Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (28): 4559-4565.doi: 10.12307/2023.700
Previous Articles Next Articles
Competing endogenous RNA regulates the development of osteoarthritis
Liu Xingyu, Liu Riguang, Li Guangdi, Wang Jian, Li Long, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi
- Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-09-26Accepted:2022-11-08Online:2023-10-08Published:2023-01-29 -
Contact:Liu Riguang, MD, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Liu Xingyu, Master candidate, Physician, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Regional Science Fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82160432 (to LGD); Guizhou Provincial Health Commission Science and Technology Fund Project, No. gzwkj2021-244 (to LGD); Basic Research Project of Guizhou Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. Qiankeheji ZK[2022]-General 427 (to LGD); National Natural Science Foundation of Guizhou Medical University, No. 20NSP045 (to LGD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Xingyu, Liu Riguang, Li Guangdi, Wang Jian, Li Long, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Competing endogenous RNA regulates the development of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4559-4565.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
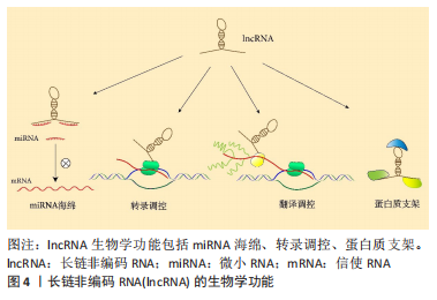
2.1 构建 ceRNA 调控网络相关 RNAs 分子特点和生物学功能 2.1.1 lncRNA分子特点和生物学功能 lncRNA是长度通常超过200个核苷酸的非编码RNA[17],在人类中发现了30 000-60 000个lncRNAs[18]。lncRNA的生物发生过程类似于信使RNA,在RNA聚合酶Ⅱ酶作用下转录,并像信使RNA一样经历选择性剪接过程,最终成熟的LncRNA转录物具有5’-端7-甲基鸟甘三磷酸(m7GTP)帽子结构和3’-端多聚腺苷酸(ployA)尾巴结构,通常位于细胞核和细胞质[19-22]。 起初,lncRNA被认为是基因组转录的“噪音”,没有生物功能,其作用机制仅为原位调节,通过募集和形成染色质修饰复合物,沉默相邻基因的转录[23]。随着更多检测技术应用于RNA研究,逐渐被发现lncRNA可以与蛋白质、DNA和RNA相互作用,以调节许多生物过程[24]。基于这些功能的性质,lncRNA 可能是不同的功能分子,包括作为信号、指导、支架、诱饵和海绵,从而在染色质重塑、转录调节、RNA剪接、翻译调节、凋亡、自噬、细胞增殖、细胞分化和信号通路等基因表达调控的所有级别中发挥重要作用[25-28],甚至一些lncRNA可被翻译成功能肽[29]。因此,lncRNA 具有多效性,可以被视为基因组的“主要调节剂”[30-31],见图4。"

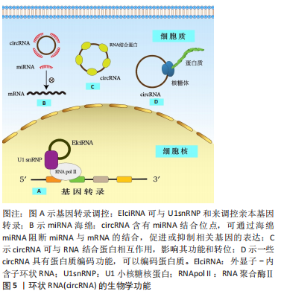
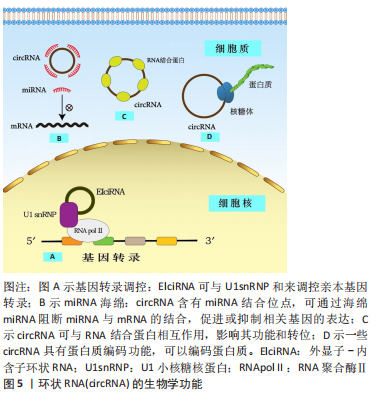
2.1.2 circRNA分子特点和生物学功能 circRNA是一类不具有5’末端m7GTP帽子和3’末端poly(A)尾巴结构,以共价键形成环形结构的非编码RNA分子。是由前体mRNA(pre-mRNA)经历剪接体剪切产生线性mRNA,并在RNA聚合酶Ⅱ(RNA Pol II)反向剪接作用下生成的连续闭环结构[32] 。目前,已阐明了3种公认的外显子环状RNA形成模型:套索驱动环化(外显子跳跃)、内含子配对驱动环化(直接反向剪接)和RNA结合蛋白(RBP)驱动环化[33-35]。在形成过程中,当外显子CircRNA 从信使 RNA 前体中释放出来并保留内含子序列时,则形成包含外显子和内含子序列的外显子-内含子环状RNA,其主要位于细胞核中;若未保留内含子序列,则形成仅有外显子序列的外显子环状RNA,该种类型最为丰富,占总CircRNA的80%以上,主要位于细胞质中,可通过外泌体运输。通过规范剪接从内含子套索产生的 circRNA 被称为内含子环状RNA,主要位于细胞核中,但由于分支酶作用,它们往往会降解,所以其含量最少,因此 circRNA根据其来源可分为3类:外显子组成的外显子环状RNA、内含子组成的内含子环状RNA以及由外显子和内含子共同组成的外显子-内含子环状RNA[36-37]。 由于circRNA是闭环结构,缺少游离的5’末端m7GTP帽子和3’末端poly(A)尾巴,使得它们对核酸外切酶具有抗性,因此,与线性形式RNA相比,circRNA含量更丰富(约为线性RNA的10倍)且高度稳定[38]。除此之外 circRNA还具有细胞和组织特异性、保守性和普遍性[39-40]。目前,已发现circRNA具有多种生物学功能,circRNA可作为ceRNA,发挥miRNA海绵功能[41-43]、与 RNA 结合蛋白相互作用影响其功能和转位[44]、参与调控基因转录[45]、编码蛋白质等功能[46]。见图5。"
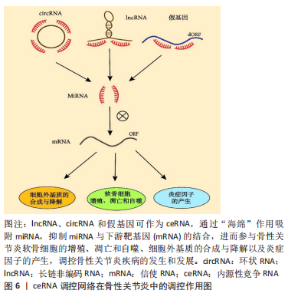
2.1.3 假基因分子特点和生物学功能 假基因中存在过早的终止密码子、基因缺失或插入以及移码突变,这些突变的积累导致了其功能丧失,因此,假基因曾被认为是基因“垃圾”[47]。JACQ等[48]首次提出“伪基因”一词,他们报告了非洲爪蟾中存在一组与5S DNA同源的未转录基因组序列,之后,随着分析技术的不断进步,已发现约16 000个已识别的假基因中有10%被转录,约19%的已知人类lncRNAs是假基因转录的产物[49-51]。近年来获得的实验数据也揭示了假基因在调控其相应的亲本基因和各种生物学机制中的重要性。根据来源,假基因可分为2大类:重复假基因和反转录假基因[52]。重复假基因由DNA复制和突变或缺失累积产生;反转录假基因,也被称为加工假基因,是通过将加工过的mRNA反转录到基因组中而产生的。越来越多的证据表明,假基因可以通过与蛋白质、RNA和DNA水平的分子相互作用调节基因表达。 2.2 ceRNA 调控网络在骨性关节炎中的调控作用 骨性关节炎是一种全关节疾病,以往骨性关节炎被认为是一种简单的“磨损”疾病。关节上的慢性超负荷和生物力学受损会导致关节软骨的破坏和由此产生的炎症,进而导致僵硬、肿胀疼痛和丧失活动能力[53]。然而随着研究深入,新的见解表明,骨性关节炎实际上是一个由关节损伤和修复不平衡引起的动态过程。骨性关节炎有许多可改变和不可改变的危险因素:遗传易感性、年龄增长、肥胖、损伤、性别和生活方式因素,这些危险因素的共同作用致使软骨代谢稳态失调进而关节软骨的结构完整性遭到破坏。骨性关节炎具体发展过程涉及构成骨性关节炎微环境的多个细胞和分子,关节软骨细胞(软骨的主要细胞成分)的功能障碍在骨性关节炎期间发挥不可或缺的作用。在初始阶段,细胞外基质的分子组成和结构发生改变,而软骨表面保持完整。同时,在生长因子、缺氧诱导因子1α和生长分化因子5等分子刺激下,软骨细胞开始获得活跃的增殖能力,并诱导基质分泌,修复细胞外基质。然而,增殖的软骨细胞可能产生大量的分解代谢酶和促炎递质,最终导致软骨细胞凋亡以及细胞外基质降解,进而软骨被破坏,功能失调,形成恶性循环。随后,骨赘形成、肌肉损伤和肌腱破坏也随之出现[54-55]。骨性关节炎疾病进展涉及了细胞衰老、机械负荷超载、炎症成分增加、代谢改变等病理过程,这些机制表型彼此相互重叠交叉,进而导致骨性关节炎的发生,因此骨性关节炎可被视为一种综合征,而不是一种单一疾病[2]。随着测序技术的不断发展,人们发现ceRNA 网络中分子之间的相互调控在骨性关节炎发病机制中扮演着重要的角色。lncRNA、circRNA 和假基因可作为 ceRNA,通过“海绵”作用吸附miRNA,抑制miRNA与下游靶基因的结合,进而参与骨性关节炎软骨细胞的增殖、凋亡和自噬、细胞外基质的合成与降解以及炎症事件的发生,见图6。"
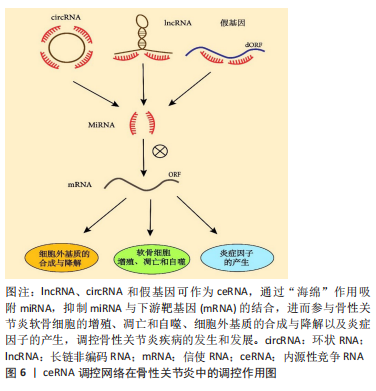
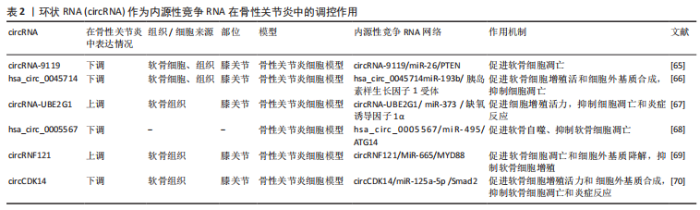
lncRNA作为ceRNA参与骨性关节炎中的许多病理过程,如细胞外基质合成与降解、细胞增殖、细胞凋亡和炎症事件。研究发现,lncRNA PVT1可作为miRNA的ceRNA,在骨性关节炎疾病进展中发挥关键作用,如细胞活力、自噬、细胞凋亡和炎症。Lu等[59]发现在骨性关节炎患者和白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞中lncRNA PVT1表达增强;沉默软骨细胞中lncRNA PVT1促进细胞存活和自噬,抑制炎症反应和细胞凋亡。miR-27b-3p被确认为lncRNA PVT1的靶点,抑制其表达逆转了lncRNA PVT1敲减对白细胞介素1β诱导软骨细胞损伤的抑制作用。此外,lncRNA PVT1通过“海绵”作用吸附miR-27b-3p间接正调控TRAF3的表达。总之,lncRNA PVT1可作为ceRNA,通过“海绵”作用吸收 miR-27b-3p,减少其表达量,从而间接上调TRAF3表达,抑制细胞活力和自噬、加重白细胞介素1β处理的软骨细胞的凋亡和炎症反应。lncRNA HOTTIP是一种重要的调节性lncRNA,可作为miR-455-3p的内源性抑制剂,主要调节骨性关节炎进展中的细胞外基质破坏。MAO等[60]研究发现,在骨性关节炎软骨组织和软骨细胞以及白细胞介素1β处理软骨细胞中lncRNA HOTTIP 和 CCL3表达显著上调,miR-455-3p 表达下调,并在白细胞介素1β处理的软骨细胞中,lncRNA HOTTIP以时间和剂量依赖性方式上调。他们的研究还表明,lncRNA HOTTIP可作为ceRNA竞争结合miR-455-3p,从而提高CCL3表达水平,并且lncRNA HOTTIP过表达降低软骨寡聚基质蛋白,Ⅰ型胶原α1链和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达,增加基质金属蛋白酶和去整合素和金属蛋白酶的表达,进而促进细胞外基质降解,得出lncRNA HOTTIP/miR-455-3p/CCL3调控轴在骨性关节炎发病机制中起关键作用,提示 HOTTIP 可能是骨性关节炎的潜在治疗靶点。HU等[61]研究发现,lncRNA HOTAIR在骨性关节炎软骨组织中高度表达,并与骨性关节炎严重程度呈正相关。过表达的lncRNA HOTAIR加重了软骨细胞损伤和凋亡,抑制软骨细胞增殖,并且Western印迹分析显示,lncRNA HOTAIR的过表达提高了降解酶如基质金属蛋白酶13和ADAMS5的水平,这些酶导致细胞外基质破坏,同时降低了有助于软骨中细胞外基质形成的胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖的水平。该研究表明,lncRNA HOTAIR可作ceRNA,竞争性结合miR-17-5p,从而增加调节Wnt/β-连环蛋白途径的FUT2表达水平从而加剧骨性关节炎的发展,表明其可能作为骨性关节炎的有用生物标志物和潜在治疗靶点。ZHANG等[62]研究发现,骨性关节炎软骨组织和脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞中lncRNA ARFRP1和TLR4表达水平升高,而miR-15a-5p表达水平降低;敲除软骨细胞中的lncRNA ARFRP1抑制了炎症因子的释放,如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素1β,从而抑制脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞损伤。研究还发现,抑制miR-15a-5p表达逆转了lncRNA ARFRP1敲除对脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞损伤的影响,并且其可以直接靶向抑制下游TLR4的表达水平。因此该研究表明,lncRNA ARFRP1可作为ceRNA,调节miR-15a-5p/TLR4轴参与骨性关节炎炎症事件的发生,从而诱导软骨细胞损伤,因此,lncRNA DANCR可能被视为骨性关节炎治疗的潜在治疗靶点。一项研究发现LncRNA LOXL1-AS1在骨性关节炎软骨组织中上调,其作为miR-423-5p的ceRNA参与骨性关节炎发生和进展。敲减LncRNA LOXL1-AS1的表达抑制了软骨细胞增殖和炎症反应,同时促进软骨细胞凋亡,该研究得出结论,lncRNA LOXL1-AS1可作为ceRNA,海绵吸附miR-423-5p,间接调节KDM5C的表达水平,从而参与骨性关节炎软骨细胞的增殖、凋亡和炎症事件的发生,这可能为骨性关节炎提供潜在的治疗靶点[63]。lncRNA XIST是骨性关节炎发展过程中的关键调节因子,LIU等[64]揭示了lncRNA XIST可作为miR-149-5p的ceRNA,在骨性关节炎软骨组织和白细胞介素1β处理的软骨细胞中高水平表达。此次研究的结果还表明,lncRNA XIST 的敲低可以通过 miR-149-5p/DNMT3A 轴促进细胞增殖活力,同时抑制细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解。 综上所述,通过检测骨性关节炎患者和健康个体软骨中的lncRNA表达水平,最终可以发现多种lncRNA的表达存在差异,lncRNA 在骨性关节炎的发生发展中发挥了重要作用,主要参与骨性关节炎软骨细胞外基质的降解、软骨细胞凋亡与增殖和炎症事件。因此,lncRNA本身及其互作蛋白或靶基因有望成为骨性关节炎的早期诊断生物标志物和新的治疗靶点。 2.2.2 circRNA作为内源性竞争因子在骨性关节炎中的调控作用 随着RNA测序技术和生物信息学分析等技术的发展,越来越多的证据表明,circRNA与骨性关节炎软骨细胞增殖、凋亡、自噬、细胞外基质代谢和炎症事件发生密切相关,circRNA可以作为ceRNA,充当 miRNA 的海绵进而调控下游靶基因的活性,从而延缓或加重骨性关节炎进展。表2列举了骨性关节炎中circRNAs可用实例的综合分析。"
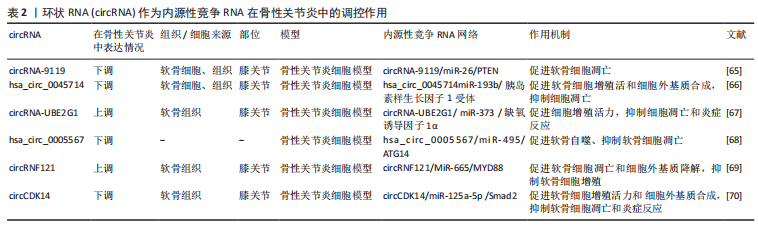

已有许多研究已证实circRNA在骨性关节炎患者各种组织中的异常表达并参与了骨性关节炎疾病的发生发展过程。CHEN等[65]研究发现在骨性关节炎软骨细胞和组织以及白细胞介素1β处理的软骨细胞中,circRNA-9119和PTEN显著降低,过表达circRNA-9119可抑制白细胞介素1β 诱导的软骨细胞凋亡,而过表达miR-26a可加重软骨细胞凋亡,过表达circRNA-9119结果显示miR-26表达水平下调而PTEN表达量增加。生物信息学分析显示miR-26a是circRNA-9119的靶点,PTEN是miR-26的靶点,以往研究已证实了PTEN相关途径与多种细胞的凋亡相关。所以得出结论,circRNA-9119可作为ceRNA 与miR-26结合,从而减少miR-26对下游靶基因PTEN的抑制作用,促进骨性关节炎患者软骨细胞的凋亡。 一项研究发现,在用肿瘤坏死因子α处理的软骨细胞中,hsa_circ_0045714表达显著下调,相反,miR-193b表达上调,胰岛素样生长因子1受体是miR-193b的关键靶基因,hsa_circ_0045714过表达能促进软骨细胞增殖活力、抑制细胞凋亡,并且提高聚集蛋白聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原和胰岛素样生长因子1受体的表达水平,而所有这些效应都被miR-193b过表达所逆转。因此得出,hsa_circ_0045714可作为ceRNA,通过“海绵”作用吸附miR-193b,间接调控下游靶基因胰岛素样生长因子1受体的表达水平,参与骨性关节炎的发病过程[66]。CHEN等[67]研究发现,circRNA-UBE2G1和缺氧诱导因子1α 在骨性关节炎组织中的表达水平显著升高,circRNA-UBE2G1过表达可增加炎症因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的产生,敲减软骨细胞中的circRNA-UBE2G1可抑制脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞损伤的作用。miR-373抑制或缺氧诱导因子1α过表达可逆转circRNA-UBE2G1敲减效应,恢复软骨细胞增殖活力以及抑制软骨细胞凋亡。因此,circRNA-UBE2G1可作为ceRNA竞争性结合miR-373,通过 miR-373/缺氧诱导因子1α轴调控炎症因子产生以及软骨细胞的增殖和凋亡。一项研究报道hsa_circ_0005567在白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞中的表达显著降低,过表达hsa_circ_0005567能够诱导软骨自噬,抑制软骨细胞凋亡,其作用机制是hsa_circ_0005567作为ceRNA,通过 hsa_circ_0005567/miR-495/ATG14轴调控软骨细胞自噬和凋亡[68]。WANG等[69]研究发现,circRNF121(has _ circ _ 0023404)在骨性关节炎软骨组织和白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞中表达显著上调,circRNF121的过表达增加了基质金属蛋白酶13和ADAMS5的水平,降低了聚集蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原的合成和分泌,并且抑制软骨细胞增殖,诱导软骨细胞凋亡;而过表达miR-665可逆转这一过程,MiR-665被确定为 circRNF121和 MYD88的直接调控靶标,由此得出circRNF121可作为ceRNA竞争性结合MiR-665,解除MiR-665对抑制作用下游靶基因MYD88进而参与骨性关节炎的发生和进展。SHEN等[70]探讨了CircCDK14在骨性关节炎发生发展中的作用,结果表明CircCDK14可作为ceRNA,充当miR-125a-5p海绵而间接调控Smad2的表达水平,从而参与骨性关节炎软骨细胞细胞外基质的降解、炎症反应的发生以及软骨细胞增殖和凋亡。 综上所述circRNA在骨性关节炎进展中发挥着重要作用,因此阐明circRNA生物学对理解骨性关节炎发生的重要性变得显而易见,circRNAs的丰度、保守性、稳定性、特异性和可检测性使其成为潜在的诊断和预后生物标志物。此外,circRNAs在与骨性关节炎发生和进展中相关的各种信号通路的上游发挥着关键的调节作用,反映了其作为骨性关节炎治疗靶点的潜力。 2.2.3 假基因作为内源性竞争因子在骨性关节炎中的调控作用 目前为止已经发现假基因参与多种疾病的发生和进展, 其中假基因作为ceRNA,在基因调控中发挥重要作用,并已在多种疾病中得到证实[71]。然而,关于假基因与骨性关节炎的研究却很少。LIU 等[72]研究发现,在受损软骨中TMSB4 假基因 lncRNA-MSR的表达水平上调,lncRNA MSR的过度表达显著降低了Ⅱ型胶原α1和蛋白聚糖的表达,并促进了软骨细胞中基质金属蛋白酶13和ADAMS5的表达导致软骨细胞细胞外基质降解,miR-152可直接靶向TMSB4和lncRNA MSR,其过表达抑制了TMSB4和lncRNA MSR的表达,由此得出,lncRNA MSR可作为ceRNA,通过竞争结合miR-152来间接调节TMSB4表达水平,从而参与骨性关节炎的发生和发展,表明假基因可能在骨性关节炎发病中起到了重要的调控作用。因此,对假基因在骨性关节炎中发挥功能和作用机制进行全面和系统的研究是必要的,这将为骨性关节炎的治疗提供潜在靶点。"

| [1] SANCHEZ-LOPEZ E, CORAS R, TORRES A, et al. Guma M. Synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis progression. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(5):258-275. [2] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072. [3] MOBASHERI A, BAY-JENSEN AC, VAN SPIL WE, et al. Levesque MC. Osteoarthritis Year in Review 2016: biomarkers (biochemical markers). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(2):199-208. [4] ALI SA, PEFFERS MJ, ORMSETH MJ, et al. The non-coding RNA interactome in joint health and disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(11):692-705. [5] GHOURI A, QUICKE JG, CONAGHAN PG. New developments in osteoarthritis pharmacological therapies. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60(Suppl 6):vi1-vi11. [6] BRUMAT P, KUNŠIČ O, NOVAK S, et al. The Surgical Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Life (Basel). 2022;12(7):982. [7] ZHOU J, XIONG W, GOU P, et al. Clinical effect of intramuscular calcitonin compared with oral celecoxib in the treatment of knee bone marrow lesions: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):230. [8] LIU D, LIANG YH, YANG YT, et al. Circular RNA in osteoarthritis: an updated insight into the pathophysiology and therapeutics. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(1):11-23. [9] BOER CG, HATZIKOTOULAS K, SOUTHAM L, et al. Deciphering osteoarthritis genetics across 826,690 individuals from 9 populations. Cell. 2021;184(18):4784-4818.e17. [10] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393 (10182): 1745-1759. [11] LIU HY, CHANG CF, LU CC, et al. The Role of Mitochondrial Metabolism, AMPK-SIRT Mediated Pathway, LncRNA and MicroRNA in Osteoarthritis. Biomedicines. 2022;10(7):1477. [12] MAO X, CAO Y, GUO Z, et al. Biological roles and therapeutic potential of circular RNAs in osteoarthritis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:856-867. [13] YAN H, BU P. Non-coding RNA in cancer. Essays Biochem. 2021;65(4):625-639. [14] SALMENA L, POLISENO L, TAY Y, et al. A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell. 2011;146(3):353-358. [15] NIE D, FU J, CHEN H, et al. Roles of MicroRNA-34a in Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition, Competing Endogenous RNA Sponging and Its Therapeutic Potential. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):861. [16] IZAURRALDE E. A role for eIF4AII in microRNA-mediated mRNA silencing. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013;20(5):543-545. [17] YAO RW, WANG Y, CHEN LL. Cellular functions of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(5):542-551. [18] RUAN X, LI P, CHEN Y, et al. In vivo functional analysis of non-conserved human lncRNAs associated with cardiometabolic traits. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):45. [19] BRIDGES MC, DAULAGALA AC, KOURTIDIS A. LNCcation: lncRNA localization and function. J Cell Biol. 2021;220(2):e202009045. [20] LI J, YANG T, TANG H, et al. Inhibition of lncRNA MAAT Controls Multiple Types of Muscle Atrophy by cis- and trans-Regulatory Actions. Mol Ther. 2021;29(3):1102-1119. [21] NAPOLI M, LI X, ACKERMAN HD, et al. Pan-cancer analysis reveals TAp63-regulated oncogenic lncRNAs that promote cancer progression through AKT activation. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):5156. [22] SHIGEYASU K, TODEN S, OZAWA T, et al. The PVT1 lncRNA is a novel epigenetic enhancer of MYC, and a promising risk-stratification biomarker in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):155. [23] KONG H, SUN ML, ZHANG XA, et al. Crosstalk Among circRNA/lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:774370. [24] GRAMMATIKAKIS I, LAL A. Significance of lncRNA abundance to function. Mamm Genome. 2022;33(2):271-280. [25] NÚÑEZ-MARTÍNEZ HN, RECILLAS-TARGA F. Emerging Functions of lncRNA Loci beyond the Transcript Itself. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6258. [26] ZHANG X, HONG R, CHEN W, et al. The role of long noncoding RNA in major human disease. Bioorg Chem. 2019;92:103214. [27] WU W, CAO L, JIA Y, et al. Emerging Roles of miRNA, lncRNA, circRNA, and Their Cross-Talk in Pituitary Adenoma. Cells. 2022;11(18):2920. [28] QIU Y, XU M, HUANG S. Long noncoding RNAs: emerging regulators of normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Blood. 2021;138(23):2327-2336. [29] HARTFORD CCR, LAL A. When Long Noncoding Becomes Protein Coding. Mol Cell Biol. 2020;40(6):e00528-e00519. [30] CHARLES RICHARD JL, EICHHORN PJA. Platforms for Investigating LncRNA Functions. SLAS Technol. 2018;23(6):493-506. [31] ROBINSON EK, COVARRUBIAS S, CARPENTER S. The how and why of lncRNA function: An innate immune perspective. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020;1863(4):194419. [32] REN S, LIN P, WANG J, et al. Circular RNAs: Promising Molecular Biomarkers of Human Aging-Related Diseases via Functioning as an miRNA Sponge. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020;18:215-229. [33] CHEN I, CHEN CY, CHUANG TJ. Biogenesis, identification, and function of exonic circular RNAs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2015;6(5):563-579. [34] SHANG Q, YANG Z, JIA R, et al. The novel roles of circRNAs in human cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):6. [35] MENG S, ZHOU H, FENG Z, et al. CircRNA: functions and properties of a novel potential biomarker for cancer. Mol Cancer. 2017;16(1):94. [36] MAO X, CAO Y, GUO Z, et al. Biological roles and therapeutic potential of circular RNAs in osteoarthritis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:856-867. [37] LI B, LI Y, HU L, et al. Role of Circular RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2020;13(4):572-583. [38] HOLDT LM, KOHLMAIER A, TEUPSER D. Molecular roles and function of circular RNAs in eukaryotic cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(6):1071-1098. [39] TANG CM, ZHANG M, HUANG L, et al. CircRNA_000203 enhances the expression of fibrosis-associated genes by derepressing targets of miR-26b-5p, Col1a2 and CTGF, in cardiac fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40342. [40] HAN B, CHAO J, YAO H. Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: From the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;187:31-44. [41] GUO L, JIA L, LUO L, et al. Critical Roles of Circular RNA in Tumor Metastasis via Acting as a Sponge of miRNA/isomiR. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(13):7024. [42] AKHBARI MH, ZAFARI Z, SHEYKHHASAN M. Competing Endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) in Colorectal Cancer: A Review. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2022;24:e27. [43] CAO M, ZHANG L, WANG JH, et al. Identifying circRNA-associated-ceRNA networks in retinal neovascularization in mice. Int J Med Sci. 2019;16(10):1356-1365. [44] LIU D, LIANG YH, YANG YT, et al. Circular RNA in osteoarthritis: an updated insight into the pathophysiology and therapeutics. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(1):11-23. [45] ZANG J, LU D, XU A. The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: An important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J Neurosci Res. 2020;98(1): 87-97. [46] KHAN FA, NSENGIMANA B, KHAN NH, et al. Chimeric Peptides/Proteins Encoded by circRNA: An Update on Mechanisms and Functions in Human Cancers. Front Oncol. 2022;12:781270. [47] STASIAK M, KOLENDA T, KOZŁOWSKA-MASŁOŃ J, et al. The World of Pseudogenes: New Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets in Cancers or Still Mystery Molecules? Life (Basel). 2021;11(12):1354. [48] JACQ C, MILLER JR, BROWNLEE GG. A pseudogene structure in 5S DNA of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1977;12(1):109-120. [49] QI Y, WANG X, LI W, et al. Pseudogenes in Cardiovascular Disease. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;7:622540. [50] LIU WH, TSAI ZT, TSAI HK. Comparative genomic analyses highlight the contribution of pseudogenized protein-coding genes to human lincRNAs. BMC Genomics. 2017;18(1):786. [51] HEZRONI H, BEN-TOV PERRY R, MEIR Z, et al. A subset of conserved mammalian long non-coding RNAs are fossils of ancestral protein-coding genes. Genome Biol. 2017;18(1):162. [52] MA Y, CHEN Z, YU J. Pseudogenes and their potential functions in hematopoiesis. Exp Hematol. 2021;103:24-29. [53] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311. [54] MAO L, WU W, WANG M, et al. Targeted treatment for osteoarthritis: drugs and delivery system. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1):1861-1876. [55] ZHANG W, QI L, CHEN R, et al Circular RNAs in osteoarthritis: indispensable regulators and novel strategies in clinical implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021; 23(1):23. [56] Tu J, Huang W, Zhang W, et al. The emerging role of lncRNAs in chondrocytes from osteoarthritis patients. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110642. [57] OKUYAN HM, BEGEN MA. LncRNAs in Osteoarthritis. Clin Chim Acta. 2022;532: 145-163. [58] XING D, LIANG JQ, LI Y, et al. Identification of long noncoding RNA associated with osteoarthritis in humans. Orthop Surg. 2014;6(4):288-293. [59] LU X, YU Y, YIN F, et al. Knockdown of PVT1 inhibits IL-1β-induced injury in chondrocytes by regulating miR-27b-3p/TRAF3 axis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;79:106052. [60] MAO G, KANG Y, LIN R, et al. Long Non-coding RNA HOTTIP Promotes CCL3 Expression and Induces Cartilage Degradation by Sponging miR-455-3p. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:161. [61] HU J, WANG Z, SHAN Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes osteoarthritis progression via miR-17-5p/FUT2/β-catenin axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(7):711. [62] ZHANG G, ZHANG Q, ZHU J, et al. LncRNA ARFRP1 knockdown inhibits LPS-induced the injury of chondrocytes by regulation of NF-κB pathway through modulating miR-15a-5p/TLR4 axis. Life Sci. 2020;261:118429. [63] CHEN K, FANG H, XU N. LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 is transcriptionally activated by JUND and contributes to osteoarthritis progression via targeting the miR-423-5p/KDM5C axis. Life Sci. 2020;258:118095. [64] LIU Y, LIU K, TANG C, et al. Long non-coding RNA XIST contributes to osteoarthritis progression via miR-149-5p/DNMT3A axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;128: 110349. [65] CHEN C, YIN P, HU S, et al. Circular RNA-9119 protects IL-1β-treated chondrocytes from apoptosis in an osteoarthritis cell model by intercepting the microRNA-26a/PTEN axis. Life Sci. 2020;256:117924. [66] LI BF, ZHANG Y, XIAO J, et al. Hsa_circ_0045714 regulates chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis and extracellular matrix synthesis by promoting the expression of miR-193b target gene IGF1R. Hum Cell. 2017;30(4):311-318. [67] CHEN G, LIU T, YU B, et al. CircRNA-UBE2G1 regulates LPS-induced osteoarthritis through miR-373/HIF-1a axis. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(13):1696-1705. [68] ZHANG J, CHENG F, RONG G, et al. Hsa_circ_0005567 Activates Autophagy and Suppresses IL-1β-Induced Chondrocyte Apoptosis by Regulating miR-495. Front Mol Biosci. 2020;7:216. [69] WANG T, HAO Z, LIU C, et al. LEF1 mediates osteoarthritis progression through circRNF121/miR-665/MYD88 axis via NF-кB signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(7):598. [70] SHEN P, YANG Y, LIU G, et al. CircCDK14 protects against Osteoarthritis by sponging miR-125a-5p and promoting the expression of Smad2. Theranostics. 2020;10(20):9113-9131. [71] CHEN X, WAN L, WANG W, et al. Re-recognition of pseudogenes: From molecular to clinical applications. Theranostics. 2020;10(4):1479-1499. [72] LIU Q, HU X, ZHANG X, et al. The TMSB4 Pseudogene LncRNA Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Promote Cartilage Degradation in Human Osteoarthritis. Mol Ther. 2016;24(10):1726-1733. [73] YU H, HUANG T, LU WW, et al. Osteoarthritis Pain. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(9):4642. [74] KONG H, SUN ML, ZHANG XA, et al. Crosstalk Among circRNA/lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:774370. [75] WANG C, LI N, LIU Q, et al. The role of circRNA derived from RUNX2 in the serum of osteoarthritis and its clinical value. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021;35(7):e23858. [76] YANG Z, TANG Y, LU H, et al. Long non-coding RNA reprogramming (lncRNA-ROR) regulates cell apoptosis and autophagy in chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(10):8432-8440. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | He Xi, Wan Yu, Tang Yuting, Yang Anning, Wu Kai, Jiao Yun, Bai Zhigang, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. Erastin inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [4] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [5] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [6] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [7] | Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Lu Dahong, Xu Junrong, Liu Xiaocui, Wang Bingyun. Clinical-grade human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells affect the improvement of neurological function in rats with traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 835-839. |
| [8] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [9] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [10] | Hao Liufang, Duan Hongmei, Wang Zijue, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Zhaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of ependymal cells after spinal cord injury in transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [11] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [12] | Zhao Siqi, Du Juan, Qu Haifeng, Li Jianmin, Zhang Yuxin, Liu Junjie. Effects of enriched environment combined with melatonin on learning and memory function and brain neuron apoptosis in SAMP8 mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 701-706. |
| [13] | Hu Xinming, Qiao Yanhua, Wang Xiaofan, Li Linyu, Zhao Bing. Mechanism of long non-coding RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 involved in pelvic organ prolapse [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 669-675. |
| [14] | Zhang Qing, Gao Chunlan, Yu Feifei, Zhang Zhenghao, Ma Fang, Gao Yuan, Li Guizhong, Jiang Yideng, Ma Shengchao. Ephrin A receptor 2 DNA methylation increases in pancreatic beta cell apoptosis induced by homocysteine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 714-719. |
| [15] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

