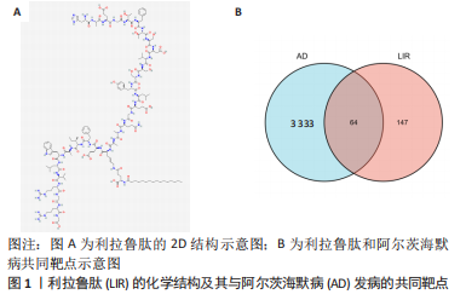
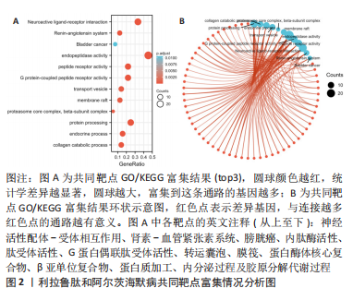
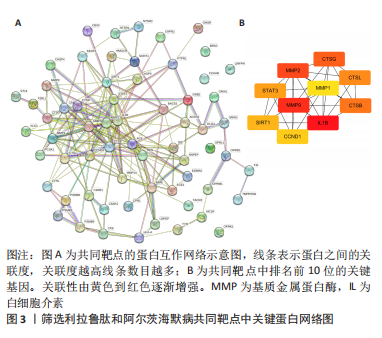
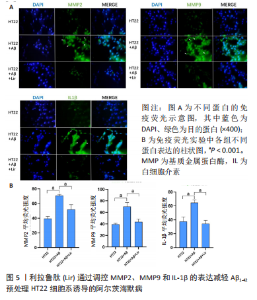
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (16): 2568-2573.doi: 10.12307/2024.306
Previous Articles Next Articles
Prediction and validation of potential targets for the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
Han Weina1, Xu Xiaoqing1, Shi Jinning1, Li Xinru2, Cai Hongyan3
- 1Department of Physiology, Puai School of Medicine (Health Science Center), Shaoyang University, Shaoyang 422000, Hunan Province, China; 2Department of Physiology, 3Department of Microbiology and Immunology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-22Accepted:2023-04-20Online:2024-06-08Published:2023-07-31 -
Contact:Han Weina, Department of Physiology, Puai School of Medicine (Health Science Center), Shaoyang University, Shaoyang 422000, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Han Weina, Master, Associate professor, Department of Physiology, Puai School of Medicine (Health Science Center), Shaoyang University, Shaoyang 422000, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82171428 (to CHY); Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province for Young Scholars, No. 2020JJ5517 (to HWN); Scientific Research Project of Education Department of Hunan Province, No. 20C1671 (to HWN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Weina, Xu Xiaoqing, Shi Jinning, Li Xinru, Cai Hongyan. Prediction and validation of potential targets for the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2568-2573.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

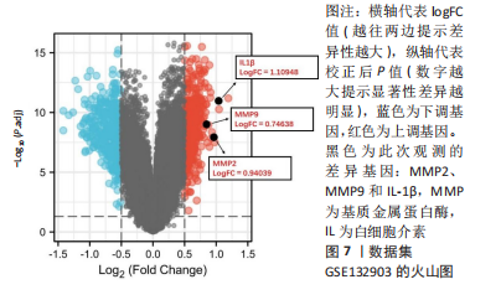
2.4 利拉鲁肽可以抑制Aβ对HT22细胞的损伤作用,且100 nmol/L为最佳浓度 实验采用CCK-8试剂盒检测了培养细胞的活性,确定100 nmol/L利拉鲁肽是拮抗Aβ1-42的最佳浓度,见图4。0 nmol/L利拉鲁肽组与对照组相比细胞活性明显下降,且有显著性差异(P < 0.001),提示Aβ有细胞毒性作用;40,80,100,150,200 nmol/L浓度的利拉鲁肽均可以拮抗Aβ的细胞毒性作用,其中100 nmol/L时细胞活性最佳,且与0 nmol/L组相比有显著性差异(P < 0.01)。由于150 nmol/L浓度的利拉鲁肽组细胞活力开始下降,因此提示100 nmol/L浓度的利拉鲁肽为拮抗Aβ1-42的最佳干预剂量。"

| [1] CARMONA S, HARDY J, GUERREIRO R. The genetic landscape of Alzheimer disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;148:395-408. [2] 2021 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2021; 17(3):327-406. [3] ZHANG Y, LI Y, MA L. Recent advances in research on Alzheimer’s disease in China. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;81:43-46. [4] KNUDSEN LB, NIELSEN PF, HUUSFELDT PO, et al. Potent derivatives of glucagon-like peptide-1 with pharmacokinetic properties suitable for once daily administration. J Med Chem. 2000;43(9):1664-1669. [5] NAUCK MA, QUAST DR, WEFERS J, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes - state-of-the-art. Mol Metab. 2021;46:101102. [6] VILSBOLL T. The effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 on the beta cell. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009;11 Suppl 3:11-18. [7] LOVSHIN JA, DRUCKER DJ. Incretin-based therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2009;5(5):262-269. [8] ROLIN B, LARSEN MO, GOTFREDSEN CF, et al. The long-acting GLP-1 derivative NN2211 ameliorates glycemia and increases beta-cell mass in diabetic mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002;283(4):E745-E752. [9] LIU XY, ZHANG N, ZHANG SX, et al. Potential new therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease: Glucagon-like peptide-1. Eur J Neurosci. 2021;54(10): 7749-7769. [10] MENG L, LI XY, SHEN L, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus drugs for alzheimer’s disease: current evidence and therapeutic opportunities. Trends Mol Med. 2020;26(6):597-614. [11] 张峥,张兆辉.阿尔茨海默病与2型糖尿病的相关性研究进展[J].卒中与神经疾病,2018,25(1):112-117. [12] PALADUGU L, GHARAIBEH A, KOLLI N, et al. Liraglutide has anti-inflammatory and anti-amyloid properties in streptozotocin-induced and 5xFAD mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):860. [13] CICCONE L, VANDOOREN J, NENCETTI S, et al. Natural marine and terrestrial compounds as modulators of matrix metalloproteinases-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9 in Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14(2):86. [14] REVUELTA M, URRUTIA J, VILLARROEL A, et al. Microglia-mediated inflammation and neural stem cell differentiation in Alzheimer’s disease: possible therapeutic role of K(V)1.3 channel blockade. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:868842. [15] PY NA, BONNET AE, BERNARD A, et al. Differential spatio-temporal regulation of MMPs in the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: evidence for a pro-amyloidogenic role of MT1-MMP. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:247. [16] HIRANO T, MORI Y. Anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory properties of glucagon-like peptide-1, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypepide, and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in experimental animals. J Diabetes Investig. 2016;7 Suppl 1:80-86. [17] MCCLEAN PL, GAULT VA, HARRIOTT P, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues enhance synaptic plasticity in the brain: a link between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010;630(1-3):158-162. [18] HAMILTON A, PATTERSON S, PORTER D, et al. Novel GLP-1 mimetics developed to treat type 2 diabetes promote progenitor cell proliferation in the brain. J Neurosci Res. 2011;89(4):481-489. [19] QI L, KE L, LIU X, et al. Subcutaneous administration of liraglutide ameliorates learning and memory impairment by modulating tau hyperphosphorylation via the glycogen synthase kinase-3beta pathway in an amyloid beta protein induced alzheimer disease mouse model. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;783:23-32. [20] 原丽,韩玲娜,常永丽,等.肠促胰岛素类似物拮抗APP/PS1转基因鼠认知功能损伤的研究[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2019,24(7):721-729. [21] HAN WN, HOLSCHER C, YUAN L, et al. Liraglutide protects against amyloid-beta protein-induced impairment of spatial learning and memory in rats. Neurobiol Aging. 2013;34(2):576-588. [22] WEINA H, YUHU N, CHRISTIAN H, et al. Liraglutide attenuates the depressive- and anxiety-like behaviour in the corticosterone induced depression model via improving hippocampal neural plasticity. Brain Res. 2018;1694:55-62. [23] MANNELLO F. New implications of the proteolytic balance between matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in migraine with and without aura. Clin Chim Acta. 2009;409(1-2):1-3. [24] REMPE RG, HARTZA, BAUER B. Matrix metalloproteinases in the brain and blood-brain barrier: versatile breakers and makers. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016;36(9):1481-1507. [25] BJERKE M, ZETTERBERG H, EDMAN A, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases in combination with subcortical and cortical biomarkers in vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;27(3):665-676. [26] BRUNO MA, MUFSON EJ, WUU J, et al. Increased matrix metalloproteinase 9 activity in mild cognitive impairment. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009; 68(12):1309-1318. [27] LORENZL S, BUERGER K, HAMPEL H, et al. Profiles of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in plasma of patients with dementia. Int Psychogeriatr. 2008;20(1):67-76. [28] MIZOGUCHI H, TAKUMA K, FUKUZAKI E, et al. Matrix metalloprotease-9 inhibition improves amyloid beta-mediated cognitive impairment and neurotoxicity in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;331(1):14-22. [29] WEEKMAN EM, WILCOCK DM. Matrix metalloproteinase in blood-brain barrier breakdown in dementia. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;49(4):893-903. [30] ROSENBERG GA. Matrix metalloproteinases and their multiple roles in neurodegenerative diseases. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(2):205-216. [31] TEIXEIRA AL, REIS HJ, COELHO FM, et al. All-or-nothing type biphasic cytokine production of human lymphocytes after exposure to Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid peptide. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;64(10):891-895. [32] HAMPEL H, CARACI F, CUELLO AC, et al. A path toward precision medicine for neuroinflammatory mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Immunol. 2020;11:456. [33] WICINSKI M, SOCHA M, MALINOWSKI B, et al. Liraglutide and its neuroprotective properties-focus on possible biochemical mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease and cerebral ischemic events. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(5):1050. [34] KHAVINSON V, LINKOVA N, DYATLOVA A, et al. Senescence-associated secretory phenotype of cardiovascular system cells and inflammaging: perspectives of peptide regulation. Cells. 2022;12(1):106. [35] SHAFTEL SS, GRIFFIN WS, O’BANION MK. The role of interleukin-1 in neuroinflammation and Alzheimer disease: an evolving perspective. J Neuroinflammation. 2008;5:7. [36] ZHENG C, ZHOU XW, WANG JZ. The dual roles of cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease: update on interleukins, TNF-alpha, TGF-beta and IFN-gamma. Transl Neurodegener. 2016;5:7. |
| [1] | Li Longyang, Zhang Songjiang, Zhao Xianmin, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng. Electroacupuncture intervention on the proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal neurons and oligodendrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | Bu Xianzhong, Bu Baoxian, Xu Wei, Zhang Chi, Zhang Yisheng, Zhong Yuanming, Li Zhifei, Tang Fubo, Mai Wei, Zhou Jinyan. Analysis of serum differential proteomics in patients with acute cervical spondylotic radiculopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 535-541. |
| [3] | Xia Tian, Li Binglin, Xiao Fayuan, Zheng Enze, Chen Yueping. CeRNA interaction network and immune manifestation of ferroptosis-related signature genes in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2561-2567. |
| [4] | Deng Longfei, Zhang Yeting, Fu Yan. Aerobic exercise inhibits neuroinflammation and alleviates cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2209-2214. |
| [5] | Yuan Tianyi, Liu Hongjiang, Yang Zengqiang, Lu Xingbao, Maimaitiyibubaji, Zhou Zhiheng, Cui Yong. Identification of differences in N6-methyladenosine-related genes in steroid-induced femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2159-2165. |
| [6] | Zuo Jun, Ma Shaolin. Bioinformatics analysis and validation of differentially expressed genes and small molecule drug prediction in proliferative scar [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2166-2172. |
| [7] | Yuan Changshen, Liao Shuning, Li Zhe, Guan Yanbing, Wu Siping, Hu Qi, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. N6-methyladenosine related regulatory factors in osteoarthritis: bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1724-1729. |
| [8] | Long Qingxi, Zhang Pingshu, Liu Qing, Ou Ya, Zhang Lili, Yuan Xiaodong. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the heterogeneity of astrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 139-146. |
| [9] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [10] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [11] | Liang Xuezhen, Luo Di, Li Jiacheng, Wen Mingtao, Zhang Jian, Xu Bo, Li Gang. PTGS2 and STAT3 in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: ferroptosis-related potential diagnostic biomarkers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5898-5904. |
| [12] | Li Xinru, Chai Shifan, Li Weiran, Cai Hongyan, Ye Yucai, Li Shuo, Hou Meng, Wang Zhaojun. Bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation of genes related to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5653-5658. |
| [13] | Tang Lu, Lin Haiqi. The power-law model-based analysis of aerobic exercise against Alzheimer’s disease in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5695-5700. |
| [14] | Long Tiaoyu, Bao Lunmin, Wan Xiufang, Li Honghong, Zhang Yundong, Jiang Hongmei. Tolerogenic dendritic cells can inhibit pyroptosis of spleen cells in collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5363-5369. |
| [15] | Du Jia, Fu Yan, Fan Jia, Zhou Miaorong, Zhang Yeting. Aerobic exercise intervenes with beta-amyloid 1-42 induced changes in hippocampal synaptic structure and proteins in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5256-5262. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||