Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (24): 3892-3900.doi: 10.12307/2023.686
Previous Articles Next Articles
Transamniotic stem cell therapy: a novel strategy for prenatal treatment of multiple congenital diseases
Cheng Xi1, Sun Baolan2, Xie Yuanyuan1, Zhang Yuquan1
- 1Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Medical School of Nantong University, Nantong 226001, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong 226001, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2022-09-06Accepted:2022-10-27Online:2023-08-28Published:2023-01-19 -
Contact:Zhang Yuquan, PhD, Professor, Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Medical School of Nantong University, Nantong 226001, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Cheng Xi, PhD candidate, Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Medical School of Nantong University, Nantong 226001, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province, No. KYCX21_3118 (to XYY); Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province, No. KYCX20_2799 (to CX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cheng Xi, Sun Baolan, Xie Yuanyuan, Zhang Yuquan. Transamniotic stem cell therapy: a novel strategy for prenatal treatment of multiple congenital diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3892-3900.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
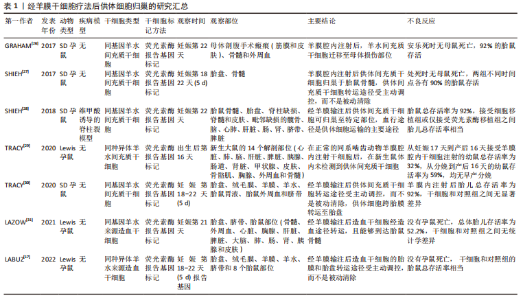
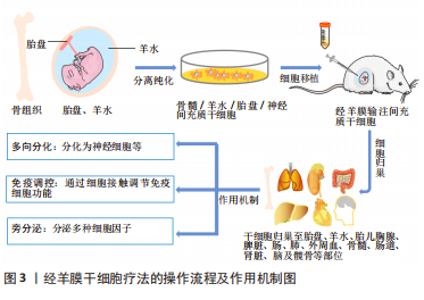
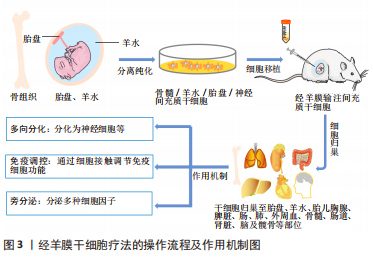
干细胞是一组同质细胞,能够分化为构成身体各种组织和器官的特定细胞类型。根据衍生来源,可将干细胞分为不同类型,即胚胎干细胞、造血干细胞、羊水间充质干细胞(amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells,afMSCs)、胎盘间充质干细胞(placental mesenchymal stem cells,pMSCs)、神经干细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞等。其中胚胎干细胞的增殖分化能力最强,然而,由于胚胎干细胞的提取过程中破坏了胚胎,胚胎干细胞的获取容易引发伦理问题;此外,严重的致瘤风险(畸胎瘤)也是限制其使用的原因之一[20]。羊水间充质干细胞和胎盘间充质干细胞均可以大量获得,而且没有相关的伦理问题,重要的是,与胚胎干细胞不同,胎盘和羊水来源的干细胞在移植后都不会引起畸胎瘤。从转化的角度来看,与其他干细胞相比,自体或同种羊水间充质干细胞可能是用于经羊膜干细胞疗法的理想细胞类型,部分原因是羊膜腔是它们的原生环境。 羊水间充质干细胞不仅可以在从孕中期开始直至出生时通过微创羊膜穿刺术获得,它还具有强大的增殖能力,在相同的培养条件时,其增殖速度比骨髓间充质干细胞和脐血间充质干细胞明显更快,少量羊水(例如3-5 mL)即可在三四周内产生数亿个细胞[10]。另一种在经羊膜干细胞疗法中使用广泛的干细胞是胎盘间充质干细胞,由于妊娠期绒毛膜绒毛取样比羊膜穿刺术更早可行,因此如果有效的话,基于自体胎盘间充质干细胞的经羊膜干细胞疗法应该比基于自体羊水间充质干细胞的经羊膜干细胞疗法更早开始[3]。除此之外,仅在某些胎儿疾病状态下才存在于羊水中的独特干细胞代表了经羊膜干细胞疗法的另一类潜在来源,例如,可以从暴露的神经管缺陷中的羊水中分离出神经干细胞[21]。这些羊水来源的神经干细胞可能不仅代表了经羊膜干细胞疗法治疗脊柱裂的新细胞来源,而且已被证明具有诊断价值[10]。虽然许多特定疾病相关的干细胞有可能在经羊膜干细胞疗法中发挥作用,但目前关于特定疾病干细胞的数据相对缺乏。因此,该综述重点关注基于羊水间充质干细胞和胎盘间充质干细胞的经羊膜干细胞疗法。 间充质干细胞的治疗作用主要通过以下3种方式实现:①间充质干细胞的分化功能使其分化成受损部位的细胞,间充质干细胞具有多系谱分化的可塑性,能够在特定的条件下向特定的细胞方向分化;②通过细胞间的接触调节免疫细胞功能,间充质干细胞可以通过细胞与细胞间的直接接触以及分泌效应生物活性因子,如生长因子、细胞因子和趋化因子等行使其免疫调节作用;③通过旁分泌作用,分泌细胞因子等对受损组织进行修复[22-24]。 产前治疗先天性疾病的优势包括:①预防出生前发生的器官受损:一些危及生命的先天性疾病在胎儿期发病,以至于在新生儿出生时就已经发生了不可逆转的器官损害,严重者可能导致流产或围产期死亡,活产儿可能需要接受终身治疗。宫内修复可能会更好地纠正缺陷,因为瘢痕相对较小,而且病理过程可能会及早中断。②靶向干细胞和祖细胞:干细胞和祖细胞可以在子宫内快速扩增,它们易于接触病毒载体,因此可以提供大量校正细胞。③剂量缩放:临床上使用的干细胞剂量通常取决于患者体质量,但可用载体或细胞的生产耗时且昂贵,胎儿相对较小的尺寸为干细胞和基因治疗提供了优势。④胎儿免疫系统发育不成熟:排斥反应是移植成功的关键,相对幼稚的胎儿免疫系统可能允许对供体细胞产生免疫耐受性。⑤产前胎儿干细胞移植后报告的植入率比产后移植更高,而且胎儿心脏右-左分流可增强细胞的全身分布,而不是像成人那样大部分细胞滞留在肺部。⑥研究发现,接受产前治疗的母亲和父亲的心理社会状况比产后治疗要好得多[20,25]。 众所周知,间充质干细胞因其自我更新和多向分化的生物学特征,强大的抗炎、促血管生成、抗氧化和免疫调节潜能,以及来源广泛、易于分离、生物学性能稳定和伦理问题少的优势,越来越多地被应用于临床。胎儿不发达的免疫系统和快速的宫内发育为有效的干细胞产前治疗创造了条件,经羊膜干细胞疗法在治疗胎儿先天性疾病中显示出广阔的应用前景。 2.2 经羊膜干细胞疗法后供体细胞归巢 经羊膜干细胞疗法后干细胞的归巢是一个活跃的研究领域。在经羊膜干细胞疗法研究中观察到的供体干细胞植入模式表明,细胞不仅可以通过直接播散对暴露的缺陷发挥作用,而且它们还可以归巢于胎盘、羊膜、绒毛膜、脐带、胎儿骨髓、脾脏、髋骨和脑等,甚至母体损伤部位,突出了血行转运是供体细胞动力学的核心组成部分[17,26-31]。经羊膜干细胞疗法后供体细胞归巢的研究汇总见表1。"
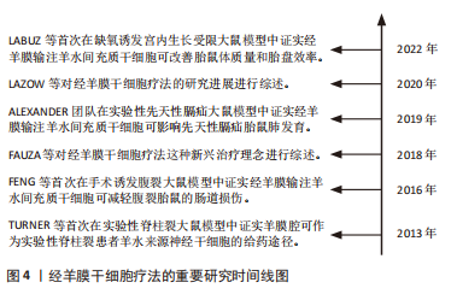
在普通羊膜腔内注射后,已在胎盘、羊膜、绒毛膜中证实存在供体干细胞。有研究确定了这种胎儿和母体循环中独特的细胞动力学过程,他们发现羊膜、绒毛膜和胎盘之间的供体干细胞荧光素酶活性存在一致的非线性胎龄依赖性关系,遵循抛物线双峰模式,其特征是妊娠第17天(E17)接受经羊膜干细胞疗法后,与E19,E20和E21相比,E18和E22(足月)的荧光素酶活性显著较高,表明供体间充质干细胞接受受控的细胞运输,而不是被动的细胞清除[30]。其他研究也显示出主动细胞转运的类似证据[17,27],其中LABUZ等[17]还发现供体干细胞首先在羊膜处达到峰值,然后在绒毛膜和胎盘处达到峰值。跨胎膜转运似乎构成了供体细胞到达胎盘的路径,胎盘是胎儿循环的已知通道,供体细胞的胎盘归巢为经羊膜干细胞疗法在胎盘疾病,如宫内生长受限中的应用提供了契机。 此外,经羊膜移植后,供体细胞还能通过血运转移至胎儿的多处器官。LABUZ等[17]发现,在正常Lewis大鼠模型中,经羊膜干细胞疗法后第2天即可在胎儿肝脏中检测到供体造血干细胞,随后逐渐在其他胎儿部位(脑、胸腺、脾脏、肠、肺、外周血和骨髓)检测到造血干细胞。与此相一致,LAZOW等[31]也在正常Lewis大鼠骨髓、胸腺、肠道、肾脏和皮肤中检测到供体造血干细胞。除健康模型外,SHIEH等[28]在实验性脊柱裂模型中探讨了经羊膜干细胞疗法后供体干细胞的归巢,在脾脏、骨髓、髋骨、缺陷和大脑中也检测到供体羊水间充质干细胞。以上结果表明,不管在正常还是疾病状态下,供体干细胞都能够归巢到胎儿骨髓,而不是仅仅通过直接播散到缺陷部位发挥作用。供体间充质干细胞的血行播散路径将显著扩展经羊膜干细胞疗法的治疗潜能,而不仅是限于暴露于羊膜腔的缺陷,事实上也正是如此,如先天性膈疝等[14]。 然而,经羊膜干细胞疗法长期细胞归巢的研究显示出有争议的结果[29,32-33]。有研究表明,健康Lewis孕鼠接受羊膜腔内输注同种羊水间充质干细胞后16 d,在新生鼠体内14个解剖部位(心脏、肺、脑、肝脏、脾脏、胰腺、肠道、肾脏、甲状腺、皮肤、骨骼肌、胸腺、外周血和骨髓)中未检测到任何供体干细胞[29]。相反地,有研究评估了经兔羊膜腔内异种移植转基因人类脂肪或肝脏组织来源的干细胞后的结果,在接受干预16周的幼兔中证实了异种转基因细胞长期稳定和低水平的植入[32-33]。 值得关注的是,在后面的两项研究中均未检测到针对异种间充质干细胞的宿主细胞免疫反应和针对转基因的体液免疫反应。针对以上有争议的结果,作者认为,差异结果可能与动物模型、细胞种属和剂量有关,而且脂肪或肝脏组织来源的干细胞并不属于羊水中存在的干细胞,因此,有必要进行更多经羊膜干细胞疗法长期细胞归巢方面的研究。 据报道,经羊膜干细胞疗法后干细胞还可以特异性归巢至母体损伤部位[26]。GRAHAM等[26]发现接受经羊膜干细胞疗法的孕鼠剖腹产筋膜瘢痕处存在羊水间充质干细胞,胎盘中供体细胞的存在与母体筋膜中的存在直接相关。供体细胞在体内可以归巢至胎膜(绒毛膜和羊膜),为母体和胎儿循环之间的转移提供了可能的途径。鉴于母体循环中胎儿微嵌合体可能产生有益和有害的影响,在经羊膜输注干细胞治疗的情况下,必须考虑供体细胞的母体归巢。然而,归巢于母体的供体羊水间充质干细胞存活多长时间仍有待确定,进一步强调了在不同疾病模型背景下进行长期随访研究的必要性,以更好地解决经羊膜干细胞疗法在母亲和新生儿中的安全性问题。 总之,经羊膜干细胞疗法以向羊水中输注特定类型浓缩干细胞的形式发挥作用,羊水为取之于羊水的供体间充质干细胞的生长和繁殖提供了绝佳的环境,供体细胞不仅可以通过增殖、迁移、侵袭至胎儿组织以及胎盘等部位,通过分化为特定类型的细胞,同时分泌多种细胞因子,达到治疗疾病的目的。此外,供体细胞在母体损伤部位的归巢也需要引起足够的重视。 2.3 经羊膜干细胞疗法的应用 经羊膜干细胞疗法代表了一种生物学上合理的、微创的和伦理上无可争议的选择,最初是在实验中应用于治疗直接暴露于羊水中的神经管缺陷和腹裂[12-13]。继发现供体干细胞归巢至胎儿骨髓和胎盘之后,国内外学者开始探索经羊膜干细胞疗法对非暴露性缺陷的适用性,如先天性膈疝和宫内生长受限[14,16]。经羊膜干细胞疗法的重要研究时间线图见图4。"
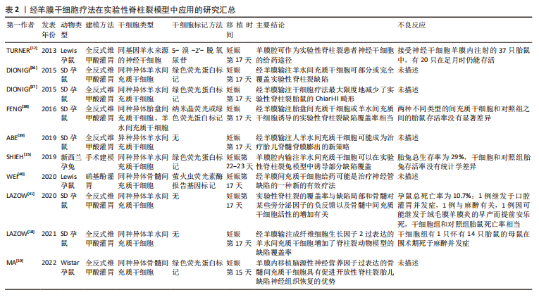
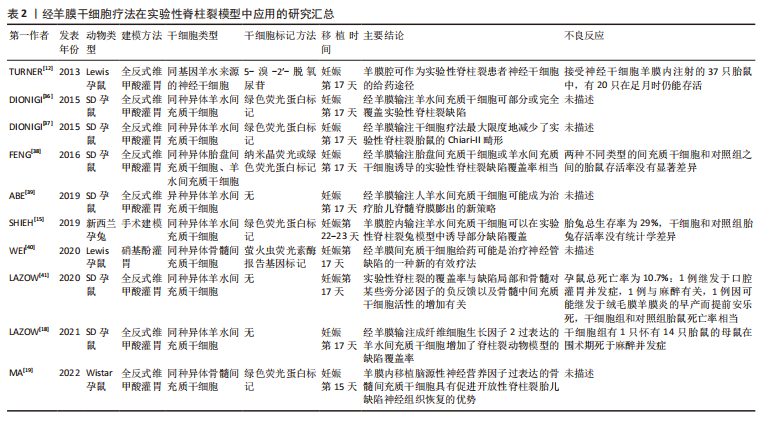
2.3.1 神经管缺陷 神经管缺陷是由于妊娠第4周神经管闭合不全导致的大脑、脊柱和脊髓的先天性异常[34]。脊柱裂是最常见的可存活神经管缺陷,据报道,1991-2011年欧洲每10 000名新生儿中约有4.63名患有脊柱裂[34]。脊柱裂最严重的形式是脊髓脊膜膨出,其中脑膜囊和脊髓都通过缺陷伸入羊膜腔。基于缝合的手术方法是脊髓脊膜膨出产前治疗的常规选择,但这是一种侵入性方法,可能导致其他并发症,如早产、无法完全闭合缺陷等[8,35]。以往研究还表明,子宫内闭合脊柱裂可能是一种有效和安全的治疗方法[34]。 目前有几项不同的研究已在脊柱裂啮齿动物或兔模型中证明了经羊膜干细胞疗法的治疗益处[12,15,18-19,36-41]。经羊膜干细胞疗法在实验性脊柱裂模型中应用的研究汇总见表2。"
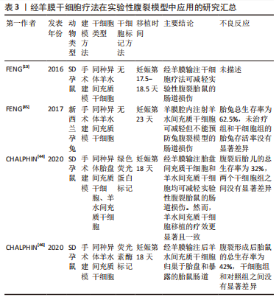
在啮齿动物研究中,基于广泛使用的维甲酸灌胃模型诱导胎儿神经管缺陷,经羊膜腔输注浓缩羊水间充质干细胞、胎盘间充质干细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞和神经干细胞等均可诱导新生皮肤部分或完全覆盖脊柱裂缺陷部[12,36,38-40]。值得注意的是,在未接受经羊膜干细胞疗法的一小部分对照啮齿动物中发现了部分缺陷覆盖,表明经羊膜干细胞疗法本质上放大了已经存在的宿主反应[36]。继啮齿动物模型中证实经羊膜干细胞疗法的有效性后,有研究通过手术暴露远端脊髓的方法构建兔脊柱裂模型,通过羊膜腔内输注羊水间充质干细胞诱导新生皮肤部分覆盖脊柱裂再次证实经羊膜干细胞疗法可能是治疗神经管缺陷的一种新的有效疗法[15]。此外,有学者发现在一个啮齿动物模型中,经羊膜干细胞疗法显著减少了小脑和脑干位移,减少了与脊柱裂密切相关的Chiari-II畸形[37]。经羊膜干细胞疗法为产前治疗神经管缺陷打开了新大门,与基于缝合的手术方法不同,经羊膜干细胞疗法是一种新型微创治疗方法,其在鼠和兔模型中显示出的治疗潜能表明有必要在大型动物模型中进行进一步研究,以证明其有效性。 随后,各国学者开始关注经羊膜干细胞疗法治疗脊柱裂的机制,主要围绕供体干细胞的旁分泌和多向分化作用。2019年,ABE等[39]在大鼠脊髓脊膜膨出模型中发现,向羊膜腔内输注羊水间充质干细胞后,神经元损伤如神经变性和星形胶质细胞增生减少。此外,在羊水间充质干细胞治疗组的病灶中,肝细胞生长因子表达上调,肝细胞生长因子阳性羊水间充质干细胞迁移到病灶部位并通过分泌肝细胞生长因子以抑制神经元损伤并诱导神经发生[39]。2020年,LAZOW等[41]通过RT-qPCR在缺陷和胎儿骨髓处定量多个旁分泌基因的表达,结果发现缺陷覆盖率与缺陷处表皮生长因子和成纤维细胞生长因子2的显著下调以及胎儿骨髓中转化生长因子β-1和CD45的显著下调相关。随后,LAZOW等[18]又发现,与单纯羊水间充质干细胞相比,使用成纤维细胞生长因子2过表达的羊水间充质干细胞经羊膜治疗脊柱裂啮齿动物模型显著提高了缺陷覆盖率,进一步证实成纤维细胞生长因子2在经羊膜干细胞疗法中的重要作用。然而,另外发表的两项经羊膜干细胞疗法作用机制方面的研究均围绕骨髓间充质干细胞展开[19,40],正常状态下羊水中不存在骨髓间充质干细胞,但经羊膜输注后,骨髓间充质干细胞可归巢至其原生环境——骨髓以及损伤部位充分发挥作用。在这两项研究中,除旁分泌外,还证实了骨髓间充质干细胞的多向分化潜能。WEI等[40]在大鼠神经管缺陷模型中发现,经羊膜移植的骨髓间充质干细胞在缺陷部位特异性分化为缺陷组织的细胞类型,包括皮肤和不同类型的神经元。同样,MA等[19]也发现脑源性神经营养因子过表达的骨髓间充质干细胞具有定向迁移至缺陷病灶的特点,羊膜腔内输注脑源性神经营养因子过表达的骨髓间充质干细胞减轻了脊髓细胞的凋亡,分化为神经元和皮肤样细胞,减少了皮损面积,改善了羊水微环境。此外,脑源性神经营养因子修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞在抑制细胞凋亡和促进神经分化方面表现出比单纯骨髓间充质干细胞更好的效果。经羊膜输注基因工程化干细胞显示出较大的治疗潜能,经羊膜干细胞疗法在脊柱裂疾病模型中作用机制的相关研究为基因工程化干细胞的使用奠定了基础。 另有研究探讨了影响神经管缺陷治疗效果的因素,包括治疗剂量、干细胞类型以及工程化干细胞等[11,18-19,38]。有研究分析了经羊膜干细胞疗法的作用是否具有剂量依赖性,比较了不同时间点的一次与两次羊膜内注射,结果发现一次注射组的缺陷覆盖率显著高于两次注射组,后者的死亡率明显更高,但不能排除多次注射可以增强更大动物模型或人类结果的可能性[11]。另一项旨在优化经羊膜干细胞疗法细胞类型的研究发现,羊膜间充质干细胞和胎盘间充质干细胞注射组对脊柱裂缺陷的部分或完全覆盖率相似[38]。如上所述,脑源性神经营养因子或成纤维细胞生长因子2修饰的间充质干细胞均表现出比单纯间充质干细胞更优的治疗效果[18-19]。未来需要在更大的疾病模型中确定经羊膜输注干细胞的给药时间、给药途径、给药剂量,以获得最大治疗益处。 2.3.2 腹裂 腹裂是脐旁全层腹壁缺损,内脏内容物(通常是大肠和小肠)直接暴露于羊水中引起显著的化学和机械损伤,导致肠壁增厚水肿、肠绞窄和可能的肠闭锁[13,42]。在过去的20年中,腹裂的患病率显著增加,原因尚不明确[11]。1995-2012年的大规模数据显示其患病率为5/10 000[43]。尽管产前诊断取得了极大进展,最早可在妊娠10周时通过超声诊断腹裂,但产前管理并没有相应的改进。除了早期分娩,已经提出了几种产前治疗方法,包括羊膜交换、羊水稀释、产前类固醇给药、诱导胎儿利尿、一氧化氮供体以及子宫内缺损修复,但都疗效甚微[13,44-46]。经羊膜干细胞疗法代表了一种可用于治疗腹裂的风险较小且微创的潜在新方法,经羊膜干细胞疗法在实验性腹裂模型中应用的研究汇总见表3。"
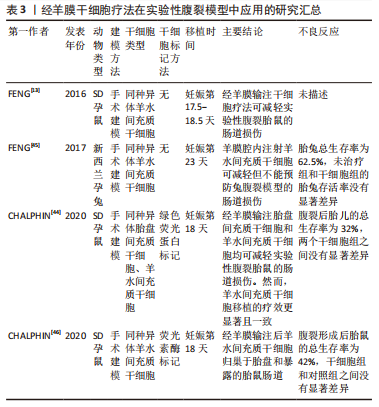

目前经羊膜干细胞疗法在实验性腹裂大鼠或模型中的应用多停留在功能或细胞归巢方面,初步证明经羊膜干细胞疗法可减轻腹裂胎鼠的肠道损伤。2016年,FENG等[13]首次报道了经羊膜干细胞疗法在实验性腹裂大鼠模型中的应用,结果发现羊膜腔内输注羊膜间充质干细胞组的总肠壁、浆膜层、肌层和黏膜层的厚度较等量盐水输注组和未治疗组显著降低,证实经羊膜干细胞疗法可能成为治疗腹裂的有效方法。随后,他们继续在更大的动物模型(新西兰兔)中研究经羊膜干细胞疗法对腹裂的治疗益处,实验结果与大鼠模型一致,进一步证实经羊膜干细胞疗法能有效减轻腹裂引发的肠道损伤[45]。2020年,有研究比较了经羊膜输注羊水间充质干细胞和胎盘间充质干细胞对腹裂的治疗效果,结果表明两者都能显著降低肠壁厚度,且羊水间充质干细胞效果更佳[44]。同年,CHALPHIN等[46]在实验性腹裂大鼠模型中全面分析了经羊膜输注羊水间充质干细胞后的细胞归巢,结果仅在暴露于羊膜腔的区域检测到羊水间充质干细胞,且胎盘和肠道的细胞归巢之间没有相互关系,表明供体细胞同时发生了直接播散和血行转运。经羊膜干细胞疗法在实验性腹裂疾病模型中治疗益处为先天性腹裂提供了一种新的治疗手段,经羊膜干细胞疗法后供体细胞发挥作用的机制可能是后期研究的核心内容。 2.3.3 先天性膈疝 先天性膈疝是一种以膈肌缺损和腹腔内容物突出到胸腔,导致肺发育不全为特征的疾病[47-48]。随着一些新的治疗方法的引入,包括胎儿气管阻塞、温和通气策略和体外膜肺氧合,先天性膈疝患者的治疗有所改善,但重度先天性膈疝婴儿的死亡率仍然很高[14,48-49]。 鉴于经羊膜干细胞疗法后供体细胞的血行路径、胎儿手术治疗方案的侵入性和争议性、以及先天性膈疝的持续高产后发病率和死亡率,2020年CHALPHIN等[14]首次将经羊膜干细胞疗法应用于不直接暴露于羊膜腔的先天性膈疝,在这项探索性研究中使用硝基芬灌胃诱导大鼠先天性膈疝模型,检测胎肺组织成纤维细胞生长因子10、血管内皮生长因子A和表面活性蛋白C的表达,结果发现该疗法显然能够影响胎儿肺血管张力的调节,并相应地影响实验性先天性膈疝中的肺小动脉形态[14]。与未处理组和生理盐水组相比,经羊膜干细胞疗法组的成纤维细胞生长因子10和血管内皮生长因子A表达显著下调;与未经治疗组相比,经羊膜干细胞疗法胎肺的表面活性蛋白C表达显著升高。血管内皮生长因子A和成纤维细胞生长因子10分别在肺血管生成和气道分支发育中起关键作用[50],两者的降低可能反映了宿主对某些有害刺激的反应较少,或者这些有害刺激可能已被其他过程逆转或抑制[51]。表面活性蛋白C是Ⅱ型肺细胞成熟的标志物,始于肺发育的假腺体期[52]。据报道,在晚期暴露于硝基芬的大鼠胎儿和患有先天性膈疝的人类新生儿中存在表面活性剂缺乏[53],CHALPHIN等[14]研究发现,经羊膜干细胞疗法可能通过显著上调表面活性蛋白C的表达影响实验性先天性膈疝肺发育。经羊膜干细胞疗法在先天性膈疝疾病模型中的应用是经羊膜干细胞疗法治疗非暴露性缺陷疾病的首次尝试,这项探索性研究证实经羊膜干细胞治疗影响实验性先天性膈疝肺发育,正如文中所言,比简单地确定这些关键基因是上调还是下调更重要的是,该研究证实经羊膜干细胞疗法可以通过某种方式影响胎儿肺发育。 随后,CHALPHIN等[49]继续探讨了经羊膜干细胞疗法对先天性膈疝肺形态和肺血管张力稳态关键介质的影响,结果发现与未处理组相比,经羊膜干细胞疗法组肺小动脉壁厚度显著降低,胎肺组织内皮一氧化氮合酶和内皮素受体A表达显著下调。一氧化氮是已知的最有效的选择性肺血管扩张剂,主要由血管内皮中的内皮一氧化氮合酶合成,不仅在血管舒张中起作用,而且在肺血管生成中也起作用[49,54]。内皮素通路是肺血管发育和血管张力稳态的另一个关键介质,内皮素受体A在血管平滑肌中表达并介导血管收缩[55]。同样,对内皮一氧化氮合酶和内皮素受体A结果的解释不能局限于上调或者下调,关键是充分说明经羊膜干细胞疗法改变了调节肺血管张力稳态的关键介质的表达。此外,有研究还分析了先天性膈疝大鼠模型中经羊膜干细胞疗法后供体细胞归巢,结果在骨髓和脐带组织中检测出供体羊水间充质干细胞,但没有发现供体细胞在胎儿肺、隔膜或心脏处的归巢,表明经羊膜干细胞疗法后观察到的基因表达和肺小动脉壁厚度的变化与羊水间充质干细胞的直接定植无关,可能主要通过旁分泌发挥作用[49]。这些初步研究结果表明,经羊膜干细胞疗法影响了实验性先天性膈疝中胎儿肺发育和肺血管张力稳态的特定调控过程,有必要在大型动物模型中进一步验证经羊膜干细胞疗法对先天性膈疝的治疗益处。 2.3.4 宫内生长受限 宫内生长受限是胎盘疾病最普遍和最严重的形式之一,继早产之后,宫内生长受限是婴儿死亡和发病的第2大原因,其患病率相当稳定,占妊娠的8%-10%[56-58]。在宫内生长受限胎盘的病理变化中,由NK细胞驱动的促炎状态被认为起主要作用[59]。目前还没有专门针对这种疾病的有效治疗方法,鉴于经羊膜干细胞疗法后供体细胞在胎盘处的定植,间充质干细胞能强烈抑制NK细胞增殖且具有明确的调节炎症的能力,2022年,LABUZ等[16]首次确定了宫内生长受限是否可以成为经羊膜干细胞疗法的治疗目标,他们通过缺氧成功诱导宫内生长受限模型,设计了两个经羊膜干细胞疗法组,一个是单纯羊水间充质干细胞组,另一个羊水间充质干细胞抗炎表型“启动”组(通过将羊水间充质干细胞暴露于添加了质量浓度30 ng/mL干扰素γ和5 ng/mL白细胞介素1β的改良培养基中);结果发 现,在两个经羊膜干细胞疗法组中胎儿体质量和胎盘效率均正常化,仅羊水间充质干细胞抗炎表型“启动”组逆转了胎盘复合体中干扰素γ (NK功能的主要标志物)的增加;同时,在两个经羊膜干细胞疗法组的胎盘中均检测到羊水间充质干细胞。这项研究表明经羊膜干细胞疗法可以逆转宫内生长受限对胎盘和胎儿体质量的不良影响,使用抗炎表型“启动”的羊水间充质干细胞效果更显著,该作用可能与异常NK细胞活性减弱相关。LABUZ等[16]的研究为经羊膜干细胞疗法在宫内生长受限中的应用开辟了新的道路,有必要进行更多的研究来验证经羊膜干细胞疗法的疗效并探讨详细的作用机制。 综上可知,经羊膜干细胞疗法在脊柱裂、腹裂、先天性膈疝和宫内生长受限的疾病模型中显示出显著疗效,遗憾的是,目前经羊膜干细胞疗法产前治疗方面的研究多停留在疗效和作用机制方面,安全性方面的分析多为母体和胎儿存活率,鲜少见其他不良反应,该点可能是限制经羊膜干细胞疗法应用于临床的主要障碍之一,未来应将经羊膜干细胞疗法产前治疗的安全性作为研究重点。 2.4 经羊膜干细胞疗法的安全性 非胚胎干细胞来源的神经干细胞和间充质干细胞通常被认为是非致瘤性的,从安全的角度来看,近20年来,在任何动物模型中都没有关于应用间充质干细胞后发生肿瘤的报道[11,60-61]。根据FDA临床使用指南,这些间充质干细胞在细胞加工过程中在遗传和表型上也具有稳定性[11]。经羊膜干细胞疗法可以将胎儿自身或同种属这种天然、未分化状态的间充质干细胞重新输注到其自身环境中,进一步强调了经羊膜干细胞疗法的安全性和实用性。如上所述,供体间充质干细胞的血行路径既为临床应用开辟了新探索方向,也提出了需要解决的安全问题,胎儿-母体微嵌合现象表明需要进行更多研究探讨经羊膜干细胞疗法对母体和新生儿的长期安全性。 异体间充质干细胞移植不会带来伦理问题,但引发机体的移植排斥反应仍值得关注。通过羊膜腔输注自体羊水或胎盘间充质干细胞可有效避免移植疫排斥反应,但是目前仅仅代表一种理想状态,细胞处理过程中可能带入外源性物质引发安全隐患,目前尚未有研究探讨回收自体干细胞经羊膜移植的可行性,有待进一步证实。"

| [1] 刘珍,周阳文,李小洪,等.出生缺陷防控健康教育专家共识[J].中国妇幼保健,2022,37(5):775-779. [2] 卫生部发布《中国出生缺陷防治报告(2012)》[J].中国药房,2012, 23(39):3693. [3] VANOVER M, WANG A, FARMER D. Potential clinical applications of placental stem cells for use in fetal therapy of birth defects. Placenta. 2017;59:107-112. [4] SHAW SW, DAVID AL, DE COPPI P. Clinical applications of prenatal and postnatal therapy using stem cells retrieved from amniotic fluid. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2011;23(2):109-116. [5] GOMBOS K, GALIK B, KALACS KI, et al. NGS-based application for routine non-invasive pre-implantation genetic assessment in IVF. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2443. [6] HUANG J, RONG L, ZENG L, et al. Embryo selection through non-invasive preimplantation genetic testing with cell-free DNA in spent culture media: a protocol for a multicentre, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2022;12(7):e057254. [7] KHALIL A, ARCHER R, HUTCHINSON V, et al. Noninvasive prenatal screening in twin pregnancies with cell-free DNA using the IONA test: a prospective multicenter study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;225(1):79 e1-79 e13. [8] MELLER C, COVINI D, AIELLO H, et al. Update on prenatal diagnosis and fetal surgery for myelomeningocele. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2021;119(3): e215-e228. [9] 揭秋玲,孙菲.宫内干细胞治疗多种胎儿遗传性疾病的可能性[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(31):5034-5039. [10] FAUZA DO. Transamniotic stem cell therapy: a novel strategy for the prenatal management of congenital anomalies. Pediatr Res. 2018; 83(1-2):241-248. [11] LAZOW SP, FAUZA DO. Transamniotic stem cell therapy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1237:61-74. [12] TURNER CG, PENNINGTON EC, GRAY FL, et al. Intra-amniotic delivery of amniotic-derived neural stem cells in a syngeneic model of spina bifida. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2013;34(1):38-43. [13] FENG C, GRAHAM CD, CONNORS JP, et al. Transamniotic stem cell therapy (TRASCET) mitigates bowel damage in a model of gastroschisis. J Pediatr Surg. 2016;51(1):56-61. [14] CHALPHIN AV, TRACY SA, LAZOW SP, et al. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia as a potential target for transamniotic stem cell therapy. J Pediatr Surg. 2020;55(2):249-252. [15] SHIEH HF, TRACY SA, HONG CR, et al. Transamniotic stem cell therapy (TRASCET) in a rabbit model of spina bifida. J Pediatr Surg. 2019; 54(2):293-296. [16] LABUZ DF, WHITLOCK AE, KYCIA I, et al. Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR) as a potential target for transamniotic stem cell therapy. J Pediatr Surg. 2022;57(6):999-1003. [17] LABUZ DF, WHITLOCK AE, KYCIA I, et al. Routing pathway of syngeneic donor hematopoietic stem cells after simple intra-amniotic delivery. J Pediatr Surg. 2022;57(6):986-990. [18] LAZOW SP, LABUZ DF, KYCIA I, et al. Enhancement of transamniotic stem cell therapy for spina bifida by genetic engineering of donor mesenchymal stem cells with an Fgf2 transgene. J Pediatr Surg. 2021; 56(6):1226-1232. [19] MA W, WEI X, GU H, et al. Intra-amniotic transplantation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor-modified mesenchymal stem cells treatment for rat fetuses with spina bifida aperta. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):413. [20] EKBLAD-NORDBERG A, WALTHER-JALLOW L, WESTGREN M, et al. Prenatal stem cell therapy for inherited diseases: past, present, and future treatment strategies. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(2):148-157. [21] CHANG YJ, SU HL, HSU LF, et al. Isolation of human neural stem cells from the amniotic fluid with diagnosed neural tube defects. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(15):1740-1750. [22] PASSERA S, BOCCAZZI M, BOKOBZA C, et al. Therapeutic potential of stem cells for preterm infant brain damage: can we move from the heterogeneity of preclinical and clinical studies to established therapeutics? Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;186:114461. [23] EBRAHIM N, MOSTAFA O, EL DOSOKY RE, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles/estrogen combined therapy safely ameliorates experimentally induced intrauterine adhesions in a female rat model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):175. [24] 李仲康,郑嘉华,田彦鹏,等.间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰的最新进展及机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(1):141-147. [25] WESTGREN M, GOTHERSTROM C. Stem cell transplantation before birth - a realistic option for treatment of osteogenesis imperfecta? Prenat Diagn. 2015;35(9):827-832. [26] GRAHAM CD, SHIEH HF, BRAZZO JA, 3RD, et al. Donor mesenchymal stem cells home to maternal wounds after transamniotic stem cell therapy (TRASCET) in a rodent model. J Pediatr Surg. 2017;52(6):1006-1009. [27] SHIEH HF, AHMED A, TRACY SA, et al. Fetal bone marrow homing of donor mesenchymal stem cells after transamniotic stem cell therapy (TRASCET). J Pediatr Surg. 2017;12:S0022-3468(17)30655-30653. [28] SHIEH HF, AHMED A, ROHRER L, et al. Donor mesenchymal stem cell linetics after transamniotic stem cell therapy (TRASCET) for experimental spina bifida. J Pediatr Surg. 2018;53(6):1134-1136. [29] TRACY SA, CHALPHIN AV, LAZOW SP, et al. Postnatal fate of donor mesenchymal stem cells after transamniotic stem cell therapy in a healthy model. J Pediatr Surg. 2020;55(6):1113-1116. [30] TRACY SA, CHALPHIN AV, KYCIA I, et al. Hematogenous donor cell routing pathway after transamniotic stem cell therapy. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(12):755-760. [31] LAZOW SP, KYCIA I, LABUZ DF, et al. Fetal hematogenous routing of a donor hematopoietic stem cell line in a healthy syngeneic model of transamniotic stem cell therapy. J Pediatr Surg. 2021;56(6):1233-1236. [32] MORENO R, MARTINEZ-GONZALEZ I, ROSAL M, et al. Fetal liver-derived mesenchymal stem cell engraftment after allogeneic in utero transplantation into rabbits. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(2):284-295. [33] MARTINEZ-GONZALEZ I, MORENO R, PETRIZ J, et al. Engraftment potential of adipose tissue-derived human mesenchymal stem cells after transplantation in the fetal rabbit. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(18): 3270-3277. [34] SOLTANI KHABOUSHAN A, SHAKIBAEI M, KAJBAFZADEH AM, et al. Prenatal neural tube anomalies: a decade of intrauterine stem cell transplantation using advanced tissue engineering methods. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(2):752-767. [35] MOLDENHAUER JS, FLAKE AW. Open fetal surgery for neural tube defects. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2019;58:121-132. [36] DIONIGI B, AHMED A, BRAZZO J 3RD, et al. Partial or complete coverage of experimental spina bifida by simple intra-amniotic injection of concentrated amniotic mesenchymal stem cells. J Pediatr Surg. 2015; 50(1):69-73. [37] DIONIGI B, BRAZZO JA, 3RD, AHMED A, et al. Trans-amniotic stem cell therapy (TRASCET) minimizes Chiari-II malformation in experimental spina bifida. J Pediatr Surg. 2015;50(6):1037-1041. [38] FENG C, C DG, CONNORS JP, et al. A comparison between placental and amniotic mesenchymal stem cells for transamniotic stem cell therapy (TRASCET) in experimental spina bifida. J Pediatr Surg. 2016; 51(6):1010-1013. [39] ABE Y, OCHIAI D, MASUDA H, et al. In utero amniotic fluid stem cell therapy protects against myelomeningocele via spinal cord coverage and hepatocyte growth factor secretion. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019; 8(11):1170-1179. [40] WEI X, MA W, GU H, et al. Transamniotic mesenchymal stem cell therapy for neural tube defects preserves neural function through lesion-specific engraftment and regeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2020; 11(7):523. [41] LAZOW SP, TRACY SA, CHALPHIN AV, et al. Initial mechanistic screening of transamniotic stem cell therapy in the rodent model of spina bifida: host bone marrow and paracrine activity. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2020; 47(12):902-911. [42] CHUAIRE NOACK L. New clues to understand gastroschisis. Embryology, pathogenesis and epidemiology. Colomb Med (Cali). 2021;52(3): e4004227. [43] JONES AM, ISENBURG J, SALEMI JL, et al. Increasing Prevalence of Gastroschisis--14 States, 1995-2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(2):23-26. [44] CHALPHIN AV, TRACY SA, LAZOW SP, et al. A comparison between placental and amniotic mesenchymal stem cells in transamniotic stem cell therapy for experimental gastroschisis. J Pediatr Surg. 2020; 55(1):49-53. [45] FENG C, GRAHAM CD, SHIEH HF, et al. Transamniotic stem cell therapy (TRASCET) in a leporine model of gastroschisis. J Pediatr Surg. 2017;52(1):30-34. [46] CHALPHIN AV, TRACY SA, KYCIA I, et al. Donor mesenchymal stem cell kinetics after transamniotic stem cell therapy (TRASCET) in a rodent model of gastroschisis. J Pediatr Surg. 2020;55(3):482-485. [47] CHATTERJEE D, ING RJ, GIEN J. Update on congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Anesth Analg. 2020;131(3):808-821. [48] KIRBY E, KEIJZER R. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: current management strategies from antenatal diagnosis to long-term follow-up. Pediatr Surg Int. 2020;36(4):415-429. [49] CHALPHIN AV, LAZOW SP, LABUZ DF, et al. Transamniotic stem cell therapy for experimental congenital diaphragmatic hernia: structural, transcriptional, and cell kinetics analyses in the nitrofen model. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2021;48(5):381-391. [50] HINES EA, SUN X. Tissue crosstalk in lung development. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(9):1469-1477. [51] BATES DO, BEAZLEY-LONG N, BENEST AV, et al. Physiological role of vascular endothelial growth factors as homeostatic regulators. Compr Physiol. 2018;8(3):955-979. [52] DI BERNARDO J, MAIDEN MM, HERSHENSON MB, et al. Amniotic fluid derived mesenchymal stromal cells augment fetal lung growth in a nitrofen explant model. J Pediatr Surg. 2014;49(6):859-864; discussion 864-855. [53] GUILBERT TW, GEBB SA, SHANNON JM. Lung hypoplasia in the nitrofen model of congenital diaphragmatic hernia occurs early in development. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000;279(6):L1159-L1171. [54] CONG P, TONG C, MAO S, et al. DDAH1 promotes lung endothelial barrier repair by decreasing leukocyte transendothelial migration and oxidative stress in explosion-induced lung injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:8407635. [55] IHUNNAH CA, GHOSH S, HAHN S, et al. Nrf2 activation with CDDO-Methyl promotes beneficial and deleterious clinical effects in transgenic mice with sickle cell anemia. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:880834. [56] KAUR G, PORTER CBM, ASHENBERG O, et al. Mouse fetal growth restriction through parental and fetal immune gene variation and intercellular communications cascade. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):4398. [57] SILBER M, DEKEL N, HEUSLER I, et al. Inflammasome activation in preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2022;88(4):e13598. [58] LI P, HE L, LAN Y, et al. Intrauterine growth restriction induces adulthood chronic metabolic disorder in cardiac and skeletal muscles. Front Nutr. 2022;9:929943. [59] TRAVIS OK, BAIK C, TARDO GA, et al. Adoptive transfer of placental ischemia-stimulated natural killer cells causes a preeclampsia-like phenotype in pregnant rats. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2021;85(6):e13386. [60] KUNISAKI SM, ARMANT M, KAO GS, et al. Tissue engineering from human mesenchymal amniocytes: a prelude to clinical trials. J Pediatr Surg. 2007;42(6):974-979; discussion 979-980. [61] STEIGMAN SA, ARMANT M, BAYER-ZWIRELLO L, et al. Preclinical regulatory validation of a 3-stage amniotic mesenchymal stem cell manufacturing protocol. J Pediatr Surg. 2008;43(6):1164-1169. |
| [1] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [2] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [4] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [6] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [7] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [8] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [9] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [10] | Chen Shisong, Liu Xiaohong, Xu Zhiyun. Current status and prospects of bioprosthetic heart valves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1096-1102. |
| [11] | Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Early thrombosis and prevention of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [12] | Tang Haotian, Liao Rongdong, Tian Jing. Application and design of piezoelectric materials for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [13] | Bai Siqi, Xiao Zhen, Liu Jing. Application potential of adipose-derived stem cells in female pelvic floor dysfunction diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 921-927. |
| [14] | Zhang Qijian, Xu Ximing. Acquisition and application of ectodermal mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| [15] | Xiong Juan, Guan Yalin, Yang Yutong, Wang Fan, Liu Zhongshan. Application of stem cells to skin anti-aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 948-954. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||