星形胶质细胞对该区域特异的神经环路形成和功能起着重要作用[43]。许多神经疾病的病灶只发生在特定的大脑区域,这意味着星形胶质细胞的空间异质性与疾病的进展密切相关。先前有研究提供了星形胶质细胞以区域依赖性方式表现出功能和分子异质性的证据,在转录、翻译及表观遗传水平详细分析了星形胶质细胞的区域异质性[44-45],区域特异性会导致星形胶质细胞的功能受限制,来自不同区域的星形胶质细胞不能相互补偿功能,星形胶质细胞的修复作用也以区域依赖的方式发生[46]。 近年来,在使用scRNA-seq技术鉴定星形胶质细胞空间特异性亚群方面也取得了很大进展,BAYRAKTAR等[47]进行了一项新的高分辨率空间转录组联合scRNA-seq研究分析,发现小鼠皮质中的星形胶质细胞出现板层分布差异和转录组不同的特征,体感皮质上层和深层的基因表达不同。Batiuk团队[19]优化了smart-seq2 单细胞RNA测序技术流程后证实成年小鼠海马区和大脑皮质中的星形胶质细胞具有显著的异质性,并确定了5个星形胶质细胞亚群(星形胶质细胞 1-5);其中,星形胶质细胞 1- 3特征更为相似且占比大,星形胶质细胞 4和星形胶质细胞 5则相对较独特而占比较小。各亚型在皮质与海马的分布明显不同,星形胶质细胞1-5各亚群特征总结如下,见表3。"

参照之前的研究,位于皮质L2-4的星形胶质细胞包含星形胶质细胞2和星形胶质细胞3共2个亚型,其体积较小,较海马CA3区星形胶质细胞发出更多分支[48]。对比Lanjakornsiripan等[49]的研究,皮质L1-6各层中星形胶质细胞的分支、体积、细胞极化方向均有差异。根据5个关键形态学特征(包括延伸率、扁平度以及若干对于细胞极化方向的测量指标)将星形胶质细胞分为了4类(A-D),结合原位杂交实验(RNAscope)结果,发现这4类的分布与相应亚群的对应为:星形胶质细胞1—D群,星形胶质细胞3—B群,星形胶质细胞2—C群。然而,A群主要分布在L5-6,无对应亚群,提示形态学和转录本之间并不完全对应。此外,Ca2+信号的异质性被认为是星形胶质细胞执行多种功能的机制,研究者根据不同Ca2+峰值参数对细胞进行聚类识别出了3个不同的功能亚群cluster 1-3,这些亚群在皮质L1、L3-5和海马CA1层中差异分布[50]。这些数据证实成年小鼠大脑内的星形胶质细胞确实存在脑区内和脑区间的异质性,也提示了星形胶质细胞在各研究层次之间异质性也存在不同之处,为以后的研究提供了思路。 通过scRNA-seq基于簇的分析能够很好地揭示每个亚型在大脑中的特定基因表达模式和不同的空间定位,它们具有不同的形态和生理学,且在小鼠脑中可以得到原位证实。通过绘制每个亚型的空间位置图,可发现更精细的星形胶质细胞亚型位置,见图6。"
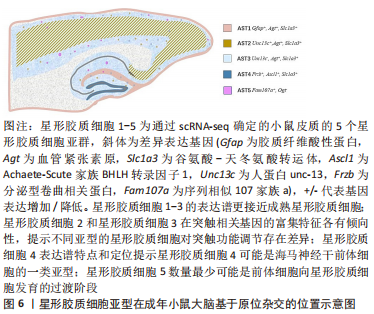

上述研究表明,在中枢神经系统的不同区域内,星形胶质细胞也可能存在功能差异。这些发现为最终阐明中枢神经系统形式和功能提供可靠依据,为完善“人类细胞图谱”计划做出贡献。总之,scRNA-seq和聚类分析可以提供对区域特异性表达模式的深入了解,可用于识别更精细的亚型,更重要的是,它为识别和评估因疾病而发生的位置特定变化提供了强有力的工具。遗憾的是,尚无人类星形胶质细胞区域异质性的scRNA-seq研究发表,如果将人scRNA-seq揭示的转录组所定义的细胞类型与特定的生理功能相匹配,这将是一个极大的进步。 2.3 scRNA-seq对星形胶质细胞异质性的研究与神经疾病 不同的星形胶质细胞可以调节突触的发生和传递,为神经元提供营养和代谢支持,循环神经递质,促进血脑屏障的形成和功能,并对环境因素做出反应。星形胶质细胞的异质性除了取决于其发育阶段和所处位置,在很大程度上也受微环境和所受刺激的影响,目前星形胶质细胞的分类与其异质性并不显著匹配,所有这些都与神经系统疾病有关。GREENHALGH等[51]的研究表明,中枢神经系统损害伴随着星形胶质细胞亚型、数量和基因表达的变化。基于scRNA-seq技术已经确定了由其分子特征和功能定义的星形胶质细胞亚群,这些亚群反映了星形胶质细胞异质性的至少2个来源:发育诱导的星形胶质细胞亚群以及刺激诱导的星形胶质细胞亚群。星形胶质细胞对大脑应激或损伤迅速反应,出现形态和分子变化后被称之为反应性星形胶质细胞(reactive Astrocytes,RAs)[52]。反应性星形胶质细胞胞体和突起肥大,细胞间重叠增多。胶质纤维酸性蛋白过量表达,内向整流型钾离子通道(KiR4.1)、谷氨酸转运体(GLT1)及谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)等下调在多篇文献中被反复提及,但这些改变被环境因素调控,可逆转。静止态的星形胶质细胞则不同,这个过程伴随基因和蛋白表达的增强。斯坦福大学Ben Barres实验室将反应性星形胶质细胞分为伤害性的A1型星形胶质细胞和保护性的A2型星形胶质细胞。但有研究表明反应性星形胶质细胞在不同的中枢神经系统区域和疾病模型中具有不同的分子状态[53]。将反应性星形胶质细胞简单地分为好与坏、神经毒性与神经保护,并不能代表反应性星形胶质细胞的异质性。scRNA-seq对星形胶质细胞状态存在的差异具有很好的分辨率。下面分别以神经退行性疾病阿尔茨海默病、神经系统机械性损伤的脊髓损伤以及慢性炎症性脱髓鞘的多发性硬化症为例,综述星形胶质细胞异质性在疾病中的研究进展。 2.3.1 阿尔茨海默病的星形胶质细胞异质性 阿尔茨海默病又称老年性痴呆,是最常见的神经退行性疾病。研究者们在阿尔茨海默病的发病机制、临床表型和生物标志物等方面做了大量的工作,提出了阿尔茨海默病发展过程中星形胶质细胞异质性的新见解[25, 54-56]。随后,有研究者发现反应性星形胶质细胞的异质性与阿尔茨海默病密切相关,来自哈佛大学Board研究所和麻省理工学院的研究人员通过scRNA-seq在阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型中鉴定出了与疾病相关的星形胶质细胞亚群,这些星形胶质细胞出现在疾病发生的早期阶段,并随着疾病的发展而增加,同时类似的现象也出现在人脑中。无症状阶段阿尔茨海默病的反应性星形胶质细胞的胶质纤维酸性蛋白和Vimentin就出现了过度表达,并重新表达Nestin(通常在未成熟的星形胶质细胞中表达)[57]。MATHYS等[55]的分析显示,阿尔茨海默病病理相关星形胶质细胞亚型中Clu是优先表达的,GRUBMAN等[25]报道称阿尔茨海默病风险基因Apoe在星形胶质细胞中被特异性抑制。阿尔茨海默病的星形胶质细胞标记基因表现出不同的表达趋势:Map1b和S100a6上调,Apoe,Nrxn1,Gabrb1和Gria2下调。这些研究均强调了阿尔茨海默病患者星形胶质细胞的异质性,并发现阿尔茨海默病诊断生物标志物的潜在可能性。 除了讨论阿尔茨海默病患者星形胶质细胞标记基因的差异表达外,有研究者还注意到阿尔茨海默病中星形胶质细胞存在物种异质性,小鼠模型中相关基因表达的变化与阿尔茨海默病患者中基因表达的变化并不匹配[56]。MATHYS等[55]在阿尔茨海默病相关转录改变中则发现显著的性别差异,女性患者阿尔茨海默病相关胶质细胞亚型表现出更高的比例,这些细胞异质性的发现在指导临床诊疗的过程中有着重要意义。近几年,不同的研究报道了星形胶质细胞系在阿尔茨海默病发展过程中发挥着重要作用,并提出基于生物标志物而不是临床表现的阿尔茨海默病诊断[58]。总之,这些研究证明了scRNA-seq识别阿尔茨海默病中星形胶质细胞亚群改变的程度和性质,以及这些改变出现的病理阶段等方面的效用。但在分子水平上星形胶质细胞类型与阿尔茨海默病的关系尚不清楚,仍缺乏能够准确测量阿尔茨海默病患者体内特异性星形胶质细胞的生物标志物,需要进一步探索相关的机制作用,单细胞分辨率下星形胶质细胞类型的相关研究可能是未来一个富有成效的方向。 2.3.2 脊髓损伤的星形胶质细胞异质性 脊髓损伤是指由于不同的因素引起脊髓结构和功能损伤,导致损伤部位以下运动和感觉障碍。哺乳动物的脊髓再生极其困难,胶质瘢痕一直被认为是限制脊髓再生的重要因素,主要由于在中枢神经系统创伤中瘢痕形成物理屏障抑制轴突跨越损伤部位[59-60]。胶质瘢痕包含众多异质性的反应星形胶质细胞群,HACKETT等[61]研究发现NG2 胶质细胞可以分化为星形胶质细胞,促进胶质瘢痕的形成。然而,没有直接证据可以证实受伤后NG2、原始星形胶质细胞以及新生星形胶质细胞之间是否存在异质性。总之,脊髓损伤后星形胶质细胞是动态变化的,并包含复杂的细胞谱系。星形胶质细胞激活是脊髓损伤后星形胶质细胞发生的主要变化,并在损伤后3 d最显著,通过scRNA-seq发现涉及星形胶质细胞激活并表达上调的基因包括Mmp9、Serpine1、白细胞介素1b、Tlr2和Cebpb。Snca基因在这一过程中表达下调,这表明Snca的表达可能抑制脊髓损伤后星形胶质细胞的激活。 星形胶质细胞虽是神经胶质瘢痕的主要成分,但脊髓损伤后星形胶质细胞是形成轴突再生的“墙”还是“桥”存在争议[62]。研究者们发现, 星形胶质细胞可以产生抑制轴突生长的硫酸软骨素蛋白多糖 [63]。通过严格的实验设计,ANDERSON等[64]则证明形成瘢痕的星形胶质细胞不阻止中枢神经系统轴突再生。星形胶质细胞存在广泛的异质性,但尚无研究表明是哪些亚型具有再生抑制特性。除此之外,长期以来人们认为胶质瘢痕形成的过程是单向不可逆的,而2017年《Nature Medicine》报道的一项研究表明,脊髓损伤引起的星形胶质细胞增生并非不可逆,逆转星形胶质细胞的命运为治疗脊髓损伤开辟了新思路。有研究者通过RNA-seq手段发现反应性星形胶质细胞具有环境依赖的可塑性,把脊髓损伤处的反应性星形胶质细胞移植回健康的脊髓,反应性星形胶质细胞可以逆变回幼稚状态,表明脊髓损伤部位的星形胶质细胞仍旧保留命运可塑性。研究者通过Integrin抗体阻断反应性星形胶质细胞与Ⅰ型胶原的相互作用,从而改善神经元轴突生长和神经功能恢复[65]。 还有研究者发现活化的星形胶质细胞亚型能够通过调控抗凋亡蛋白 Bcl-2和促凋亡蛋白 Bax的表达,抑制神经元的凋亡,这为中枢神经系统外源性细胞移植的研究提供了理论支撑[66]。来自迈阿密大学医学院等机构的研究人员,通过对脊髓损伤部位进行scRNA-seq,完成了损伤区域所有细胞类型测序,最终发现了多种新的细胞亚群和功能注释信息,并通过细胞的异质性评估,揭示胶质细胞增生过程中星形胶质细胞的特定作用。他们也提出减少星形胶质细胞增生防止血管成熟的可能性,从而导致白细胞浸润在损伤周围实质浸润增加[67]。总之,scRNA-seq数据集不仅可用于评估损伤部位的星形胶质细胞异质性,还可用于评估损伤部位细胞相互作用的信号通路,这些新的见解可以帮助解读构成脊髓损伤病理生物学基础的复杂过程。虽然对脊髓损伤后星形胶质细胞的异质性知之甚少,但可以明确的是未来可以通过激活有益亚型、抑制有害亚型或者人为调节细胞环境的策略来应对哺乳动物脊髓再生的挑战。 2.3.3 多发性硬化症的星形胶质细胞异质性 多发性硬化症是中枢神经系统的慢性炎症性疾病,多发性硬化症确切的发病机制虽尚不清楚,但普遍认为是在易感基因的基础上,受环境因素触发,CD4+ T细胞介导的中枢神经系统自身免疫性疾病。多发性硬化症具有时间和空间多发的特点,每个病灶都具有明显的异质性。多发性硬化症的一个重要特征就是出现反应性星形胶质细胞,且呈明显的异质性,病变斑块的反应性星形胶质细胞出现核分裂星形胶质细胞及creuzfeldt-peters细胞(核呈碎屑状的星形胶质细胞)[68]。实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎是目前国际公认的多发性硬化症理想动物模型,它是一种以特异性致敏的CD4+ T细胞介导为主,对实验动物进行髓鞘蛋白免疫构建的疾病模型,与人类多发性硬化症在临床、生化、免疫及病理等诸多方面具有相同的特征[69]。Wheeler等[26]发表于《Nature》的文章表明实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎期间星形胶质细胞具有多种转录状态,研究者通过scRNA-seq分析表达经典星形胶质细胞标记基因(S100b,Gja1,Aldh1l1,Gfap和Aqp4)的星形胶质细胞确定了其亚群,扩张最广的亚群与促炎及神经毒性相关。在多发性硬化症发生过程中,中枢神经系统与A2型星形胶质细胞相关的NRF2表达降低、MAFG表达升高,促进甲基化过程从而限制基因表达、抑制抗炎因子的转录过程。也有研究者发现,脂多糖激活的小胶质细胞分泌的白细胞介素1α、肿瘤坏死因子α和C1q诱导反应性星形胶质细胞中的神经毒性表型,使其产生尚未确定的神经毒性因子,降低了吞噬细胞活性以及神经营养因子的表达。值得注意的是,在多发性硬化症脱髓鞘病变周围检测到 SHH+反应性星形胶质细胞,并且内皮细胞中 SHH 受体的表达上调,而 SHH 是一种星形胶质细胞发育期间起着重要作用的形态发生素,可以增强血脑屏障完整性的因子[70]。总之,利用scRNA-seq剖析星形胶质细胞对炎性损伤反应的研究可以看出,星形胶质细胞的亚型会经历不同的炎症转变,并有明确的转录组图谱,这些发现定义了先前未描述的多发性硬化症发病机制,并确定表观遗传修饰作为抑制多发性硬化症中星形胶质细胞致病活性的候选靶点。虽然还需要进一步研究来确定这些基因的影响及其在多发性硬化症发病机制中的作用,但这些结果揭示了scRNA-seq作为在细胞和分子水平上评估疾病状态以及确定多发性硬化症候选治疗靶标的强大潜力。 星形胶质细胞生物学的中心问题是星形胶质细胞异质性的程度[71-74]。scRNA-seq研究方法能够确定不同的ST亚群,识别出星形胶质细胞在健康和疾病中的新功能,发现它们作为治疗靶点的潜力,其中一些因素也为神经疾病的治疗干预提供了明确的分子靶点。然而,通过单细胞转录组学定义星形胶质细胞亚群与神经元活动、行为和疾病特征联系起来仍然是该领域的重大挑战之一。"

| [1] PRABHAKAR P, PIELOT R, LANDGRAF P, et al. Monitoring regional astrocyte diversity by cell type-specific proteomic labeling in vivo. Glia. 2022. doi: 10.1002/glia.24304. [2] WANG X, ALMET AA, NIE Q. Analyzing network diversity of cell-cell interactions in COVID-19 using single-cell transcriptomics. Front Genet. 2022;13:948508. [3] TANG F, BARBACIORU C, WANG Y, et al. mRNA-Seq whole-transcriptome analysis of a single cell. Nat Methods. 2009;6(5):377-382. [4] LI L, XIONG F, WANG Y, et al. What are the applications of single-cell RNA sequencing in cancer research:a systematic review. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40(1):163. [5] JACKSON K, MILNER RJ, DOTY A, et al. Analysis of canine myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) utilizing fluorescence-activated cell sorting, RNA protection mediums to yield quality RNA for single-cell RNA sequencing. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2021;231:110144. [6] ZEB Q, WANG C, SHAFIQ S, et al. Chapter 6 - An Overview of Single-Cell Isolation Techniques. Barh D, Azevedo V, editor, Single-Cell Omics: Academic Press. 2019:101-135. [7] ZHANG Z, CUI F, LIN C, et al. Critical downstream analysis steps for single-cell RNA sequencing data. Brief Bioinform. 2021;22(5):bbab105. [8] MARCHETTO MC, HRVOJ-MIHIC B, KERMAN BE, et al. Species-specific maturation profiles of human, chimpanzee and bonobo neural cells. Elife. 2019;8:e37527. [9] POLIOUDAKIS D, DE LA TORRE-UBIETA L, LANGERMAN J, et al. A single-cell transcriptomic atlas of human neocortical development during mid-gestation. Neuron. 2019;103(5):785-801.e8. [10] TELLEY L, AGIRMAN G, PRADOS J, et al. Temporal patterning of apical progenitors and their daughter neurons in the developing neocortex. Science. 2019;364(6440):aav2522. [11] JäKEL S, AGIRRE E, MENDANHA FALCãO A, et al. Altered human oligodendrocyte heterogeneity in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 2019;566 (7745):543-547. [12] 邓晓林,蔡文琴.星形胶质细胞的异质性及胶质网络[J].解剖科学进展,1997,3(1):46-51. [13] OBERHEIM NA, TAKANO T, HAN X, et al. Uniquely hominid features of adult human astrocytes. J Neurosci. 2009;29(10):3276-3287. [14] CAJAL SR. Texture of the Nervous System of Man and the Vertebrates. 1. Springer Science & Business Media. 1999. [15] WILKIN GP, MARRIOTT DR, CHOLEWINSKI AJ. Astrocyte heterogeneity. Trends Neurosci. 1990;13(2):43-46. [16] HOCHSTIM C, DENEEN B, LUKASZEWICZ A, et al. Identification of positionally distinct astrocyte subtypes whose identities are specified by a homeodomain code. Cell. 2008;133(3):510-522. [17] ZHANG Y, CHEN K, SLOAN SA, et al. An RNA-sequencing transcriptome and splicing database of glia, neurons, and vascular cells of the cerebral cortex. J Neurosci. 2014;34(36):11929-11947. [18] SRINIVASAN R, LU TY, CHAI H, et al. New transgenic mouse lines for selectively targeting astrocytes and studying calcium signals in astrocyte processes in situ and in vivo. Neuron. 2016;92(6):1181-1195. [19] BATIUK MY, MARTIROSYAN A, WAHIS J, et al. Identification of region-specific astrocyte subtypes at single cell resolution. Nat Commun. 2020; 11(1):1220. [20] BLUM JA, KLEMM S, SHADRACH JL, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of the adult mouse spinal cord reveals molecular diversity of autonomic and skeletal motor neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24(4):572-583. [21] ROSENBERG AB, ROCO CM, MUSCAT RA, et al. Single-cell profiling of the developing mouse brain and spinal cord with split-pool barcoding. Science. 2018;360(6385):176-182. [22] XU X, STOYANOVA EI, LEMIESZ AE, et al. Species and cell-type properties of classically defined human and rodent neurons and glia. Elife. 2018;7:e37551. [23] ZEISEL A, HOCHGERNER H, LöNNERBERG P, et al. Molecular architecture of the mouse nervous system. Cell. 2018;174(4):999-1014.e22. [24] CHABOUB LS, MANALO JM, LEE HK, et al. Temporal profiling of astrocyte precursors reveals parallel roles for asef during development and after injury. J Neurosci. 2016;36(47):11904-11917. [25] GRUBMAN A, CHEW G, OUYANG JF, et al. A single-cell atlas of entorhinal cortex from individuals with Alzheimer’s disease reveals cell-type-specific gene expression regulation. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22(12):2087-2097. [26] WHEELER MA, CLARK IC, TJON EC, et al. MAFG-driven astrocytes promote CNS inflammation. Nature. 2020;578(7796):593-599. [27] NEFF RA, WANG M, VATANSEVER S, et al. Molecular subtyping of Alzheimer’s disease using RNA sequencing data reveals novel mechanisms and targets. Sci Adv. 2021;7(2):abb5398. [28] HODGE RD, BAKKEN TE, MILLER JA, et al. Conserved cell types with divergent features in human versus mouse cortex. Nature. 2019;573(7772):61-68. [29] SONG HW, FOREMAN KL, GASTFRIEND BD, et al. Transcriptomic comparison of human and mouse brain microvessels. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):12358. [30] LI J, PAN L, PEMBROKE WG, et al. Conservation and divergence of vulnerability and responses to stressors between human and mouse astrocytes. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3958. [31] PAI B, TOME-GARCIA J, CHENG WS, et al. High-resolution transcriptomics informs glial pathology in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022;10(1):149. [32] GALATRO TF, HOLTMAN IR, LERARIO AM, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of purified human cortical microglia reveals age-associated changes. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20(8):1162-1171. [33] BOGHDADI AG, SPURRIER J, TEO L, et al. NogoA-expressing astrocytes limit peripheral macrophage infiltration after ischemic brain injury in primates. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):6906. [34] FRANJIC D, SKARICA M, MA S, et al. Transcriptomic taxonomy and neurogenic trajectories of adult human, macaque, and pig hippocampal and entorhinal cells. Neuron. 2022;110(3):452-469.e14. [35] NOCTOR SC, MARTíNEZ-CERDEñO V, IVIC L, et al. Cortical neurons arise in symmetric and asymmetric division zones and migrate through specific phases. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7(2):136-144. [36] ARELLANO JI, MOROZOV YM, MICALI N, et al. Radial glial cells: new views on old questions. Neurochem Res. 2021;46(10):2512-2524. [37] SLOAN SA, DARMANIS S, HUBER N, et al. Human astrocyte maturation captured in 3D cerebral cortical spheroids derived from pluripotent stem cells. Neuron. 2017;95(4):779-790.e6. [38] YANG L, LI Z, LIU G, et al. Developmental origins of human cortical oligodendrocytes and astrocytes. Neurosci Bull. 2022;38(1):47-68. [39] LATTKE M, GUILLEMOT F. Understanding astrocyte differentiation: clinical relevance, technical challenges, and new opportunities in the omics era. WIREs Mech Dis. 2022;14(5):e1557. [40] LI X, LIU G, YANG L, et al. Decoding cortical glial cell development. Neurosci Bull. 2021;37(4):440-460. [41] BOISVERT MM, ERIKSON GA, SHOKHIREV MN, et al. The aging astrocyte transcriptome from multiple regions of the mouse brain. Cell Rep. 2018; 22(1):269-285. [42] TSAI HH, LI H, FUENTEALBA LC, et al. Regional astrocyte allocation regulates CNS synaptogenesis and repair. Science. 2012;337(6092):358-362. [43] MOLOFSKY AV, KELLEY KW, TSAI HH, et al. Astrocyte-encoded positional cues maintain sensorimotor circuit integrity. Nature. 2014;509(7499):189-194. [44] HERRERO-NAVARRO Á, PUCHE-AROCA L, MORENO-JUAN V, et al. Astrocytes and neurons share region-specific transcriptional signatures that confer regional identity to neuronal reprogramming. Sci Adv. 2021; 7(15):eabe8978. [45] JOHN LIN CC, YU K, HATCHER A, et al. Identification of diverse astrocyte populations and their malignant analogs. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20(3):396-405. [46] LUNDQUIST AJ, PARIZHER J, PETZINGER GM, et al. Exercise induces region-specific remodeling of astrocyte morphology and reactive astrocyte gene expression patterns in male mice. J Neurosci Res. 2019;97(9):1081-1094. [47] BAYRAKTAR OA, BARTELS T, HOLMQVIST S, et al. Astrocyte layers in the mammalian cerebral cortex revealed by a single-cell in situ transcriptomic map. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23(4):500-509. [48] CHAKER Z, CODEGA P, DOETSCH F. A mosaic world:puzzles revealed by adult neural stem cell heterogeneity. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2016; 5(6):640-658. [49] LANJAKORNSIRIPAN D, PIOR BJ, KAWAGUCHI D, et al. Layer-specific morphological and molecular differences in neocortical astrocytes and their dependence on neuronal layers. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1623. [50] YU X, MOYE SL, KHAKH BS. Local and CNS-wide astrocyte intracellular calcium signaling attenuation in vivo with CalEx (flox) mice. J Neurosci. 2021;41(21):4556-4574. [51] GREENHALGH AD, DAVID S, BENNETT FC. Immune cell regulation of glia during CNS injury and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020;21(3):139-152. [52] SOFRONIEW MV. Astrocyte reactivity: subtypes, states, and functions in cns innate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2020;41(9):758-770. [53] LIDDELOW SA, BARRES BA. Reactive astrocytes: production, function, and therapeutic potential. Immunity. 2017;46(6):957-967. [54] DEL-AGUILA JL, LI Z, DUBE U, et al. A single-nuclei RNA sequencing study of Mendelian and sporadic AD in the human brain. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019;11(1):71. [55] MATHYS H, DAVILA-VELDERRAIN J, PENG Z, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 2019;570(7761):332-337. [56] ZHOU Y, SONG WM, ANDHEY PS, et al. Human and mouse single-nucleus transcriptomics reveal TREM2-dependent and TREM2-independent cellular responses in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med. 2020;26(1):131-142. [57] ESCARTIN C, GALEA E, LAKATOS A, et al. Reactive astrocyte nomenclature, definitions, and future directions. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24(3):312-325. [58] FERRARI-SOUZA JP, FERREIRA PCL, BELLAVER B, et al. Astrocyte biomarker signatures of amyloid-β and tau pathologies in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27(11):4781-4789. [59] YANG T, XING L, YU W, et al. Astrocytic reprogramming combined with rehabilitation strategy improves recovery from spinal cord injury. FASEB J. 2020;34(11):15504-15515. [60] 李剑锋,闫金玉,夏润福,等.脊髓损伤胶质瘢痕形成及星形胶质细胞作用的研究与转化意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(37): 5609-5616. [61] HACKETT AR, YAHN SL, LYAPICHEV K, et al. Injury type-dependent differentiation of NG2 glia into heterogeneous astrocytes. Exp Neurol. 2018;308:72-79. [62] SILVER J, MILLER JH. Regeneration beyond the glial scar. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5(2):146-56. [63] FRANCOS-QUIJORNA I, SáNCHEZ-PETIDIER M, BURNSIDE ER, et al. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans prevent immune cell phenotypic conversion and inflammation resolution via TLR4 in rodent models of spinal cord injury. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):2933. [64] ANDERSON MA, BURDA JE, REN Y, et al. Astrocyte scar formation aids central nervous system axon regeneration. Nature. 2016;532(7598):195-200. [65] HARA M, KOBAYAKAWA K, OHKAWA Y, et al. Interaction of reactive astrocytes with type I collagen induces astrocytic scar formation through the integrin-N-cadherin pathway after spinal cord injury. Nat Med. 2017;23(7):818-828. [66] 张丽丽,欧亚,元小冬,等.脂肪基质细胞诱导分化为星形胶质细胞过程中Bax/Bcl-2蛋白与细胞凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(31): 4982-4987. [67] ARJMAND G, ABBAS-ZADEH M, FARDAEI M, et al. The effect of short-term mediterranean-DASH intervention for neurodegenerative delay (MIND) diet on hunger hormones, anthropometric parameters, and brain structures in middle-aged overweight and obese women: a randomized controlled trial. Iran J Med Sci. 2022;47(5):422-432. [68] 王丹丹,朴月善,卢德宏.多发性硬化症的神经病理学进展[J].北京医学,2013,35(5):374-376. [69] 赵培源,陈少昀,刘喜红,等.多发性硬化实验动物模型的研究与应用进展[J].中国实验动物学报,2020,28(3):405-409. [70] XIONG XY, TANG Y, YANG QW. Metabolic changes favor the activity and heterogeneity of reactive astrocytes. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2022; 33(6):390-400. [71] LINNERBAUER M, WHEELER MA, QUINTANA FJ. Astrocyte crosstalk in CNS inflammation. Neuron. 2020;108(4):608-622. [72] LI Q, CHENG Z, ZHOU L, et al. Developmental heterogeneity of microglia and brain myeloid cells revealed by deep single-cell RNA sequencing. Neuron. 2019;101(2):207-223.e10. [73] JIANG J, WANG C, QI R, et al. scREAD: a single-cell RNA-seq database for alzheimer’s disease. iScience. 2020;23(11):101769. [74] BRANDEBURA AN, PAUMIER A, ONUR TS, et al. Astrocyte contribution to dysfunction, risk and progression in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2023;24(1):23-29. |
| [1] | Cheng Haotian, Zhao Xiaofeng, Lu Xiangdong, Zhao Yibo, Fan Zhifeng, Qi Detai, Wang Xiaonan, Zhou Runtian, Jin Xinjie, Zhao Bin. Single-cell RNA sequencing and the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 93-99. |
| [2] | Yang Ting, Ding Zhibin, Jiang Nan, Han Hongxia, Hou Miaomiao, Ma Cungen, Song Lijuan, Li Xinyi. Astrocytes regulate glial scar formation in cerebral ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 131-138. |
| [3] | Zheng Mingkui, Xue Chenhui, Guan Xiaoming, Ma Xun. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes reduce the permeability of blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 50-55. |
| [4] | He Wanyu, Cheng Leping. Strategies and advance on stem cell transplantation for repair of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [5] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [6] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [7] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [8] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [9] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [10] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [11] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [12] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [13] | Yang Jiujie, Li Zhi, Wang Shujie, Tian Ye, Zhao Wei. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of functional changes following durotomy with decompression for acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [14] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [15] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||