Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (28): 4554-4558.doi: 10.12307/2023.683
Previous Articles Next Articles
Key pathways and hub genes of osteoarthritis based on transcriptome data of sports injury synovial tissue
Fu Dongge, He Jingzi
- Physical Culture Institute, Yanan University, Yanan 716000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2022-08-22Accepted:2022-10-19Online:2023-10-08Published:2023-01-29 -
Contact:He Jingzi, PhD, Physical Culture Institute, Yanan University, Yanan 716000, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Fu Dongge, PhD, Physical Culture Institute, Yanan University, Yanan 716000, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Doctoral Research Startup Fund of Yanan University, No. YDBK2022-20 (to FDG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fu Dongge, He Jingzi. Key pathways and hub genes of osteoarthritis based on transcriptome data of sports injury synovial tissue[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4554-4558.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
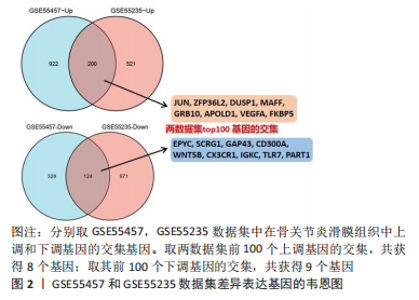
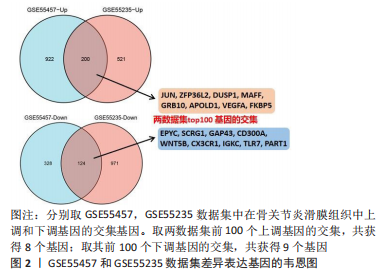
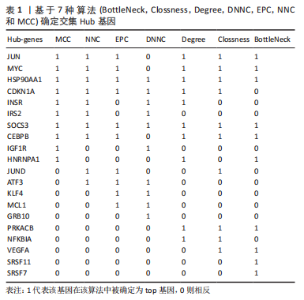
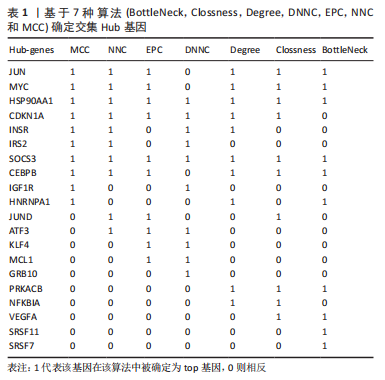
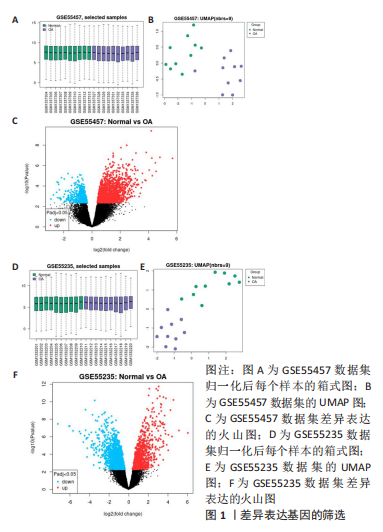
2.1 差异表达基因的筛选 研究选择的数据集GSE55457,包括10例骨关节炎滑膜组织样本和10例健康者滑膜组织样本,所选样本转录组数据分布情况见图1A,其UMAP图见图1B。基于筛选标准adjust P < 0.05,共筛选出1 574个差异表达基因,包括1 122个上调表达基因,452个下调表达基因,火山图如图1C。数据集GSE55235,包括10例骨关节炎滑膜组织样本和10例健康者滑膜组织样本,所选样本转录组数据分布情况见图1D,其UMAP图见图1E。基于筛选标准adjust P < 0.05,共筛选出1 816个差异表达基因,包括721个上调表达基因,1 095个下调表达基因,火山图如图1F。随后,对上下调基因分别取两数据集的交集,见图2,其中上调基因200个,下调基因124个。取两数据集前100个上调基因的交集,共获得8个基因(JUN,ZFP36L2,DUSP1,MAFF,GRB10,APOLD1,VEGFA,FKBP5);取其前100个下调基因的交集,共获得9个基因(EPYC,SCRG1,GAP43,CD300A,WNT5B,CX3CR1,IGKC,TLR7,PART1)。"

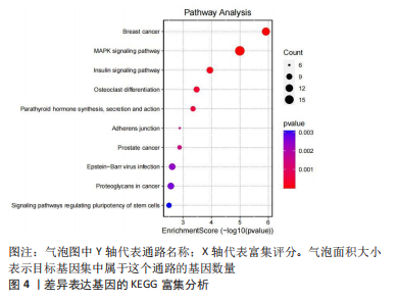
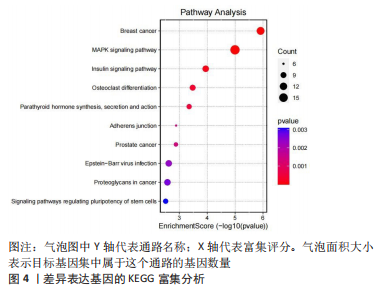
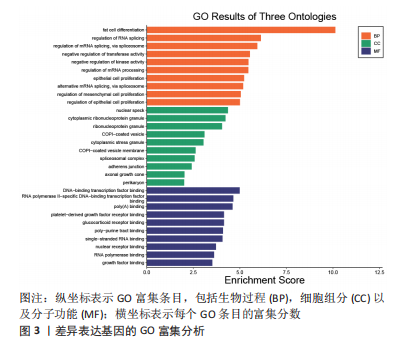
2.2 差异基因的功能富集分析 将筛选得到的324个差异表达基因进行GO功能注释和KEGG富集分析,GO分析结果表明差异表达基因生物学过程主要和脂肪细胞分化、RNA剪接调控、通过剪接体调控mRNA的剪接、转移酶活性的负调控、激酶活性的负调控有关;细胞组分主要和核斑点、细胞质核糖核蛋白颗粒、核糖核蛋白颗粒、Copi涂层囊泡、细胞质应激颗粒有关,而分子功能主要与DNA结合转录因子结合、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ特异性DNA结合转录因子结合、poly(A) 结合、血小板源性生长因子受体结合、糖皮质激素受体结合有关,见图3。而KEGG主要富集在MAPK信号通路、胰岛素信号通路、破骨细胞分化、甲状旁腺激素的合成、分泌和作用等通路,见图4。"
| [1] MOTTA F, BARONE E, SICA A, et al. Inflammaging and Osteoarthritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol.2022 Jun 18. doi: 10.1007/s12016-022-08941-1. [2] MA L, CHHETRI JK, ZHANG L, et al. Cross-sectional study examining the status of intrinsic capacity decline in community-dwelling older adults in China: prevalence, associated factors and implications for clinical care. BMJ Open. 2021;11(1):e043062. [3] LO J, CHAN L, FLYNN S. A Systematic Review of the Incidence, Prevalence, Costs, and Activity and Work Limitations of Amputation, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Back Pain, Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord Injury, Stroke, and Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: A 2019 Update. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102(1):115-131. [4] HUNTER D J, MARCH L, CHEW M. Osteoarthritis in 2020 and beyond: a Lancet Commission. Lancet. 2020;396(10264):1711-1712. [5] GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators.Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396(10258):1204-1222. [6] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759. [7] 苏剑清, 孙波, 丁韵蓉, 等. 基于“损伤-修复-再损伤”方法制备兔膝骨关节炎滑膜炎模型[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(23):3738-3743. [8] SANCHEZ-LOPEZ E, CORAS R, TORRES A, et al. Synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis progression. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(5):258-275. [9] ZHANG L, XING R, HUANG Z, et al. Synovial Fibrosis Involvement in Osteoarthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:684389. [10] KULKARNI P, MARTSON A, VIDYA R, et al. Pathophysiological landscape of osteoarthritis. Adv Clin Chem. 2021;100:37-90. [11] DE REZENDE MU, DE CAMPOS GC. Is osteoarthritis a mechanical or inflammatory disease?. Rev Bras Ortop. 2013;48(6):471-474. [12] SMITH MM, CAKE MA, GHOSH P, et al. Significant synovial pathology in a meniscectomy model of osteoarthritis: modification by intra-articular hyaluronan therapy. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(8): 1172-1178. [13] 张虎林, 王亮, 喻琳, 等. 滑膜巨噬细胞在骨性关节炎发病机制中的作用及其潜在性应用研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(4):590-595. [14] XIE J, HUANG Z, YU X, et al. Clinical implications of macrophage dysfunction in the development of osteoarthritis of the knee. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;46:36-44. [15] ALAHDAL M, ZHANG H, HUANG R, et al. Potential efficacy of dendritic cell immunomodulation in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60(2):507-517. [16] MATHIESSEN A, CONAGHAN PG. Synovitis in osteoarthritis: current understanding with therapeutic implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):18. [17] MURPHY CA, GARG AK, SILVA-CORREIA J, et al. The Meniscus in Normal and Osteoarthritic Tissues: Facing the Structure Property Challenges and Current Treatment Trends. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2019;21:495-521. [18] ZHAO Y, LV J, ZHANG H, et al. Gene Expression Profiles Analyzed Using Integrating RNA Sequencing, and Microarray Reveals Increased Inflammatory Response, Proliferation, and Osteoclastogenesis in Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:665442. [19] MAKSYMOWYCH WP, RUSSELL AS, CHIU P, et al. Targeting tumour necrosis factor alleviates signs and symptoms of inflammatory osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(5):R206. [20] ZHANG L, CHEN X, CAI P, et al. Reprogramming Mitochondrial Metabolism in Synovial Macrophages of Early Osteoarthritis by a Camouflaged Meta-Defensome. Adv Mater. 2022;34(30):e2202715. [21] GUI T, LUO L, CHHAY B, et al. Superoxide dismutase-loaded porous polymersomes as highly efficient antioxidant nanoparticles targeting synovium for osteoarthritis therapy. Biomaterials. 2022;283:121437. [22] LI M, HAN H, CHEN L, et al. Platelet-rich plasma contributes to chondroprotection by repairing mitochondrial function via AMPK/NF-κB signaling in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Tissue Cell. 2022;77:101830. [23] CAI Y, WANG Z, LIAO B, et al. Anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effects of platelet-derived growth factor-BB on osteoarthritis rat models. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022;glac118. [24] MALAISE O, RELIC B, CHARLIER E, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ) is involved in glucocorticoid-induced and mineralocorticoid-induced leptin production by osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016; 18(1):219. [25] SAVVIDOU O, MILONAKI M, GOUMENOS S, et al. Glucocorticoid signaling and osteoarthritis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019;480:153-166. [26] ZHANG Y, PIZZUTE T, PEI M. A review of crosstalk between MAPK and Wnt signals and its impact on cartilage regeneration. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;358(3):633-649. [27] SCHETT G, KLEYER A, PERRICONE C, et al. Diabetes is an independent predictor for severe osteoarthritis: results from a longitudinal cohort study Diabetes Care. 2013;36(2):403-409. [28] HAMADA D, MAYNARD R, SCHOTT E, et al. Suppressive Effects of Insulin on Tumor Necrosis Factor-Dependent Early Osteoarthritic Changes Associated With Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(6):1392-1402. [29] GRIFFIN TM, HUFFMAN KM. Editorial: Insulin Resistance: Releasing the Brakes on Synovial Inflammation and Osteoarthritis?. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(6):1330-1333. [30] TSAI CH, CHIANG YC, CHEN HT, et al. High glucose induces vascular endothelial growth factor production in human synovial fibroblasts through reactive oxygen species generation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1830(3):2649-2658. [31] WANG Z, QI G, LI Z, et al. Effects of urolithin A on osteoclast differentiation induced by receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand via bone morphogenic protein 2. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):5064-5078. [32] KIM GM, PARK H, LEE SY. Roles of osteoclast-associated receptor in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2022;89(5):105400. [33] XU Y, XUE S, ZHANG T, et al. Toddalolactone protects against osteoarthritis by ameliorating chondrocyte inflammation and suppressing osteoclastogenesis. Chin Med. 2022;17(1):18. [34] JIANG S, ZHANG C, LU Y, et al. The molecular mechanism research of cartilage calcification induced by osteoarthritis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(5):13082-13088. [35] CUNNINGHAM CC, CORR EM, MCCARTHY GM, et al. Intra-articular basic calcium phosphate and monosodium urate crystals inhibit anti-osteoclastogenic cytokine signalling. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(12):2141-2152. [36] TAKAHASHI K, KUBO T, ARAI Y, et al. Localization of heat shock protein in osteoarthritic cartilage. Scand J Rheumatol. 1997;26(5):368-375. [37] NGARMUKOS S, SCARAMUZZA S, THEERAWATTANAPONG N, et al. Circulating and Synovial Fluid Heat Shock Protein 70 Are Correlated with Severity in Knee Osteoarthritis. Cartilage. 2020;11(3):323-328. [38] SON YO, KIM HE, CHOI WS, et al. RNA-binding protein ZFP36L1 regulates osteoarthritis by modulating members of the heat shock protein 70 family. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):77. [39] GUI T, HE BS, GAN Q, et al. Enhanced SOCS3 in osteoarthiritis may limit both proliferation and inflammation. Biotech Histochem. 2017;92(2):107-114. |
| [1] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [3] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [4] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [5] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [6] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [7] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [8] | Yu He, Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Guan Shengyi. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis with blood supplied fibular flap combined with hollow screw in the treatment of end-stage ankle osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 588-593. |
| [9] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [10] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [11] | Huang Yuying, Guo Yi, Han Xinzuo, Min Hongwei, Li Xuemei, Liu Kemin. Functional correlation between the elasticity of the quadriceps and its tendons and osteoarthritis of the knee based on shear wave elastography measurements [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4971-4976. |
| [12] | Chen Jingtao, Chen You, Li Yujing, Liu Zhigang. Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor kappaB p65 pathway in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5002-5008. |
| [13] | Chen Jianchao, Song Huiping. Distribution characteristics of bone mass in different parts of postmenopausal women with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5035-5039. |
| [14] | Yang Chaoqiang, Zhang Hulin, Wang Xiaomin, Wang Liang, Wang Yican. Prevention and treatment of bone-related diseases by regulating macrophages with Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5064-5070. |
| [15] | Chen Changmei, Zeng Xianchun, Wang Rongpin, Wu Jiahong. Sex and age differences in the anatomical parameters of normal knee joints evaluated by X-ray [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4647-4651. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||